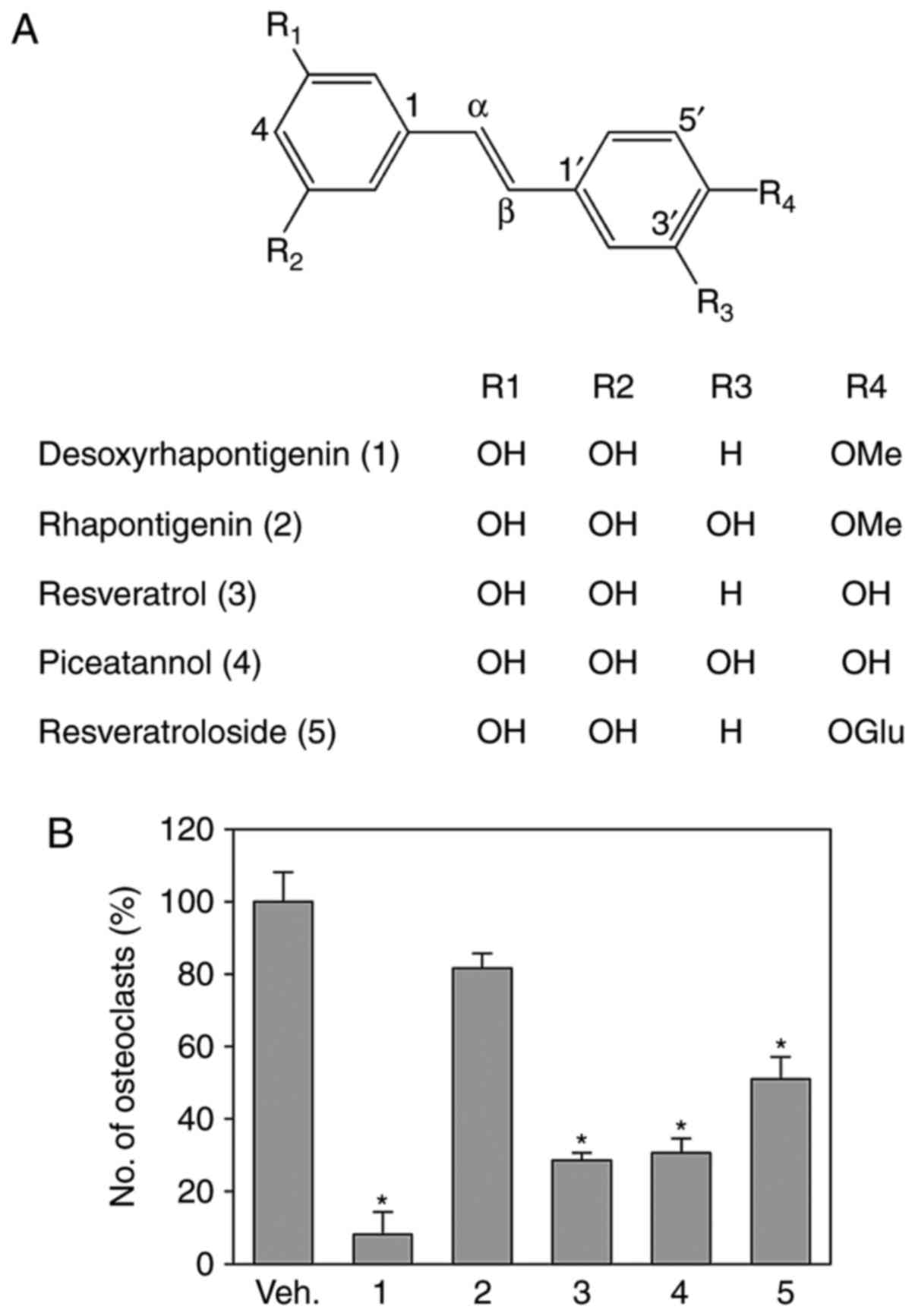
|
1
|
Robling AG, Castillo AB and Turner CH:
Biomechanical and molecular regulation of bone remodeling. Annu Rev
Biomed Eng. 8:455–498. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Boyce BF, Rosenberg E, de Papp AE and
Duong LT: The osteoclast, bone remodelling and treatment of
metabolic bone disease. Eur J Clin Invest. 42:1332–1341. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feng X and McDonald JM: Disorders of bone
remodeling. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:121–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hienz SA, Paliwal S and Ivanovski S:
Mechanisms of bone resorption in periodontitis. J Immunol Res.
2015:6154862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Crockett JC, Rogers MJ, Coxon FP, Hocking
LJ and Helfrich MHL: Bone remodelling at a glance. J Cell Sci.
124:991–998. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bonewald LF: The amazing osteocyte. J Bone
Miner Res. 26:229–238. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Asagiri M and Takayanagi H: The molecular
understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 40:251–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chambers TJ: Regulation of the
differentiation and function of osteoclasts. J Pathol. 192:4–13.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wada T, Nakashima T, Hiroshi N and
Penninger JM: RANKL-RANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone
disease. Trends Mol Med. 12:17–25. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
He Y, Staser K, Rhodes SD, Liu Y, Wu X,
Park SJ, Yuan J, Yang X, Li X, Jiang L, et al: Erk1 positively
regulates osteoclast differentiation and bone resorptive activity.
PLoS One. 6:e247802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamamoto A, Miyazaki T, Kadono Y,
Takayanagi H, Miura T, Nishina H, Katada T, Wakabayashi K, Oda H,
Nakamura K and Tanaka S: Possible involvement of IkappaB kinase 2
and MKK7 in osteoclastogenesis induced by receptor activator of
nuclear factor kappaB ligand. J Bone Miner Res. 17:612–621. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumoto M, Sudo T, Saito T, Osada H and
Tsujimoto M: Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
signaling pathway in osteoclastogenesis mediated by receptor
activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL). J Biol Chem.
275:31155–31161. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fu Y, Gu J, Wang Y, Yuan Y, Liu X, Bian J
and Liu Z: Involvement of the mitogenactivated protein kinase
signaling pathway in osteoprotegerininduced inhibition of
osteoclast differentiation and maturation. Mol Med Rep.
12:6939–6945. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Asagiri M, Sato K, Usami T, Ochi S,
Nishina H, Yoshida H, Morita I, Wagner EF, Mak TW, Serfling E and
Takayanagi H: Autoamplification of NFATc1 expression determines its
essential role in bone homeostasis. J Exp Med. 202:1261–1269. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Logar DB, Komadina R, Prezelj J, Ostanek
B, Trost Z and Marc J: Expression of bone resorption genes in
osteoarthritis and in osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 25:219–225.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Harvey AL: Natural products in drug
discovery. Drug Discov Today. 13:894–901. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
An J, Hao D, Zhang Q, Chen B, Zhang R,
Wang Y and Yang H: Natural products for treatment of bone erosive
diseases: The effects and mechanisms on inhibiting
osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. Int Immunopharmacol.
36:118–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He ZH, He MF, Ma SC and But PP:
Anti-angiogenic effects of rhubarb and its anthraquinone
derivatives. J Ethnopharmacol. 121:313–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Matsuda H, Tewtrakul S, Morikawa T and
Yoshikawa M: Anti-allergic activity of stilbenes from Korean
rhubarb (Rheum undulatum L.): Structure requirements for inhibition
of antigen-induced degranulation and their effects on the release
of TNF-alpha and IL-4 in RBL-2H3 cells. Bioorg Med Chem.
12:4871–4876. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Paneitz A and Westendorf J: Anthranoid
contents of rhubarb (Rheum undulatum L.) and other Rheum species
and their toxicological relevance. Eur Food Res Technol.
210:97–101. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Toguchida I, Park
JY, Harima S and Yoshikawa M: Antioxidant constituents from
rhubarb: Structural requirements of stilbenes for the activity and
structures of two new anthraquinone glucosides. Bioorg Med Chem.
9:41–50. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi RJ, Chun J, Khan S and Kim YS:
Desoxyrhapontigenin, a potent anti-inflammatory phytochemical,
inhibits LPS-induced inflammatory responses via suppressing NF-κB
and MAPK pathways in RAW 264.7 cells. Int Immunopharmacol.
18:182–190. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Choi SZ, Lee SO, Jang KU, Chung SH, Park
SH, Kang HC, Yang EY, Cho HJ and Lee KR: Antidiabetic stilbene and
anthraquinone derivatives from Rheum undulatum. Arch Pharm Res.
28:1027–1030. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Redlich K and Smolen JS: Inflammatory bone
loss: Pathogenesis and therapeutic intervention. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:234–250. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-delta deltaC(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ngoc TM, Minh PT, Hung TM, Thuong PT, Lee
I, Min BS and Bae K: Lipoxygenase inhibitory constituents from
Rhubarb. Arch Pharm Res. 31:598–605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi B, Kim S, Jang BG and Kim MJ:
Piceatannol, a natural analogue of resveratrol, effectively reduced
beta-amyloid levels via activation of alpha-secretase and matrix
metalloproteinase-9. J Funct Foods. 23:124–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pawlus AD, Sahli R, Bisson J, Rivière C,
Delaunay JC, Richard T, Gomès E, Bordenave L, Waffo-Téguo P and
Mérillon JM: Stilbenoid profiles of canes from vitis and
muscandinia species. J Agric Food Chem. 61:501–511. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
He X, Andersson G, Lindgren U and Li Y:
Resveratrol prevents RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation of
murine osteoclast progenitor RAW 264.7 cells through inhibition of
ROS production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 401:356–362. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamasaki T, Ariyoshi W, Okinaga T, Adachi
Y, Hosokawa R, Mochizuki S, Sakurai K and Nishihara T: The dectin 1
agonist curdlan regulates osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting nuclear
factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic 1 (NFATc1) through Syk
kinase. J Biol Chem. 289:19191–19203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wilson SR, Peters C, Saftig P and Brömme
D: Cathepsin K activity-dependent regulation of osteoclast actin
ring formation and bone resorption. J Biol Chem. 284:2584–2592.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shen T, Wang XN and Lou HX: Natural
stilbenes: An overview. Nat Prod Rep. 26:916–935. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chachay VS, Kirkpatrick CM, Hickman IJ,
Ferguson M, Prins JB and Martin JH: Resveratrol-pills to replace a
healthy diet? Br J Clin Pharmacol. 72:27–38. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tou JC: Resveratrol supplementation
affects bone acquisition and osteoporosis: Pre-clinical evidence
toward translational diet therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1186–1194. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim JH and Kim N: Regulation of NFATc1 in
osteoclast differentiation. J Bone Metab. 21:233–241. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ikeda F, Nishimura R, Matsubara T, Tanaka
S, Inoue J, Reddy SV, Hata K, Yamashita K, Hiraga T, Watanabe T, et
al: Critical roles of c-Jun signaling in regulation of NFAT family
and RANKL-regulated osteoclast differentiation. J Clin Invest.
114:475–484. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Böhm C, Hayer S, Kilian A, Zaiss MM,
Finger S, Hess A, Engelke K, Kollias G, Krönke G, Zwerina J, et al:
The alpha-isoform of p38 MAPK specifically regulates arthritic bone
loss. J Immunol. 183:5938–5947. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee SE, Woo KM, Kim SY, Kim HM, Kwack K,
Lee ZH and Kim HH: The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, p38, and
extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways are involved in
osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 30:71–77. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|