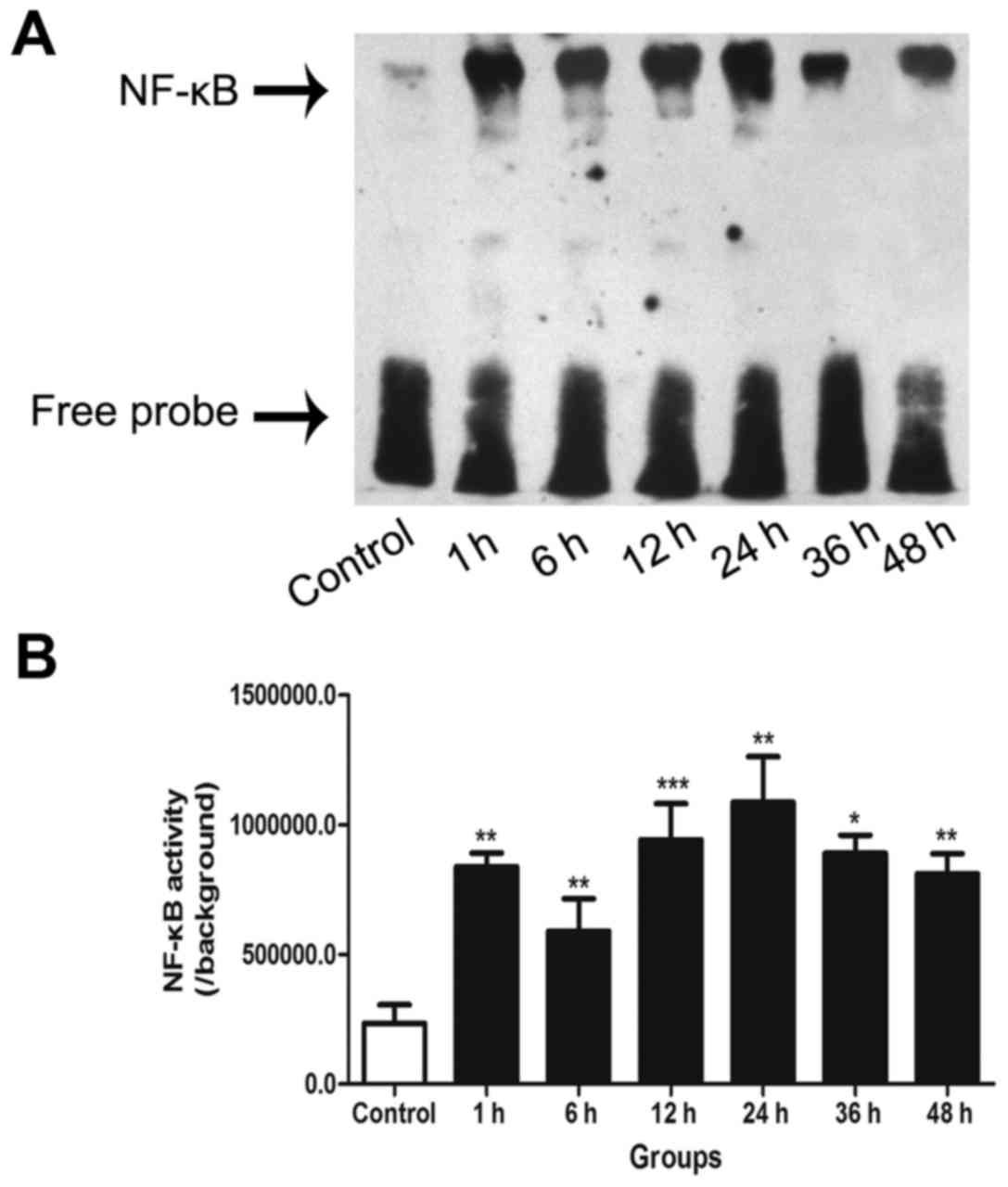
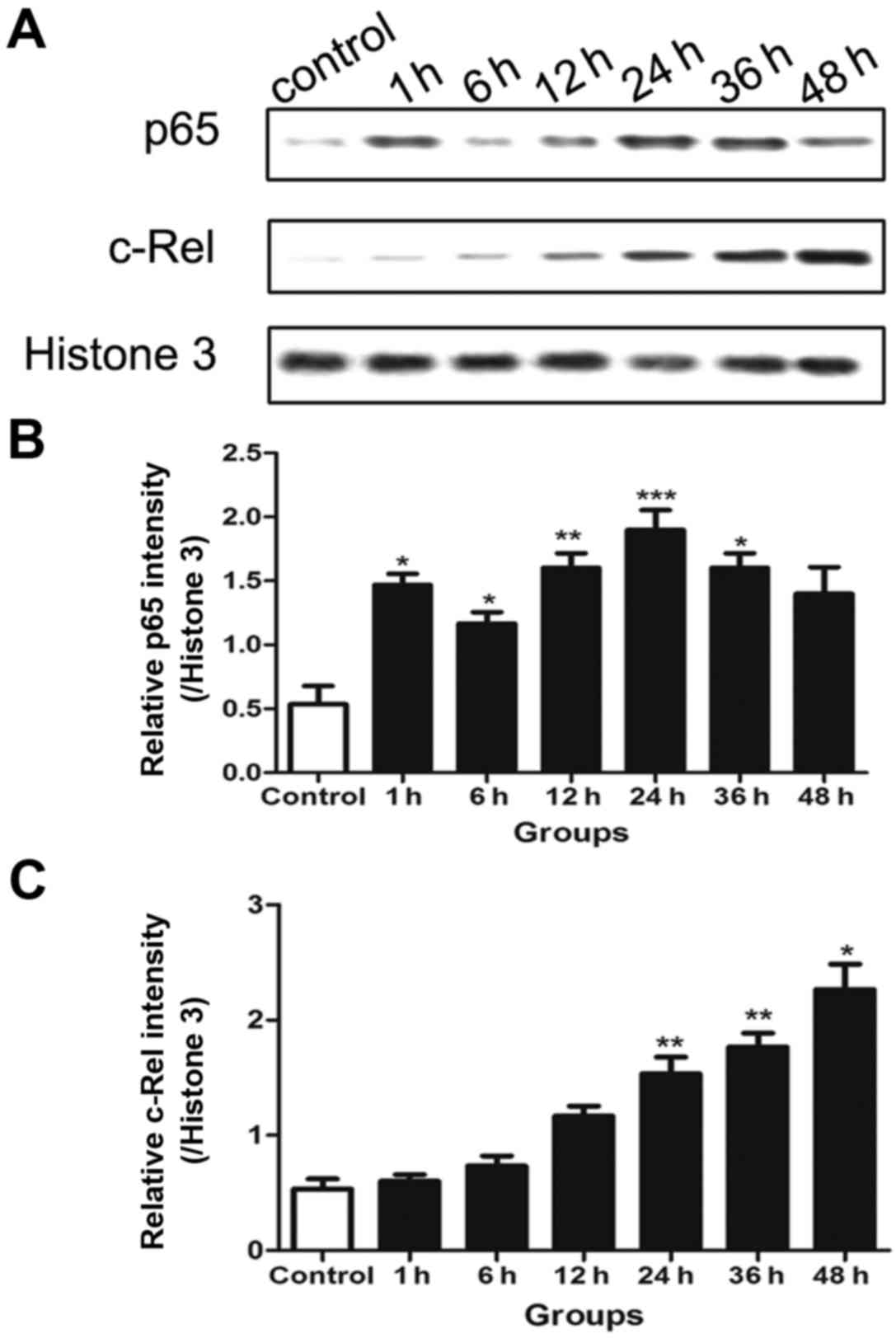
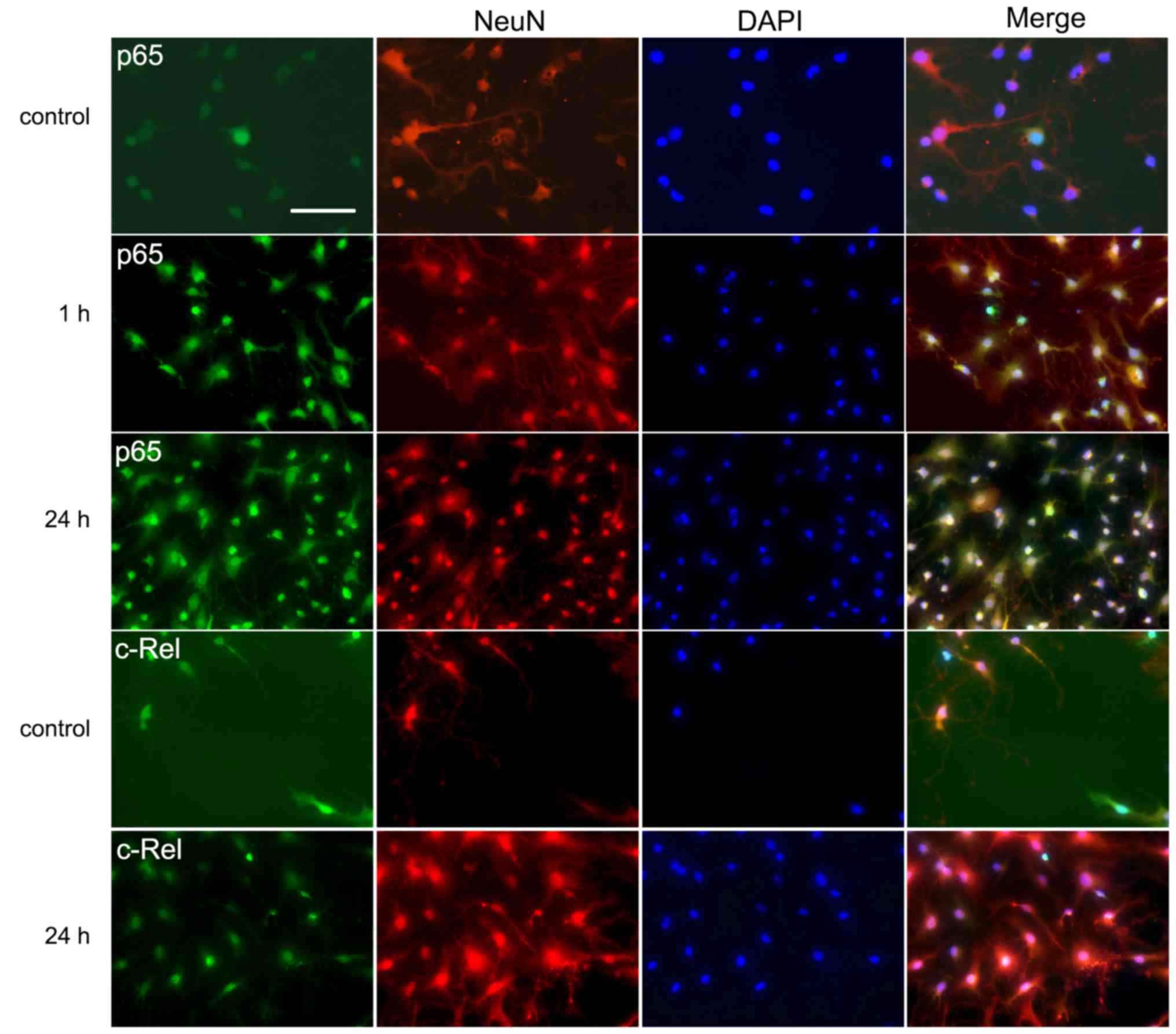
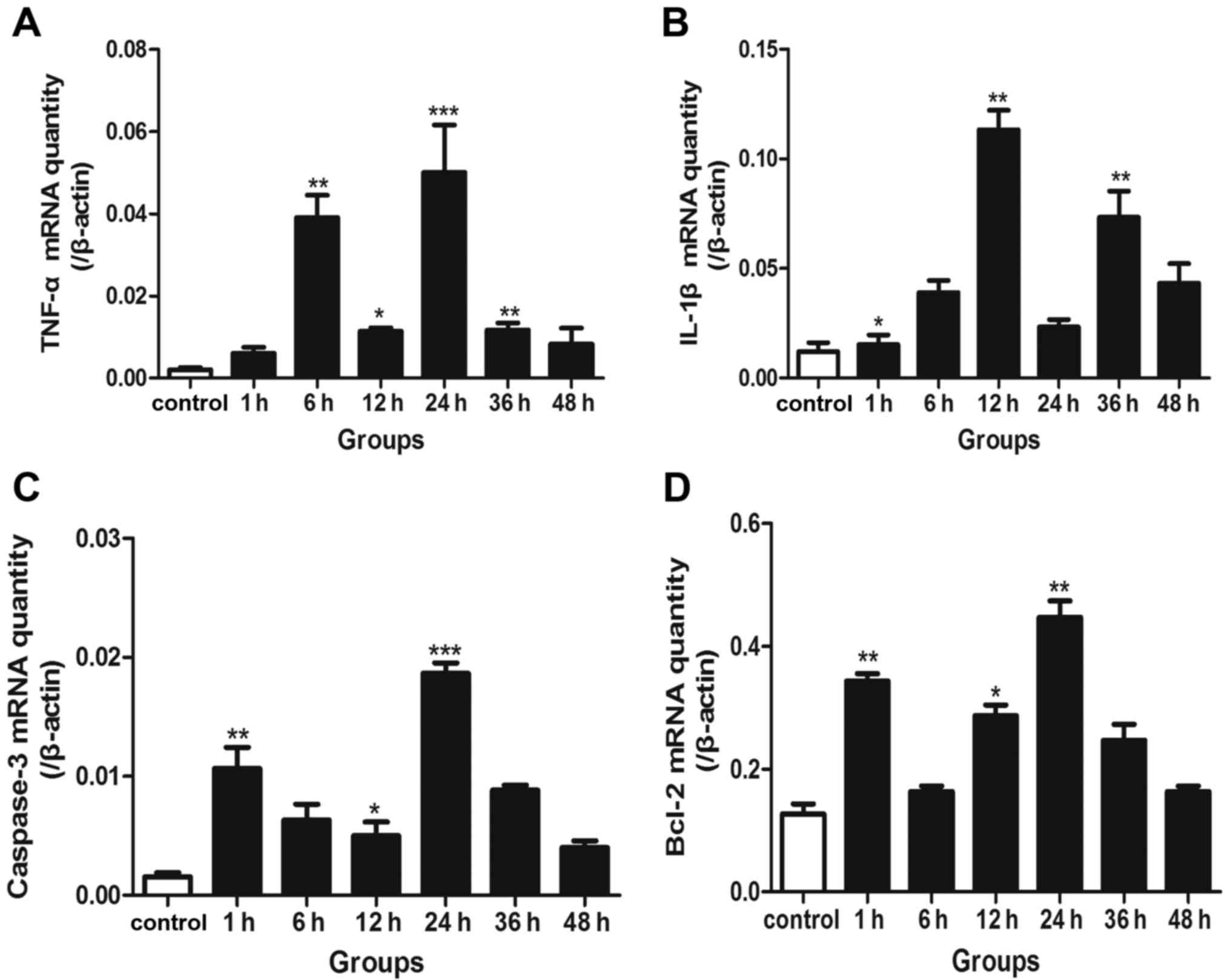
|
1
|
Lescot T, Abdennour L, Degos V, Boch AL
and Puybasset L: Management of severe traumatic brain injury.
Presse Med. 36:1117–1126. 2007.In French. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen T, Liu W, Chao X, Zhang L, Qu Y, Huo
J and Fei Z: Salvianolic acid B attenuates brain damage and
inflammation after traumatic brain injury in mice. Brain Res Bull.
84:163–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Greve MW and Zink BJ: Pathophysiology of
traumatic brain injury. Mt Sinai J Med. 76:97–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu J, Goh SJ, Tng PY, Deng YY, Ling EA and
Moochhala S: Systemic inflammatory response following acute
traumatic brain injury. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:3795–3813.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Bhakar AL, Tannis LL, Zeindler C, Russo
MP, Jobin C, Park DS, MacPherson S and Barker PA: Constitutive
nuclear factor-kappa B activity is required for central neuron
survival. J Neurosci. 22:8466–8475. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Signaling to
NF-kappaB. Genes Dev. 18:2195–2224. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-kappa B and I kappa
B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol.
14:649–683. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mattson MP and Meffert MK: Roles for
NF-kappaB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell
Death Differ. 13:852–860. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shimada M, Satoh N and Yokosawa H:
Involvement of Rel/NF-kappaB in regulation of ascidian notochord
formation. Dev Growth Differ. 43:145–154. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang R, Xue YY, Lu SD, Wang Y, Zhang LM,
Huang YL, Signore AP, Chen J and Sun FY: Bcl-2 enhances
neurogenesis and inhibits apoptosis of newborn neurons in adult rat
brain following a transient middle cerebral artery occlusion.
Neurobiol Dis. 24:345–356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Y, Liu J, Yao S, Li F, Xin L, Lai M,
Bracchi-Ricard V, Xu H, Yen W, Meng W, et al: Nuclear factor kappa
B signaling initiates early differentiation of neural stem cells.
Stem Cells. 30:510–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Biscetti F, Ghirlanda G and Flex A:
Therapeutic potential of high mobility group box-1 in ischemic
injury and tissue regeneration. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 9:677–681.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Basu S, Rajakaruna S and Menko AS:
Insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 and nuclear factor κB are
crucial survival signals that regulate caspase-3-mediated lens
epithelial cell differentiation initiation. J Biol Chem.
287:8384–8397. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Youssef S and Steinman L: At once harmful
and beneficial: The dual properties of NF-kappaB. Nat Immunol.
7:901–902. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pizzi M, Goffi F, Boroni F, Benarese M,
Perkins SE, Liou HC and Spano P: Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel
factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited
by glutamate and interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem. 277:20717–20723.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
You WC, Li W, Zhuang Z, Tang Y, Lu HC, Ji
XJ, Shen W, Shi JX and Zhou ML: Biphasic activation of nuclear
factor-kappa B in experimental models of subarachnoid hemorrhage in
vivo and in vitro. Mediators Inflamm. 2012:7862422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nijboer CH, Heijnen CJ, Groenendaal F, May
MJ, van Bel F and Kavelaars A: A dual role of the NF-kappaB pathway
in neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Stroke. 39:2578–2586.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen T, Fei F, Jiang XF, Zhang L, Qu Y,
Huo K and Fei Z: Down-regulation of Homer1b/c attenuates
glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity through endoplasmic reticulum and
mitochondria pathways in rat cortical neurons. Free Radic Biol Med.
52:208–217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y, Luo P, Guo Q, Li S, Zhang L, Zhao
M, Xu H, Yang Y, Poon W and Fei Z: Interactions between SIRT1 and
MAPK/ERK regulate neuronal apoptosis induced by traumatic brain
injury in vitro and in vivo. Exp Neurol. 237:489–498. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tecoma ES, Monyer H, Goldberg MP and Choi
DW: Traumatic neuronal injury in vitro is attenuated by NMDA
antagonists. Neuron. 2:1541–1545. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou ML, Shi JX, Hang CH, Cheng HL, Qi XP,
Mao L, Chen KF and Yin HX: Potential contribution of nuclear
factor-kappaB to cerebral vasospasm after experimental subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rabbits. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:1583–1592.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rogers B, Yakopson V, Teng ZP, Guo Y and
Regan RF: Heme oxygenase-2 knockout neurons are less vulnerable to
hemoglobin toxicity. Free Radic Biol Med. 35:872–881. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hatic H, Kane MJ, Saykally JN and Citron
BA: Modulation of transcription factor Nrf2 in an in vitro model of
traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 29:1188–1196. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D: I kappa B: A
specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science.
242:540–546. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lezoualc'h F, Sagara Y, Holsboer F and
Behl C: High constitutive NF-kappaB activity mediates resistance to
oxidative stress in neuronal cells. J Neurosci. 18:3224–3232.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mattson MP, Goodman Y, Luo H, Fu W and
Furukawa K: Activation of NF-kappaB protects hippocampal neurons
against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis: Evidence for induction
of manganese superoxide dismutase and suppression of peroxynitrite
production and protein tyrosine nitration. J Neurosci Res.
49:681–697. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Grilli M, Pizzi M, Memo M and Spano P:
Neuroprotection by aspirin and sodium salicylate through blockade
of NF-kappaB activation. Science. 274:1383–1385. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Clemens JA, Stephenson DT, Dixon EP,
Smalstig EB, Mincy RE, Rash KS and Little SP: Global cerebral
ischemia activates nuclear factor-kappa B prior to evidence of DNA
fragmentation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 48:187–196. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qin ZH, Wang Y, Nakai M and Chase TN:
Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to excitotoxin-induced apoptosis
in rat striatum. Mol Pharmacol. 53:33–42. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hu YC, Sun Q, Li W, Zhang DD, Ma B, Li S,
Li WD, Zhou ML and Hang CH: Biphasic activation of nuclear factor
kappa B and expression of p65 and c-Rel after traumatic brain
injury in rats. Inflamm Res. 63:109–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lin SC, Wortis HH and Stavnezer J: The
ability of CD40L, but not lipopolysaccharide, to initiate
immunoglobulin switching to immunoglobulin G1 is explained by
differential induction of NF-kappaB/Rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol.
18:5523–5532. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Perkins ND: Achieving transcriptional
specificity with NF-kappaB. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 29:1433–1448.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Roshak AK, Jackson JR, McGough K,
Chabot-Fletcher M, Mochan E and Marshall LA: Manipulation of
distinct NFkappaB proteins alters interleukin-1beta-induced human
rheumatoid synovial fibroblast prostaglandin E2 formation. J Biol
Chem. 271:31496–31501. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Leker RR and Shohami E: Cerebral ischemia
and trauma-different etiologies yet similar mechanisms:
Neuroprotective opportunities. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 39:55–73.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu J, Wang H, Ding K, Zhang L, Wang C, Li
T, Wei W and Lu X: Luteolin provides neuroprotection in models of
traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2-ARE pathway. Free Radic Biol
Med. 71:186–195. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kuwana T and Newmeyer DD: Bcl-2-family
proteins and the role of mitochondria in apoptosis. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 15:691–699. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mattson MP and Camandola S: NF-kappaB in
neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. J Clin Invest.
107:247–254. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cederberg D and Siesjö P: What has
inflammation to do with traumatic brain injury? Childs Nerv Syst.
26:221–226. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Barone FC and Feuerstein GZ: Inflammatory
mediators and stroke: New opportunities for novel therapeutics. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 19:819–834. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|