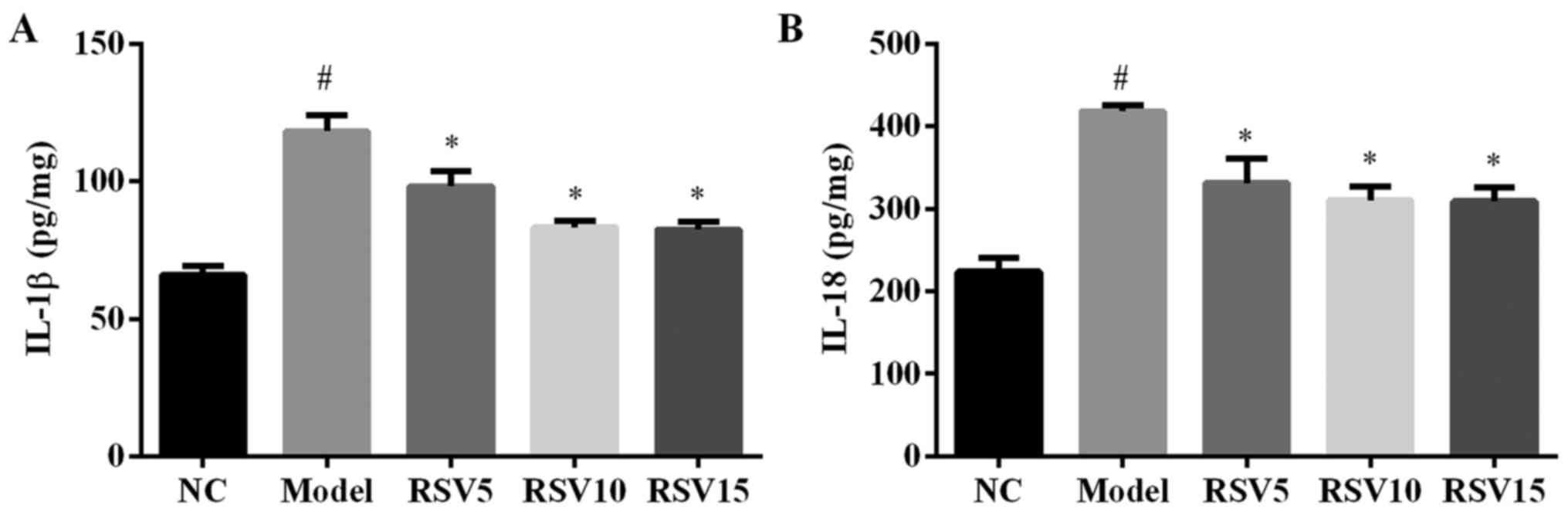
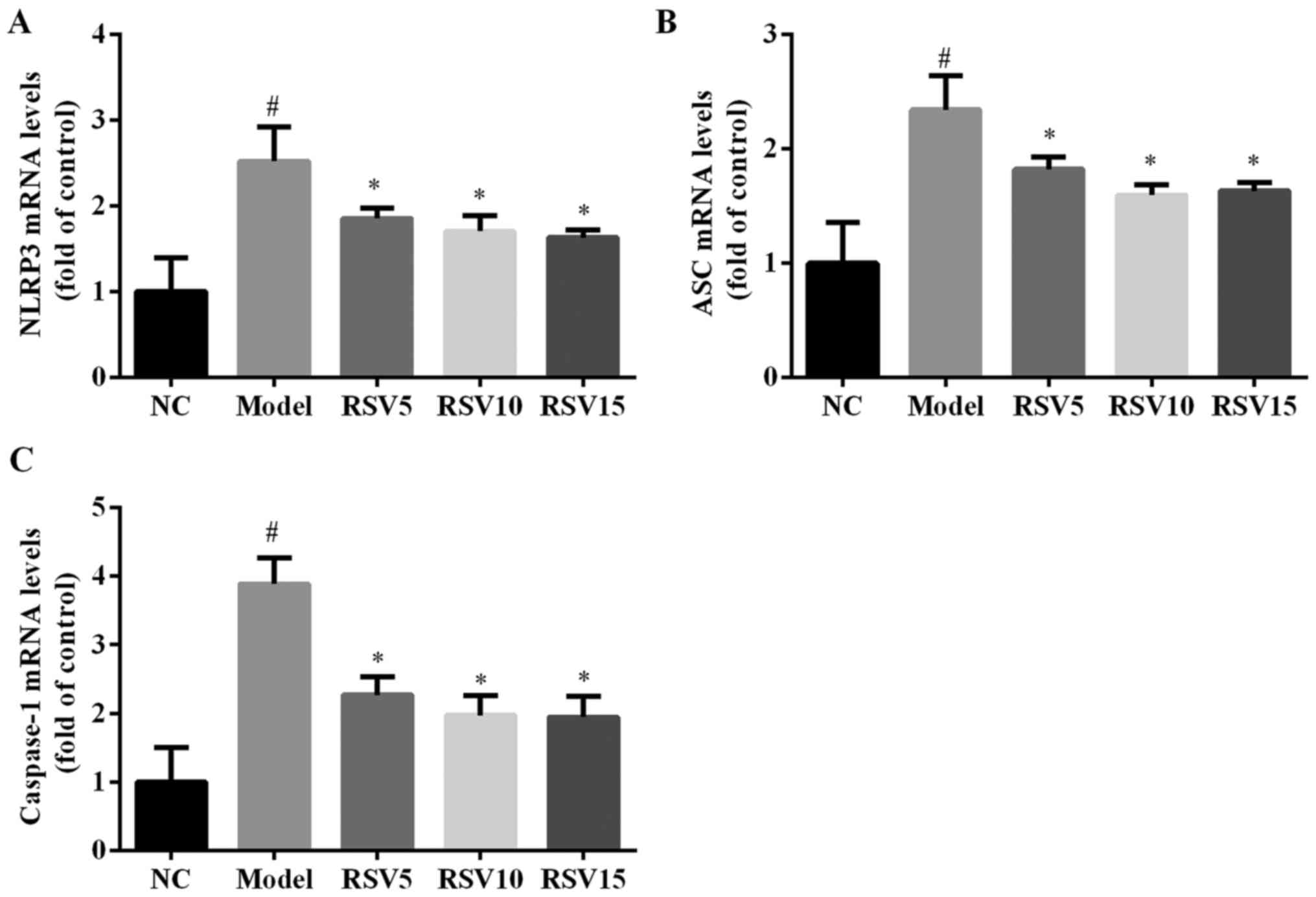
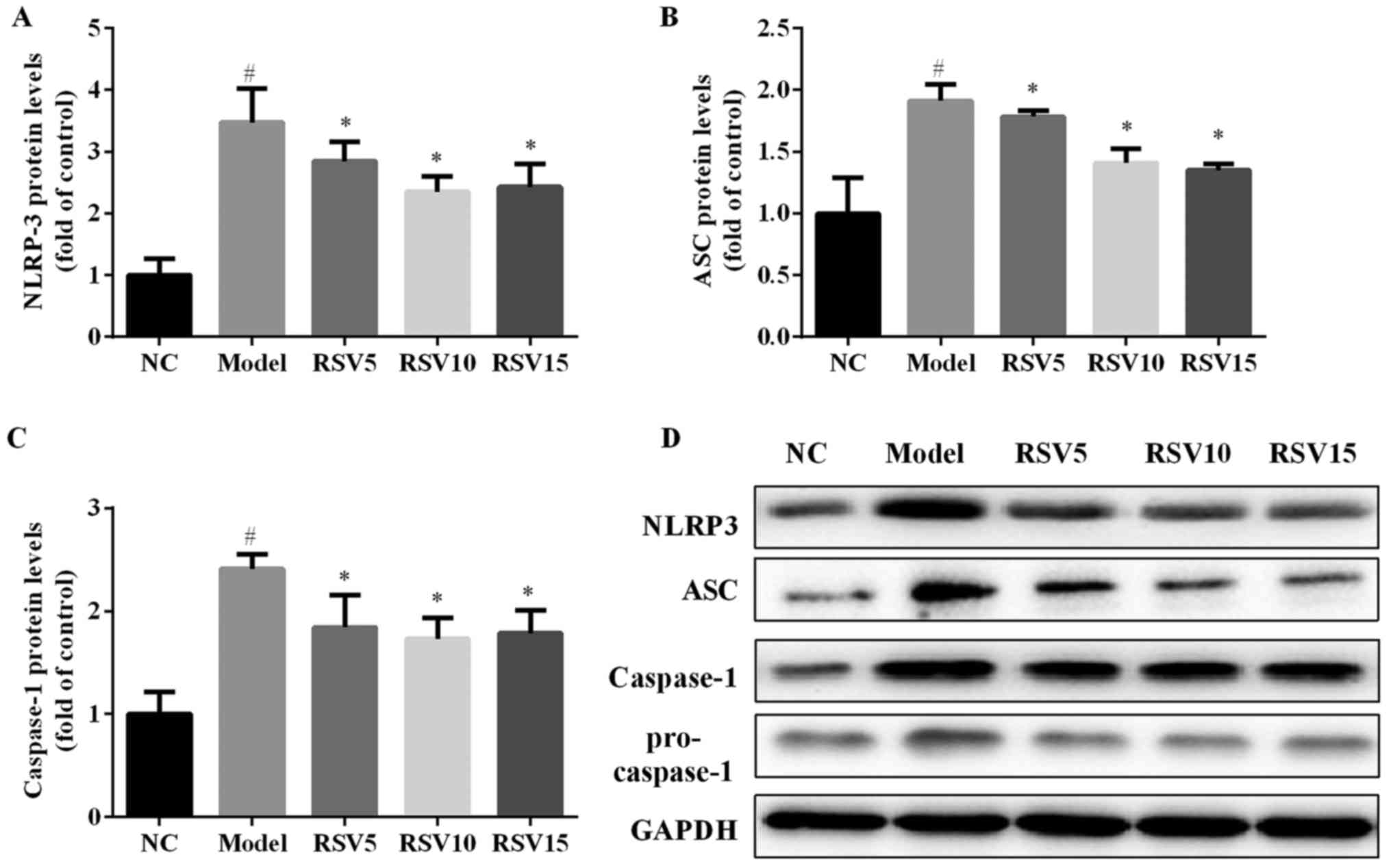
|
1
|
Eltzschig HK and Eckle T: Ischemia and
reperfusion - from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 17:1391–1401.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Whellan DJ: Heart failure disease
management: Implementation and outcomes. Cardiol Rev. 13:231–239.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nichols M, Townsend N, Scarborough P and
Rayner M: Cardiovascular disease in Europe 2014: Epidemiological
update. Eur Heart J. 35:2929–2933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reed GW, Rossi JE and Cannon CP: Acute
myocardial infarction. Lancet. 389:197–210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
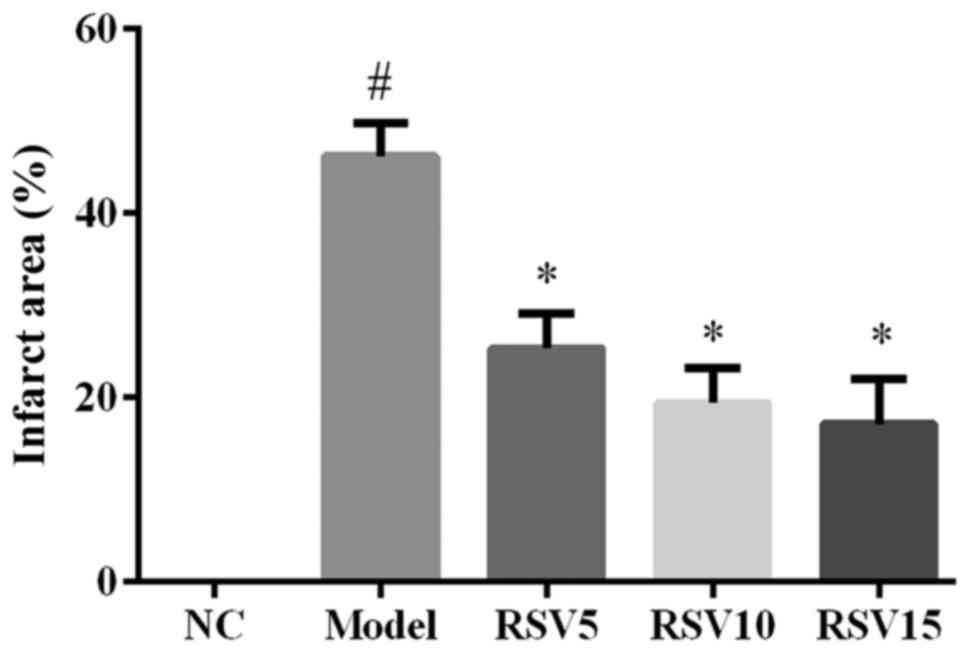
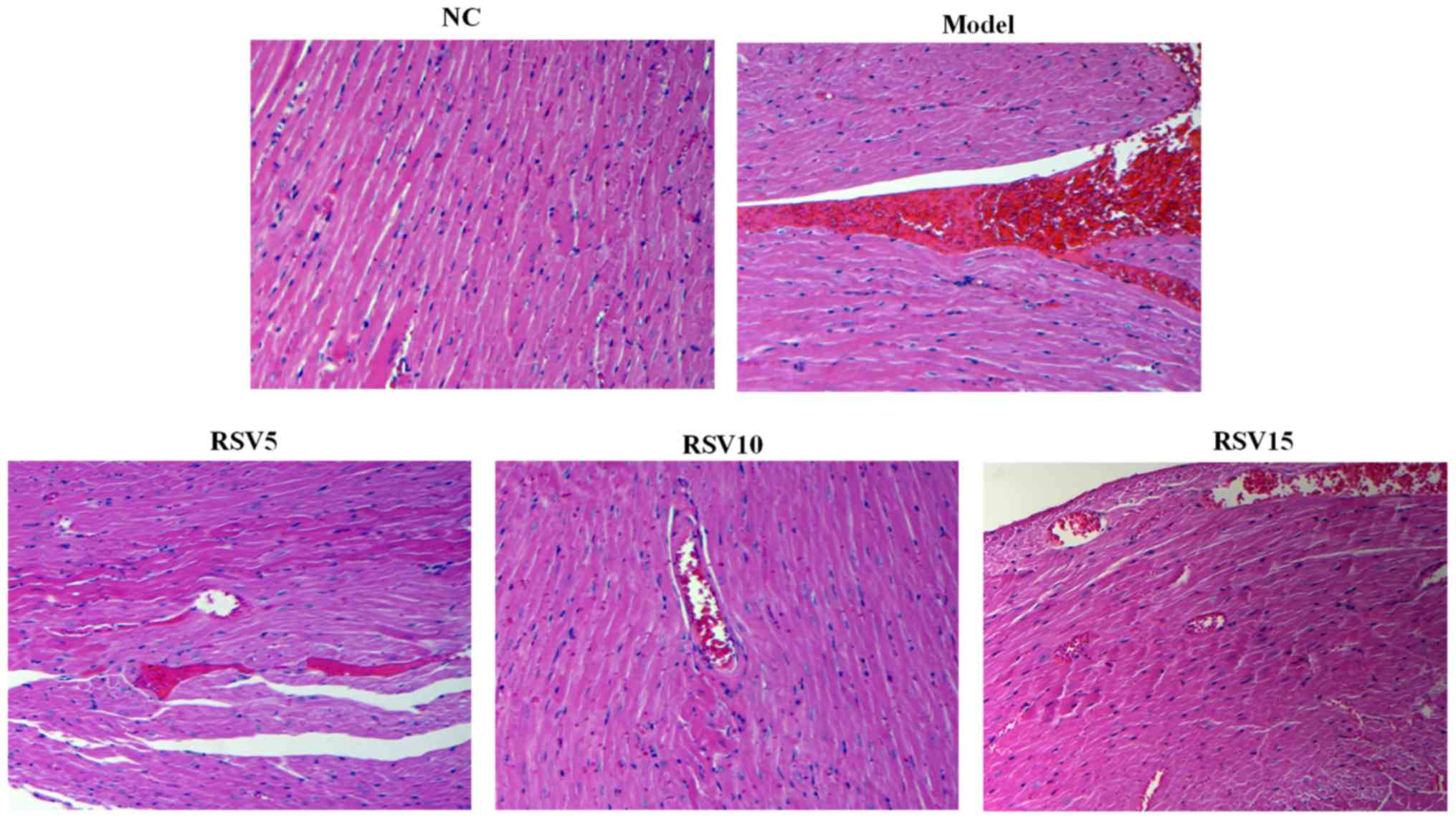
Sawyer DB, Siwik DA, Xiao L, Pimentel DR,
Singh K and Colucci WS: Role of oxidative stress in myocardial
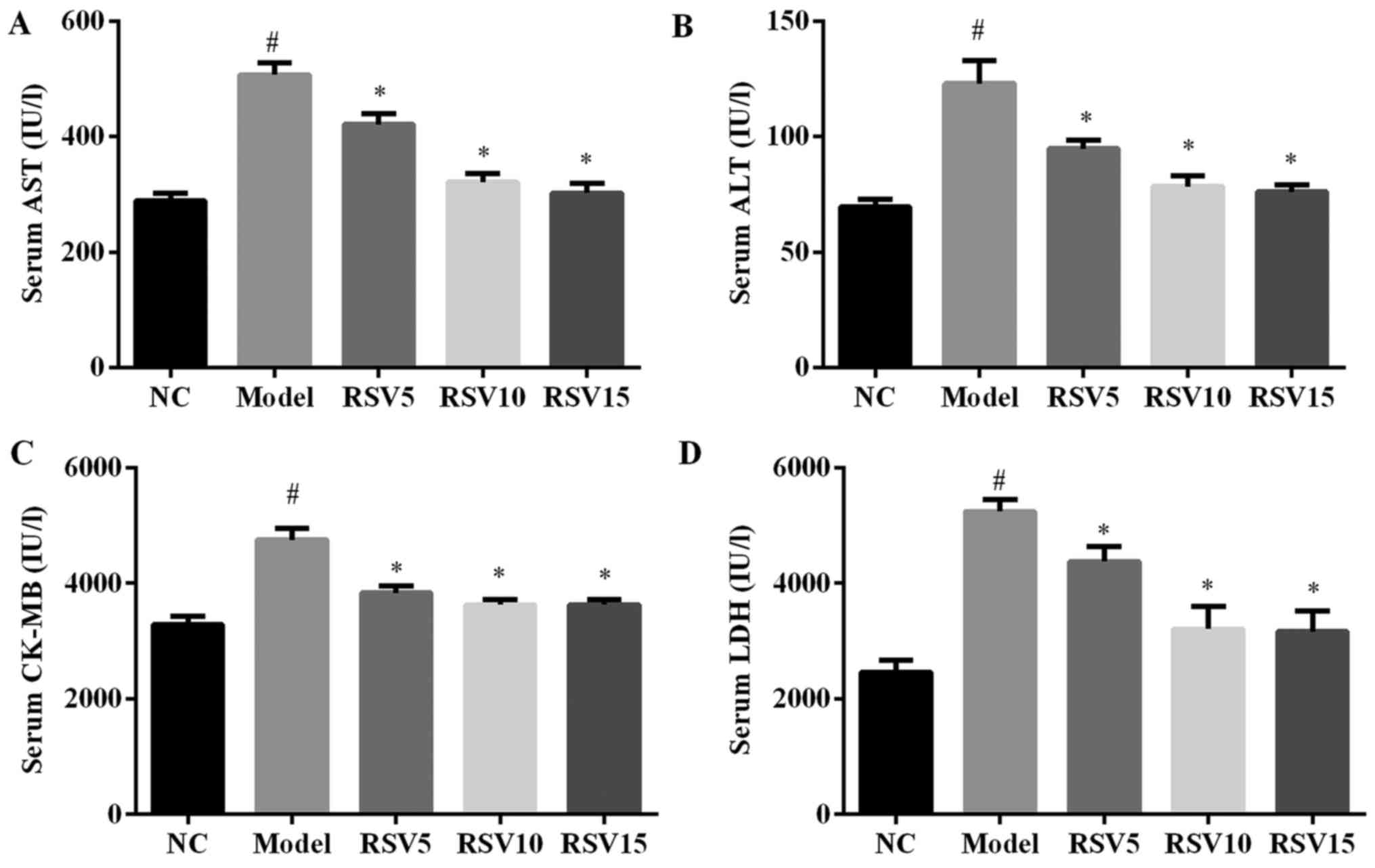
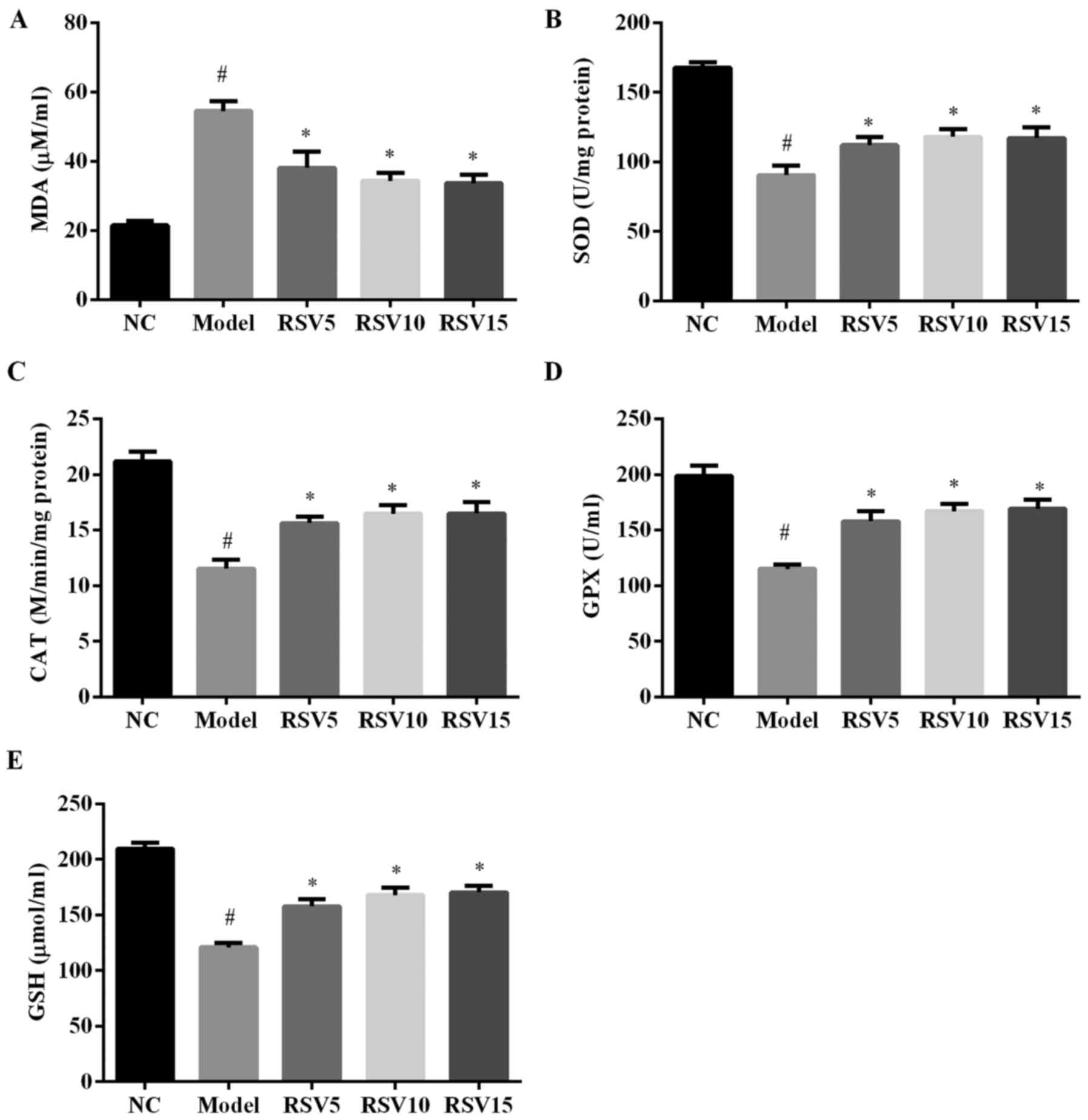
hypertrophy and failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 34:379–388. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Neri M, Fineschi V, Di Paolo M, Pomara C,
Riezzo I, Turillazzi E and Cerretani D: Cardiac oxidative stress
and inflammatory cytokines response after myocardial infarction.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:26–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kumar M, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN, Dahiya V
and Lahkar M: Baicalein protects isoproterenol induced myocardial
ischemic injury in male Wistar rats by mitigating oxidative stress
and inflammation. Inflamm Res. 65:613–622. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen M, Wang M, Yang Q, Wang M, Wang Z,
Zhu Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Jia Y, Li Y, et al: Antioxidant effects of
hydroxysafflor yellow A and acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid in
combination on isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats. Int
J Mol Med. 37:1501–1510. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li H, Xie YH, Yang Q, Wang SW, Zhang BL,
Wang JB, Cao W, Bi LL, Sun JY, Miao S, et al: Cardioprotective
effect of paeonol and danshensu combination on
isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats. PLoS One.
7:e488722012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Suchal K, Bhatia J, Malik S, Malhotra RK,
Gamad N, Goyal S, Nag TC, Arya DS and Ojha S: Seabuckthorn pulp oil
protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
through activation of Akt/eNOS. Front Pharmacol. 7:1552016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang M, Chen J, Zhao J and Meng M:
Etanercept attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by
decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress. PLoS One.
9:e1080242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abderrazak A, Syrovets T, Couchie D, El
Hadri K, Friguet B, Simmet T and Rouis M: NLRP3 inflammasome: From
a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and
inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 4:296–307. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ogura Y, Sutterwala FS and Flavell RA: The
inflammasome: First line of the immune response to cell stress.
Cell. 126:659–662. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu P, Duan L, Chen J, Xiong A, Xu Q,
Zhang H, Zheng F, Tan Z, Gong F and Fang M: Gene silencing of NALP3
protects against liver ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Hum
Gene Ther. 22:853–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shigeoka AA, Mueller JL, Kambo A, Mathison
JC, King AJ, Hall WF, Correia JS, Ulevitch RJ, Hoffman HM and McKay
DB: An inflammasome-independent role for epithelial-expressed Nlrp3
in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Immunol. 185:6277–6285.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Lian K, Zhang L, Wang R, Yi F, Gao
C, Xin C, Zhu D, Li Y, Yan W, et al: TXNIP mediates NLRP3
inflammasome activation in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells
as a novel mechanism in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Basic Res Cardiol. 109:4152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kawaguchi M, Takahashi M, Hata T, Kashima
Y, Usui F, Morimoto H, Izawa A, Takahashi Y, Masumoto J, Koyama J,
et al: Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential
for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation.
123:594–604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Monetti M, Canavesi M, Camera M, Parente
R, Paoletti R, Tremoli E, Corsini A and Bellosta S: Rosuvastatin
displays anti-atherothrombotic and anti-inflammatory properties in
apoE-deficient mice. Pharmacol Res. 55:441–449. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Funderburg N, Clagett B, Jiang Y, Debanne
S, Storer N, Labbato D, Juchnowski S, Ferrari B, Lederman M and
McComsey GA: Rosuvastatin reduces immune activation and
inflammation in treated HIV infection. In: Conference on
Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; Boston, MA. 2014, Poster
335.
|
|
20
|
Duarte T, da Cruz IB, Barbisan F,
Capelleto D, Moresco RN and Duarte MM: The effects of rosuvastatin
on lipid-lowering, inflammatory, antioxidant and fibrinolytics
blood biomarkers are influenced by Val16Ala superoxide dismutase
manganese-dependent gene polymorphism. Pharmacogenomics J.
16:501–506. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liang D, Zhang Q, Yang H, Zhang R, Yan W,
Gao H, Wang J, Zhang X, Chen Y and Cao F: Anti-oxidative stress
effect of loading-dose rosuvastatin prior to percutaneous coronary
intervention in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A
prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Clin Drug
Investig. 34:773–781. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ke D, Fang J, Fan L, Chen Z and Chen L:
Regulatory T cells contribute to rosuvastatin-induced
cardioprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Coron Artery
Dis. 24:334–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Z, Cao Y, Qian J, Ma J, Zou Y and Ge
J: Cardioprotection of rosuvastatin against cardiac dysfunction
after coronary microembolization via alleviating inflammatory
induced micro-infarctions. Circulation. 132:A134342015.
|
|
24
|
Ma M, Uekawa K, Hasegawa Y, Nakagawa T,
Katayama T, Sueta D, Toyama K, Kataoka K, Koibuchi N, Kuratsu J, et
al: Pretreatment with rosuvastatin protects against focal cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through attenuation of
oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res. 1519:87–94. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zaitone SA and Abo-Gresha NM: Rosuvastatin
promotes angiogenesis and reverses isoproterenol-induced acute
myocardial infarction in rats: Role of iNOS and VEGF. Eur J
Pharmacol. 691:134–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo B, Li B, Wang W, Liu X, Liu X, Xia Y,
Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhang M and An F: Rosuvastatin alleviates
diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and MAPK
pathways in a type 2 diabetes rat model. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther.
28:33–43. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Altaf A, Qu P, Zhao Y, Wang H, Lou D and
Niu N: NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood monocytes of acute
coronary syndrome patients and its relationship with statins. Coron
Artery Dis. 26:409–421. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kumar M, Kasala ER, Bodduluru LN, Dahiya
V, Sharma D, Kumar V and Lahkar M: Animal models of myocardial
infarction: Mainstay in clinical translation. Regul Toxicol
Pharmacol. 76:221–230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han S, Cai W, Yang X, Jia Y, Zheng Z, Wang
H, Li J, Li Y, Gao J, Fan L, et al: ROS-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome
activity is essential for burn-induced acute lung injury. Mediators
Inflamm. 2015:7204572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karthikeyan K, Bai BR and Devaraj SN:
Cardioprotective effect of grape seed proanthocyanidins on
isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury in rats. Int J Cardiol.
115:326–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Abbas AM: Cardioprotective effect of
resveratrol analogue isorhapontigenin versus omega-3 fatty acids in
isoproterenol-induced myocardial infarction in rats. J Physiol
Biochem. 72:469–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Geng ZH, Huang L, Song MB and Song YM:
Protective effect of a polysaccharide from Salvia miltiorrhiza on
isoproterenol (ISO)-induced myocardial injury in rats. Carbohydr
Polym. 132:638–642. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hill MF and Singal PK: Antioxidant and
oxidative stress changes during heart failure subsequent to
myocardial infarction in rats. Am J Pathol. 148:291–300.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Madole MB, Bachewar NP and Aiyar CM: Study
of oxidants and antioxidants in patients of acute myocardial
infarction. Adv Biomed Res. 4:2412015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Patil N, Chavan V and Karnik ND:
Antioxidant status in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Indian J Clin Biochem. 22:45–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wattanapitayakul SK and Bauer JA:
Oxidative pathways in cardiovascular disease: Roles, mechanisms,
and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 89:187–206. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sandanger Ø, Ranheim T, Vinge LE, Bliksøen
M, Alfsnes K, Finsen AV, Dahl CP, Askevold ET, Florholmen G,
Christensen G, et al: The NLRP3 inflammasome is up-regulated in
cardiac fibroblasts and mediates myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion
injury. Cardiovasc Res. 99:164–174. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pomerantz BJ, Reznikov LL, Harken AH and
Dinarello CA: Inhibition of caspase 1 reduces human myocardial
ischemic dysfunction via inhibition of IL-18 and IL-1beta. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:2871–2876. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guillén I, Blanes M, Gómez-Lechón MJ and
Castell JV: Cytokine signaling during myocardial infarction:
Sequential appearance of IL-1 beta and IL-6. Am J Physiol.
269:R229–R235. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|