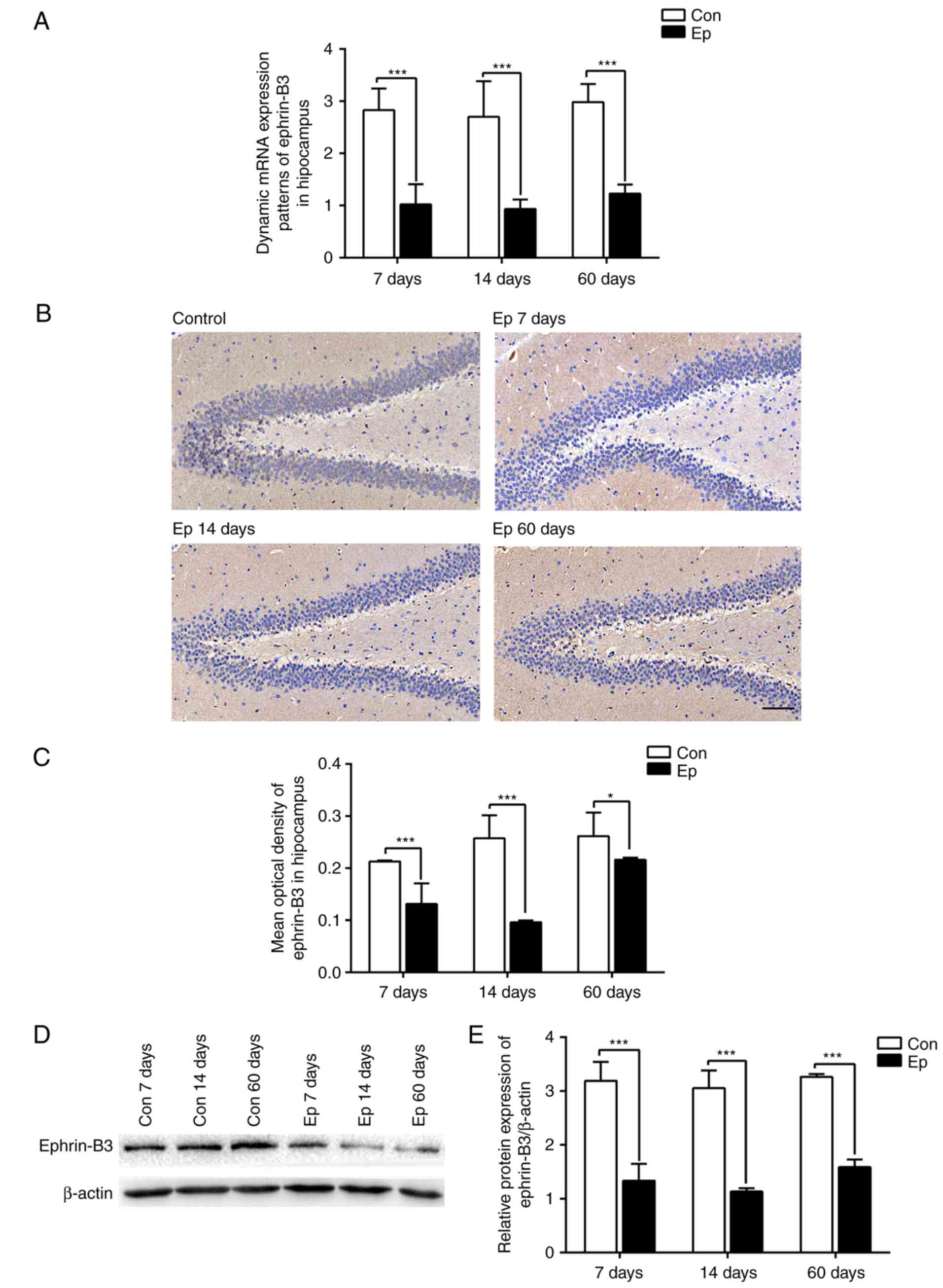
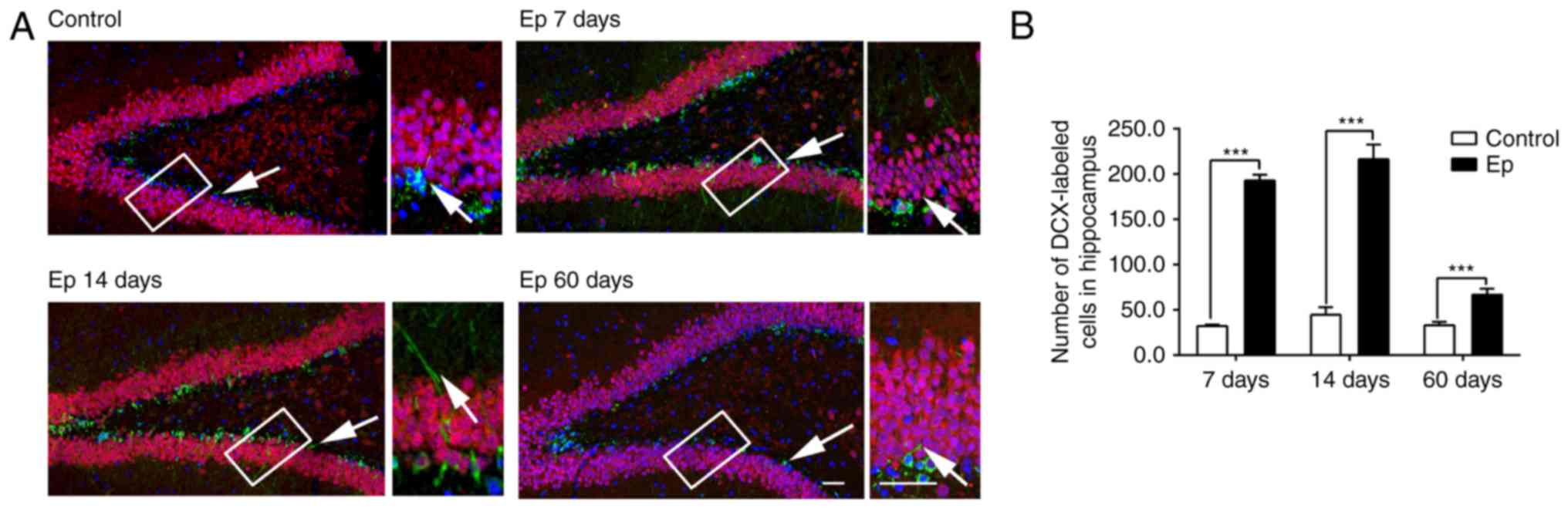
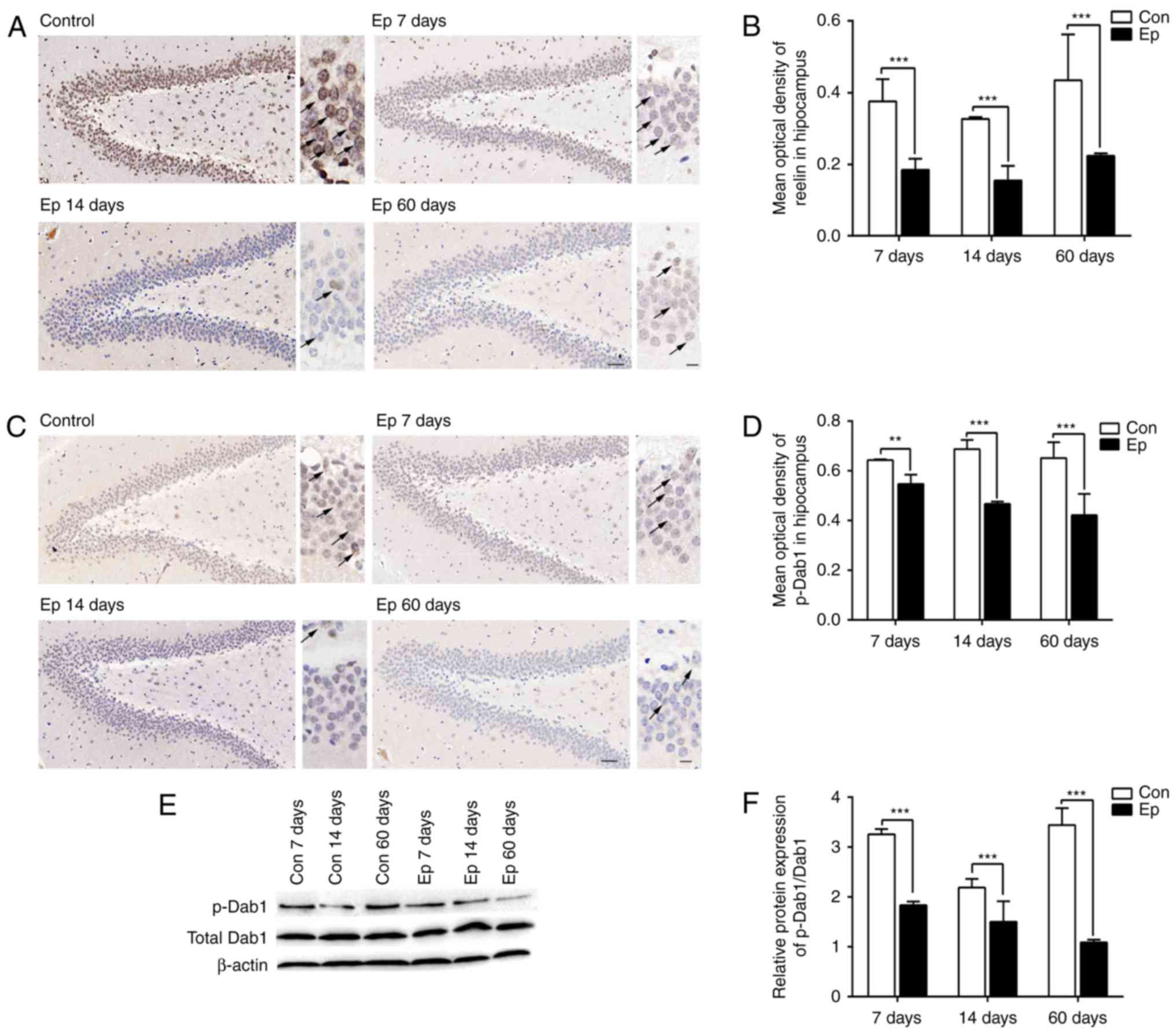
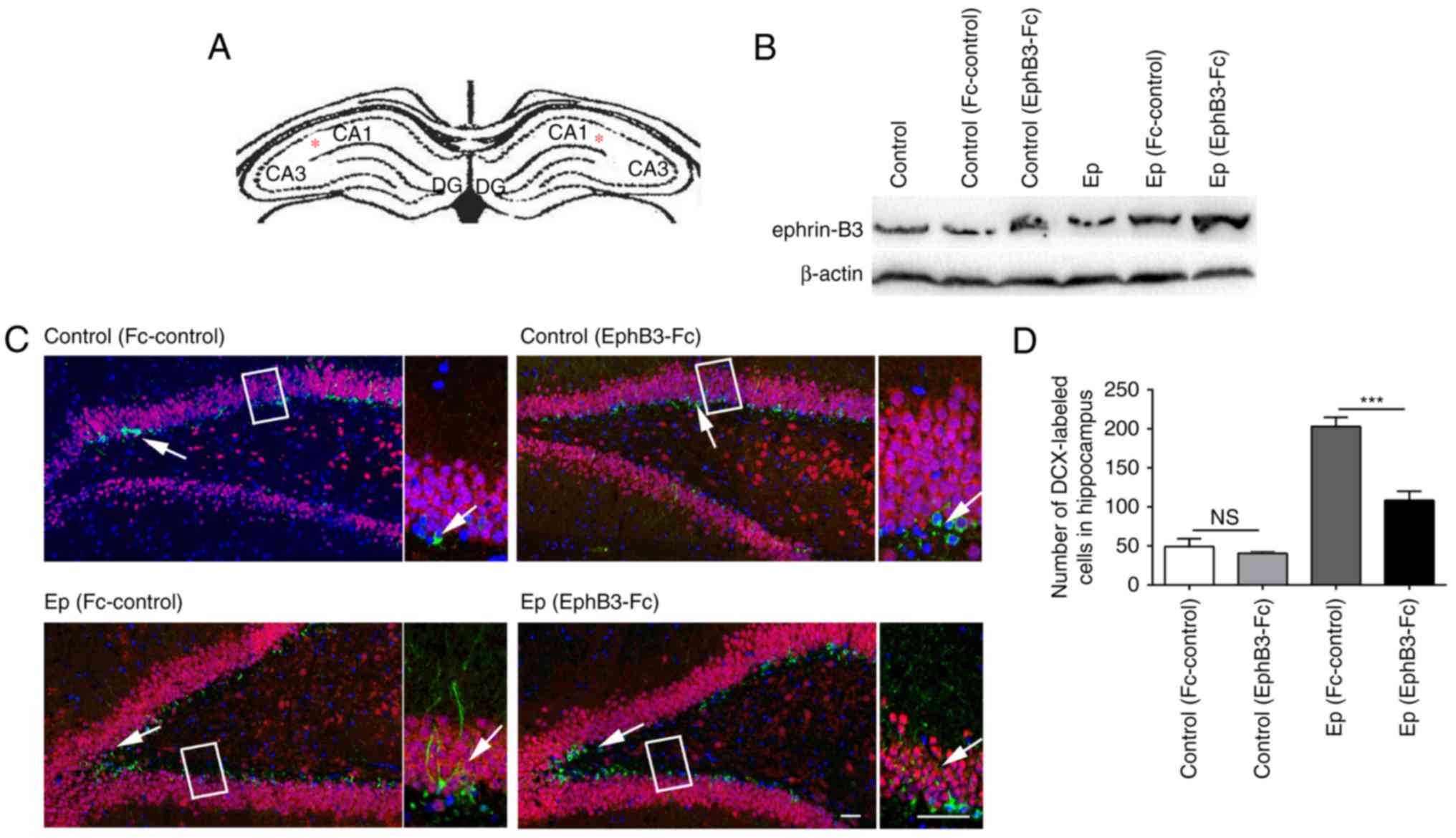
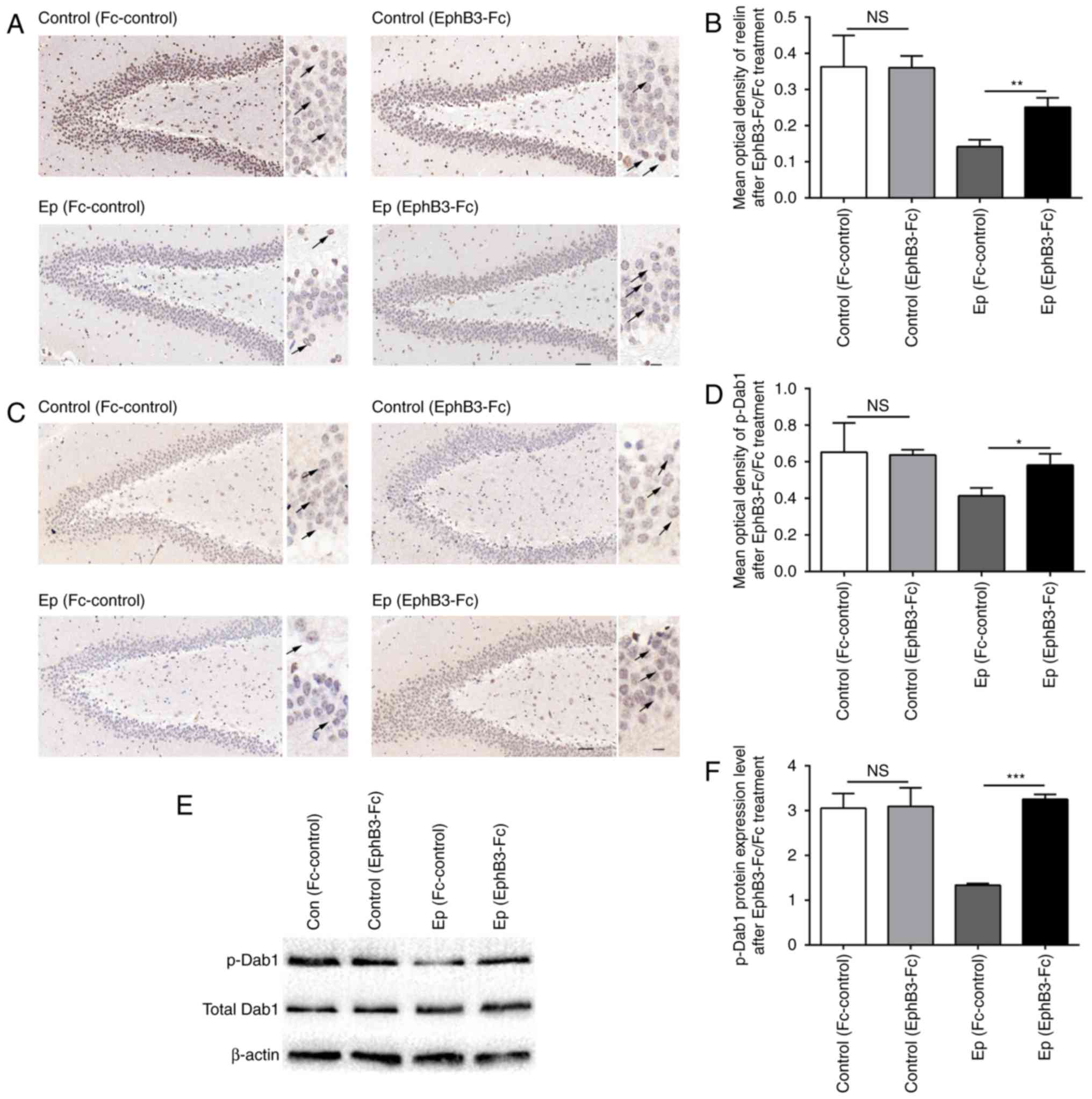
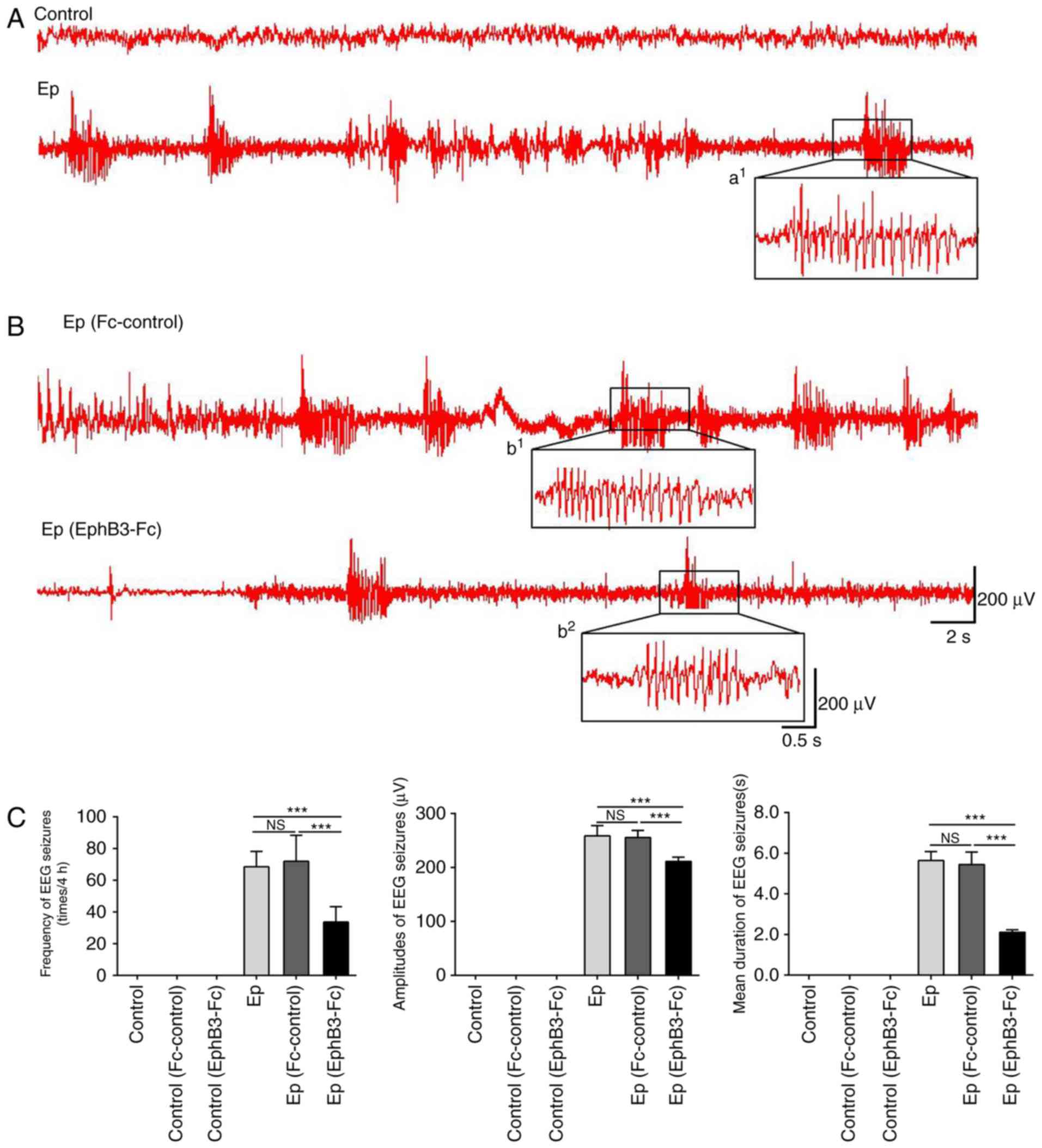
|
1
|
Moshe SL, Perucca E, Ryvlin P and Tomson
T: Epilepsy: New advances. Lancet. 385:884–898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu TT, Feng L, Liu HF, Shu Y and Xiao B:
Altered axon initial segment in hippocampal newborn neurons,
associated with recurrence of temporal lobe epilepsy in rats. Mol
Med Rep. 16:3169–3178. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Peng Z, Xiao B and Houser CR:
Activation of ERK by spontaneous seizures in neural progenitors of
the dentate gyrus in a mouse model of epilepsy. Exp Neurol.
224:133–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
von Bohlen und Halbach O:
Immunohistological markers for proliferative events, gliogenesis,
and neurogenesis within the adult hippocampus. Cell Tissue Res.
345:1–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Parent JM and Kron MM: Neurogenesis and
Epilepsy. 2012.
|
|
6
|
Ishii K, Kubo K, Endo T, Yoshida K, Benner
S, Ito Y, Aizawa H, Aramaki M, Yamanaka A, Tanaka K, et al:
Neuronal Heterotopias affect the activities of distant brain areas
and lead to behavioral deficits. J Neurosci. 35:12432–12445. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Klein R and Kania A: Ephrin signalling in
the developing nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 27C:16–24.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chumley MJ, Catchpole T, Silvany RE,
Kernie SG and Henkemeyer M: EphB receptors regulate stem/progenitor
cell proliferation, migration, and polarity during hippocampal
neurogenesis. J Neurosci. 27:13481–13490. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Furne C, Ricard J, Cabrera JR, Pays L,
Bethea JR, Mehlen P and Liebl DJ: EphrinB3 is an anti-apoptotic
ligand that inhibits the dependence receptor functions of EphA4
receptors during adult neurogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1793:231–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Antion MD, Christie LA, Bond AM, Dalva MB
and Contractor A: Ephrin-B3 regulates glutamate receptor signaling
at hippocampal synapses. Mol Cell Neurosci. 45:378–388. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forster E: Reelin, neuronal polarity and
process orientation of cortical neurons. Neuroscience. 269:102–111.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Senturk A, Pfennig S, Weiss A, Burk K and
Acker-Palmer A: Ephrin Bs are essential components of the Reelin
pathway to regulate neuronal migration. Nature. 472:356–360. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leeb C, Eresheim C and Nimpf J: Clusterin
is a ligand for apolipoprotein E receptor 2 (ApoER2) and very low
density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and signals via the
Reelin-signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 289:4161–4172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bosch C, Masachs N, Exposito-Alonso D,
Martínez A, Teixeira CM, Fernaud I, Pujadas L, Ulloa F, Comella JX,
DeFelipe J, et al: Reelin regulates the maturation of dendritic
spines, synaptogenesis and glial ensheathment of newborn granule
cells. Cereb Cortex. 26:4282–4298. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Racine RJ: Modification of seizure
activity by electrical stimulation. II. Motor seizure.
Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 32:281–294. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khazipov R, Zaynutdinova D, Ogievetsky E,
Valeeva G, Mitrukhina O, Manent JB and Represa A: Atlas of the
postnatal rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Front Neuroanat.
9:1612015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kanamori K: Faster flux of
neurotransmitter glutamate during seizure-Evidence from
13C-enrichment of extracellular glutamate in kainate rat model.
PLoS One. 12:e01748452017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wu Q, Li Y, Shu Y, Feng L, Zhou L, Yue ZW,
Luo ZH, Wu ZG and Xiao B: NDEL1 was decreased in the CA3 region but
increased in the hippocampal blood vessel network during the
spontaneous seizure period after pilocarpine-induced status
epilepticus. Neuroscience. 268:276–283. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G and Pasquale EB:
Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hruska M and Dalva MB: Ephrin regulation
of synapse formation, function and plasticity. Mol Cell Neurosci.
50:35–44. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ricard J, Salinas J, Garcia L and Liebl
DJ: EphrinB3 regulates cell proliferation and survival in adult
neurogenesis. Mol Cell Neurosci. 31:713–722. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Piccinin S, Cinque C, Calo L, Molinaro G,
Battaglia G, Maggi L, Nicoletti F, Melchiorri D, Eusebi F, Massey
PV, et al: Interaction between Ephrins and mGlu5 metabotropic
glutamate receptors in the induction of long-term synaptic
depression in the hippocampus. J Neurosci. 30:2835–2843. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shu Y, Xiao B, Wu Q, Liu T, Du Y, Tang H,
Chen S, Feng L, Long L and Li Y: The Ephrin-A5/EphA4 interaction
modulates neurogenesis and angiogenesis by the p-Akt and p-ERK
pathways in a mouse model of TLE. Mol Neurobiol. 53:561–576. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kron MM, Zhang H and Parent JM: The
developmental stage of dentate granule cells dictates their
contribution to seizure-induced plasticity. J Neurosci.
30:2051–2059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parent JM, Yu TW, Leibowitz RT, Geschwind
DH, Sloviter RS and Lowenstein DH: Dentate granule cell
neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant
network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci.
17:3727–3738. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song C, Xu W, Zhang X, Wang S, Zhu G, Xiao
T, Zhao M and Zhao C: CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 suppresses the
long-term abnormal structural changes of newborn neurons in the
intraventricular kainic acid model of epilepsy. Mol Neurobiol.
53:1518–1532. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kobow K, Jeske I, Hildebrandt M, Hauke J,
Hahnen E, Buslei R, Buchfelder M, Weigel D, Stefan H, Kasper B, et
al: Increased reelin promoter methylation is associated with
granule cell dispersion in human temporal lobe epilepsy. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 68:356–364. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haas CA and Frotscher M: Reelin deficiency
causes granule cell dispersion in epilepsy. Exp Brain Res.
200:141–149. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Michelucci R, Pulitano P, Di Bonaventura
C, Binelli S, Luisi C, Pasini E, Striano S, Striano P, Coppola G,
La Neve A, et al: The clinical phenotype of autosomal dominant
lateral temporal lobe epilepsy related to reelin mutations.
Epilepsy Behav. 68:103–107. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Baek ST, Copeland B, Yun EJ, Kwon SK,
Guemez-Gamboa A, Schaffer AE, Kim S, Kang HC, Song S, Mathern GW,
et al: An AKT3-FOXG1-reelin network underlies defective migration
in human focal malformations of cortical development. Nat Med.
21:1445–1454. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Korn MJ, Mandle QJ and Parent JM:
Conditional disabled-1 deletion in mice alters hippocampal
neurogenesis and reduces seizure threshold. Front Neurosci.
10:632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dobrzanski P, Hunter K, Jones-Bolin S,
Chang H, Robinson C, Pritchard S, Zhao H and Ruggeri B:
Antiangiogenic and anti-tumor efficacy of EphA2 receptor
antagonist. Cancer Res. 64:910–919. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|