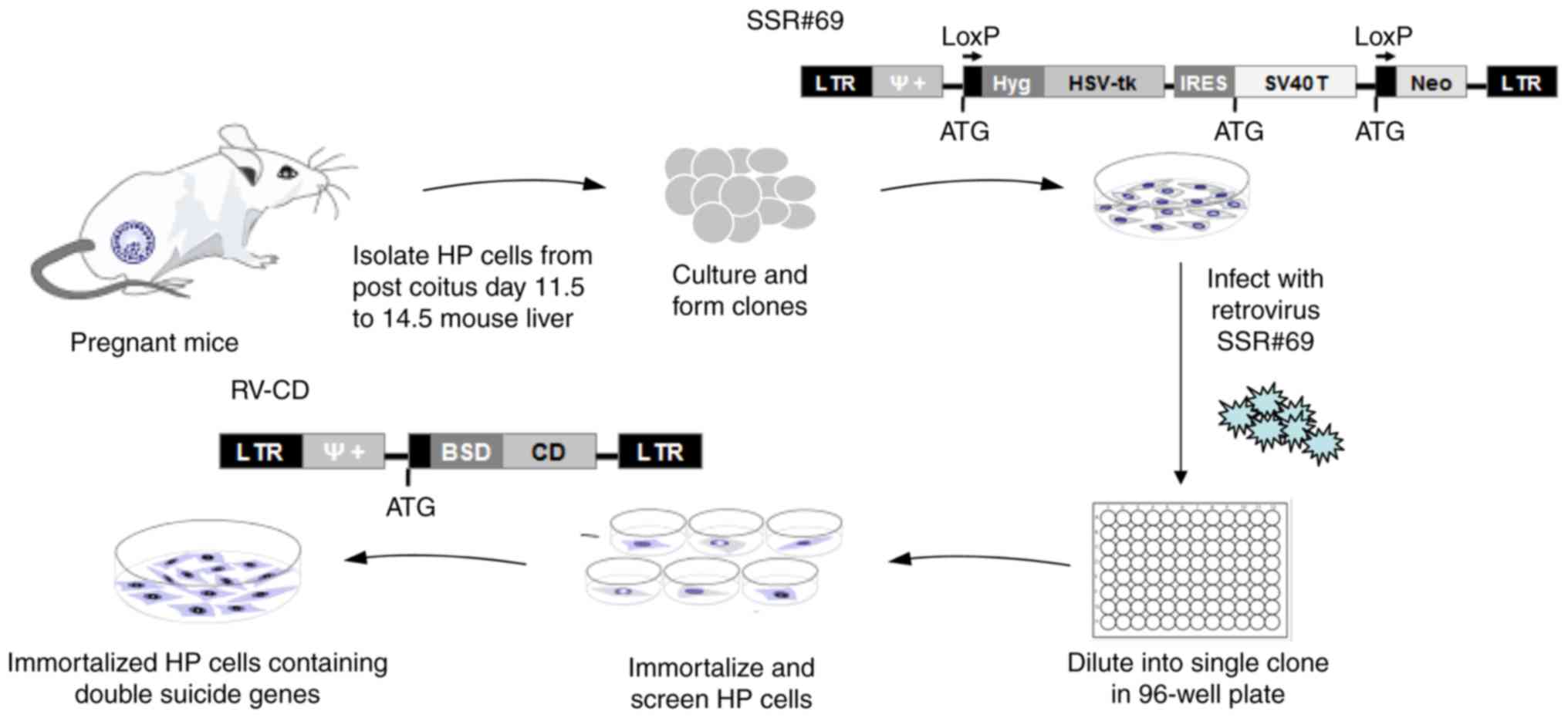
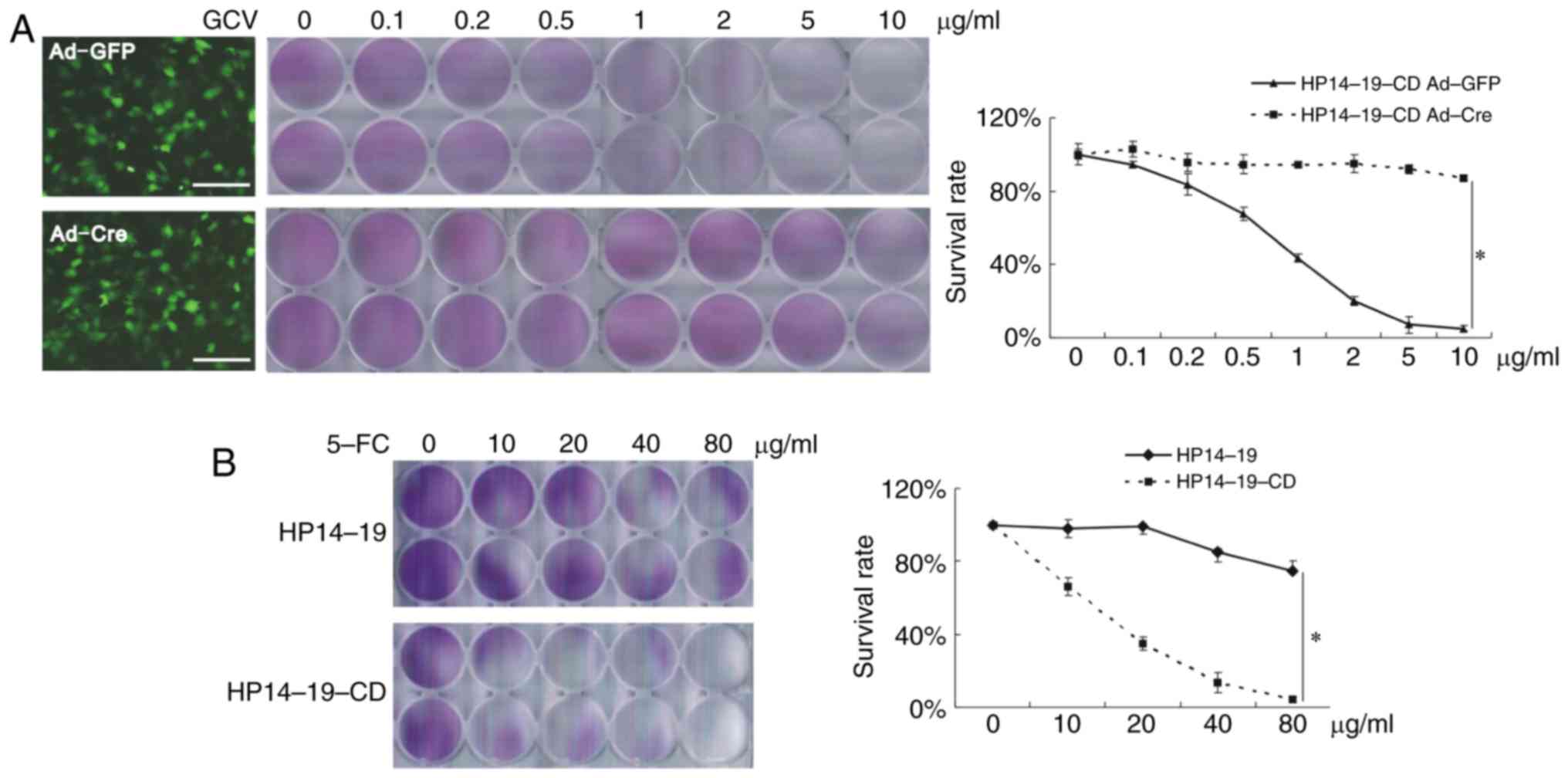
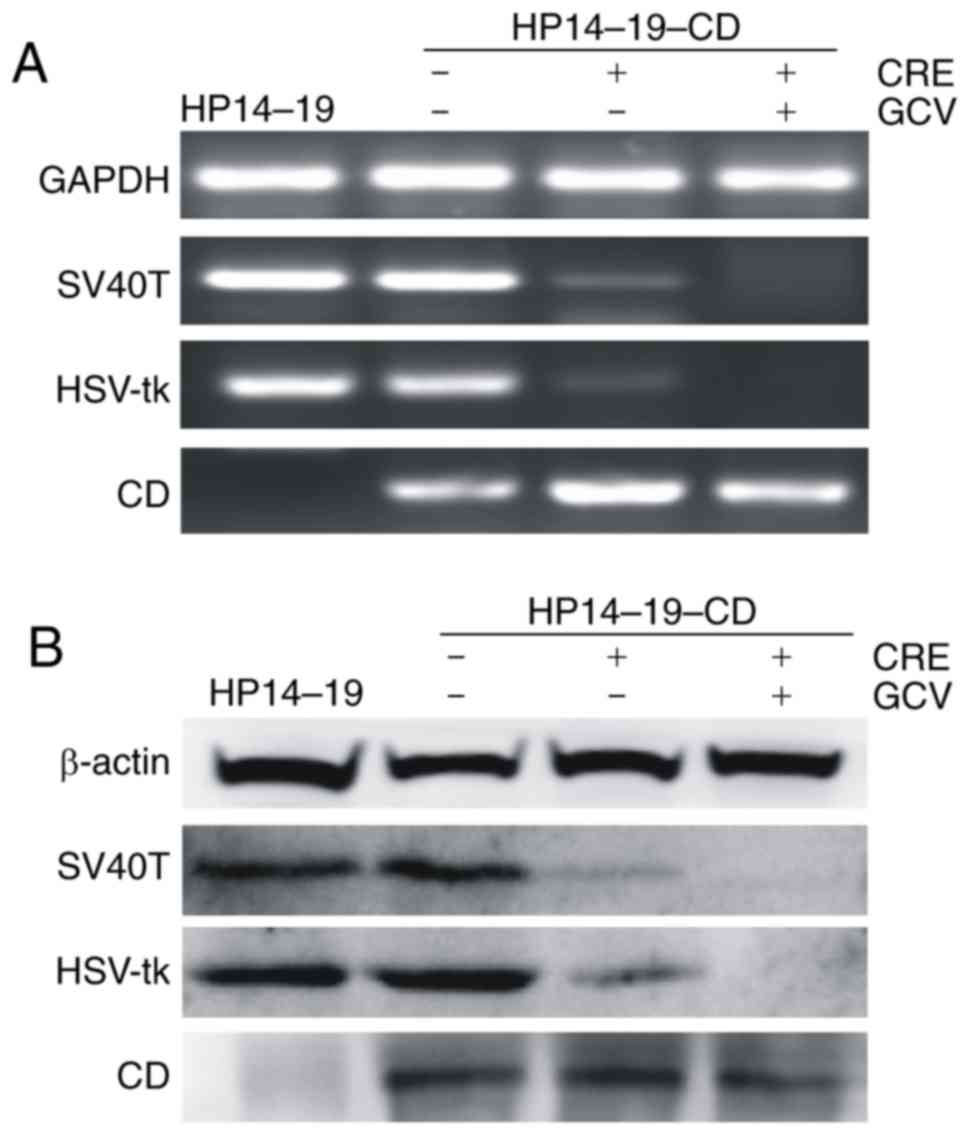
|
1
|
Bunchorntavakul C and Reddy KR: Acute
Liver Failure. Clin Liver Dis. 21:769–792. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jiang W, Li J, Guo Q, Sun J, Chen C and
Shen Z: Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Drug
Discov Ther. 9:331–334. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Al MI, Abaalkhail FA, Bahili HA, Abdo AH,
Elsiesy HA, Al MS, El Sheikh YM, Hegab BS, Kamel YM, AlGoufi TT, et
al: Liver transplantation at KFSHRC: Achievement and challenges.
Ann Saudi Med. 34:103–106. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pan XP and Li LJ: Advances in cell sources
of hepatocytes for bioartificial liver. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 11:594–605. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nibourg GA, Chamuleau RA, van der Hoeven
TV, Maas MA, Ruiter AF, Lamers WH, Oude Elferink RP, van Gulik TM
and Hoekstra R: Liver progenitor cell line HepaRG differentiated in
a bioartificial liver effectively supplies liver support to rats
with acute liver failure. PLoS One. 7:e387782012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sakiyama R, Blau BJ and Miki T: Clinical
translation of bioartificial liver support systems with human
pluripotent stem cell-derived hepatic cells. World J Gastroenterol.
23:1974–1979. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nguyen TH, Mai G, Villiger P, Oberholzer
J, Salmon P, Morel P, Bühler L and Trono D: Treatment of
acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in the mouse with
conditionally immortalized human hepatocytes. J Hepatol.
43:1031–1037. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Meng FY, Liu L, Yang FH, Li CY, Liu J and
Zhou P: Reversible immortalization of human hepatocytes mediated by
retroviral transfer and site-specific recombination. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:13119–13126. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chendeb M, Schneider R, Davidson I and
Fadloun A: Selective elimination of long Interspersed element-1
expressing tumour cells by targeted expression of the HSV-TK
suicide gene. Oncotarget. 8:38239–38250. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chai LP, Wang ZF, Liang WY, Chen L, Chen
D, Wang AX and Zhang ZQ: In vitro and in vivo effect of 5-FC
combined gene therapy with TNF-α and CD suicide gene on human
laryngeal carcinoma cell line Hep-2. PLoS One. 8:e611362013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bi Y, He Y, Huang J, Su Y, Zhu GH, Wang Y,
Qiao M, Zhang BQ, Zhang H, Wang Z, et al: Functional
characteristics of reversibly immortalized hepatic progenitor cells
derived from mouse embryonic liver. Cell Physiol Biochem.
34:1318–1338. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Westerman KA and Leboulch P: Reversible
immortalization of mammalian cells mediated by retroviral transfer
and site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
93:8971–8976. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ezzat T, Dhar DK, Malago M and Olde Damink
SW: Dynamic tracking of stem cells in an acute liver failure model.
World J Gastroenterol. 18:507–516. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hu G, Xu JJ, Deng ZH, Feng J and Jin Y:
Supernatant of bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells induces
peripheral blood mononuclear cells possessing mesenchymal features.
Int J Biol Sci. 7:364–375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wei L, Fraser JL, Lu ZY, Hu X and Yu SP:
Transplantation of hypoxia preconditioned bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells enhances angiogenesis and neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 46:635–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao LF, Pan XP and Li LJ: Key challenges
to the development of extracorporeal bioartificial liver support
systems. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 11:243–249. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
van Wenum M, Adam AA, Hakvoort TB,
Hendriks EJ, Shevchenko V, van Gulik TM, Chamuleau RA and Hoekstra
R: Selecting cells for bioartificial liver devices and the
importance of a 3D culture environment: A functional comparison
between the HepaRG and C3A cell lines. Int J Biol Sci. 12:964–978.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu H, You S, Rong Y, Wu Y, Zhu B, Wan Z,
Liu W, Mao P and Xin S: Newly established human liver cell line: A
potential cell source for the bioartificial liver in the future.
Hum Cell. 26:155–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yu Y, Wang X and Nyberg SL: Potential and
challenges of induced pluripotent stem cells in liver diseases
treatment. J Clin Med. 3:997–1017. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nibourg GA, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM and
Hoekstra R: Proliferative human cell sources applied as
biocomponent in bioartificial livers: A review. Expert Opin Biol
Ther. 12:905–921. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Wenum M, Chamuleau RA, van Gulik TM,
Siliakus A, Seppen J and Hoekstra R: Bioartificial livers in vitro
and in vivo: Tailoring biocomponents to the expanding variety of
applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 14:1745–1760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ordovás L, Park Y and Verfaillie CM: Stem
cells and liver engineering. Biotechnol Adv. 31:1094–1107. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fiers W, Contreras R, Haegemann G, Rogiers
R, Van de Voorde A, Van Heuverswyn H, Van Herreweghe J, Volckaert G
and Ysebaert M: Complete nucleotide sequence of SV40 DNA. Nature.
273:113–120. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tevethia MJ and Ozer HL: SV40-mediated
immortalization. Methods Mol Biol. 165:185–199. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shay JW, Pereira-Smith OM and Wright WE: A
role for both RB and p53 in the regulation of human cellular
senescence. Exp Cell Res. 196:33–39. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shahid JM, Iwamuro M, Sasamoto H, Kubota
Y, Seita M, Kawamoto H, Nakaji S, Noguchi H, Yamamoto K and
Kobayashi N: Establishment of an immortalized porcine liver cell
line JSNK-1 with retroviral transduction of SV40T. Cell Transplant.
19:849–856. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Prives C: The replication functions of
SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 61:735–738.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsumura T, Takesue M, Westerman KA,
Okitsu T, Sakaguchi M, Fukazawa T, Totsugawa T, Noguchi H, Yamamoto
S, Stolz DB, et al: Establishment of an immortalized human-liver
endothelial cell line with SV40T and hTERT. Transplantation.
77:1357–1365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramboer E, De Craene B, De Kock J,
Vanhaecke T, Berx G, Rogiers V and Vinken M: Strategies for
immortalization of primary hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 61:925–943.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pan X, Wang Y, Yu X, Li J, Zhou N, Du W,
Zhang Y, Cao H, Zhu D, Chen Y and Li L: Establishment and
characterization of an immortalized human hepatic stellate cell
line for applications in co-culturing with immortalized human
hepatocytes. Int J Med Sci. 12:248–255. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kobayashi N, Noguchi H, Westerman KA,
Watanabe T, Matsumura T, Totsugawa T, Fujiwara T, Leboulch P and
Tanaka N: Cre/loxP-based reversible immortalization of human
hepatocytes. Cell Transplant. 10:383–386. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kobayashi N, Noguchi H, Totsugawa T,
Watanabe T, Matsumura T, Fujiwara T, Miyazaki M, Fukaya K, Namba M
and Tanaka N: Insertion of a suicide gene into an immortalized
human hepatocyte cell line. Cell Transplant. 10:373–376.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zeng Y, Sun S, Zhang J,
Zhang B, Zhu M, Ouyang R, Ma B, Ye M, et al: Knockout of 4.1B
triggers malignant transformation in SV40T-immortalized mouse
embryo fibroblast cells. Mol Carcinog. 56:538–549. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tátrai P, Szepesi Á, Matula Z, Szigeti A,
Buchan G, Mádi A, Uher F and Német K: Combined introduction of
Bmi-1 and hTERT immortalizes human adipose tissue-derived stromal
cells with low risk of transformation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
422:28–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Van De Klundert FA and Bloemendal H: SV40
large T antigen-induced inhibition of terminal differentiation of
primary skeletal muscle cells is associated with a block in the
expression of MyoD and myogenin. Mol Biol Rep. 20:143–148.
1994–1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Li M, Chen Y, Bi Y, Jiang W, Luo Q, He Y,
Su Y, Liu X, Cui J, Zhang W, et al: Establishment and
characterization of the reversibly immortalized mouse fetal heart
progenitors. Int J Med Sci. 10:1035–1046. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|