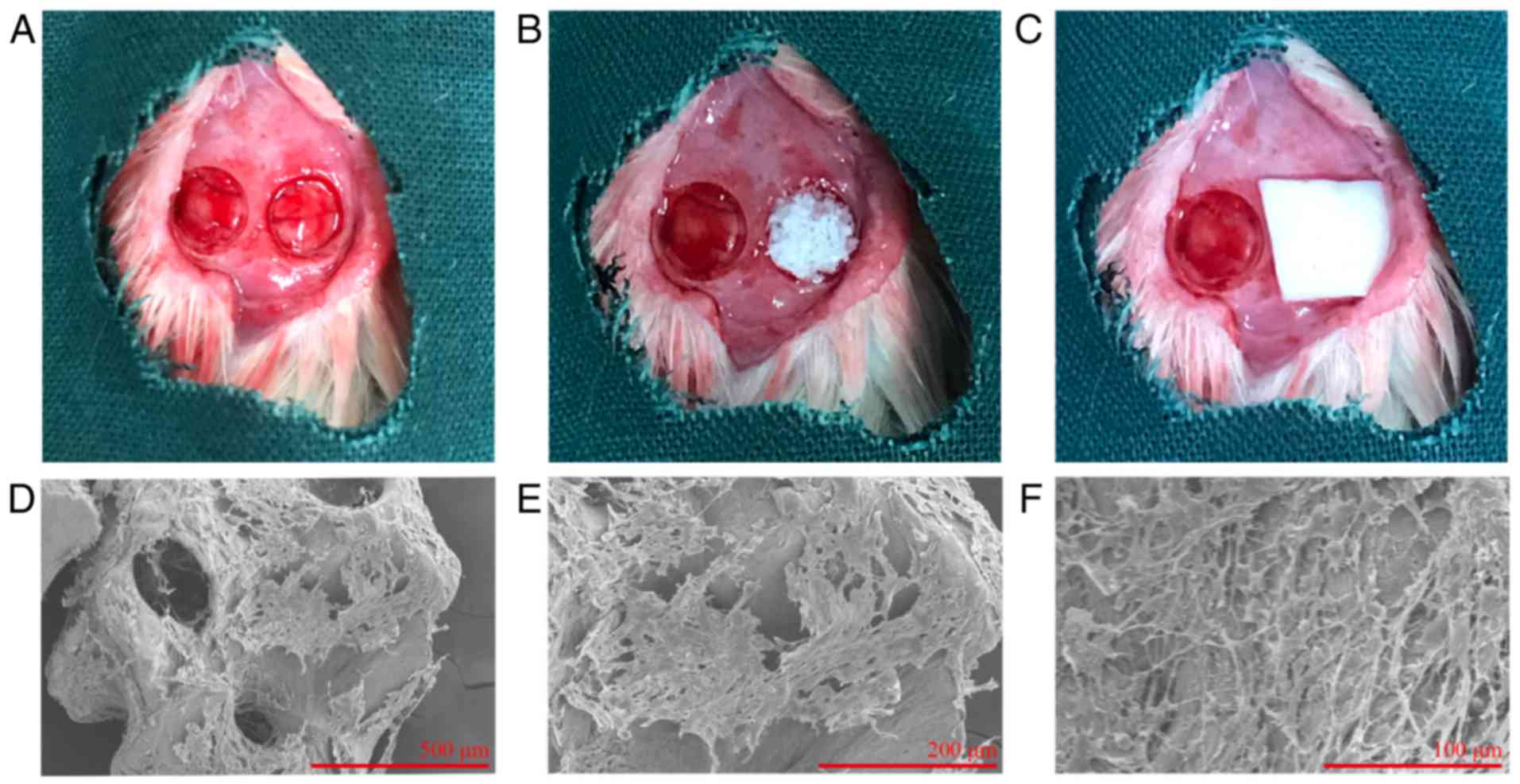
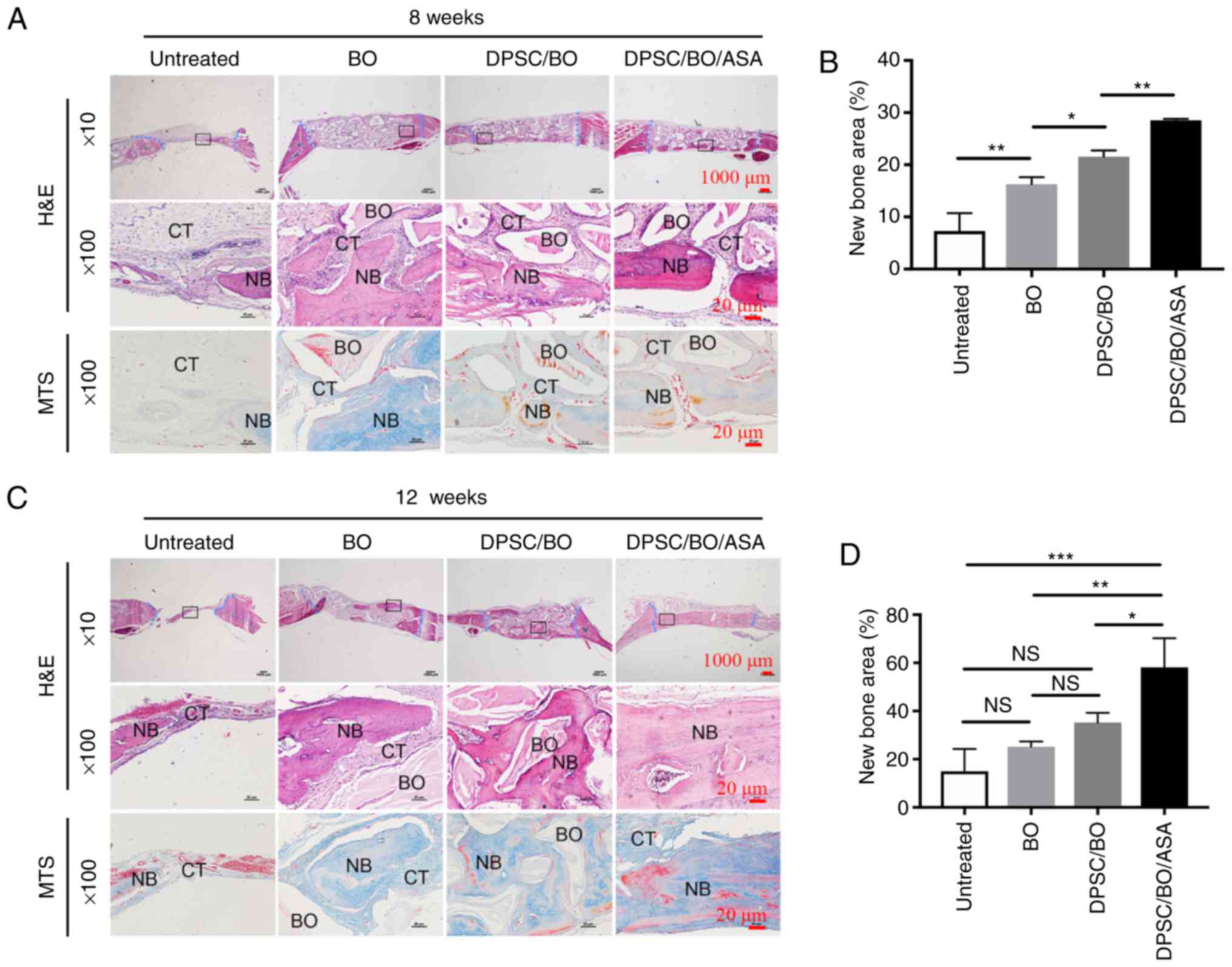
|
1
|
Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, Robey PG
and Shi S: Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro
and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:13625–13630. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei X, Ling J, Wu L, Liu L and Xiao Y:
Expression of mineralization markers in dental pulp cells. J Endod.
33:703–708. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gronthos S, Brahim J, Li W, Fisher LW,
Cherman N, Boyde A, DenBesten P, Robey PG and Shi S: Stem cell
properties of human dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 81:531–535.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu H, Gronthos S and Shi S: Dental pulp
stem cells. Methods Enzymol. 419:99–113. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
About I, Bottero MJ, de Denato P, Camps J,
Franquin JC and Mitsiadis TA: Human dentin production in vitro. Exp
Cell Res. 258:33–41. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Wang L, Jin Y and Shi S: Fas
ligand regulates the immu-nomodulatory properties of dental pulp
stem cells. J Dent Res. 91:948–954. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Smith JB and Willis AL: Aspirin
selectively inhibits pros-taglandin production in human platelets.
Nat New Biol. 231:235–237. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamaza T, Miura Y, Bi Y, Liu Y, Akiyama K,
Sonoyama W, Patel V, Gutkind S, Young M, Gronthos S, et al:
Pharmacologic stem cell based intervention as a new approach to
osteoporosis treatment in rodents. PLoS One. 3:e26152008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu Y, Wang L, Kikuiri T, Akiyama K, Chen
C, Xu X, Yang R, Chen W, Wang S and Shi S: Mesenchymal stem
cell-based tissue regeneration is governed by recipient T
lymphocytes via IFN-γ and TNF-α. Nat Med. 17. pp. 1594–1601. 2011,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cao Y, Xiong J, Mei S, Wang F, Zhao Z,
Wang S and Liu Y: Aspirin promotes bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cell-based calvarial bone regeneration in mini swine. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 6:2102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Chen C, Liu S, Liu D, Xu X, Chen X
and Shi S: Acetylsalicylic acid treatment improves differentiation
and immunomodulation of SHED. J Dent Res. 94:209–218. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
12
|
Abd Rahman F, Mohd Ali J, Abdullah M, Abu
Kasim NH and Musa S: Aspirin enhances osteogenic potential of
periodontal ligament stem cells (PDLSCs) and modulates the
expression profile of growth factor-associated genes in PDLSCs. J
Periodontol. 87:837–847. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu H, Li W, Liu Y, Zhang X and Zhou Y:
Co-administration of aspirin and allogeneic adipose-derived stromal
cells attenuates bone loss in ovariectomized rats through the
anti-inflammatory and chemotactic abilities of aspirin. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 6:2002015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bauer DC, Orwoll ES, Fox KM, Vogt TM, Lane
NE, Hochberg MC, Stone K and Nevitt MC: Aspirin and NSAID use in
older women: Effect on bone mineral density and fracture risk. J
Bone Miner Res. 11:29–35. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kuznetsov SA, Krebsbach PH, Satomura K,
Kerr J, Riminucci M, Benayahu D and Robey PG: Single-colony derived
strains of human marrow stromal fibroblasts form bone after
transplantation in vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 12:1335–1347. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei M, Li K, Li B, Gao LN, Chen FM and Jin
Y: Mesenchymal stem cell characteristics of dental pulp and
periodontal ligament stem cells after in vivo transplantation.
Biomaterials. 35:6332–6343. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔC T method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Spicer PP, Kretlow JD, Young S, Jansen JA,
Kasper FK and Mikos AG: Evaluation of bone regeneration using the
rat critical size calvarial defect. Nat Protoc. 7:1918–1929. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shi S, Gronthos S, Chen S, Reddi A,
Counter CM, Robey PG and Wang CY: Bone formation by human postnatal
bone marrow stromal stem cells is enhanced by telomerase
expression. Nat Biotechnol. 20:587–591. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nuti N, Corallo C, Chan BM, Ferrari M and
Gerami-Naini B: Multipotent differentiation of human dental pulp
stem cells: A literature review. Stem Cell Rev. 12:511–523. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu M, Sun Y, Liu Y, Yuan M, Zhang Z and
Hu W: Modulation of the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells
by different concentrations of β-glycerophosphate. Molecules.
17:1219–1232. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Yao J, Yuan M, Zhang Z and Hu W:
Osteoblasts can induce dental pulp stem cells to undergo osteogenic
differentiation. Cytotechnology. 65:223–231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Ferro F, Spelat R, Beltrami AP, Cesselli D
and Curcio F: Isolation and characterization of human dental pulp
derived stem cells by using media containing low human serum
percentage as clinical grade substitutes for bovine serum. PLoS
One. 7:e489452012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi S and Gronthos S: Perivascular niche
of postnatal mesen-chymal stem cells in human bone marrow and
dental pulp. J Bone Miner Res. 18:696–704. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gronthos S and Zannettino AC: A method to
isolate and purify human bone marrow stromal stem cells. Methods
Mol Biol. 449:45–57. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu J, He H, Tang C, Zhang G, Li Y, Wang R,
Shi J and Jin Y: Differentiation potential of STRO-1+
dental pulp stem cells changes during cell passaging. BMC Cell
Biol. 11:322010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tang J, Xiong J, Wu T, Tang Z, Ding G,
Zhang C, Wang S and Liu Y: Aspirin treatment improved mesenchymal
stem cell immunomodulatory properties via the
15d-PGJ2/PPARγ/TGF-β1 pathway. Stem Cells Dev.
23:2093–2103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Blair HC, Peng Y, Zaidi N, Adebanjo
OA, Wu XB, Wu XY, Iqbal J, Epstein S, Abe E, et al: Calcineurin
regulates bone formation by the osteoblast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:17130–17135. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wiesmann HP, Meyer U, Plate U and Höhling
HJ: Aspects of collagen mineralization in hard tissue formation.
Int Rev Cytol. 242:121–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Graziano A, D'Aquino R, Laino G and
Papaccio G: Dental pulp stem cells: A promising tool for bone
regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 4:21–26. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Morad G, Kheiri L and Khojasteh A: Dental
pulp stem cells for in vivo bone regeneration: A systematic review
of literature. Arch Oral Biol. 58:1818–1827. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sculean A, Chiantella GC, Windisch P, Gera
I and Reich E: Clinical evaluation of an enamel matrix protein
derivative (Emdogain) combined with a bovine-derived xenograft
(Bio-Oss) for the treatment of intrabony periodontal defects in
humans. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 22:259–267.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Valentini P and Abensur DJ: Maxillary
sinus grafting with anorganic bovine bone: A clinical report of
long-term results. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 18:556–560.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Klinge B, Alberius P, Isaksson S and
Jönsson J: Osseous reponse to implant natural bone mineral and
synthetic hydroxylapatite ceramic in the repair of experimental
skull bone defects. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 50:241–249. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jensen SS, Aaboe M, Pinholt EM,
Hjørting-Hansen E, Melsen F and Ruyter IE: Tissue reaction and
material characteristics of four bone substitutes. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Implants. 11:55–66. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Berglundh T and Lindhe J: Healing around
implants placed in bone defects treated with Bio-Oss. An
experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 8:117–124.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Piattelli M, Favero GA, Scarano A, Orsini
G and Piattelli A: Bone reactions to anorganic bovine bone
(Bio-Oss) used in sinus augmentation procedures: A histologic
long-term report of 20 cases in humans. Int J Oral Maxillofac
Implants. 14:835–840. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cowan CM, Shi YY, Aalami OO, Chou YF, Mari
C, Thomas R, Quarto N, Contag CH, Wu B and Longaker MT:
Adipose-derived adult stromal cells heal critical-size mouse
calvarial defects. Nat Biotechnol. 22:560–567. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|