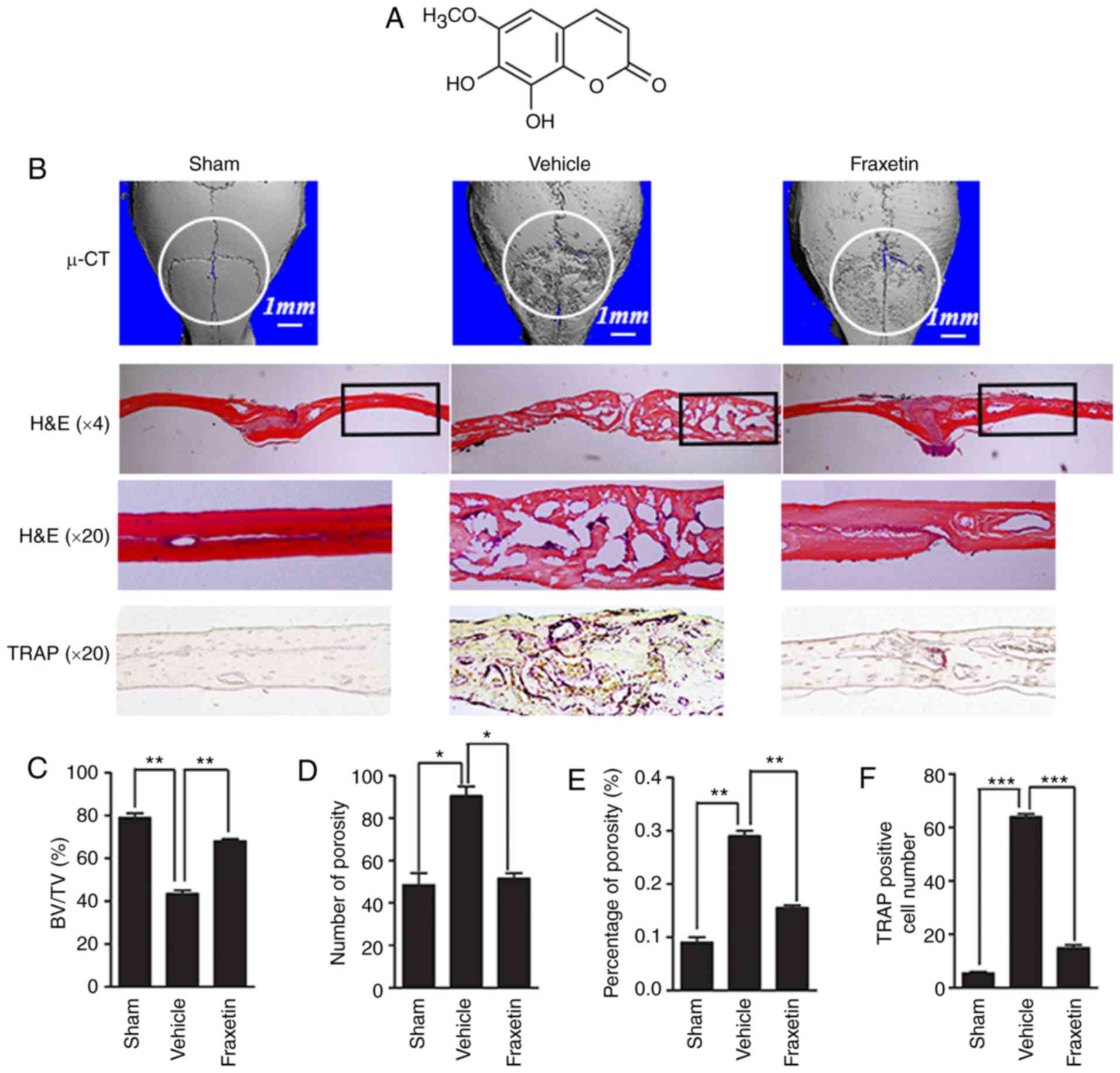
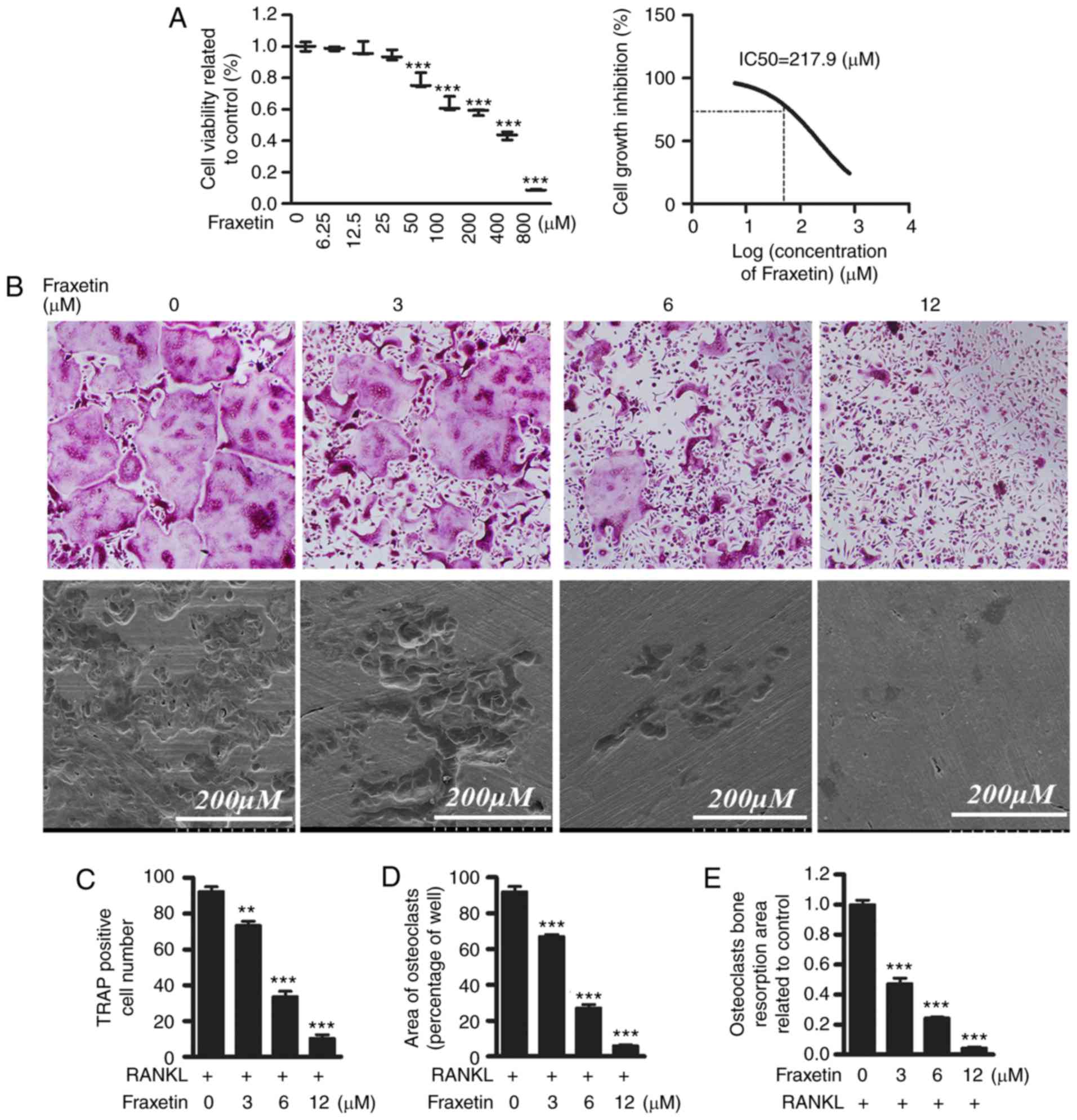
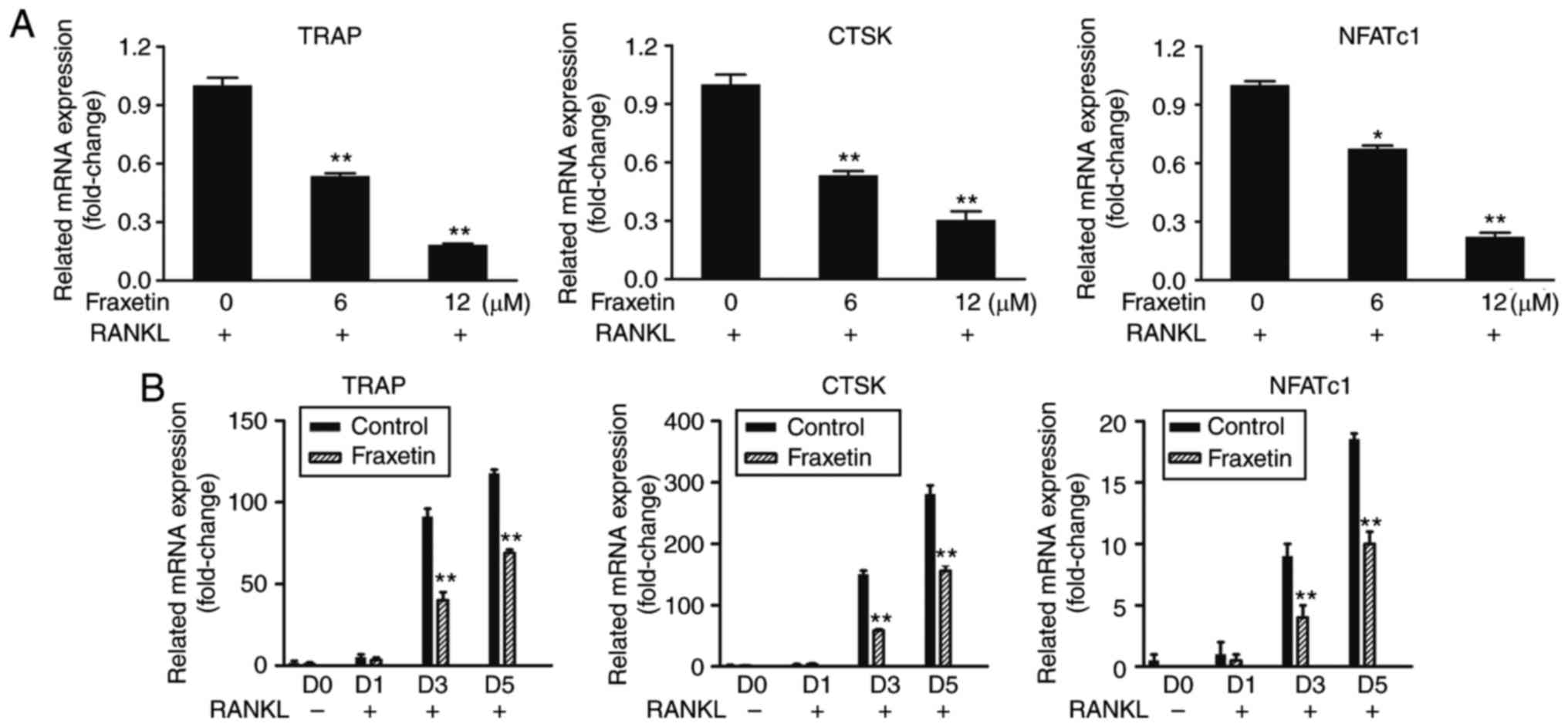
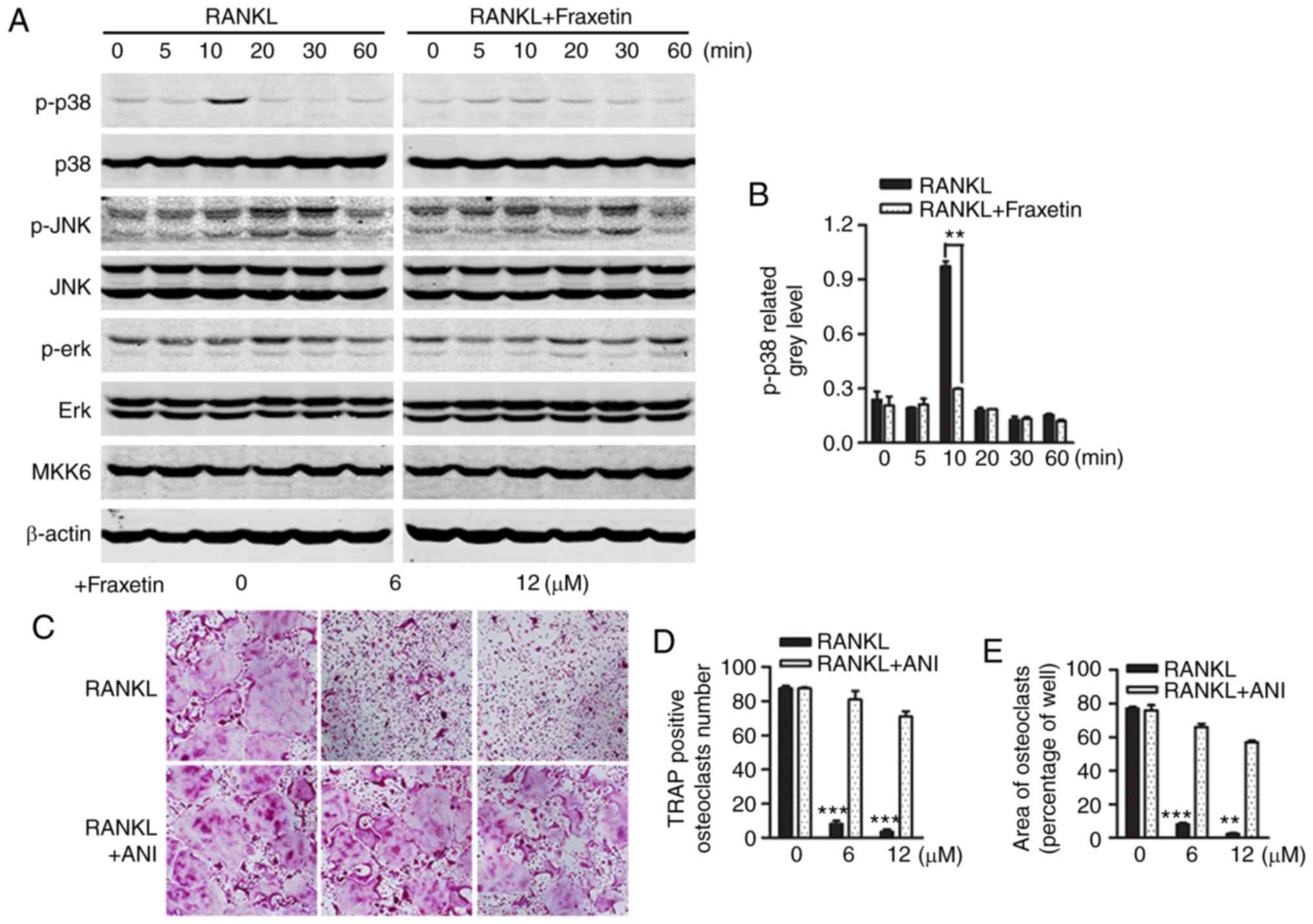
|
1
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodan GA and Martin TJ: Therapeutic
approaches to bone diseases. Science. 289:1508–1514. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Helfrich MH: Osteoclast diseases and
dental abnormalities. Arch Oral Biol. 50:115–122. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abu-Amer Y, Darwech I and Clohisy JC:
Aseptic loosening of total joint replacements: Mechanisms
underlying osteolysis and potential therapies. Arthritis Res Ther.
9(Suppl 1): S62007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Anderson JM, Rodriguez A and Chang DT:
Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin Immunol. 20:86–100.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Long M and Rack HJ: Titanium alloys in
total joint replacement-a materials science perspective.
Biomaterials. 19:1621–1639. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Holt G, Murnaghan C, Reilly J and Meek RM:
The biology of aseptic osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.
460:240–252. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Udagawa N, Takahashi N, Akatsu T, Tanaka
H, Sasaki T, Nishihara T, Koga T, Martin TJ and Suda T: Origin of
osteo-clasts: Mature monocytes and macrophages are capable of
differentiating into osteoclasts under a suitable microenvironment
prepared by bone marrow-derived stromal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 87:7260–7264. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Novack DV: Role of NF-kappaB in the
skeleton. Cell Res. 21:169–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng X: RANKing intracellular signaling in
osteoclasts. IUBMB Life. 57:389–395. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Witaicenis A, Seito LN, da Silveira Chagas
A, de Almeida LD Jr, Luchini AC, Rodrigues-Orsi P, Cestari SH and
Di Stasi LC: Antioxidant and intestinal anti-inflammatory effects
of plant-derived coumarin derivatives. Phytomedicine. 21:240–246.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Murali R, Srinivasan S and Ashokkumar N:
Antihyperglycemic effect of fraxetin on hepatic key enzymes of
carbohydrate metabolism in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Biochimie. 95:1848–1854. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kuo PL, Huang YT, Chang CH and Chang JK:
Fraxetin inhibits the induction of anti-Fas IgM, tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta-mediated apoptosis by Fas
pathway inhibition in human osteoblastic cell line MG-63. Int
Immunopharmacol. 6:1167–1175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jin S, Park JY, Hong JM, Kim TH, Shin HI,
Park EK and Kim SY: Inhibitory effect of (-)-epigallocatechin
gallate on titanium particle-induced TNF-alpha release and in vivo
osteolysis. Exp Mol Med. 43:411–418. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu F, Zhu Z, Mao Y, Liu M, Tang T and Qiu
S: Inhibition of titanium particle-induced osteoclastogenesis
through inactivation of NFATc1 by VIVIT peptide. Biomaterials.
30:1756–1762. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Knoch M, Jewison DE, Sibonga JD,
Sprecher C, Morrey BF, Loer F, Berry DJ and Scully SP: The
effectiveness of polyethylene versus titanium particles in inducing
osteolysis in vivo. J Orthop Res. 22:237–243. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee SS, Woo CH, Chang JD and Kim JH: Roles
of Rac and cytosolic phospholipase A2 in the intracellular
signalling in response to titanium particles. Cell Signal.
15:339–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qin A, Cheng TS, Lin Z, Cao L, Chim SM,
Pavlos NJ, Xu J, Zheng MH and Dai KR: Prevention of wear
particle-induced osteolysis by a novel V-ATPase inhibitor
saliphenylhalamide through inhibition of osteoclast bone
resorption. PloS One. 7:e341322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wedemeyer C, Xu J, Neuerburg C,
Landgraeber S, Malyar NM, von Knoch F, Gosheger G, von Knoch M,
Löer F and Saxler G: Particle-induced osteolysis in
three-dimensional micro-computed tomography. Calcif Tissue Int.
81:394–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cano E, Hazzalin CA and Mahadevan LC:
Anisomycin-activated protein kinases p45 and p55 but not
mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK-1 and -2 are implicated in
the induction of c-fos and c-jun. Mol Cell Biol. 14:7352–7362.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hazzalin CA, Le Panse R, Cano E and
Mahadevan LC: Anisomycin selectively desensitizes signalling
components involved in stress kinase activation and fos and jun
induction. Mol Cell Biol. 18:1844–1854. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lin C, Shao Y, Zeng C, Zhao C, Fang H,
Wang L, Pan J, Liu L, Qi W, Feng X, et al: Blocking PI3K/AKT
signaling inhibits bone sclerosis in subchondral bone and
attenuates post-traumatic osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol.
233:6135–6147. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Stevenson DA, Schwarz EL, Carey JC,
Viskochil DH, Hanson H, Bauer S, Weng HY, Greene T, Reinker K,
Swensen J, et al: Bone resorption in syndromes of the Ras/MAPK
pathway. Clin Genet. 80:566–573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang H, Chang EJ, Ryu J, Lee ZH, Lee Y
and Kim HH: Induction of c-Fos and NFATc1 during RANKL-stimulated
osteoclast differentiation is mediated by the p38 signaling
pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 351:99–105. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zwerina J, Hayer S, Redlich K, Bobacz K,
Kollias G, Smolen JS and Schett G: Activation of p38 MAPK is a key
step in tumor necrosis factor-mediated inflammatory bone
destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 54:463–472. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang L and Karin M: Mammalian MAP kinase
signalling cascades. Nature. 410:37–40. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lucas JJ, Yamamoto A, Scearce-Levie K,
Saudou F and Hen R: Absence of fenfluramine-induced anorexia and
reduced c-Fos induction in the hypothalamus and central amygdaloid
complex of serotonin 1B receptor knock-out mice. J Neurosci.
18:5537–5544. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sharma SM, Bronisz A, Hu R, Patel K,
Mansky KC, Sif S and Ostrowski MC: MITF and PU.1 recruit p38 MAPK
and NFATc1 to target genes during osteoclast differentiation. J
Biol Chem. 282:15921–15929. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsumoto M, Kogawa M, Wada S, Takayanagi
H, Tsujimoto M, Katayama S, Hisatake K and Nogi Y: Essential role
of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in cathepsin K gene
expression during osteoclastogenesis through association of NFATc1
and PU.1. J Biol Chem. 279:45969–45979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kyriakis JM and Avruch J: Mammalian MAPK
signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation:
A 10-year update. Physiol Rev. 92:689–737. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hirakawa K, Bauer TW, Stulberg BN and
Wilde AH: Comparison and quantitation of wear debris of failed
total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Biomed Mater Res.
31:257–263. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baumann B, Seufert J, Jakob F, Nöth U,
Rolf O, Eulert J and Rader CP: Activation of NF-kappaB signalling
and TNFalpha-expression in THP-1 macrophages by TiAlV- and
polyethylene-wear particles. J Orthop Res. 23:1241–1248.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Masui T, Sakano S, Hasegawa Y, Warashina H
and Ishiguro N: Expression of inflammatory cytokines, RANKL and OPG
induced by titanium, cobalt-chromium and polyethylene particles.
Biomaterials. 26:1695–1702. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Baumann B, Rader CP, Seufert J, Nöth U,
Rolf O, Eulert J and Jakob F: Effects of polyethylene and TiAlV
wear particles on expression of RANK, RANKL and OPG mRNA. Acta
Orthop Scand. 75:295–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|