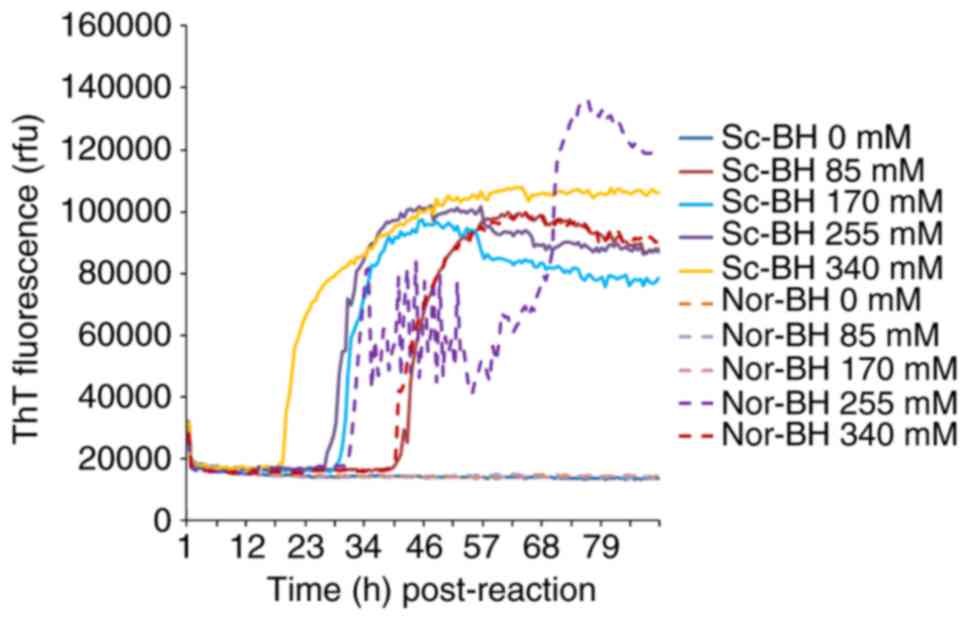
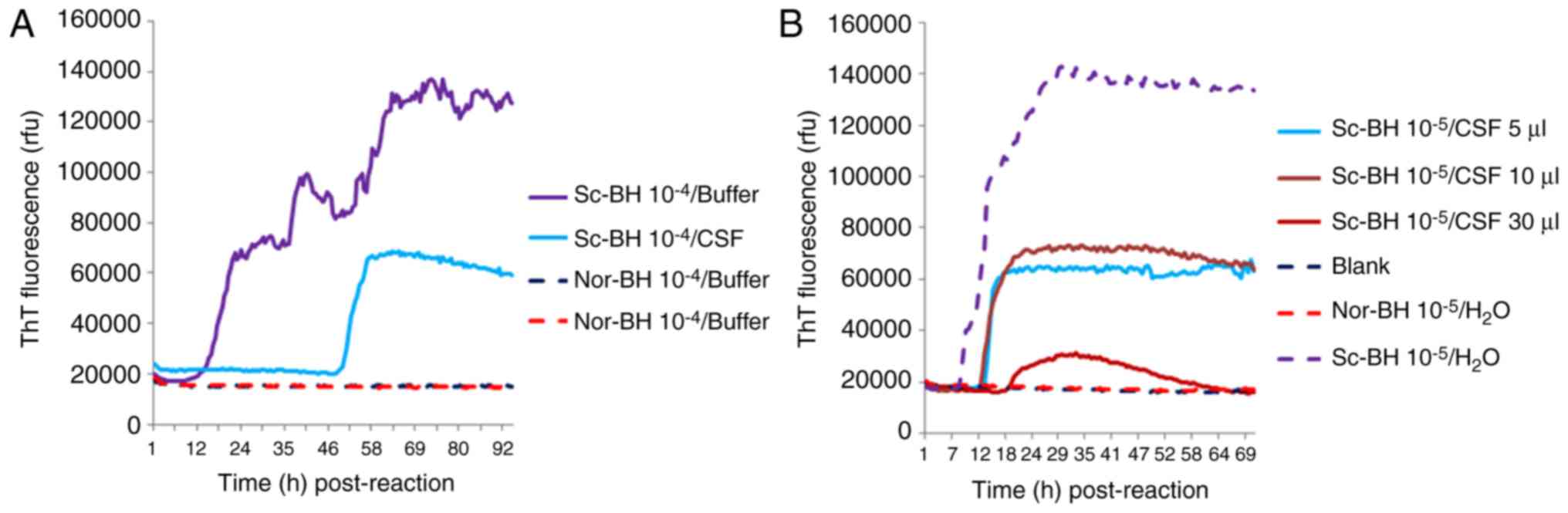
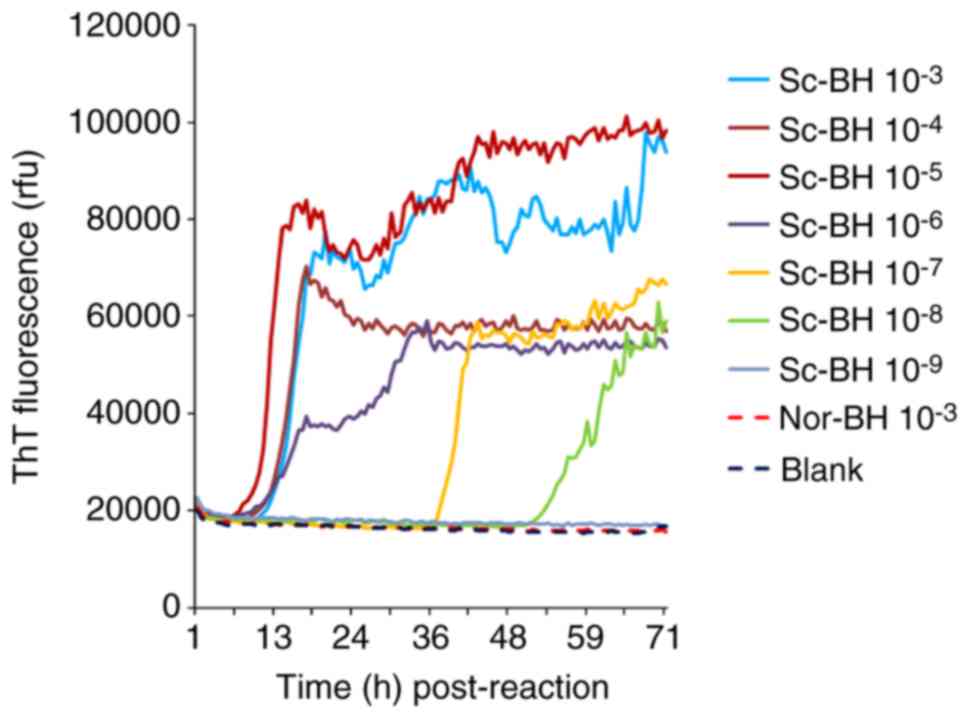
|
1
|
Prusiner SB: Prions Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:13363–13383. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ladogana A, Puopolo M, Croes EA, Budka H,
Jarius C, Collins S, Klug GM, Sutcliffe T, Giulivi A, Alperovitch
A, et al: Mortality from Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and related
disorders in Europe, Australia, and Canada. Neurology.
64:1586–1591. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen C and Dong XP: Epidemiological
characteristics of human prion diseases. Infect Dis Poverty.
5:472016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Budka H, Aguzzi A, Brown P, Brucher JM,
Bugiani O, Gullotta F, Haltia M, Hauw JJ, Ironside JW, Jellinger K,
et al: Neuropathological diagnostic criteria for Creutzfeldt-Jakob
disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion
diseases). Brain Pathol. 5:459–466. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Borchelt DR, Scott M, Taraboulos A, Stahl
N and Prusiner SB: Scrapie and cellular prion proteins differ in
their kinetics of synthesis and topology in cultured cells. J Cell
Biol. 110:743–752. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prusiner SB: Novel properties and biology
of scrapie prions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 172:233–257.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Manix M, Kalakoti P, Henry M, Thakur J,
Menger R, Guthikonda B and Nanda A: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease:
Updated diagnostic criteria, treatment algorithm, and the utility
of brain biopsy. Neurosurg Focus. 39:E22015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zerr I, Kallenberg K, Summers DM, Romero
C, Taratuto A, Heinemann U, Breithaupt M, Varges D, Meissner B,
Ladogana A, et al: Updated clinical diagnostic criteria for
sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain. 132:2659–2668. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi Q, Zhou W, Chen C, Gao C, Xiao K, Wang
J, Zhang BY, Wang Y, Zhang F and Dong XP: Quality evaluation for
the surveillance system of human prion diseases in China based on
the data from 2010 to 2016. Prion. 10:484–491. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hsich G, Kenney K, Gibbs CJ, Lee KH and
Harrington MG: The 14-3-3 brain protein in cerebrospinal fluid as a
marker for transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. N Engl J Med.
335:924–930. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sanchez-Juan P, Sanchez-Valle R, Green A,
Ladogana A, Cuadrado-Corrales N, Mitrová E, Stoeck K, Sklaviadis T,
Kulczycki J, Hess K, et al: Influence of timing on CSF tests value
for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease diagnosis. J Neurol. 254:901–906.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Otto M, Wiltfang J, Cepek L, Neumann M,
Mollenhauer B, Steinacker P, Ciesielczyk B, Schulz-Schaeffer W,
Kretzschmar HA and Poser S: Tau protein and 14-3-3 protein in the
differential diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology.
58:192–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beaudry P, Cohen P, Brandel JP,
Delasnerie-Lauprêtre N, Richard S, Launay JM and Laplanche JL:
14-3-3 protein, neuron-specific enolase, and S-100 protein in
cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.
Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 10:40–46. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Collins S, Boyd A, Fletcher A, Gonzales M,
McLean CA, Byron K and Masters CL: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease:
Diagnostic utility of 14-3-3 protein immunodetection in
cerebrospinal fluid. J Clin Neurosci. 7:203–208. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Q, Gao C, Zhou W, Zhang BY, Chen JM,
Tian C, Jiang HY, Han J, Xiang NJ, Wang XF, et al: Surveillance for
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in China from 2006 to 2007. BMC Public
Health. 8:3602008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McGuire LI, Peden AH, Orru CD, Wilham JM,
Appleford NE, Mallinson G, Andrews M, Head MW, Caughey B, Will RG,
et al: Real time quaking-induced conversion analysis of
cerebrospinal fluid in sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann
Neurol. 72:278–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Atarashi R, Satoh K, Sano K, Fuse T,
Yamaguchi N, Ishibashi D, Matsubara T, Nakagaki T, Yamanaka H,
Shirabe S, et al: Ultrasensitive human prion detection in
cerebrospinal fluid by real-time quaking-induced conversion. Nat
Med. 17:175–178. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilham JM, Orru CD, Bessen RA, Atarashi R,
Sano K, Race B, Meade-White KD, Taubner LM, Timmes A and Caughey B:
Rapid end-point quantitation of prion seeding activity with
sensitivity comparable to bioassays. PLoS Pathog. 6:e10012172010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang GR, Shi S, Gao C, Zhang BY, Tian C,
Dong CF, Zhou RM, Li XL, Chen C and Dong XP: Alternations of tau
protein and its phosphorylated profiles in the experimental
hamsters infected by scrapie agents 263K and 139A. Bing Du Xue Bao.
25:202–207. 2009.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang BY, Tian C, Han J, Gao C, Shi Q,
Chen JM, Jiang HY, Zhou W and Dong XP: Establishment of a stable
PrP(Sc) panel from brain tissues of experimental hamsters with
scrapie strain 263K. Biomed Environ Sci. 22:151–156. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Chen L, Zhang BY, Han J, Xiao XL,
Tian HY, Li BL, Gao C, Gao JM, Zhou XB, et al: Comparison study on
clinical and neuropathological characteristics of hamsters
inoculated with scrapie strain 263K in different challenging
pathways. Biomed Environ Sci. 17:65–78. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao JM, Gao C, Han J, Zhou XB, Xiao XL,
Zhang J, Chen L, Zhang BY, Hong T and Dong XP: Dynamic analyses of
PrP and PrP(Sc) in brain tissues of golden hamsters infected with
scrapie strain 263K revealed various PrP forms. Biomed Environ Sci.
17:8–20. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zanusso G, Monaco S, Pocchiari M and
Caughey B: Advanced tests for early and accurate diagnosis of
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 12:325–333. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ladner-Keay CL, Griffith BJ and Wishart
DS: Shaking alone induces de novo conversion of recombinant prion
proteins to beta-sheet rich oligomers and fibrils. PLoS One.
9:e987532014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yuan Z, Yang L, Chen B, Zhu T, Hassan MF,
Yin X, Zhou X and Zhao D: Protein misfolding cyclic amplification
induces the conversion of recombinant prion protein to PrP
oligomers causing neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem. 133:722–729.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Biancalana M and Koide S: Molecular
mechanism of Thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1804.1405–1412. 2010.
|
|
27
|
Orru CD, Wilham JM, Vascellari S, Hughson
AG and Caughey B: New generation QuIC assays for prion seeding
activity. Prion. 6:147–152. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|