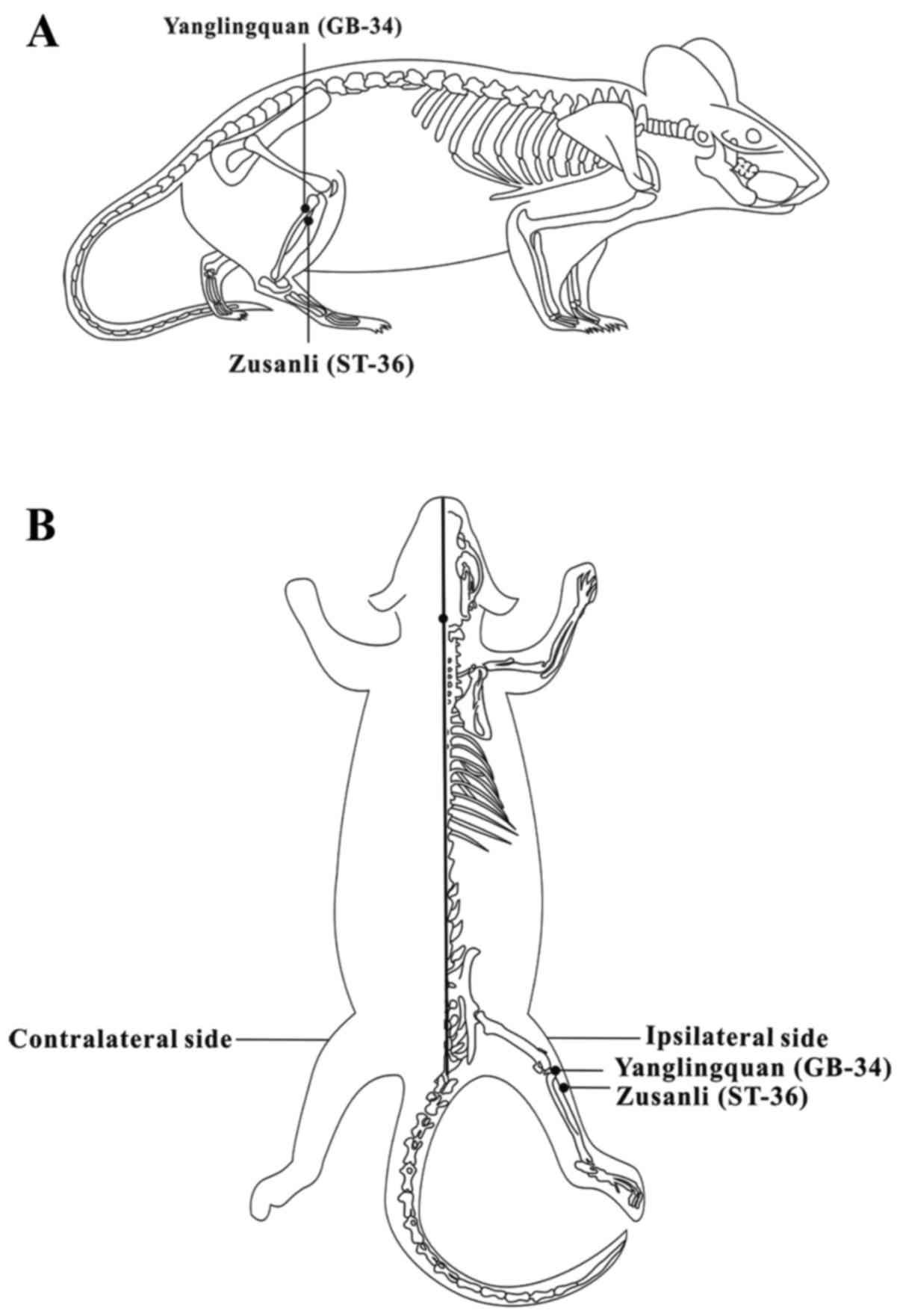
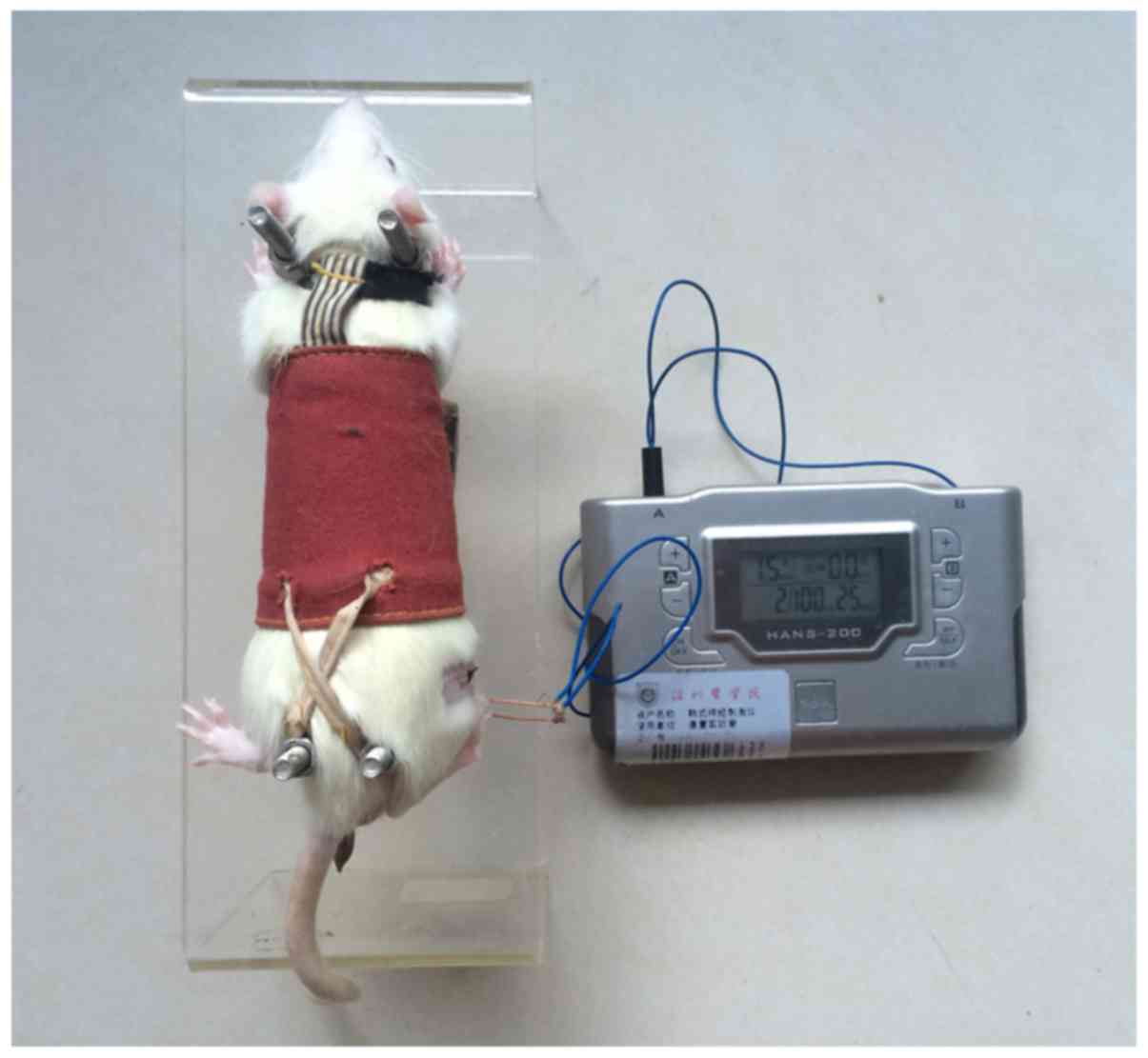
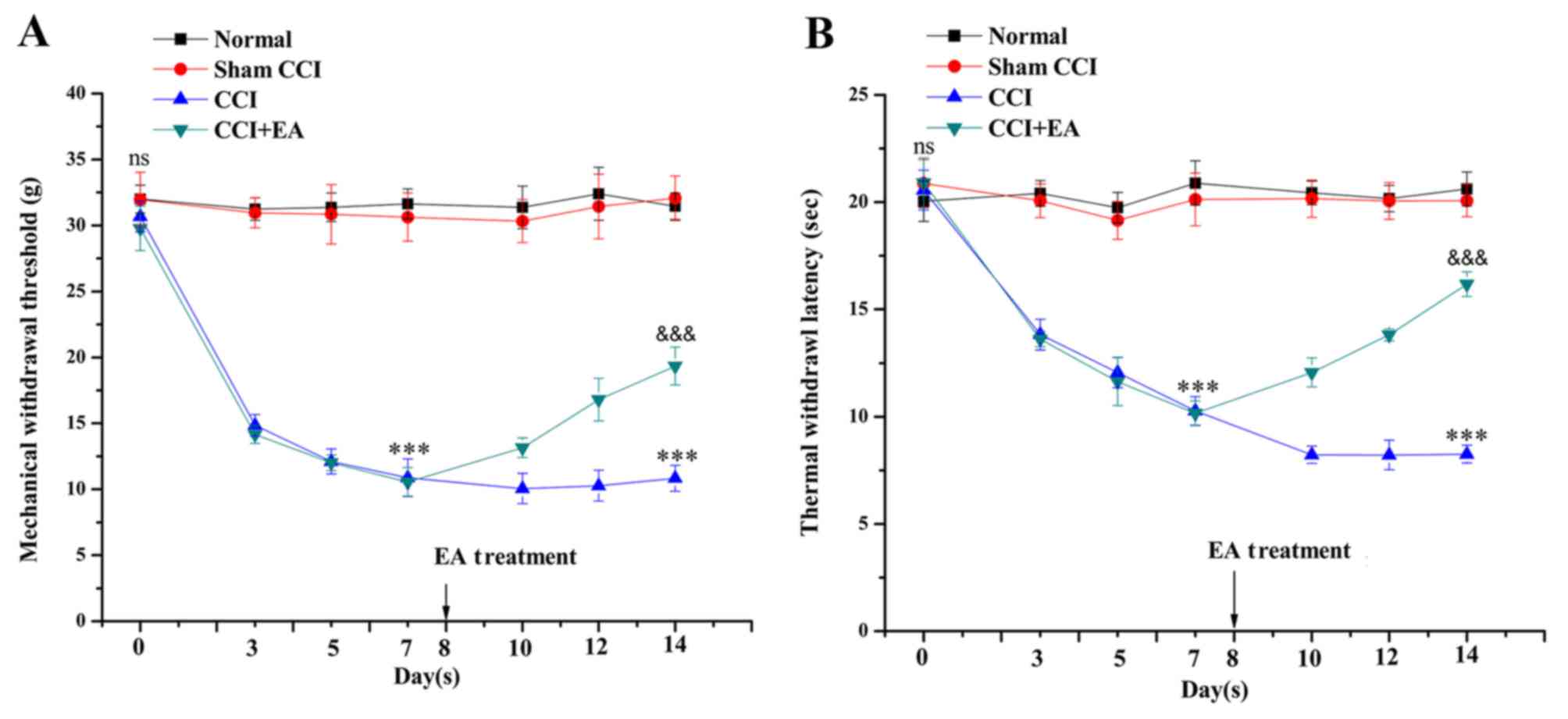
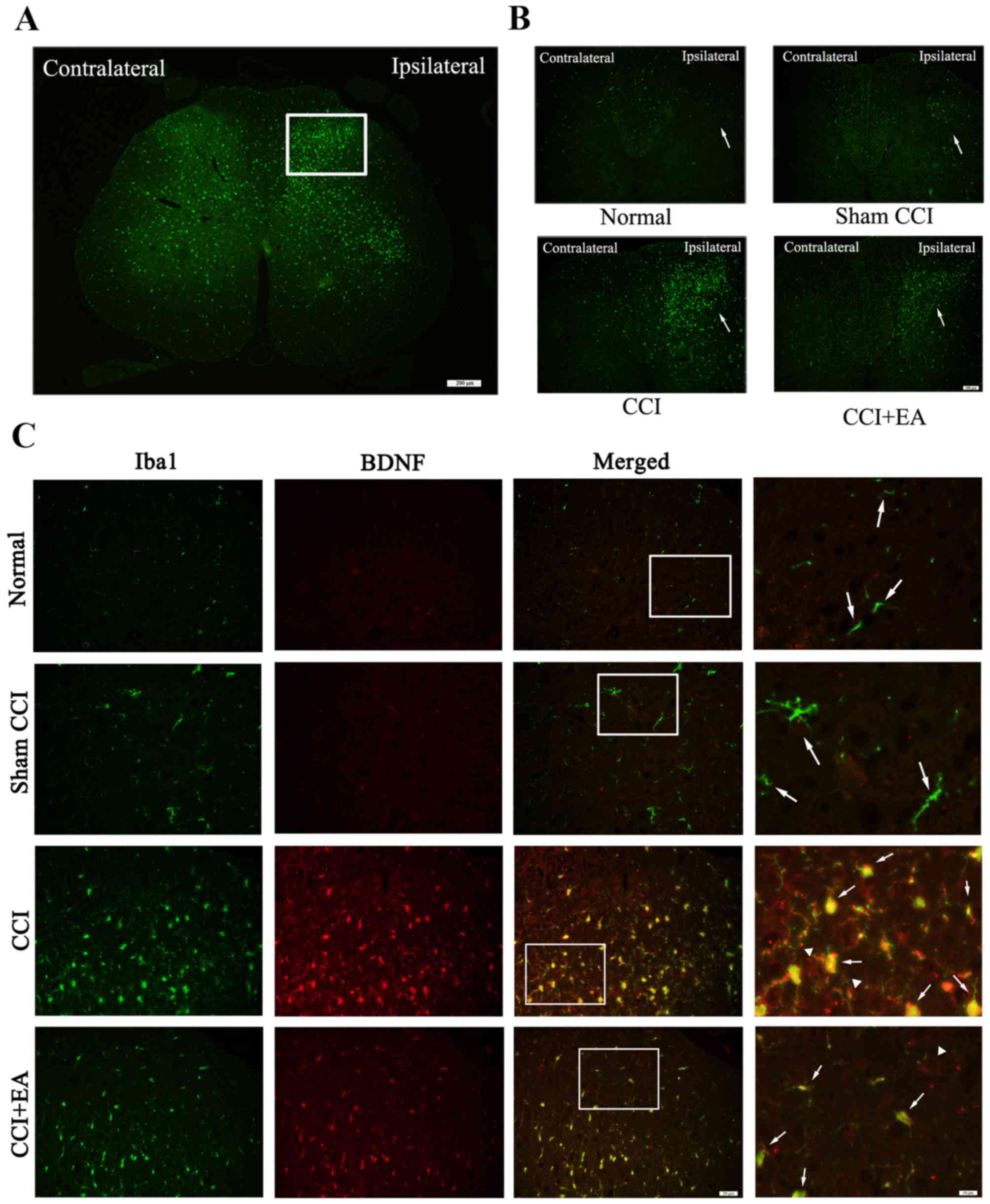
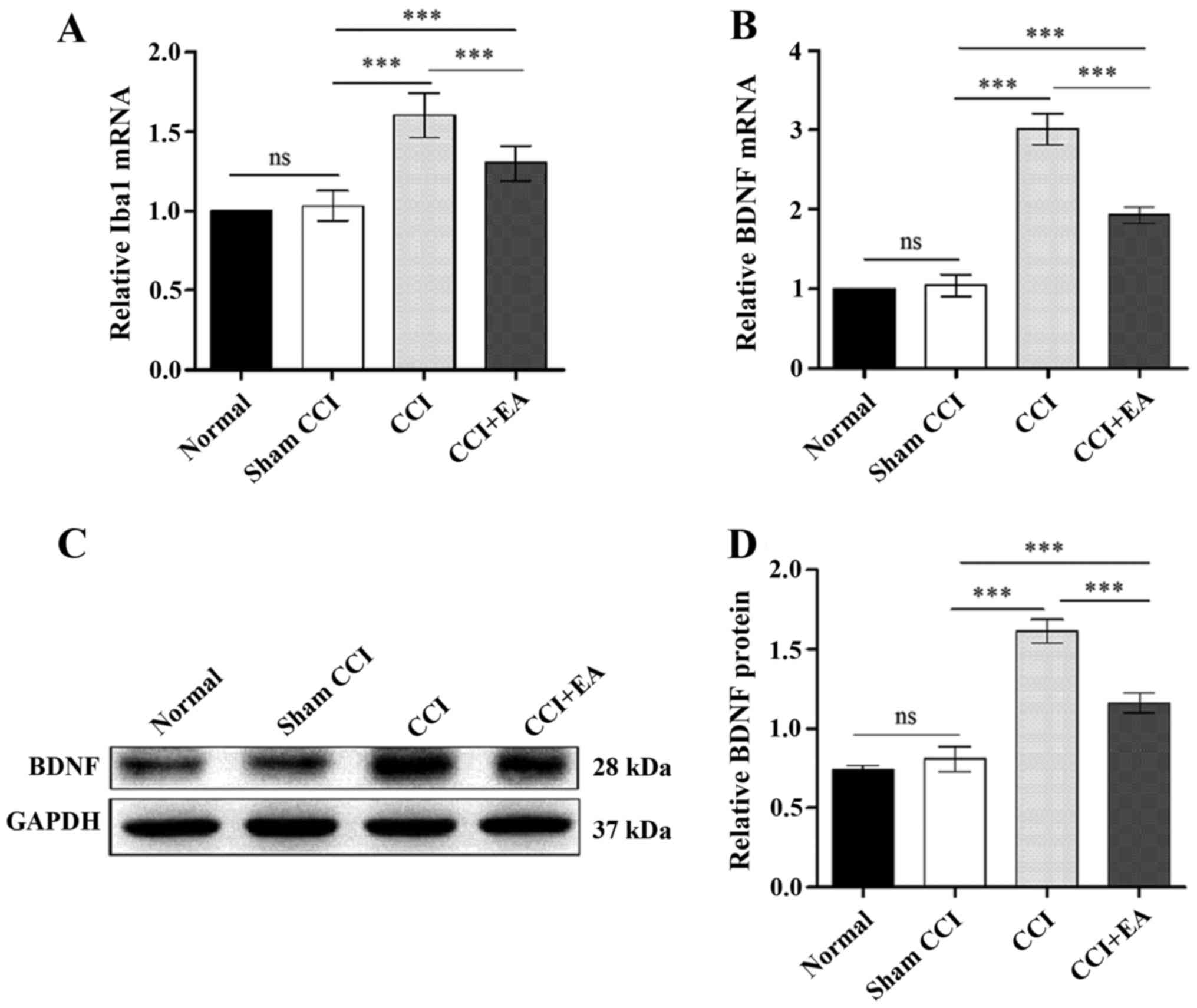
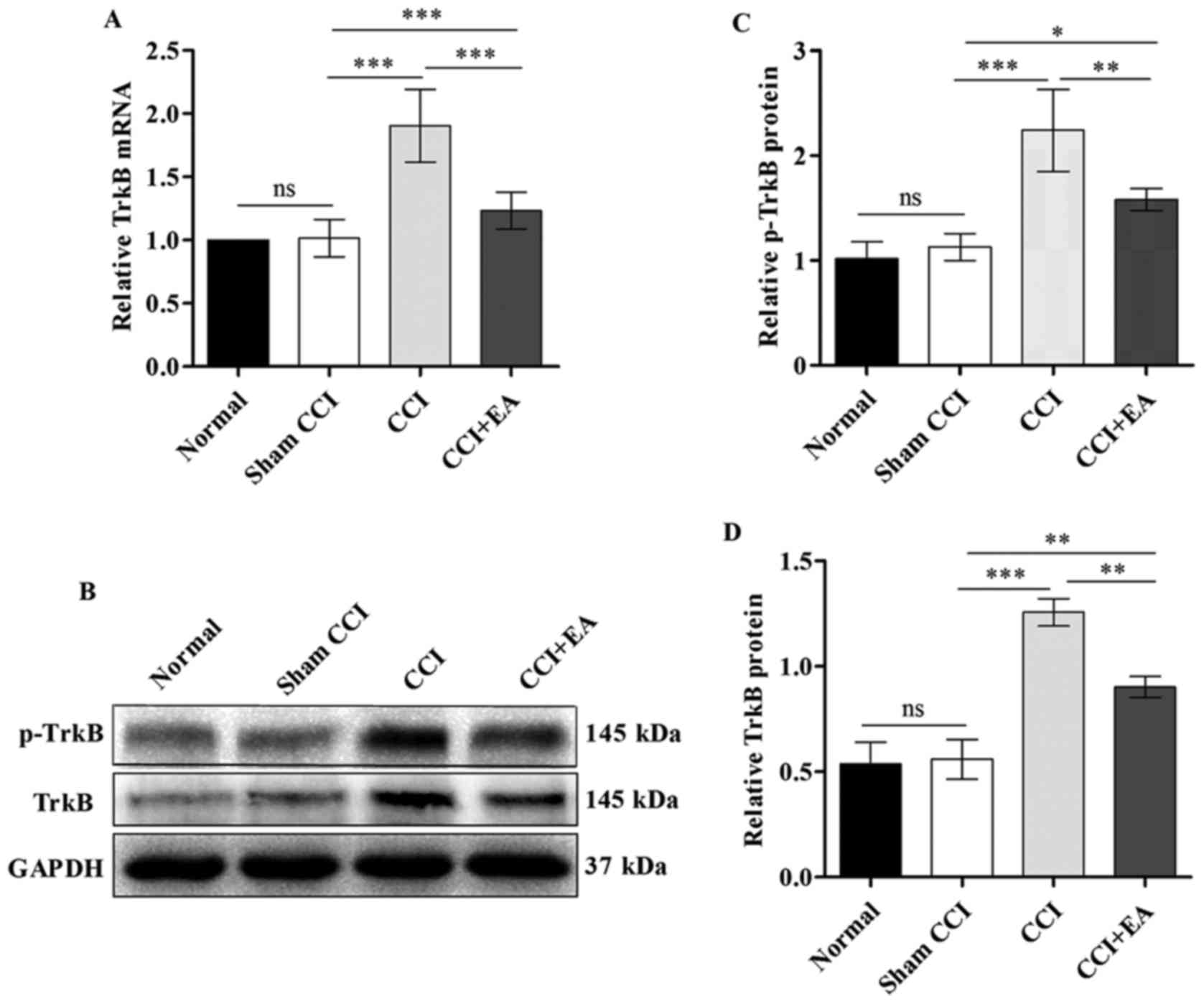
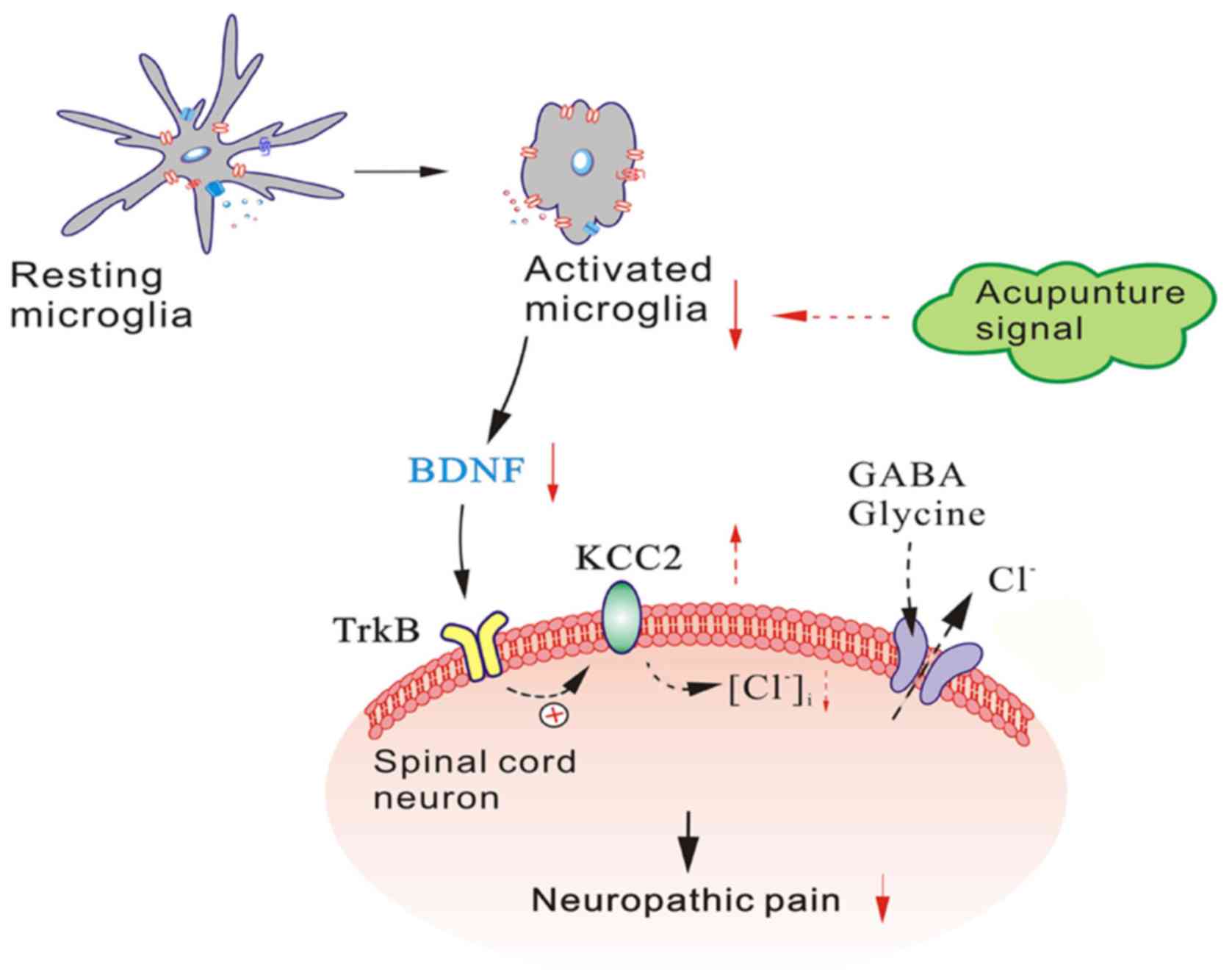
|
1
|
Baron R: Neuropathic pain: A clinical
perspective. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 194:3–30. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Goettl VM, Huang Y, Hackshaw KV and
Stephens RL Jr: Reduced basal release of serotonin from the
ventrobasal thalamus of the rat in a model of neuropathic pain.
Pain. 99:359–366. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Smith HS: Opioids and neuropathic pain.
Pain Physician. 15(Suppl 3): ES93–ES110. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ren W, Tu W, Jiang S, Cheng R and Du Y:
Electroacupuncture improves neuropathic pain: Adenosine, adenosine
5′-triphosphate disodium and their receptors perhaps change
simultaneously. Neural Regen Res. 7:2618–2623. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tu W, Wang W, Xi H, He R, Gao L and Jiang
S: Regulation of neurotrophin-3 and interleukin-1beta and
inhibition of spinal glial activation contribute to the analgesic
effect of electroacu-puncture in chronic neuropathic pain states of
rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015:6420812015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tsuda M, Beggs S, Salter MW and Inoue K:
Microglia and intractable chronic pain. Glia. 61:55–61. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Xu Y, Wang J, Zhou Q, Pu S, Jiang
W and Du D: The effect of intrathecal administration of glial
activation inhibitors on dorsal horn BDNF overexpression and hind
paw mechanical allodynia in spinal nerve ligated rats. J Neural
Transm Vienna. 119:329–336. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pandya CD, Kutiyanawalla A and Pillai A:
BDNF-TrkB signaling and neuroprotection in schizophrenia. Asian J
Psychiatr. 6:22–28. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xing GG, Liu FY, Qu XX, Han JS and Wan Y:
Long-term synaptic plasticity in the spinal dorsal horn and its
modulation by electroacupuncture in rats with neuropathic pain. Exp
Neurol. 208:323–332. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim SK, Park JH, Bae SJ, Kim JH, Hwang BG,
Min BI, Park DS and Na HS: Effects of electroacupuncture on cold
allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain: Mediation by spinal
adrenergic and serotonergic receptors. Exp Neurol. 195:430–436.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lau WK, Lau YM, Zhang HQ, Wong SC and Bian
ZX: Electroacupuncture versus celecoxib for neuropathic pain in rat
SNL model. Neuroscience. 170:655–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Zhao ZQ and
Zhang YQ: Evidence for suppression of electroacupuncture on spinal
glial activation and behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of
monoarthritis. Brain Res Bull. 75:83–93. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Fox A, Kesingland A, Gentry C, McNair K,
Patel S, Urban L and James I: The role of central and peripheral
Cannabinoid1 receptors in the antihyperalgesic activity of
cannabinoids in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain. 92:91–100. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang C, Li HT, Shi YS, Han JS and Wan Y:
Ketamine potentiates the effect of electroacupuncture on mechanical
allodynia in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett.
368:327–331. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao YH, Wang JY, Qiao LN, Chen SP, Tan LH,
Xu QL and Liu JL: NK cells mediate the cumulative analgesic effect
of electroacupuncture in a rat model of neuropathic pain. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 14:3162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tu WZ, Cheng RD, Cheng B, Lu J, Cao F, Lin
HY, Jiang YX, Wang JZ, Chen H and Jiang SH: Analgesic effect of
electroacupuncture on chronic neuropathic pain mediated by P2X3
receptors in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurochem Int.
60:379–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang WS, Tu WZ, Cheng RD, He R, Ruan LH,
Zhang L, Gong YS, Fan XF, Hu J, Cheng B, et al: Electroacupuncture
and A-317491 depress the transmission of pain on primary afferent
mediated by the P2X3 receptor in rats with chronic neuropathic pain
states. J Neurosci Res. 92:1703–1713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Silva JR, Silva ML and Prado WA: Analgesia
induced by 2- or 100-Hz electroacupuncture in the rat tail-flick
test depends on the activation of different descending pain
inhibitory mechanisms. J Pain. 12:51–60. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Filshie J: The non-drug treatment of
neuralgic and neuropathic pain of malignancy. Cancer Surv.
7:161–193. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wong JY and Rapson LM: Acupuncture in the
management of pain of musculoskeletal and neurologic origin. Phys
Med Rehabil Clin N Am. 10:531–545. vii–viii. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qin Z, Liu X, Yao Q, Zhai Y and Liu Z:
Acupuncture for treating sciatica: A systematic review protocol.
BMJ Open. 5:e0074982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao ZQ: Neural mechanism underlying
acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol. 85:355–375. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen S, Wang S, Rong P, Wang J, Qiao L,
Feng X, Liu J and Zhang J: Acupuncture for visceral pain: neural
substrates and potential mechanisms. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2014:6095942014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Trang T, Beggs S and Salter MW:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor from microglia: A molecular
substrate for neuropathic pain. Neuron Glia Biol. 7:99–108. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mika J, Zychowska M, Popiolek-Barczyk K,
Rojewska E and Przewlocka B: Importance of glial activation in
neuropathic pain. Eur J Pharmacol. 716:106–119. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Inoue K, Tsuda M and Tozaki-Saitoh H: Role
of the glia in neuropathic pain caused by peripheral nerve injury.
Brain Nerve. 64:1233–1239. 2012.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang LL, Yang JL, Lü N, Gu XY, Zhang YQ
and Zhao ZQ: Synergetic analgesia of propentofylline and
electroacupuncture by interrupting spinal glial function in rats.
Neurochem Res. 35:1780–1786. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi DC, Lee JY, Lim EJ, Baik HH, Oh TH
and Yune TY: Inhibition of ROS-induced P38MAPK and ERK activation
in microglia by acupuncture relieves neuropathic pain after spinal
cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 236:268–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shan S, Qi-Liang MY, Hong C, Tingting L,
Mei H, Haili P, Yan-Qing W, Zhi-Qi Z and Yu-Qiu Z: Is functional
state of spinal microglia involved in the anti-allodynic and
anti-hyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture in rat model of
monoarthritis? Neurobiol Dis. 26:558–568. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Narita M, Yoshida T, Nakajima M, Narita M,
Miyatake M, Takagi T, Yajima Y and Suzuki T: Direct evidence for
spinal cord microglia in the development of a neuropathic pain-like
state in mice. J Neurochem. 97:1337–1348. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Coull JA, Beggs S, Boudreau D, Boivin D,
Tsuda M, Inoue K, Gravel C, Salter MW and De Koninck Y: BDNF from
microglia causes the shift in neuronal anion gradient underlying
neuropathic pain. Nature. 438:1017–1021. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang W, Liu LY and Xu TL: Reduced
potassium-chloride co-transporter expression in spinal cord dorsal
horn neurons contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity in
rats. Neuroscience. 152:502–510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rivera C, Voipio J, Thomas-Crusells J, Li
H, Emri Z, Sipilä S, Payne JA, Minichiello L, Saarma M and Kaila K:
Mechanism of activity-dependent downregulation of the
neuron-specific K-Cl cotransporter KCC2. J Neurosci. 24:4683–4691.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Coull JA, Boudreau D, Bachand K, Prescott
SA, Nault F, Sík A, De Koninck P and De Koninck Y: Trans-synaptic
shift in anion gradient in spinal lamina I neurons as a mechanism
of neuropathic pain. Nature. 424:938–942. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Biggs JE, Lu VB, Stebbing MJ,
Balasubramanyan S and Smith PA: Is BDNF sufficient for information
transfer between microglia and dorsal horn neurons during the onset
of central sensitization? Mol Pain. 6:442010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kahle KT, Staley KJ, Nahed BV, Gamba G,
Hebert SC, Lifton RP and Mount DB: Roles of the cation-chloride
cotransporters in neurological disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol.
4:490–503. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cordero-Erausquin M, Coull JA, Boudreau D,
Rolland M and De Koninck Y: Differential maturation of GABA action
and anion reversal potential in spinal lamina I neurons: Impact of
chloride extrusion capacity. J Neurosci. 25:9613–9623. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|