|
1
|
Balcells G, Matabosch X and Ventura R:
Detection of stanozolol O- and N-sulfate metabolites and their
evaluation as additional markers in doping control. Drug Test Anal.
9:1001–1010. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tsitsimpikou C, Vasilaki F, Tsarouhas K,
Fragkiadaki P, Tzardi M, Goutzourelas N, Nepka C, Kalogeraki A,
Heretis I, Epitropaki Z, et al: Nephrotoxicity in rabbits after
long-term nandrolone decanoate administration. Toxicol Lett.
259:21–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
World Anti-doping Agency: The 2017 list of
prohibited substances and methods. https://www.wada-ama.org/.
Accessed Feb 14, 2018.
|
|
4
|
Kioukia-Fougia N, Georgiadis N, Tsarouhas
K, Vasilaki F, Fragiadaki P, Meimeti E and Tsitsimpikou C:
Synthetic and natural nutritional supplements: Health 'allies' or
risks to public health. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov.
10:72–85. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tsitsimpikou C, Chrisostomou N, Papalexis
P, Tsarouhas K, Tsatsakis A and Jamurtas A: The use of nutritional
supplements among recreational athletes in Athens, Greece. Int J
Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 21:377–384. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sagoe D, Molde H, Andreassen CS, Torsheim
T and Pallesen S: The global epidemiology of anabolic-androgenic
steroid use: A meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. Ann
Epidemiol. 24:383–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ampuero J, García ES, Lorenzo MM, Calle R,
Ferrero P and Gómez MR: Stanozolol-induced bland cholestasis.
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 37:71–72. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bausserman LL, Saritelli AL and Herbert
PN: Effects of short-term stanozolol administration on serum
lipoproteins in hepatic lipase deficiency. Metabolism. 46:992–996.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
El-Serag HB, Kramer J, Duan Z and Kanwal
F: Racial differences in the progression to cirrhosis and
hepatocellular carcinoma in HCV-infected veterans. Am J
Gastroenterol. 109:1427–1435. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hansma P, Diaz FJ and Njiwaji C: Fatal
liver cyst rupture due to anabolic steroid use: A case
presentation. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 37:21–22. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Harkin KR, Cowan LA, Andrews GA, Basaraba
RJ, Fischer JR, DeBowes LJ, Roush JK, Guglielmino ML and Kirk CA:
Hepatotoxicity of stanozolol in cats. J Am Vet Med Assoc.
217:681–684. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Socas L, Zumbado M, Pérez-Luzardo O, Ramos
A, Pérez C, Hernández JR and Boada LD: Hepatocellular adenomas
associated with anabolic androgenic steroid abuse in bodybuilders:
A report of two cases and a review of the literature. Br J Sports
Med. 39:e272005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Stimac D, Milić S, Dintinjana RD, Kovac D
and Ristić S: Androgenic/anabolic steroid-induced toxic hepatitis.
J Clin Gastroenterol. 35:350–352. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deshmukh NI, Zachar G, Petróczi A, Székely
AD, Barker J and Naughton DP: Determination of stanozolol and
3′-hydroxystanozolol in rat hair, urine and serum using liquid
chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Chem Cent J. 6:1622012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mateus-Avois L, Mangin P and Saugy M: Use
of ion trap gas chromatography-multiple mass spectrometry for the
detection and confirmation of 3′hydroxystanozolol at trace levels
in urine for doping control. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed
Life Sci. 816:193–201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kicman AT: Pharmacology of anabolic
steroids. Br J Pharmacol. 154:502–521. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Büttner A and Thieme D: Side effects of
anabolic androgenic steroids: Pathological findings and
structure-activity relationships. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 195:459–484.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rentoukas E, Tsarouhas K, Kaplanis I,
Korou E, Nikolaou M, Marathonitis G, Kokkinou S, Haliassos A,
Mamalaki A, Kouretas D, et al: Connection between telomerase
activity in PBMC and markers of inflammation and endothelial
dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome. PLoS One.
7:e357392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kumar M, Lechel A and Güneş Ç: Telomerase:
The devil inside. Genes (Basel). 7:E432016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xu Y and Goldkorn A: Telomere and
telomerase therapeutics in cancer. Genes (Basel). 7:E222016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou X, Zhu H and Lu J: PTEN and hTERT
gene expression and the correlation with human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 211:316–319. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wojtyla A, Gladych M and Rubis B: Human
telomerase activity regulation. Mol Biol Rep. 38:3339–3349. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Yang C, Li S, Wang M, Chang AK, Liu Y,
Zhao F, Xiao L, Han L, Wang D, Li S and Wu H: PTEN suppresses the
oncogenic function of AIB1 through decreasing its protein stability
via mechanism involving Fbw7 alpha. Mol Cancer. 12:212013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jung S, Li C, Jeong D, Lee S, Ohk J, Park
M, Han S, Duan J, Kim C, Yang Y, et al: Oncogenic function of
p34SEI-1 via NEDD4 1 mediated PTEN ubiquitination/degradation and
activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:1587–1595.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
OECD: Guidance document on the
recognition, assessment, and use of clinical signs as humane
endpoints for experimental animals used in safety evaluation. OECD;
Paris: 2000
|
|
26
|
Cherici Camargo IC, Barreiros de Souza R,
de Fátima Paccola Mesquita S, Chuffa LG and Frei F: Ovarian
histology and follicular score in female rats treated with
nandrolone decanoate and submitted to physical effort. Acta Biol
Hung. 60:253–261. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
de Almeida Chuffa LG, de Souza RB, Frei F,
de Fátima Paccola Mesquita S and Camargo IC: Nandrolone decanoate
and physical effort: Histological and morphometrical assessment in
adult rat uterus. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 294:335–341. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gopinathan S, O'Neill E, Rodriguez LA,
Champ R, Phillips M, Nouraldeen A, Wendt M, Wilson AGE and Kramer
JA: In vivo toxicology of excipients commonly employed in drug
discovery in rats. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 68:284–295. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Healing G, Sulemann T, Cotton P, Harris J,
Hargreaves A, Finney R, Kirk S, Schramm C, Garner C, Pivette P and
Burdett L: Safety data on 19 vehicles for use in 1 month oral
rodent pre-clinical studies: Administration of
hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin causes renal toxicity. J Appl Toxicol.
36:140–150. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Aye M, Di Giorgio C, De Mo M, Botta A,
Perrin J and Courbiere B: Assessment of the genotoxicity of three
cryoprotectants used for human oocyte vitrification: Dimethyl
sulfoxide, ethylene glycol and propylene glycol. Food Chem Toxicol.
48:1905–1912. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Berthelot-Ricou A, Perrin J, di Giorgio C,
de Meo M, Botta A and Courbiere B: Assessment of 1,2-propanediol
(PrOH) genotoxicity on mouse oocytes by comet assay. Fertil Steril.
96:1002–1007. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cunningham RL and McGinnis MY: Physical
provocation of pubertal anabolic androgenic steroid exposed male
rats elicits aggression towards females. Horm Behav. 50:410–416.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Matrisciano F, Modafferi AM, Togna GI,
Barone Y, Pinna G, Nicoletti F and Scaccianoce S: Repeated anabolic
androgenic steroid treatment causes antidepressant-reversible
alterations of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, BDNF levels
and behavior. Neuropharmacology. 58:1078–1084. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tucci P, Morgese MG, Colaianna M, Zotti M,
Schiavone S, Cuomo V and Trabace L: Neurochemical consequence of
steroid abuse: Stanozolol-induced monoaminergic changes. Steroids.
77:269–275. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kara M, Ozcagli E, Fragkiadaki P, Kotil T,
Stivaktakis PD, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis AM and Alpertunga B:
Determination of DNA damage and telomerase activity in
stanozolol-treated rats. Exp Ther Med. 13:614–618. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tsitsimpikou C, Tzatzarakis M, Fragkiadaki
P, Kovatsi L, Stivaktakis P, Kalogeraki A, Kouretas D and Tsatsakis
AM: Histopathological lesions, oxidative stress and genotoxic
effects in liver and kidneys following long term exposure of
rabbits to diazinon and propoxur. Toxicology. 307:109–114. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Solbach P, Potthoff A, Raatschen HJ,
Soudah B, Lehmann U, Schneider A, Gebel MJ, Manns MP and Vogel A:
Testosterone-receptor positive hepatocellular carcinoma in a
29-year old bodybuilder with a history of anabolic androgenic
steroid abuse: A case report. BMC Gastroenterol. 15:602015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−4Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kesler T, Sandhu RS and Krishnamoorthy S:
Hepatology: Hepatocellular carcinoma in a young man secondary to
androgenic anabolic steroid abuse. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
29:18522014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boada LD, Zumbado M, Torres S, López A,
Díaz-Chico BN, Cabrera JJ and Luzardo OP: Evaluation of acute and
chronic hepatotoxic effects exerted by anabolic-androgenic steroid
stanozolol in adult male rats. Arch Toxicol. 73:465–472. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kanayama G, Hudson JI and Pope HG Jr:
Long-term psychiatric and medical consequences of
anabolic-androgenic steroid abuse: A looming public health concern?
Drug Alcohol Depend. 98:1–12. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ornish D, Lin J, Chan JM, Epel E, Kemp C,
Weidner G, Marlin R, Frenda SJ, Magbanua MJM, Daubenmier J, et al:
Effect of comprehensive lifestyle changes on telomerase activity
and telomere length in men with biopsy-proven low-risk prostate
cancer: 5-year follow-up of a descriptive pilot study. Lancet
Oncol. 14:1112–1120. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mishra S, Kumar R, Malhotra N, Singh N and
Dada R: Mild oxidative stress is beneficial for sperm telomere
length maintenance. World J Methodol. 6:163–170. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zar T, Graeber C and Perazella MA:
Recognition, treatment, and prevention of propylene glycol
toxicity. Semin Dial. 20:217–219. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Djojosubroto MW, Chin AC, Go N,
Schaetzlein S, Manns MP, Gryaznov S, Harley CB and Rudolph KL:
Telomerase antagonists GRN163 and GRN163L inhibit tumor growth and
increase chemosensitivity of human hepatoma. Hepatology.
42:1127–1136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vasilaki F, Tsitsimpikou C, Tsarouhas K,
Germanakis I, Tzardi M, Kavvalakis M, Ozcagli E, Kouretas D and
Tsatsakis AM: Cardiotoxicity in rabbits after long-term nandrolone
decanoate administration. Toxicol Lett. 241:143–151. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Pilati C, Letouzé E, Nault JC, Imbeaud S,
Boulai A, Calderaro J, Poussin K, Franconi A, Couchy G, Morcrette
G, et al: Genomic profiling of hepatocellular adenomas reveals
recurrent FRK-activating mutations and the mechanisms of malignant
transformation. Cancer Cell. 25:428–441. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Akincilar SC, Unal B and Tergaonkar V:
Reactivation of telomerase in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci.
73:1659–1670. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jungermann K and Kietzmann T: Zonation of
parenchymal and nonparenchymal metabolism in liver. Annu Rev Nutr.
16:179–203. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jungermann K: Metabolic zonation of liver
parenchyma. Semin Liver Dis. 8:329–341. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Salvador JP, Sánchez-Baeza F and Marco MP:
Simultaneous immunochemical detection of stanozolol and the main
human metabolite, 3′-hydroxy-stanozolol, in urine and serum
samples. Anal Biochem. 376:221–228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chilton WL, Marques FZ, West J,
Kannourakis G, Berzins SP, O'Brien BJ and Charchar FJ: Acute
exercise leads to regulation of telomere-associated genes and
microRNA expression in immune cells. PLoS One. 9:e920882014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ludlow AT, Gratidão L, Ludlow LW,
Spangenburg EE and Roth SM: Acute exercise activates p38 MAPK and
increases the expression of telomere-protective genes in cardiac
muscle. Exp Physiol. 102:397–410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Vardavas AI, Stivaktakis PD, Tzatzarakis
MN, Fragkiadaki P, Vasilaki F, Tzardi M, Datseri G, Tsiaoussis J,
Alegakis AK, Tsitsimpikou C, et al: Long-term exposure to
cypermethrin and piperonyl butoxide cause liver and kidney
inflammation and induce genotoxicity in New Zealand white male
rabbits. Food Chem Toxicol. 94:250–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Huang CC, Chiang WD, Huang WC, Huang CY,
Hsu MC and Lin WT: Hepatoprotective effects of swimming exercise
against D-galactose-induced senescence rat model. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:2754312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yi X, Cao S, Chang B, Zhao D, Gao H, Wan
Y, Shi J, Wei W and Guan Y: Effects of acute exercise and chronic
exercise on the liver leptin-AMPK-ACC signaling pathway in rats
with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Res. 2013:9464322013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pettersson J, Hindorf U, Persson P,
Bengtsson T, Malmqvist U, Werkström V and Ekelund M: Muscular
exercise can cause highly pathological liver function tests in
healthy men. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 65:253–259. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Brustia R, Savier E and Scatton O:
Physical exercise in cirrhotic patients: Towards prehabilitation on
waiting list for liver transplantation. A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. Nov 18–2017.Epub
ahead of print. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
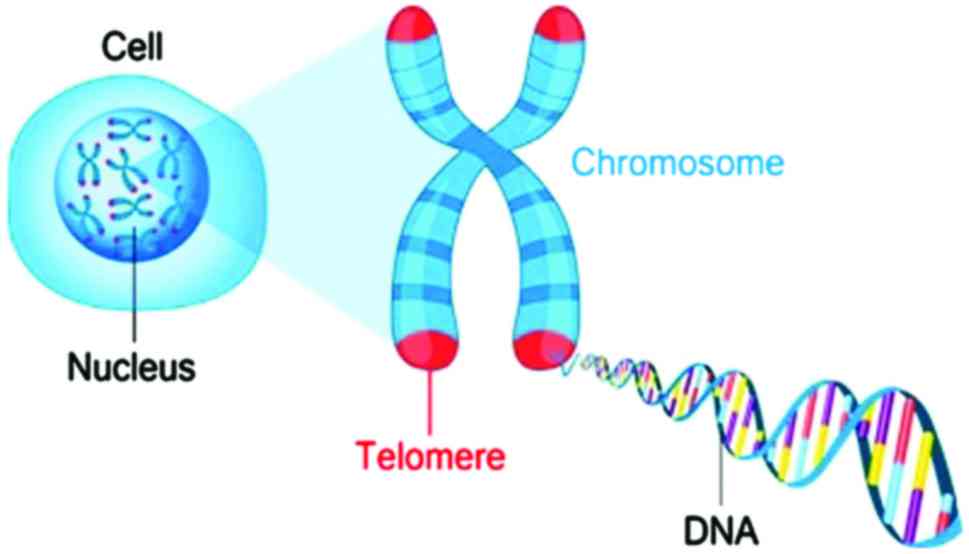
Tapis F: Telomeres are protective caps on
the end of chromosomes. Cell, chromosome and DNA vector
illustration. Digital image ID: 710795275, Shutterstock. https://www.shutterstock.com/image-illustration/telomeres-protective-caps-on-end-chromosomes-735264379.
|