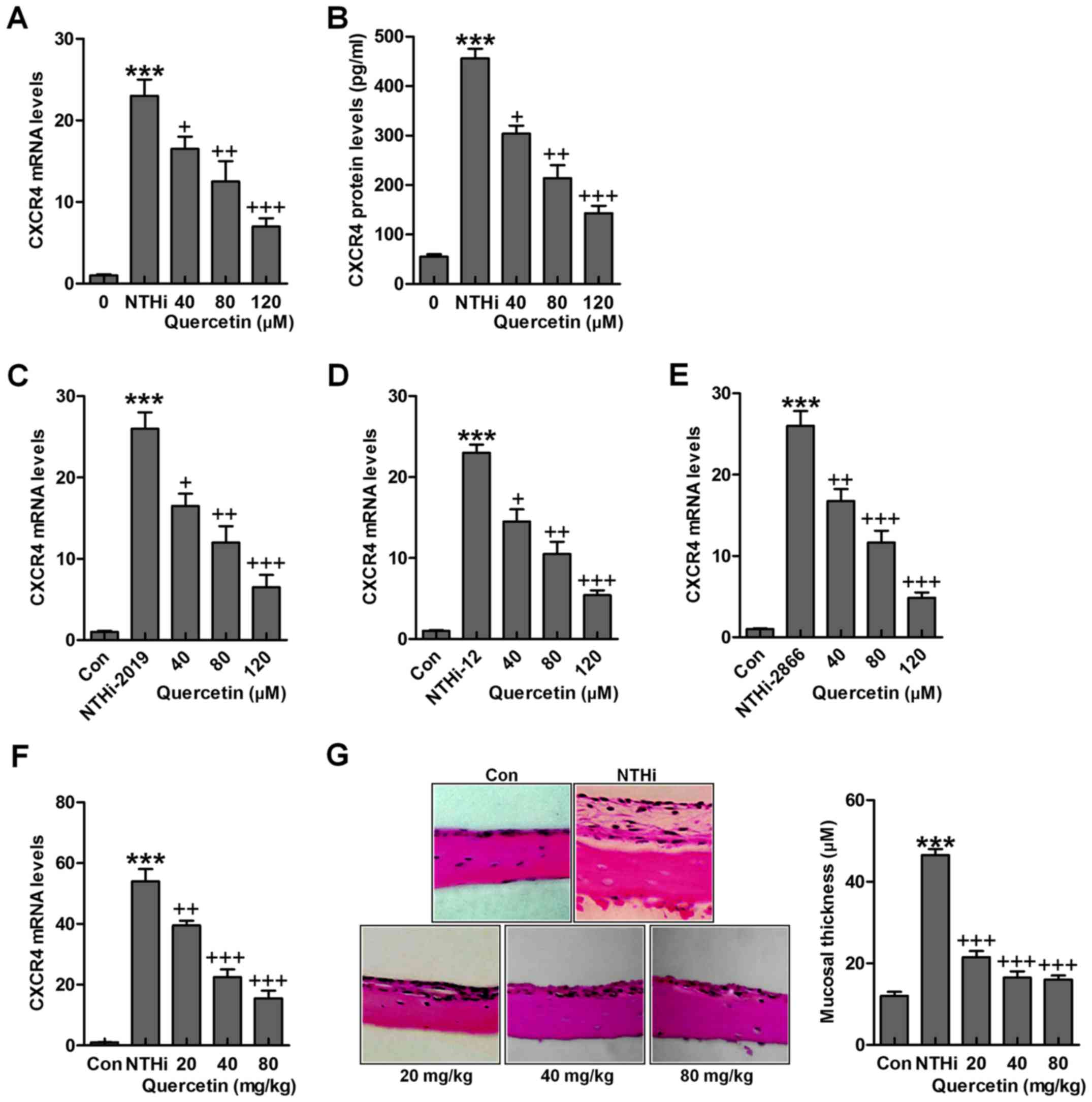
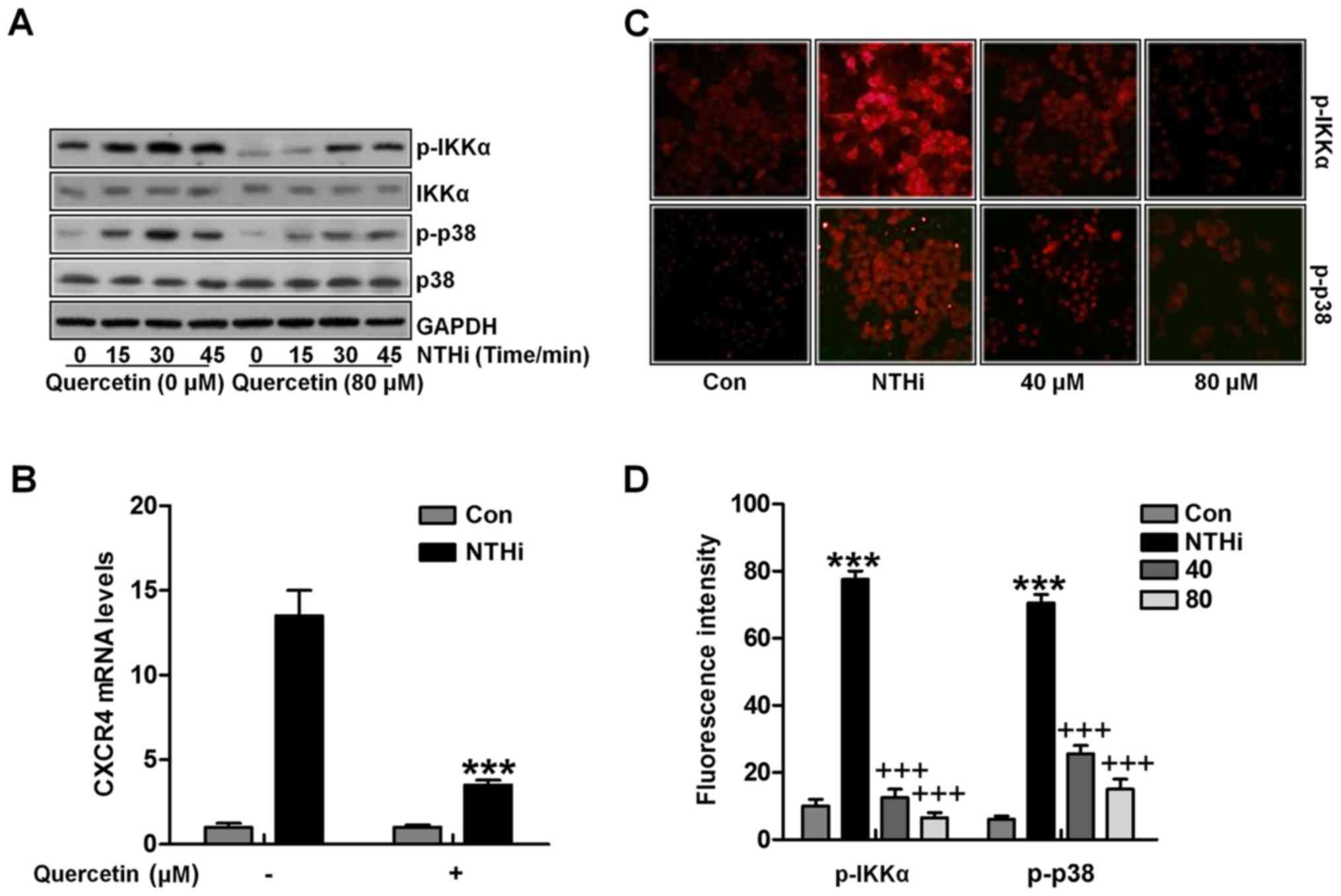
|
1
|
Morris LM, DeGagne JM, Kempton JB, Hausman
F and Trune DR: Mouse middle ear ion homeostasis channels and
intercellular junctions. PLoS One. 7:e390042012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Topcuoglu N, Keskin F, Ciftci S, Paltura
C, Kulekci M, Ustek D and Kulekci G: Relationship between oral
anaerobic bacteria and otitis media with effusion. Int J Med Sci.
9:256–261. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bluestone CD and Klein JO: Physiology,
pathophysiology and pathogenesis Otitis Media in Infants and
Children. 4th edition. BC Decker; pp. 41–42. 2007
|
|
4
|
Post JC: Direct evidence of bacterial
biofilms in otitis media. Laryngoscope. 111:2083–2094. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Darrow DH, Dash N and Derkay CS: Otitis
media: Concepts and controversies. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 11:416–423. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ting PJ, Lin CH, Huang FL, Lin MC, Hwang
KP, Huang YC, Chiu CH, Lin TY and Chen PY: Epidemiology of acute
otitis media among young children: A multiple database study in
Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 45:453–458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cayé-Thomasen P, Hermansson A, Bakaletz L,
Hellstrøm S, Kanzaki S, Kerschner J, Lim D, Lin J, Mason K and
Spratley J: Panel 3: Recent advances in anatomy, pathology, and
cell biology in relation to otitis media pathogenesis. Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 148(Suppl): E37–E51. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Movahedan A, Majdi M, Afsharkhamseh N,
Sagha HM, Saadat NS, Shalileh K, Milani BY, Ying H and Djalilian
AR: Notch inhibition during corneal epithelial wound healing
promotes migration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:7476–7483. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Burns JM, Summers BC, Wang Y, Melikian A,
Berahovich R, Miao Z, Penfold ME, Sunshine MJ, Littman DR, Kuo CJ,
et al: A novel chemokine receptor for SDF-1 and I-TAC involved in
cell survival, cell adhesion, and tumor development. J Exp Med.
203:2201–2213. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balabanian K, Lagane B, Infantino S, Chow
KY, Harriague J, Moepps B, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Thelen M and
Bachelerie F: The chemokine SDF-1/CXCL12 binds to and signals
through the orphan receptor RDC1 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem.
280:35760–35766. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu DY, Tang CH, Yeh WL, Wong KL, Lin CP,
Chen YH, Lai CH, Chen YF, Leung YM and Fu WM: SDF-1alpha
upregulates interleukin-6 through CXCR4, PI3K/Akt, ERK, and
NF-kappaB-dependent pathway in microglia. Eur J Pharmacol.
613:146–154. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ganesan S, Faris AN, Comstock AT, Wang Q,
Nanua S, Hershenson MB and Sajjan US: Quercetin inhibits rhinovirus
replication in vitro and in vivo. Antiviral Res. 94:258–271. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choi HJ, Song JH and Kwon DH: Quercetin
3-rhamnoside exerts antiinfluenza A virus activity in mice.
Phytother Res. 26:462–464. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Slusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS,
Drenkhahn SK, Narula AS, MacDonald RS, Besch-Williford CL and
Lubahn DB: Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog
signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3382–3390.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Casey JR, Kaur R, Friedel VC and
Pichichero ME: Acute otitis media otopathogens during 2008 to 2010
in Rochester, New York. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 32:805–809.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Roier S, Leitner DR, Iwashkiw J,
Schild-Prüfert K, Feldman MF, Krohne G, Reidl J and Schild S:
Intranasal immunization with nontypeabl Haemophilus influenzae
outer membrane vesicles induces cross-protective immunity in mice.
PLoS One. 7:e426642012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nakajima F, Aratani S, Fujita H, Yagishita
N, Ichinose S, Makita K, Setoguchi Y and Nakajima T: Synoviolin
inhibitor LS-102 reduces endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
collagen secretion in an in vitro model of stress-related
interstitial pneumonia. Int J Mol Med. 35:110–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jiang GX, Cao LP, Kang PC, Zhong XY, Lin
TY and Cui YF: Interleukin 6 induces epithelial mesenchymal
transition in human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells. Mol Med
Rep. 13:1563–1569. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jiang HY, Wang F, Chen HM and Yan XJ:
κ-carrageenan induces the disruption of intestinal epithelial
Caco-2 monolayers by promoting the interaction between intestinal
epithelial cells and immune cells. Mol Med Rep. 8:1635–1642. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takeda K and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
in innate immunity. Int Immunol. 17:1–14. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R and
Flavell RA: Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of
NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature. 413:732–738. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang X, Chen Q and Xing D: Focal adhesion
kinase activates NF-κB via the ERK1/2 and p38MAPK pathways in
amyloid-β25–35--induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Alzheimers Dis.
32:77–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sloane JA, Blitz D, Margolin Z and
Vartanian T: A clear and present danger: Endogenous ligands of
Toll-like receptors. Neuromolecular Med. 12:149–163. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Euba B, Moleres J, Segura V, Viadas C,
Morey P, Moranta D, Leiva J, de-Torres JP, Bengoechea JA and
Garmendia J: Genome expression profiling-based identification and
administration efficacy of host-directed antimicrobial drugs
against respiratory infection by nontypeabl Haemophilus influenzae.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 59:7581–7592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kyo Y, Kato K, Park YS, Gajghate S,
Umehara T, Lillehoj EP, Suzaki H and Kim KC: Antiinflammatory role
of MUC1 mucin during infection with nontypeabl Haemophilus
influenzae. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 46:149–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lai WW, Hsu SC, Chueh FS, Chen YY, Yang
JS, Lin JP, Lien JC, Tsai CH and Chung JG: Quercetin inhibits
migration and invasion of SAS human oral cancer cells through
inhibition of NF-κB and matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 signaling
pathways. Anticancer Res. 33:1941–1950. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Xu M, Zheng Q, Zhang Y, Ma W and
Zhang Z: Blocking macrophage migration inhibitory factor activity
alleviates mouse acute otitis media in vivo. Immunol Lett.
162:101–108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chu TG, Cachola DR III, Regal MA, Llamas
AC, Martinez NV and Santos WR: Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
(non-typeable haemophilus influenzae (NTHi) protein D, diphtheria
or tetanus toxoid conjugates) in prevention of acute otitis media
in children: A Cohort Study. Philipp J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
31:13–15. 2016.
|
|
29
|
Borska S, Chmielewska M, Wysocka T,
Drag-Zalesinska M, Zabel M and Dziegiel P: In vitro effect of
quercetin on human gastric carcinoma: Targeting cancer cells death
and MDR. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:3375–3383. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Slusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS,
Drenkhahn SK, Narula AS, MacDonald RS, Besch-Williford CL and
Lubahn DB: Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog
signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 70:3382–3390.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cohen R, Bingen E, Levy C, Thollot F,
Boucherat M, Derkx V and Varon E: Nasopharyngeal flora in children
with acute otitis media before and after implementation of 7 valent
pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in France. BMC Infect Dis.
12:522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pichichero ME, Kaur R, Casey JR, Xu Q,
Almudevar A and Ochs M: Antibody response to Streptococcus
pneumoniae proteins PhtD, LytB, PcpA, PhtE and Ply after
nasopharyngeal colonization and acute otitis media in children. Hum
Vaccin Immunother. 8:799–805. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Pumarola F, Marès J, Losada I, Minguella
I, Moraga F, Tarragó D, Aguilera U, Casanovas JM, Gadea G, Trías E,
et al: Microbiology of bacteria causing recurrent acute otitis
media (AOM) and AOM treatment failure in young children in Spain:
Shifting pathogens in the post-pneumococcal conjugate vaccination
era. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 77:1231–1236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vindrieux D, Escobar P and Lazennec G:
Emerging roles of chemokines in prostate cancer. Endocr Relat
Cancer. 16:663–673. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang JJ, Zhu S, Bruggeman R, Zaino RJ,
Evans DB, Fleming JB, Gomez HF, Zander DS and Wang H: High levels
of expression of human stromal cell-derived factor-1 are associated
with worse prognosis in patients with stage II pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:2598–2604.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Castellone MD, Guarino V, De Falco V,
Carlomagno F, Basolo F, Faviana P, Kruhoffer M, Orntoft T, Russell
JP, Rothstein JL, et al: Functional expression of the CXCR4
chemokine receptor is induced by RET/PTC oncogenes and is a common
event in human papillary thyroid carcinomas. Oncogene.
23:5958–5967. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Torregrossa L, Giannini R, Borrelli N,
Sensi E, Melillo RM, Leocata P, Materazzi G, Miccoli P, Santoro M
and Basolo F: CXCR4 expression correlates with the degree of tumor
infiltration and BRAF status in papillary thyroid carcinomas. Mod
Pathol. 25:46–55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Su L, Zhang J, Xu H, Wang Y, Chu Y, Liu R
and Xiong S: Differential expression of CXCR4 is associated with
the metastatic potential of human non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:8273–8280. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nguyen TT, Tran E, Nguyen TH, Do PT, Huynh
TH and Huynh H: The role of activated MEK-ERK pathway in
quercetin-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis in A549 lung
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 25:647–659. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Meisgen F, Xu Landén N, Wang A, Réthi B,
Bouez C, Zuccolo M, Gueniche A, Ståhle M, Sonkoly E, Breton L, et
al: MiR-146a negatively regulates TLR2-induced inflammatory
responses in keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 134:1931–1940. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Blasius AL and Beutler B: Intracellular
Toll-like receptors. Immunity. 32:305–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lombardo E, DelaRosa O, Mancheño-Corvo P,
Menta R, Ramírez C and Büscher D: Toll-like receptor-mediated
signaling in human adipose-derived stem cells: Implications for
immunogenicity and immunosuppressive potential. Tissue Eng Part A.
15:1579–1589. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cassatella MA, Mosna F, Micheletti A, Lisi
V, Tamassia N, Cont C, Calzetti F, Pelletier M, Pizzolo G and
Krampera M: Toll-like receptor-3-activated human mesenchymal
stromal cells significantly prolong the survival and function of
neutrophils. Stem Cells. 29:1001–1011. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kim KN, Ham YM, Moon JY, Kim MJ, Jung YH,
Jeon YJ, Lee NH, Kang N, Yang HM, Kim D, et al: Acanthoic acid
induces cell apoptosis through activation of the p38 MAPK pathway
in HL-60 human promyelocytic leukaemia. Food Chem. 135:2112–2117.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hyun MS, Hur JM, Mun YJ, Kim D and Woo WH:
BBR induces apoptosis in HepG2 cell through an
Akt-ASK1-ROS-p38MAPKs-linked cascade. J Cell Biochem. 109:329–338.
2010.
|
|
46
|
Liu N, Tian J, Cheng J and Zhang J:
Migration of CXCR4 gene-modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal
stem cells to the acute injured kidney. J Cell Biochem.
114:2677–2689. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|