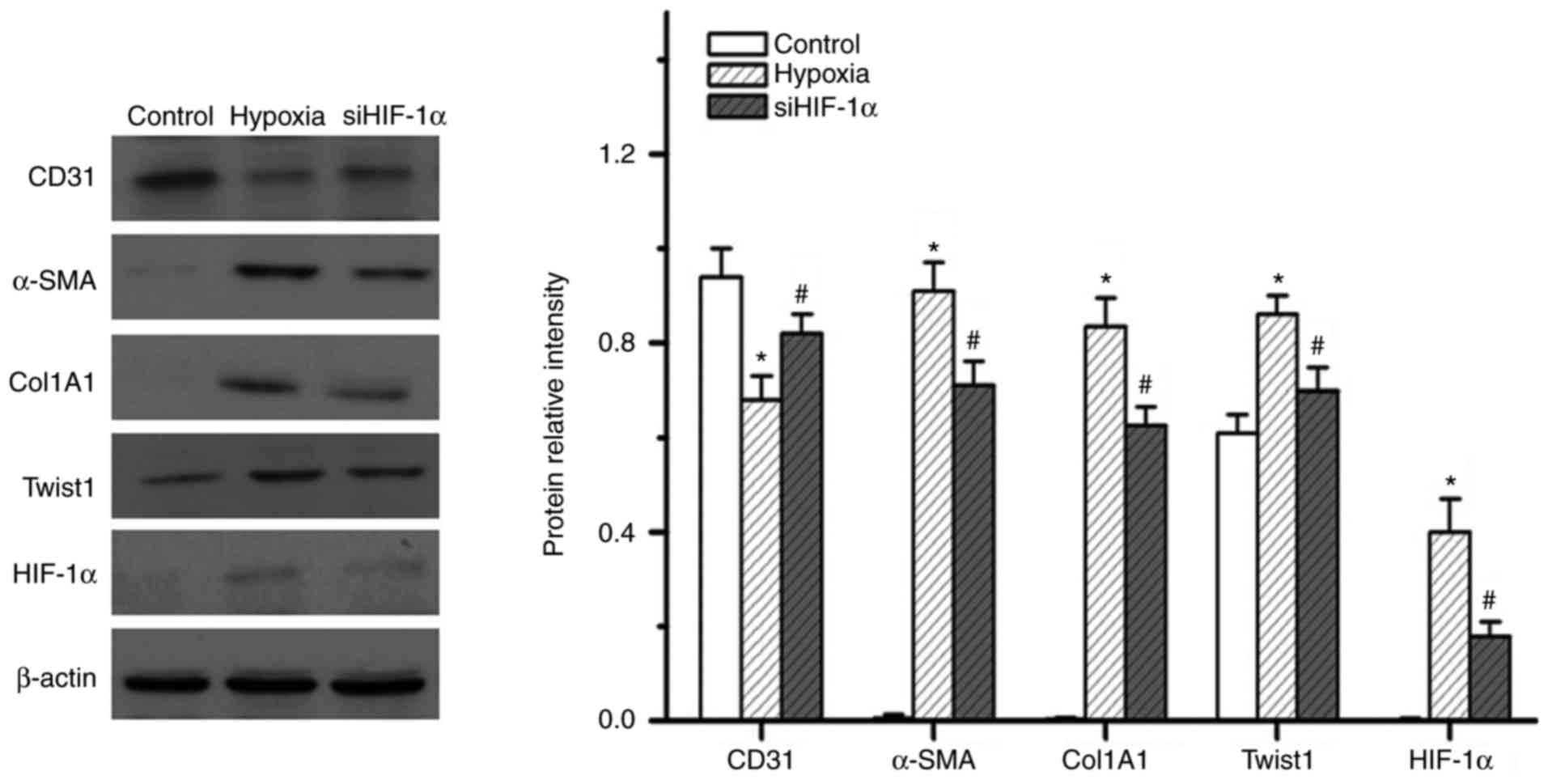
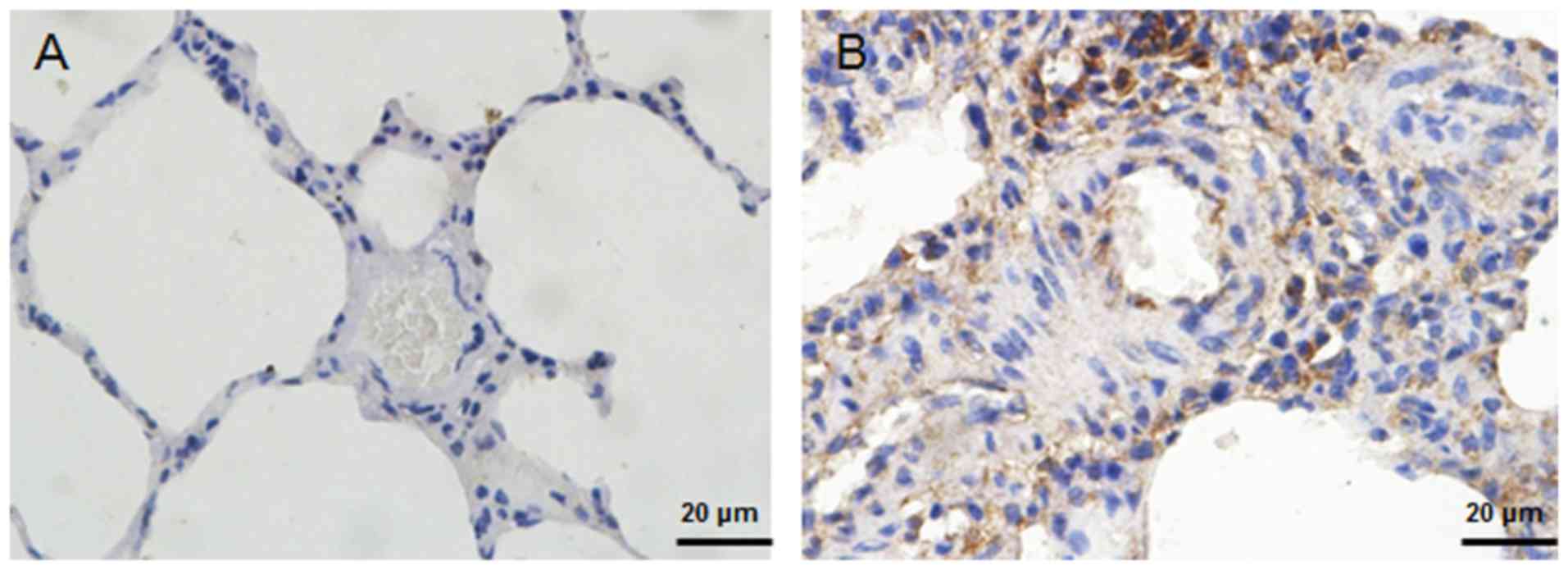
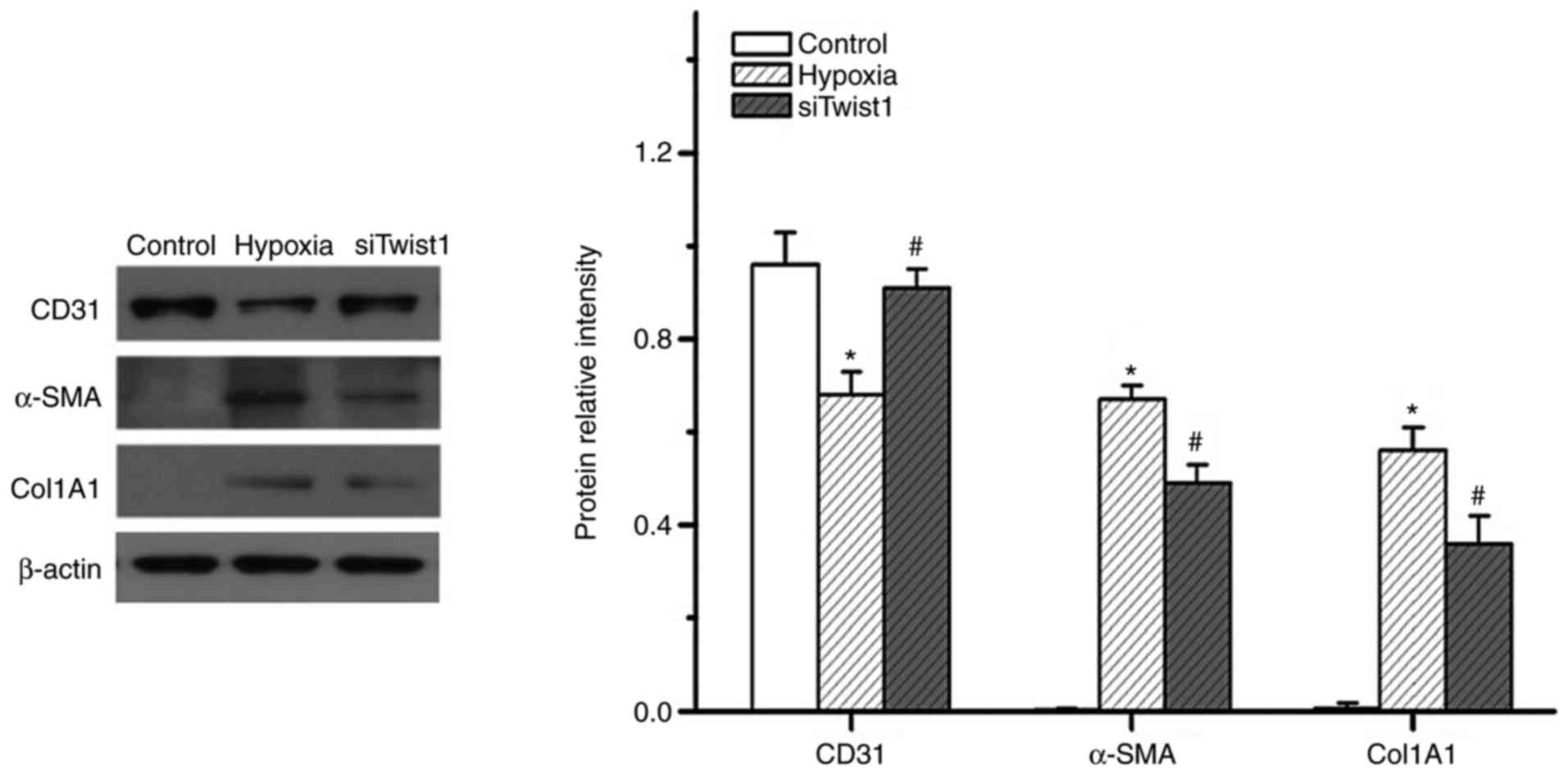
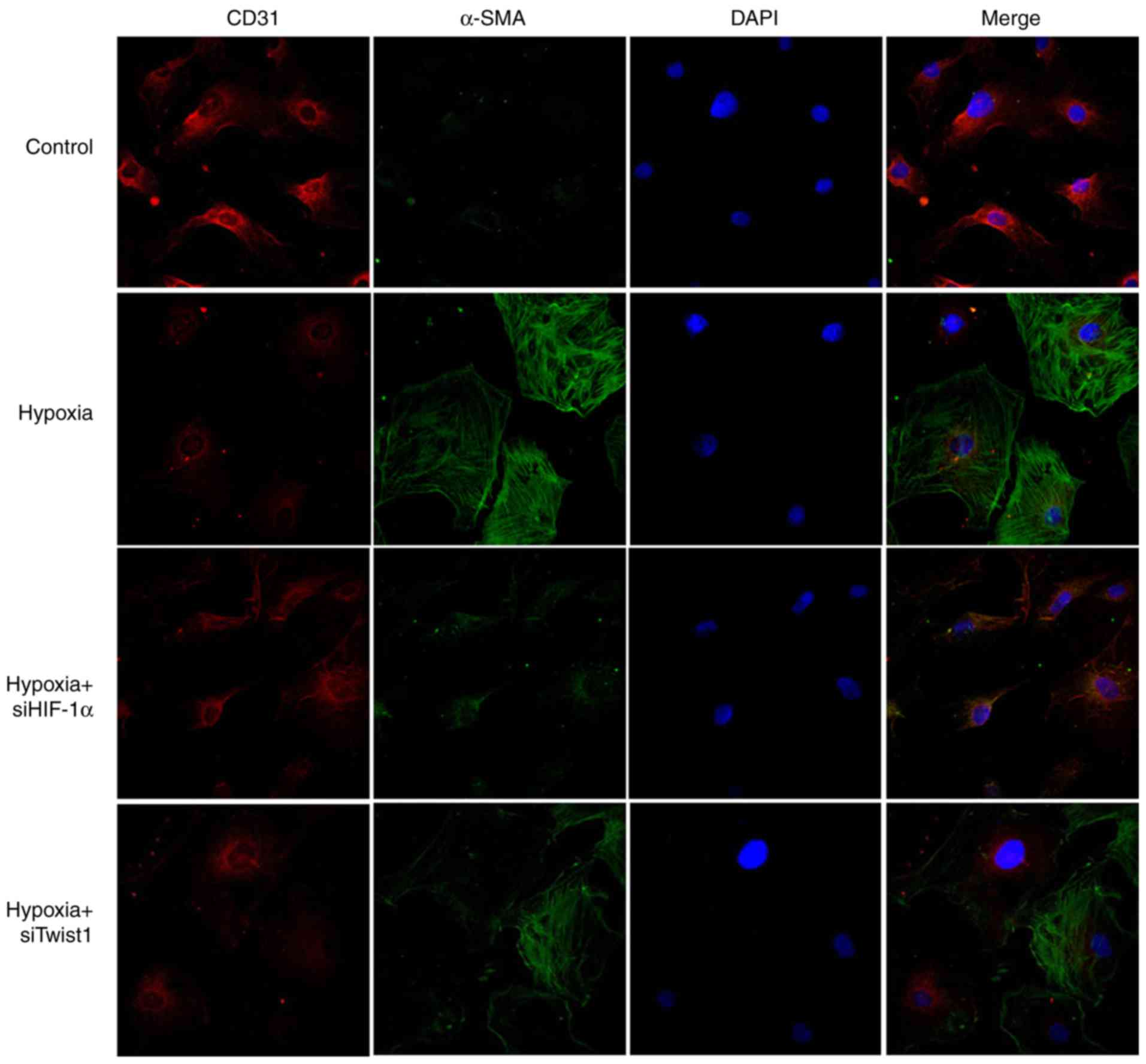
|
1
|
Morrell NW, Adnot S, Archer SL, Dupuis J,
Jones PL, MacLean MR, McMurtry IF, Stenmark KR, Thistlethwaite PA,
Weissmann N, et al: Cellular and molecular basis of pulmonary
arterial hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 54(1 Suppl): S20–S31.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stenmark KR, Fagan KA and Frid MG:
Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling: Cellular and
molecular mechanisms. Circ Res. 99:675–691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hay ED: An overview of
epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat. 154:8–20. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arciniegas E, Neves CY, Carrillo LM,
Zambrano EA and Ramirez R: Endothelial-mesenchymal transition
occurs during embryonic pulmonary artery development. Endothelium.
12:193–200. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Armstrong EJ and Bischoff J: Heart valve
development: Endothelial cell signaling and differentiation. Circ
Res. 95:459–470. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hashimoto N, Phan SH, Imaizumi K, Matsuo
M, Nakashima H, Kawabe T, Shimokata K and Hasegawa Y:
Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary
fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 43:161–172. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li J, Qu X, Yao J, Caruana G, Ricardo SD,
Yamamoto Y, Yamamoto H and Bertram JF: Blockade of
endothelial-mesenchymal transition by a Smad3 inhibitor delays the
early development of streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 59:2612–2624. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liebner S, Cattelino A, Gallini R, Rudini
N, Iurlaro M, Piccolo S and Dejana E: Beta-catenin is required for
endothelial-mesenchymal transformation during heart cushion
development in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 166:359–367. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Potenta S, Zeisberg E and Kalluri R: The
role of endothe-lial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Br J Cancer. 99:1375–1379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zeisberg EM, Tarnavski O, Zeisberg M,
Dorfman AL, McMullen JR, Gustafsson E, Chandraker A, Yuan X, Pu WT,
Roberts AB, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. 13:952–961. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Humbert M, Montani D, Perros F, Dorfmüller
P, Adnot S and Eddahibi S: Endothelial cell dysfunction and cross
talk between endothelium and smooth muscle cells in pulmonary
arterial hypertension. Vascul Pharmacol. 49:113–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ranchoux B, Antigny F, Rucker-Martin C,
Hautefort A, Péchoux C, Bogaard HJ, Dorfmüller P, Remy S, Lecerf F,
Planté S, et al: Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in pulmonary
hypertension. Circulation. 131:1006–1018. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wojciak-Stothard B, Tsang LY and Haworth
SG: Rac and Rho play opposing roles in the regulation of
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced permeability changes in pulmonary
artery endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
288:L749–L760. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang MH and Wu KJ: TWIST activation by
hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1): Implications in metastasis and
development. Cell Cycle. 7:2090–2096. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang MH, Wu MZ, Chiou SH, Chen PM, Chang
SY, Liu CJ, Teng SC and Wu KJ: Direct regulation of TWIST by
HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:295–305. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Desprez PY, Sumida T and Coppe JP:
Helix-loop-helix proteins in mammary gland development and breast
cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 8:225–239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, Cao X, Shih JY, Wei
Y, Abbruzzese JL, Hortobagyi GN and Hung MC: Epidermal growth
factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene expression. Cancer
Res. 67:9066–9076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pozharskaya V, Torres-Gonzalez E, Rojas M,
Gal A, Amin M, Dollard S, Roman J, Stecenko AA and Mora AL: Twist:
A regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung fibrosis.
PLoS One. 4:e75592009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frid MG, Brunetti JA, Burke DL, Carpenter
TC, Davie NJ, Reeves JT, Roedersheimer MT, van Rooijen N and
Stenmark KR: Hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling requires
recruitment of circulating mesenchymal precursors of a
monocyte/macrophage lineage. Am J Pathol. 168:659–669. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Spencer VA, Sun JM, Li L and Davie JR:
Chromatin immunoprecipitation: A tool for studying histone
acetylation and transcription factor binding. Methods. 31:67–75.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wohrley JD, Frid MG, Moiseeva EP, Orton
EC, Belknap JK and Stenmark KR: Hypoxia selectively induces
proliferation in a specific subpopulation of smooth muscle cells in
the bovine neonatal pulmonary arterial media. J Clin Invest.
96:273–281. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arciniegas E, Frid MG, Douglas IS and
Stenmark KR: Perspectives on endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Potential contribution to vascular remodeling in chronic pulmonary
hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 293:L1–L8. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stenmark KR, Davie N, Frid M,
Gerasimovskaya E and Das M: Role of the adventitia in pulmonary
vascular remodeling. Physiology. 21:134–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arciniegas E, Sutton AB, Allen TD and
Schor AM: Transforming growth factor beta 1 promotes the
differentiation of endothelial cells into smooth muscle-like cells
in vitro. J Cell Sci. 103:521–529. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu P, Huang L, Ge X, Yan F, Wu R and Ao
Q: Transdifferentiation of pulmonary arteriolar endothelial cells
into smooth muscle-like cells regulated by myocardin involved in
hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodelling. Int J Exp Pathol.
87:463–474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jones R and Reid L: Vascular Remodeling in
Clinical and Experimental Pulmonary Hypertensions. Portland Press;
London: 1995
|
|
28
|
Yu AY, Shimoda LA, Iyer NV, Huso DL, Sun
X, McWilliams R, Beaty T, Sham JS, Wiener CM, Sylvester JT and
Semenza GL: Impaired physiological responses to chronic hypoxia in
mice partially deficient for hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha. J
Clin Invest. 103:691–696. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM,
Shrimanker N, Akai Y, Hohenstein B, Saito Y, Johnson RS, Kretzler
M, Cohen CD, et al: Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1
stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest.
117:3810–3820. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ansieau S, Bastid J, Doreau A, Morel AP,
Bouchet BP, Thomas C, Fauvet F, Puisieux I, Doglioni C, Piccinin S,
et al: Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of
tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell.
14:79–89. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL, Ramaswamy S,
Itzykson RA, Come C, Savagner P, Gitelman I, Richardson A and
Weinberg RA: Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an
essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell. 117:927–939. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sun S, Ning X, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Nie Y, Han
S, Liu L, Du R, Xia L, He L and Fan D: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha induces Twist expression in tubular epithelial cells
subjected to hypoxia, leading to epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Kidney Int. 75:1278–1287. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|