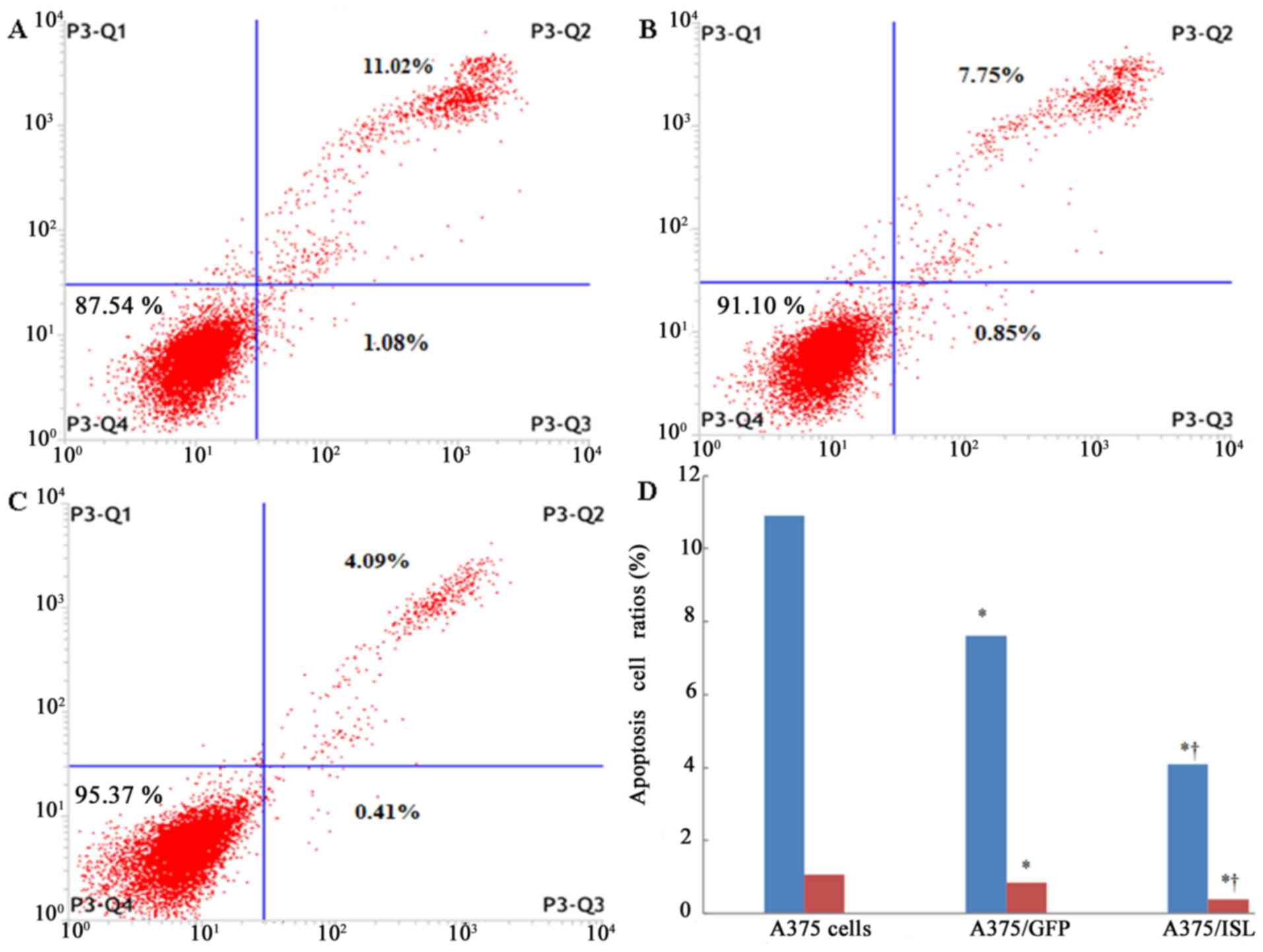
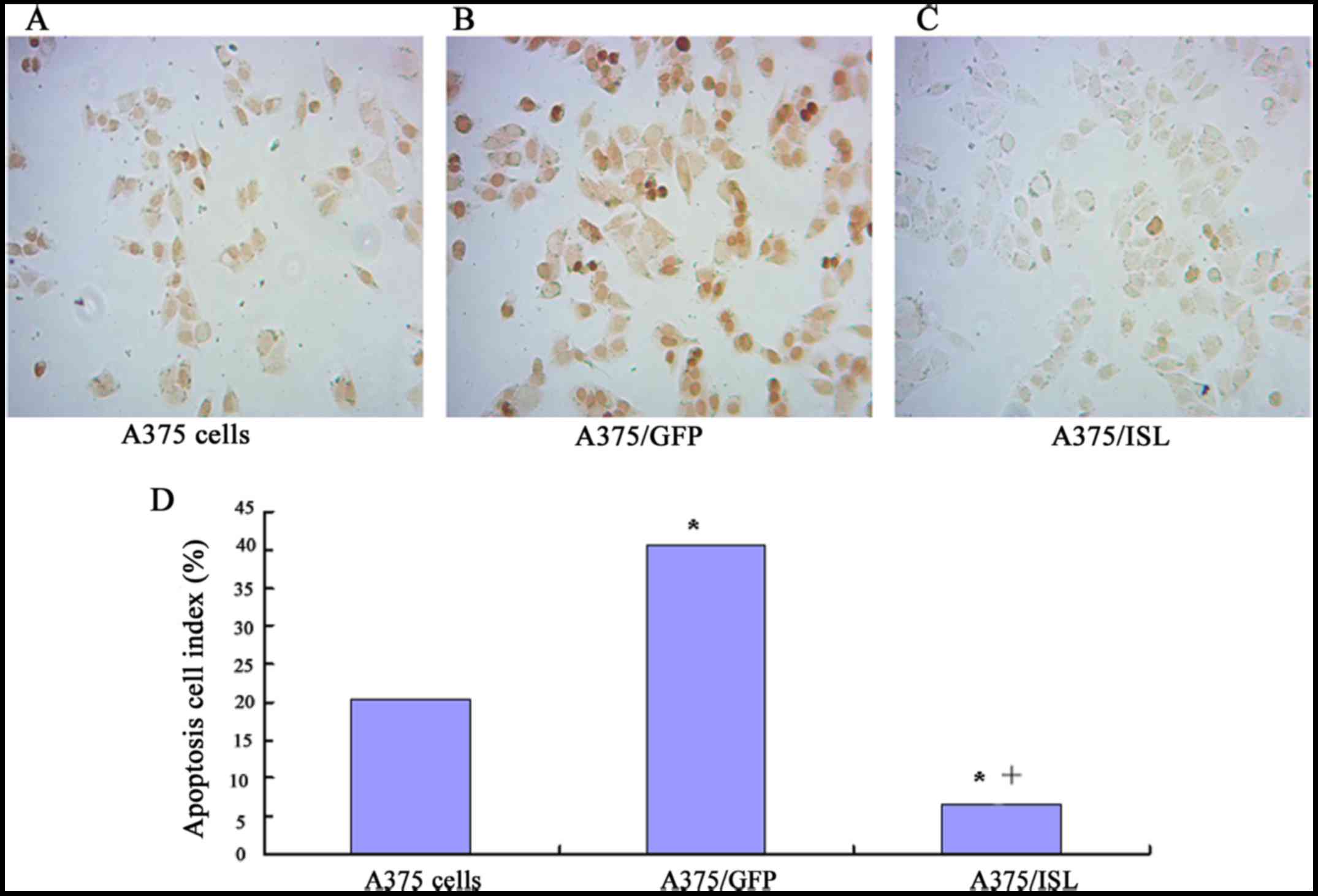
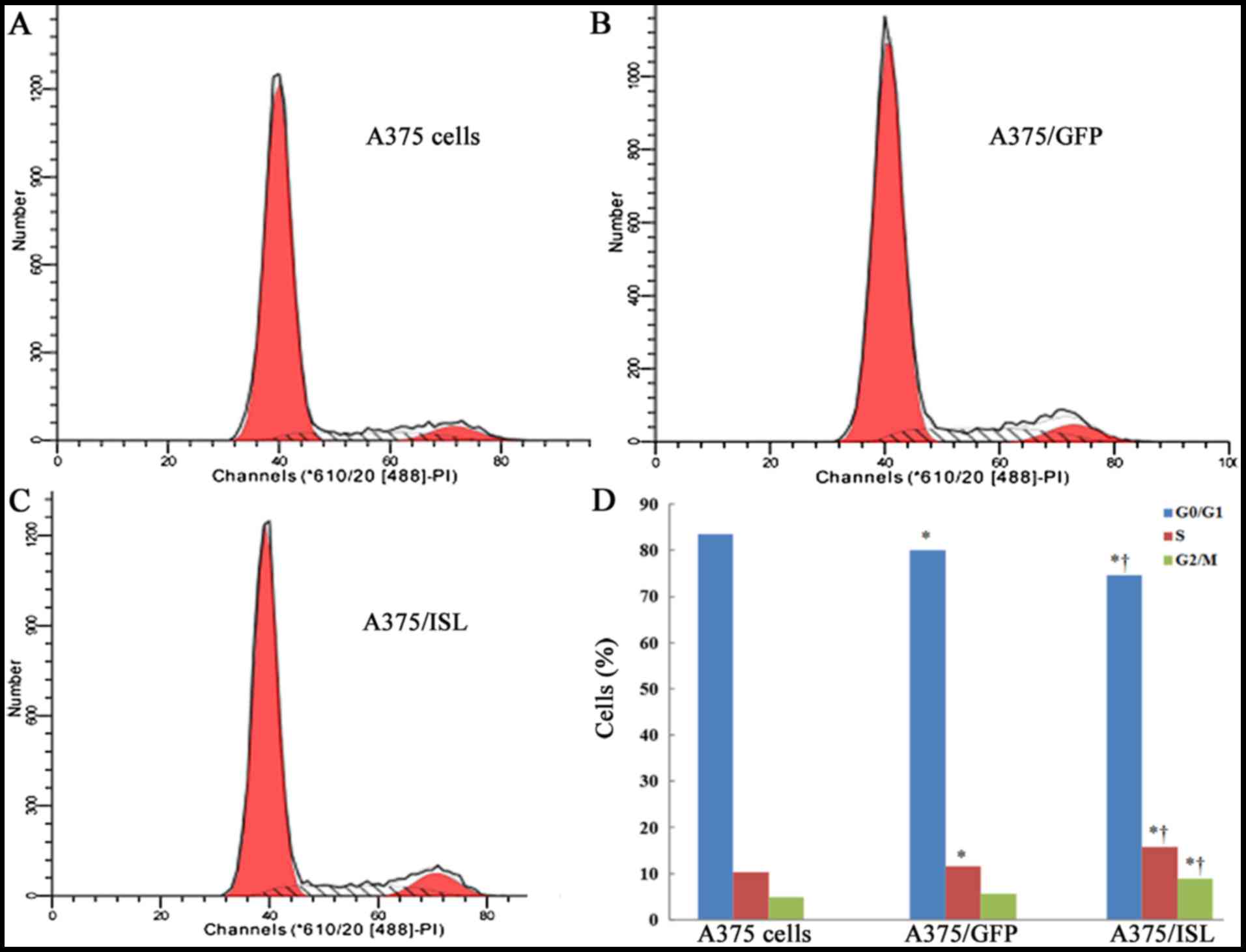
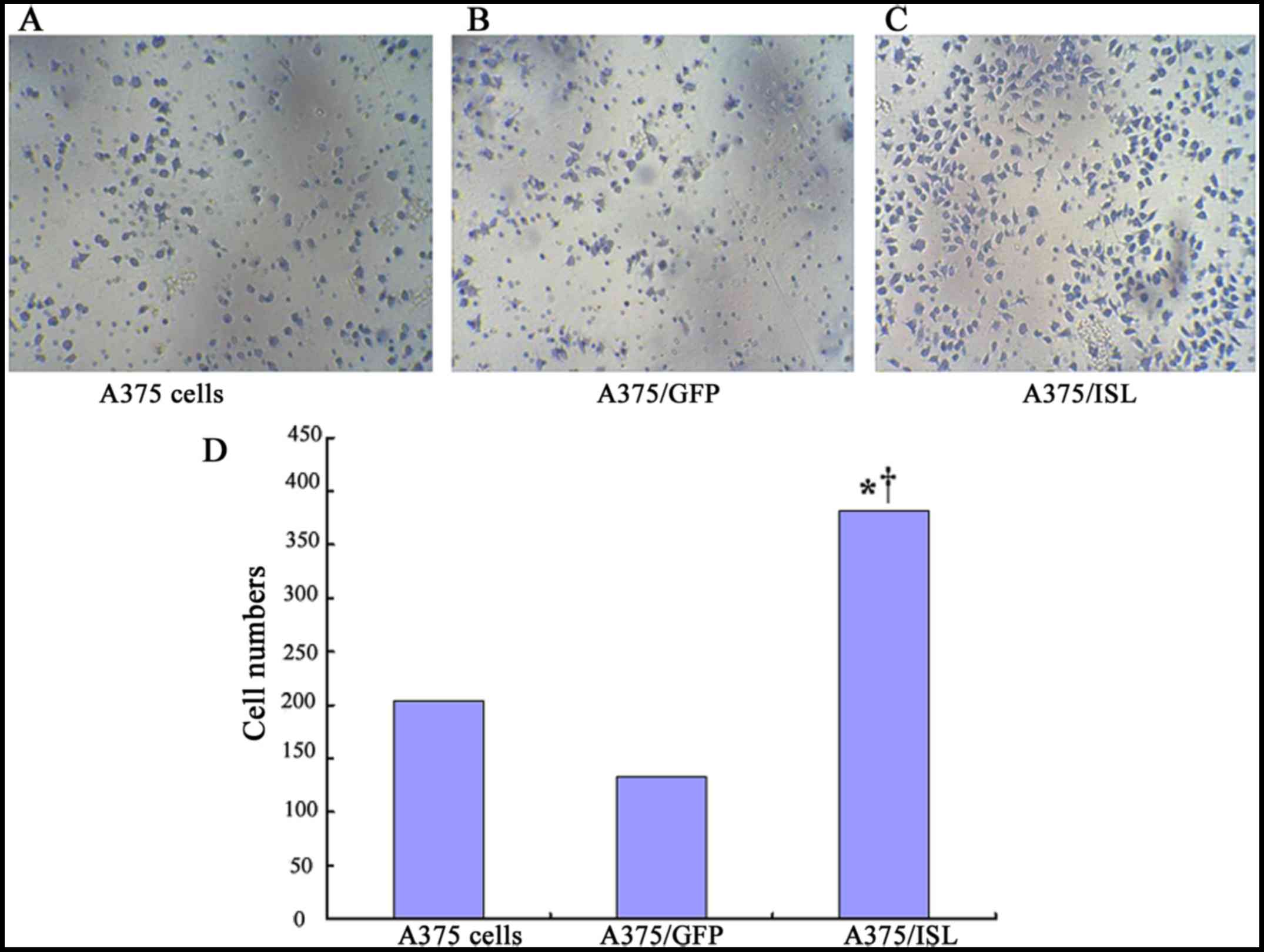
|
1
|
Misu M, Ouji Y, Kawai N, Nishimura F,
Nakamura-Uchiyama F and Yoshikawa M: Effects of Wnt-10b on
proliferation and differentiation of murine melanoma cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 463:618–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Raghunath A, Sambarey A, Sharma N,
Mahadevan U and Chandra N: A molecular systems approach to
modelling human skin pigmentation: identifying underlying pathways
and critical components. BMC Res Notes. 8:1702015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:9–29. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Karlsson O, Thor S, Norberg T, Ohlsson H
and Edlund T: Insulin gene enhancer binding protein Isl-1 is a
member of a novel class of proteins containing both a homeo- and a
Cys-His domain. Nature. 344:879–882. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nasif S, de Souza FS, González LE,
Yamashita M, Orquera DP, Low MJ and Rubinstein M: Islet 1 specifies
the identity of hypothalamic melanocortin neurons and is critical
for normal food intake and adiposity in adulthood. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 112:E1861–E1870. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cai CL, Liang X, Shi Y, Chu PH, Pfaff SL,
Chen J and Evans S: Isl1 identifies a cardiac progenitor population
that proliferates prior to differentiation and contributes a
majority of cells to the heart. Dev Cell. 5:877–889. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huber GF: Modern management of Merkel cell
carcinoma. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 22:109–115. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Agaimy A, Erlenbach-Wünsch K, Konukiewitz
B, Schmitt AM, Rieker RJ, Vieth M, Kiesewetter F, Hartmann A,
Zamboni G, Perren A, et al: ISL1 expression is not restricted to
pancreatic well-differentiated neuroendocrine neoplasms, but is
also commonly found in well and poorly differentiated
neuroendocrine neoplasms of extrapancreatic origin. Mod Pathol.
26:995–1003. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Su X, Wang P, Wang X, Cao B, Li L and Liu
Q: Apoptosis of U937 cells induced by hematoporphyrin monomethyl
ether-mediated sonodynamic action. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
28:207–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao Q, Li W, Zhang C, Qin X, Xue X, Li M,
Shu Z, Xu T, Xu Y, Wang W, et al: TNFα induced FOXP3-NFκB
interaction dampens the tumor suppressor role of FOXP3 in gastric
cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:436–441. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Piérard-Franchimont C, Hermanns-Lê T,
Delvenne P and Piérard GE: Dormancy of growth-stunted malignant
melanoma: sustainable and smoldering patterns. Oncol Rev.
8:2522014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aris M and Barrio MM: Combining
immunotherapy with oncogene-targeted therapy: a new road for
melanoma treatment. Front Immunol. 6:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Graham RP, Shrestha B, Caron BL, Smyrk TC,
Grogg KL, Lloyd RV and Zhang L: Islet-1 is a sensitive but not
entirely specific marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms
and their metastases. Am J Surg Pathol. 37:399–405. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bu L, Jiang X, Martin-Puig S, Caron L, Zhu
S, Shao Y, Roberts DJ, Huang PL, Domian IJ and Chien KR: Human ISL1
heart progenitors generate diverse multipotent cardiovascular cell
lineages. Nature. 460:113–117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi Y, Zhao S, Li J and Mao B: Islet-1 is
required for ventral neuron survival in Xenopus. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 388:506–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo T, Wang W, Zhang H, Liu Y, Chen P, Ma
K and Zhou C: ISL1 promotes pancreatic islet cell proliferation.
PLoS One. 6:e223872011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ediger BN, Du A, Liu J, Hunter CS, Walp
ER, Schug J, Kaestner KH, Stein R, Stoffers DA and May CL: Islet-1
is essential for pancreatic β-cell function. Diabetes.
63:4206–4217. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Weinberger F, Mehrkens D, Starbatty J,
Nicol P and Eschenhagen T: Assessment of DNA synthesis in
Islet-1+ cells in the adult murine heart. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 456:294–297. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kilk K, Magzoub M, Pooga M, Eriksson LE,
Langel U and Gräslund A: Cellular internalization of a cargo
complex with a novel peptide derived from the third helix of the
islet-1 homeodomain. Comparison with the penetratin peptide.
Bioconjug Chem. 12:911–916. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Koo J, Mertens RB, Mirocha JM, Wang HL and
Dhall D: Value of Islet 1 and PAX8 in identifying metastatic
neuroendocrine tumors of pancreatic origin. Mod Pathol. 25:893–901.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ferrara N, Carver-Moore K, Chen H, Dowd M,
Lu L, O'Shea KS, Powell-Braxton L, Hillan KJ and Moore MW:
Heterozygous embryonic lethality induced by targeted inactivation
of the VEGF gene. Nature. 380:439–442. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Barzelay A, Ben-Shoshan J, Entin-Meer M,
Maysel-Auslender S, Afek A, Barshack I, Keren G and George J: A
potential role for islet-1 in post-natal angiogenesis and
vasculogenesis. Thromb Haemost. 103:188–197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Linning KD, Tai MH, Madhukar BV, Chang CC,
Reed DN Jr, Ferber S, Trosko JE and Olson LK: Redox-mediated
enrichment of self-renewing adult human pancreatic cells that
possess endocrine differentiation potential. Pancreas. 29:e64–e76.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|