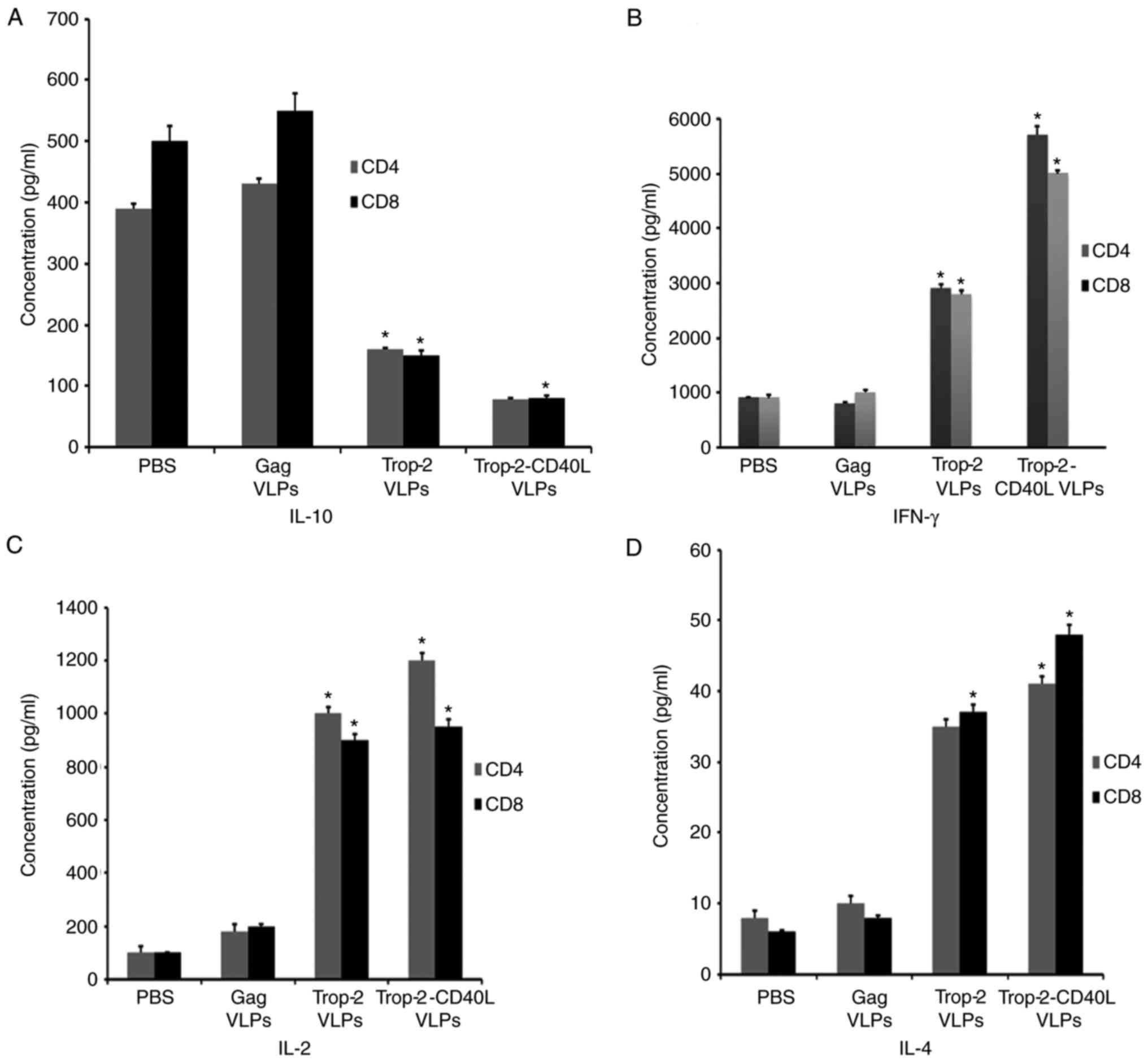
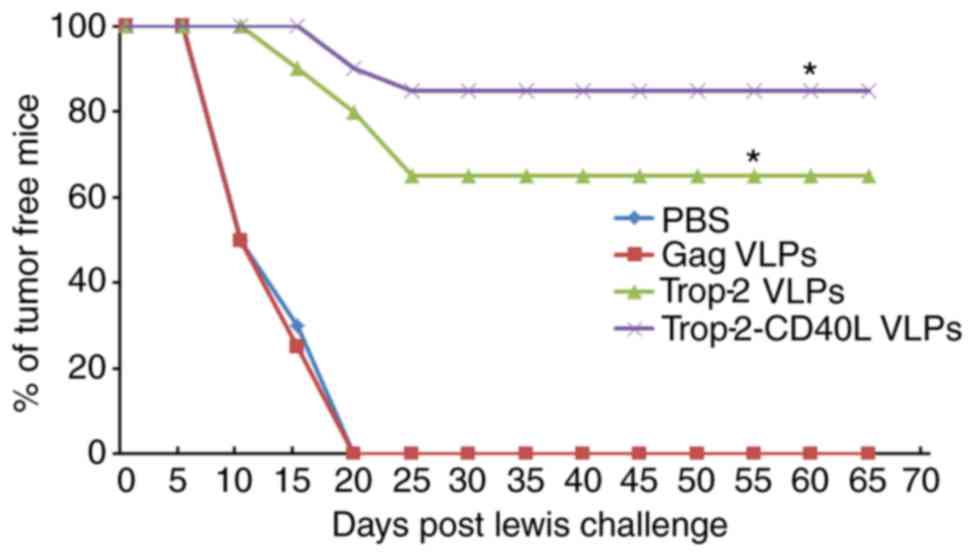
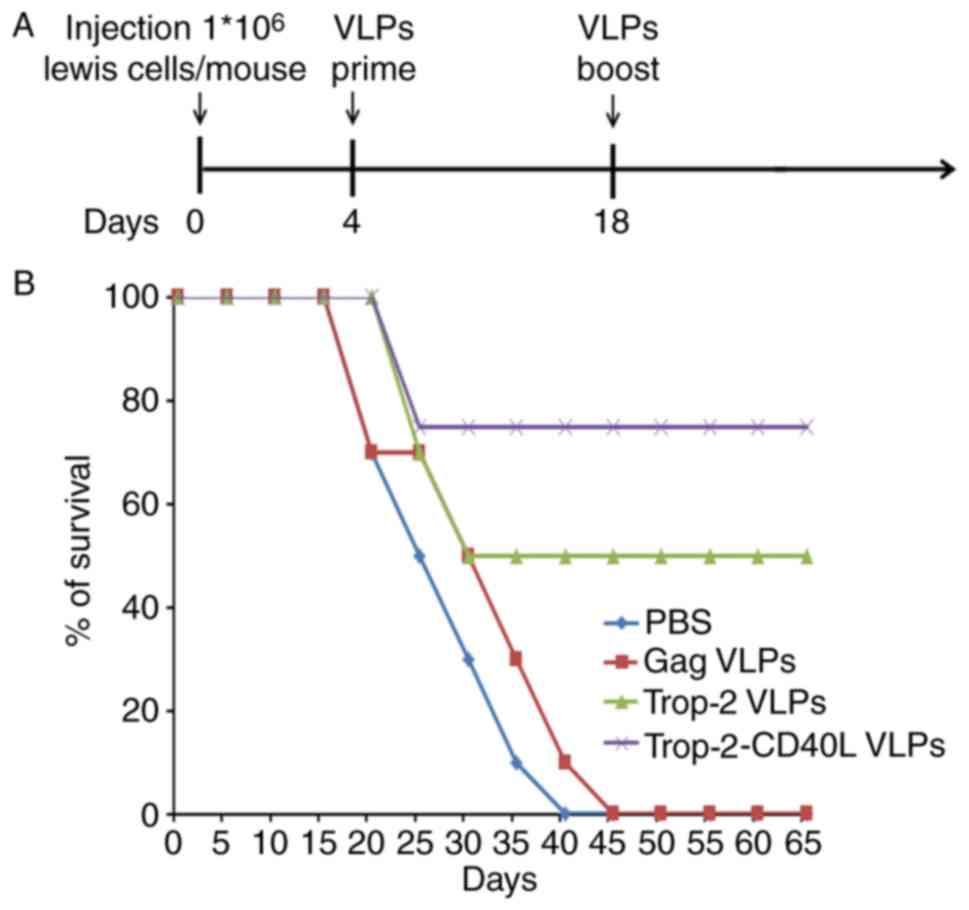
|
1
|
Fong D, Moser P, Krammel C, Gostner JM,
Margreiter R, Mitterer M, Gastl G and Spizzo G: High expression of
TROP2 correlates with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Br J
Cancer. 99:1290–1295. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Simms A, Jacob RP, Cohen C and Siddiqui
MT: TROP-2 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Potential
diagnostic utility. Diagn Cytopathol. 44:26–31. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Trerotola M, Ganguly KK, Fazli L, Fedele
C, Lu H, Dutta A, Liu Q, De Angelis T, Riddell LW, Riobo NA, et al:
Trop-2 is up-regulated in invasive prostate cancer and displaces
FAK from focal contacts. Oncotarget. 6:14318–14328. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang J, Day R, Dong Y, Weintraub SJ and
Michel L: Identification of Trop-2 as an oncogene and an attractive
therapeutic target in colon cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:280–285.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stepan LP, Trueblood ES, Hale K, Babcook
J, Borges L and Sutherland CL: Expression of Trop-2 cell surface
glycoprotein in normal and tumor tissues: Potential implications as
a cancer therapeutic target. J Histochem Cytochem. 59:701–710.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ambrogi F, Fornili M, Boracchi P,
Trerotola M, Relli V, Simeone P, La Sorda R, Lattanzio R, Querzoli
P, Pedriali M, et al: Trop-2 is a determinant of breast cancer
survival. PLoS One. 9:e969932014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bignotti E, Zanotti L, Calza S, Falchetti
M, Lonardi S, Ravaggi A, Romani C, Todeschini P, Bandiera E, Tassi
RA, et al: Trop-2 protein overexpression is an independent marker
for predicting disease recurrence in endometrioid endometrial
carcinoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 12:222012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bignotti E, Todeschini P, Calza S,
Falchetti M, Ravanini M, Tassi RA, Ravaggi A, Bandiera E, Romani C,
Zanotti L, et al: Trop-2 overexpression as an independent marker
for poor overall survival in ovarian carcinoma patients. Eur J
Cancer. 46:944–953. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang A, Gao X, Zhang D, Zhang L and Lu H:
Expression and clinical significance of the Trop-2 gene in advanced
non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 6:375–380. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pushko P, Tretyakova I, Hidajat R, Zsak A,
Chrzastek K, Tumpey TM and Kapczynski DR: Virus-like particles
displaying H5, H7, H9 hemagglutinins and N1 neuraminidase elicit
protective immunity to heterologous avian influenza viruses in
chickens. Virology. 501:176–182. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
Hill BD, Zak A, Khera E and Wen F:
Engineering virus-like particles for antigen and drug delivery.
Curr Protein Pept Sci. 19:112–127. 2018.
|
|
12
|
Zdanowicz M and Chroboczek J: Virus-like
particles as drug delivery vectors. Acta Biochim Pol. 63:469–473.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Fang Y, Zhou P, Lu Y, Zhang Q, Xiao
S, Dong Z, Pan L, Lv J, Zhang Z, et al: Chimeric virus-like
particles elicit protective immunity against serotype O
foot-and-mouth disease virus in guinea pigs. Appl Microbiol
Biotechnol. 101:4905–4914. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeong H and Seong BL: Exploiting
virus-like particles as innovative vaccines against emerging viral
infections. J Microbiol. 55:220–230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mohan T, Berman Z, Luo Y, Wang C, Wang S,
Compans RW and Wang BZ: Chimeric virus-like particles containing
influenza HA antigen and GPI-CCL28 induce long-lasting mucosal
immunity against H3N2 viruses. Sci Rep. 7:402262017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Robert MA, Lytvyn V, Deforet F, Gilbert R
and Gaillet B: Virus-like particles derived from HIV-1 for delivery
of duclear proteins: Improvement of production and activity by
protein engineering. Mol Biotechnol. 59:9–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feng Q, He Y and Lu J: Virus-like
larticles lroduced in lichia lastoris induce protective immune
responses against Coxsackievirus A16 in mice. Med Sci Monit.
22:3370–3382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan Q, Wu L, Chen L, Qin Y, Pan Z and Chen
M: Vesicular stomatitis virus-based vaccines expressing EV71
virus-like particles elicit strong immune responses and protect
newborn mice from lethal challenges. Vaccine. 34:4196–4204. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Xiao X, Zhao M, Liu W, Pang L, Sun
X, Cen S, Yang BB, Huang Y, Sheng W and Zeng Y: EV71 virus-like
particles produced by co-expression of capsid proteins in yeasT
cells elicit humoral protective response against EV71 lethal
challenge. BMC Res Notes. 9:422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alshaikhahmed K and Roy P: Generation of
virus-like particles for emerging epizootic haemorrhagic disease
virus: Towards the development of safe vaccine candidates. Vaccine.
34:1103–1108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ludwig C and Wagner R: Virus-like
particles-universal molecular toolboxes. Curr Opin Biotechnol.
18:537–545. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Deml L, Speth C, Dierich MP, Wolf H and
Wagner R: Recombinant HIV-1 Pr55gag virus-like particles: Potent
stimulators of innate and acquired immune responses. Mol Immunol.
42:259–277. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Figgett WA, Vincent FB, Saulep-Easton D
and Mackay F: Roles of ligands from the TNF superfamily in B cell
development, function, and regulation. Semin Immunol. 26:191–202.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bazzoni F and Beutler B: The tumor
necrosis factor ligand and receptor families. N Engl J Med.
334:1717–1725. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta S, Termini JM, Kanagavelu S and
Stone GW: Design of vaccine adjuvants incorporating TNF superfamily
ligands and TNF superfamily molecular mimics. Immunol Res.
57:303–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song I, Kim J, Kwon K, Koo S and Jo D:
Expression of CD154 (CD40L) on stimulated T lymphocytes in patients
with idopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Hematology. 21:187–192.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Quezada SA, Jarvinen LZ, Lind EF and
Noelle RJ: CD40/CD154 interactions at the interface of tolerance
and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 22:307–328. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tripp RA, Jones L, Anderson LJ and Brown
MP: CD40 ligand (CD154) enhances the Th1 and antibody responses to
respiratory syncytial virus in the C57BL/6 mouse. J Immunol.
164:5913–5921. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cheng LF, Wang F, Zhang L, Yu L, Ye W, Liu
ZY, Ying QK, Wu XA, Xu ZK and Zhang FL: Incorporation of GM-CSF or
CD40L enhances the immunogenicity of Hantaan virus-like particles.
FronT cell Infect Microbiol. 6:1852016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Stone GW, Barzee S, Snarsky V, Kee K,
Spina CA, Yu XF and Kornbluth RS: Multimeric soluble CD40 ligand
and GITR ligand as adjuvants for human immunodeficiency virus DNA
vaccines. J Virol. 80:1762–1772. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Skountzou I, Quan FS, Gangadhara S, Ye L,
Vzorov A, Selvaraj P, Jacob J, Compans RW and Kang SM:
Incorporation of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor or CD40 ligand
enhances immunogenicity of chimeric simian immunodeficiency
virus-like particles. J Virol. 81:1083–1094. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Daniel RA and Errington J: Control of cell
morphogenesis in bacteria: two distinct ways to make a rod-shaped
cell. Cell. 113:767–776. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Zeng H and Zhang S:
Epidemiology of lung cancer in China. Thorac Cancer. 6:209–215.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Somasundaram A and Burns TF: The next
generation of immunotherapy: Keeping lung cancer in check. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cubas R, Zhang S, Li M, Chen C and Yao Q:
Chimeric Trop-2 virus-like particles: A potential immunotherapeutic
approach against pancreatic cancer. J Immunother. 34:251–263. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Wang YM, Wang Y, Zheng G, Zhang
GY, Zhou JJ, Tan TK, Cao Q, Hu M, Watson D, et al: DNA vaccine
encoding CD40 targeted to dendritic cells in situ prevents the
development of Heymann nephritis in rats. Kidney Int. 83:223–232.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kwa S, Sadagopal S, Shen X, Hong JJ,
Gangadhara S, Basu R, Victor B, Iyer SS, LaBranche CC, Montefiori
DC, et al: CD40L-adjuvanted DNA/modified vaccinia virus Ankara
simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) vaccine enhances protection
against neutralization-resistant mucosal SIV infection. J Virol.
89:4690–4695. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|