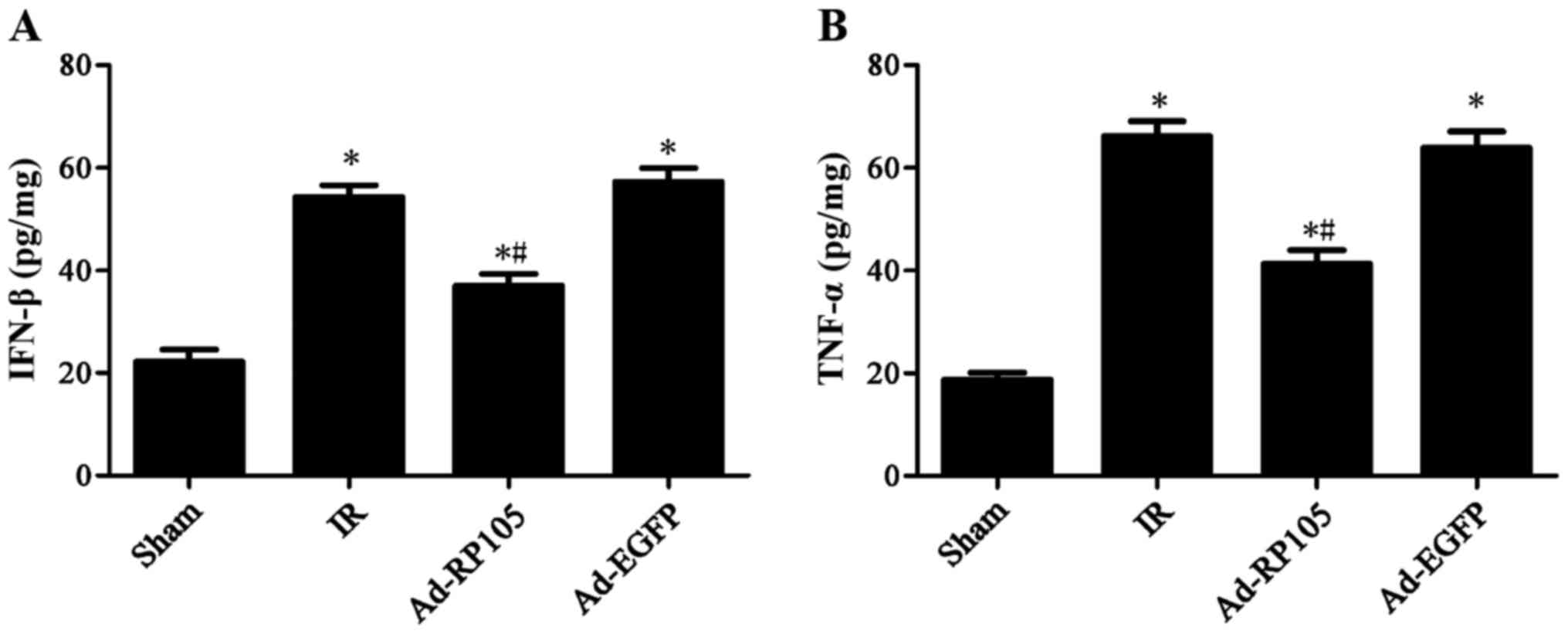
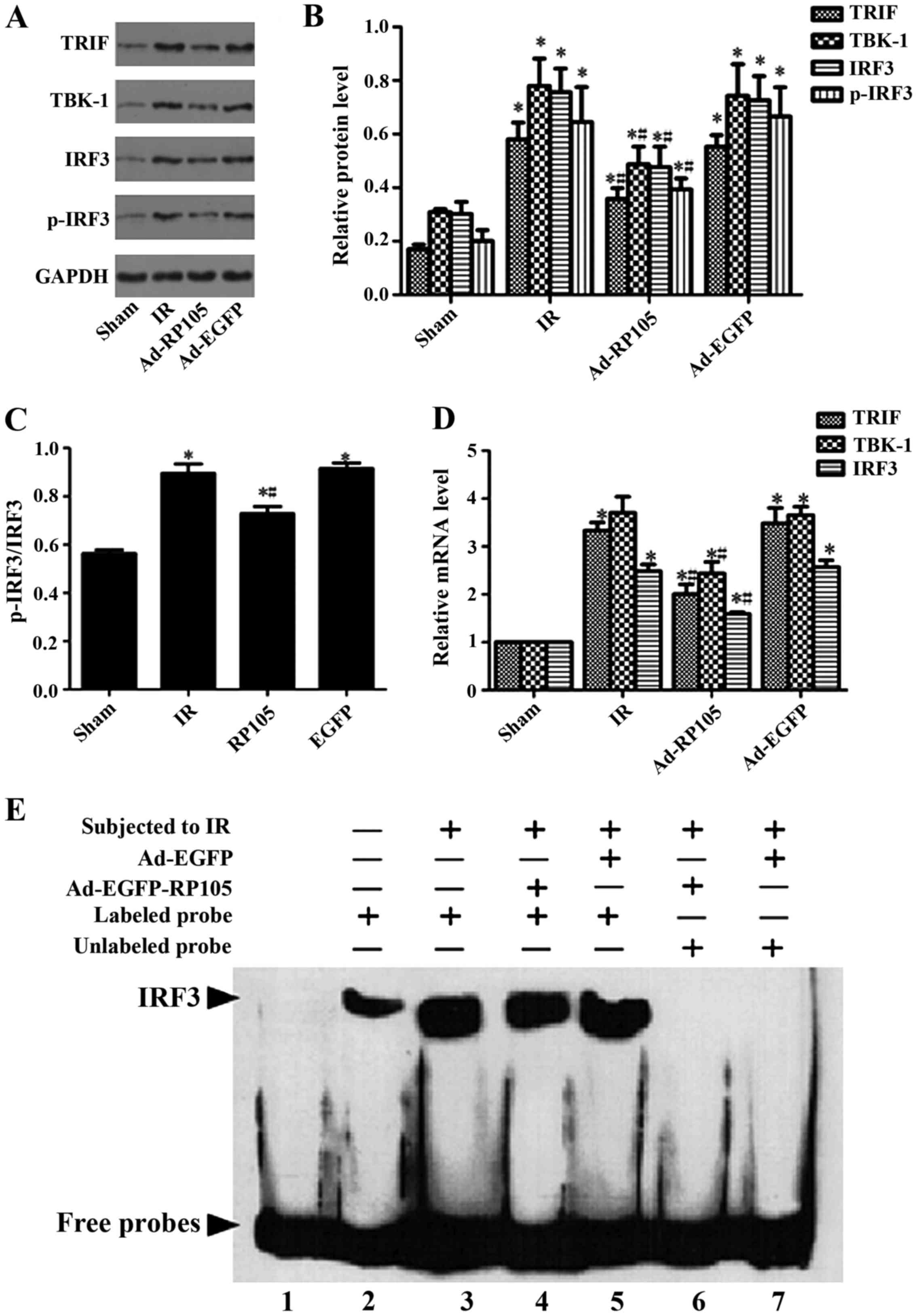
|
1
|
Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin
EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, et al
American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee: Executive summary: Heart disease and
stroke statistics - 2014 update: a report from the American Heart
Association. Circulation. 129:399–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fang Y and Hu J: Toll-like receptor and
its roles in myocardial ischemic/reperfusion injury. Med Sci Monit.
17:RA100–RA109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang M, Chen J, Zhao J and Meng M:
Etanercept attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress. PLoS One.
9:e1080242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma HJ, Li Q, Ma HJ, Guan Y, Shi M, Yang J,
Li DP and Zhang Y: Chronic intermittent hypobaric hypoxia
ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced calcium overload in heart
via Na/Ca2 exchanger in developing rats. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:313–324. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ilczuk T, Wasiutynski A, Wilczek E and
Gornicka B: The study of the protein complement in myocardial
infarction. Immunol Lett. 162:262–268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu J, Qin X, Cai X, Yang L, Xing Y, Li J,
Zhang L, Tang Y, Liu J, Zhang X, et al: Mitochondrial JNK
activation triggers autophagy and apoptosis and aggravates
myocardial injury following ischemia/reperfusion. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1852:262–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kim MY, Lim SH and Lee J: Intake of hot
water-extracted apple protects against myocardial injury by
inhibiting apoptosis in an ischemia/reperfusion rat model. Nutr
Res. 34:951–960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Frangogiannis NG, Smith CW and Entman ML:
The inflammatory response in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res.
53:31–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chao W: Toll-like receptor signaling: A
critical modulator of cell survival and ischemic injury in the
heart. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 296:H1–H12. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Ding HS, Yang J, Gong FL, Yang J, Ding JW,
Li S and Jiang YR: High mobility group [corrected] box 1 mediates
neutrophil recruitment in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
through toll like receptor 4-related pathway. Gene. 509:149–153.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Akira S, Uematsu S and Takeuchi O:
Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 124:783–801. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF,
Madan R, Golenbock DT, visintin A, Finberg RW, Tarakhovsky A, Vogel
SN, Belkaid Y, et al: Inhibition of TLR-4/MD-2 signaling by
RP105/MD-1. J Endotoxin Res. 11:363–368. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Divanovic S, Trompette A, Atabani SF,
Madan R, Golenbock DT, visintin A, Finberg RW, Tarakhovsky A, Vogel
SN, Belkaid Y, et al: Negative regulation of Toll-like receptor 4
signaling by the Toll-like receptor homolog RP105. Nat Immunol.
6:571–578. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wezel A, van der velden D, Maassen JM,
Lagraauw HM, de vries MR, Karper JC, Kuiper J, Bot I and Quax PH:
RP105 deficiency attenuates early atherosclerosis via decreased
monocyte influx in a CCR2 dependent manner. Atherosclerosis.
238:132–139. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ohto U, Miyake K and Shimizu T: Crystal
structures of mouse and human RP105/MD-1 complexes reveal unique
dimer organization of the toll-like receptor family. J Mol Biol.
413:815–825. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kimoto M, Nagasawa K and Miyake K: Role of
TLR4/MD-2 and RP105/MD-1 in innate recognition of
lipopolysaccharide. Scand J Infect Dis. 35:568–572. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang J1, Guo X, Yang J, Ding JW, Li S,
Yang R, Fan ZX and Yang CJ: RP105 protects against apoptosis in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage in rats by
suppressing TLR4-mediated signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
36:2137–2148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Chen L, Yang J, Ding J, Li S, Wu
H, Zhang J, Fan Z, Dong W and Li X: MicroRNA-22 targeting CBP
protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through
anti-apoptosis in rats. Mol Biol Rep. 41:555–561. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
vilahur G and Badimon L:
Ischemia/reperfusion activates myocardial innate immune response:
The key role of the toll-like receptor. Front Physiol. 5:4962014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Miyake K, Yamashita Y, Hitoshi Y, Takatsu
K and Kimoto M: Murine B cell proliferation and protection from
apoptosis with an antibody against a 105-kD molecule:
Unresponsiveness of X-linked immunodeficient B cells. J Exp Med.
180:1217–1224. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ogata H, Su I, Miyake K, Nagai Y, Akashi
S, Mecklenbräuker I, Rajewsky K, Kimoto M and Tarakhovsky A: The
toll-like receptor protein RP105 regulates lipopolysaccharide
signaling in B cells. J Exp Med. 192:23–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bastiaansen AJ, Karper JC, Wezel A, de
Boer HC, Welten SM, de Jong RC, Peters EA, de vries MR, van
Oeveren-Rietdijk AM, van Zonneveld AJ, et al: TLR4 accessory
molecule RP105 (CD180) regulates monocyte-driven arteriogenesis in
a murine hind limb ischemia model. PLoS One. 9:e998822014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hoebe K, Du X, Georgel P, Janssen E,
Tabeta K, Kim SO, Goode J, Lin P, Mann N, Mudd S, et al:
Identification of Lps2 as a key transducer of MyD88-independent TIR
signalling. Nature. 424:743–748. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Akashi S1, Shimazu R, Ogata H, Nagai Y,
Takeda K, Kimoto M and Miyake K: Cutting edge: cell surface
expression and lipopolysaccharide signaling via the toll-like
receptor 4-MD-2 complex on mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Immunol.
164:3471–3475. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Louwe MC, Karper JC, de vries MR, Nossent
AY, Bastiaansen AJ, van der Hoorn JW, Willems van Dijk K, Rensen
PC, Steendijk P, Smit JW, et al: RP105 deficiency aggravates
cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in mice. Int J
Cardiol. 176:788–793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu S, Cai X, Wu J, Cong Q, Chen X, Li T,
Du F, Ren J, Wu YT, Grishin NV, et al: Phosphorylation of innate
immune adaptor proteins MAvS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3
activation. Science. 347:aaa26302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Covert MW, Leung TH, Gaston JE and
Baltimore D: Achieving stability of lipopolysaccharide-induced
NF-kappaB activation. Science. 309:1854–1857. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fitzgerald KA, McWhirter SM, Faia KL, Rowe
DC, Latz E, Golenbock DT, Coyle AJ, Liao SM and Maniatis T:
IKKepsilon and TBK1 are essential components of the IRF3 signaling
pathway. Nat Immunol. 4:491–496. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S
and Medzhitov R: TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4
to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol. 9:361–368. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
O'Neill LA and Bowie AG: The family of
five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in Toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:353–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bowie AG and Haga IR: The role of
Toll-like receptors in the host response to viruses. Mol Immunol.
42:859–867. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Perry AK, Chen G, Zheng D, Tang H and
Cheng G: The host type I interferon response to viral and bacterial
infections. Cell Res. 15:407–422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Toshchakov V, Jones BW, Perera PY, Thomas
K, Cody MJ, Zhang S, Williams BR, Major J, Hamilton TA, Fenton MJ,
et al: TLR4, but not TLR2, mediates IFN-beta-induced
STAT1alpha/beta-dependent gene expression in macrophages. Nat
Immunol. 3:392–398. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Samavati L, Rastogi R, Du W, Hüttemann M,
Fite A and Franchi L: STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical
for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to
lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol Immunol. 46:1867–1877.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hui KP1, Lee SM, Cheung CY, Ng IH, Poon
LL, Guan Y, Ip NY, Lau AS and Peiris JS: Induction of
proinflammatory cytokines in primary human macrophages by influenza
A virus (H5N1) is selectively regulated by IFN regulatory factor 3
and p38 MAPK. J Immunol. 182:1088–1098. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang JW, Koh EJ and Lee SM: Melatonin
protects liver against ischemia and reperfusion injury through
inhibition of toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J Pineal Res.
50:403–411. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kang JW and Lee SM: Melatonin inhibits
type 1 interferon signaling of toll-like receptor 4 via heme
oxygenase-1 induction in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. J Pineal
Res. 53:67–76. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang HF, Zeng Z, Wang KH, Zhang HY, Wang
S, Zhou WX, Wang ZB, Xu WG and Duan J: Heme oxygenase-1 protects
rat liver against warm ischemia/reperfusion injury via
TLR2/TLR4-triggered signaling pathways. World J Gastroenterol.
21:2937–2948. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mahmoud MF, Gamal S and El-Fayoumi HM:
Limonin attenuates hepatocellular injury following liver ischemia
and reperfusion in rats via toll-like receptor dependent pathway.
Eur J Pharmacol. 740:676–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dvoriantchikova G, Santos AR, Danek D,
Dvoriantchikova X and Ivanov D: The TIR-domain-containing adapter
inducing interferon-β-dependent signaling cascade plays a crucial
role in ischemia-reperfusion-induced retinal injury, whereas the
contribution of the myeloid differentiation primary response
88-dependent signaling cascade is not as pivotal. Eur J Neurosci.
40:2502–2512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang J, He GZ, Wang YK, Zhu QK, Chen W and
Guo T: TLR4-HMGB1-, MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling in mouse
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury. World J Gastroenterol.
21:8314–8325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lyon AR, Sato M, Hajjar RJ, Samulski RJ
and Harding SE: Gene therapy: Targeting the myocardium. Heart.
94:89–99. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mason D, Chen YZ, Krishnan HV and Sant S:
Cardiac gene therapy: Recent advances and future directions. J
Control Release. 215:101–111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang ZJ, Xu SL, Chen B, Zhang SL, Zhang
YL, Wei W, Ma DC, Wang LS, Zhu TB, Li CJ, et al: Hepatocyte growth
factor plays a critical role in the regulation of cytokine
production and induction of endothelial progenitor cell
mobilization: A pilot gene therapy study in patients with coronary
heart disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 36:790–796. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sasano T, Kikuchi K, McDonald AD, Lai S
and Donahue JK: Targeted high-efficiency, homogeneous myocardial
gene transfer. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 42:954–961. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|