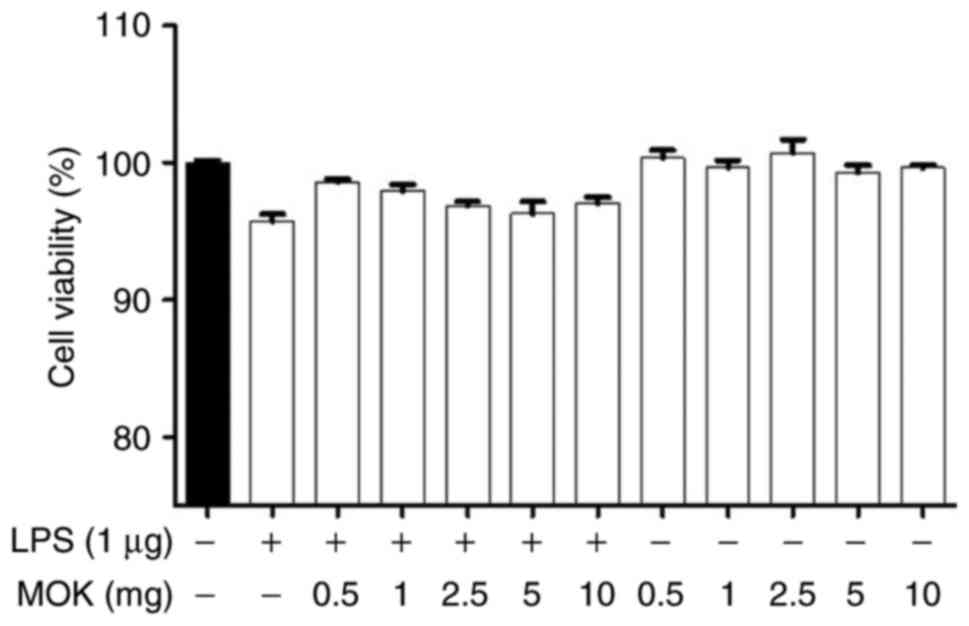
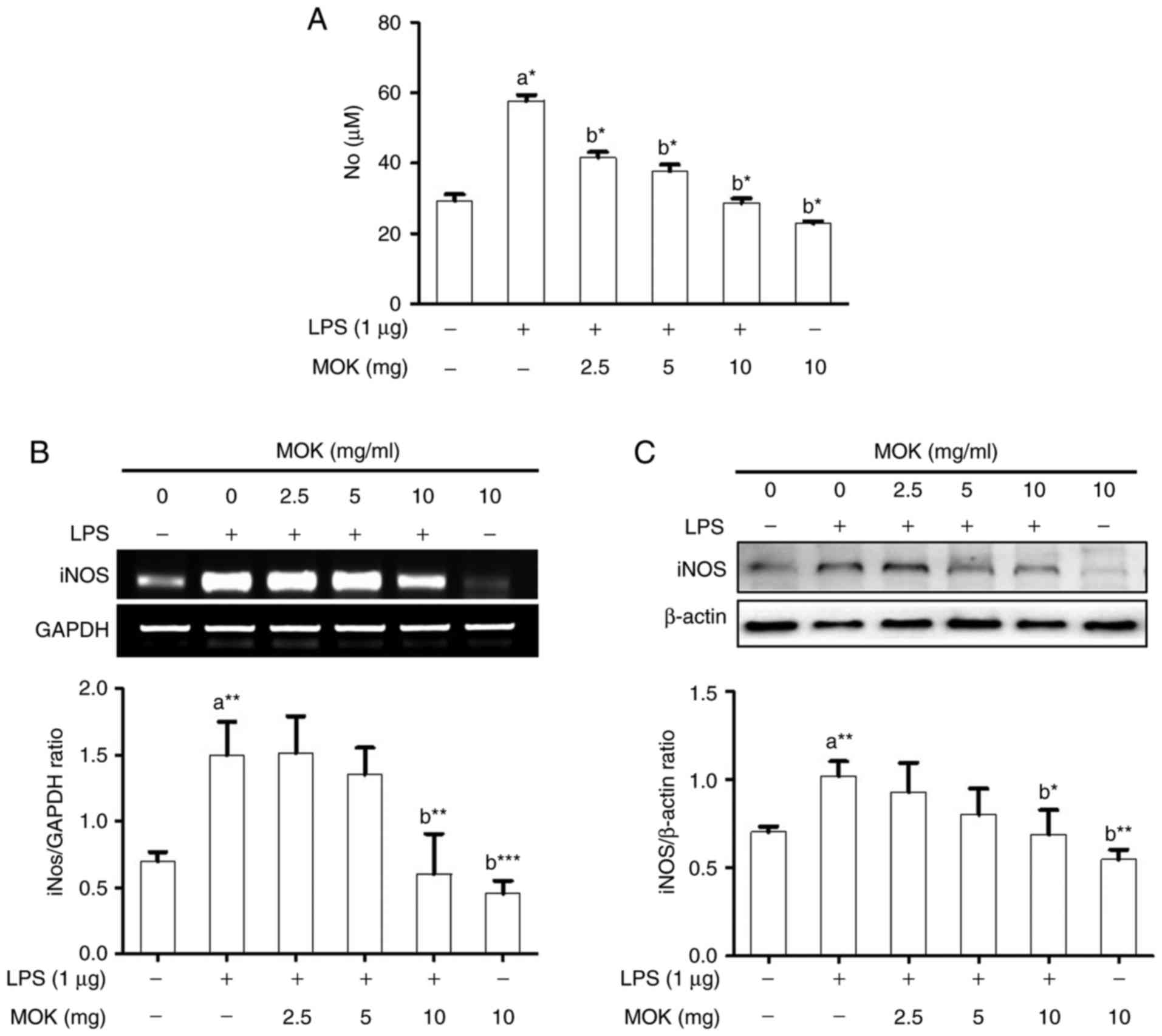
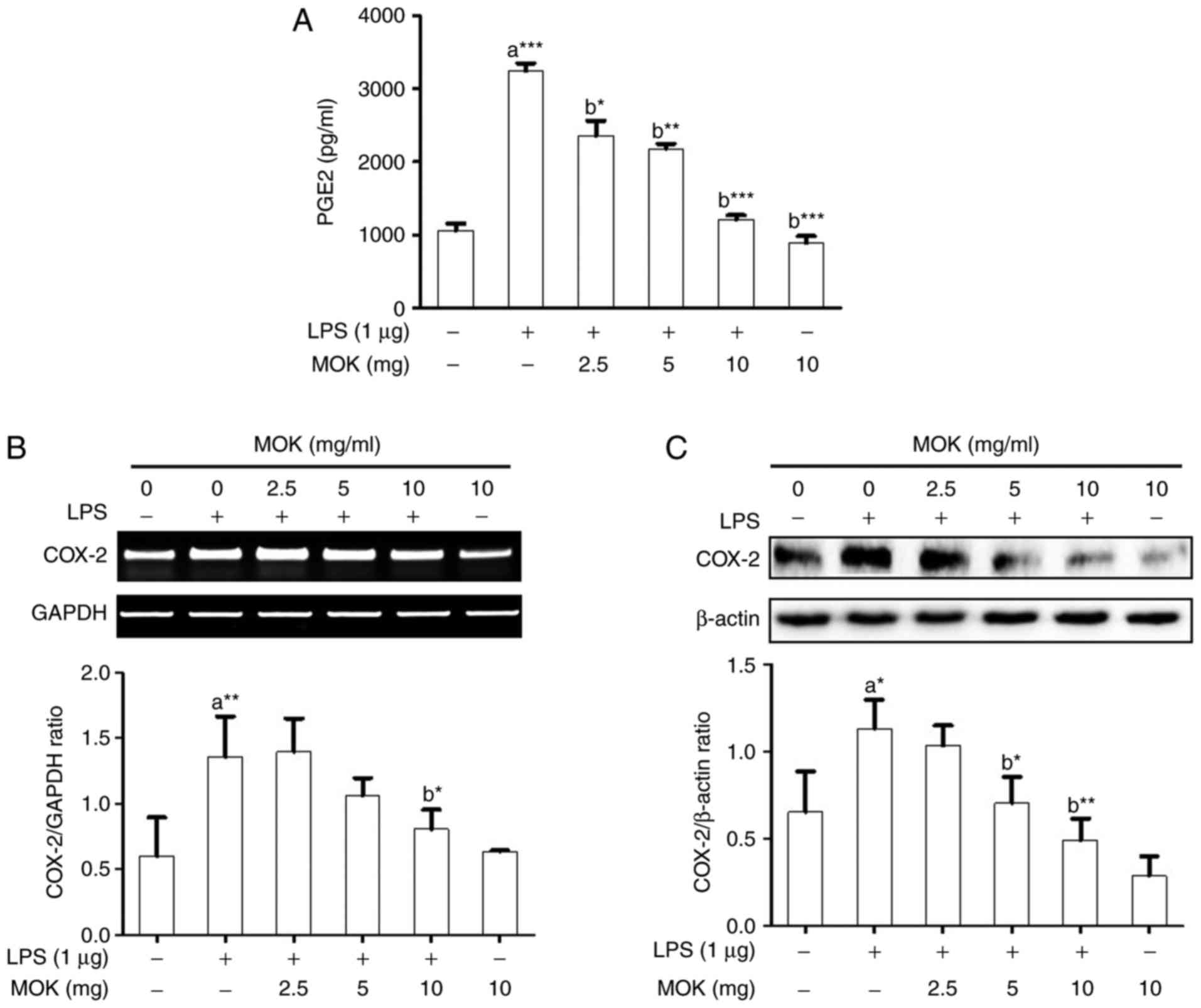
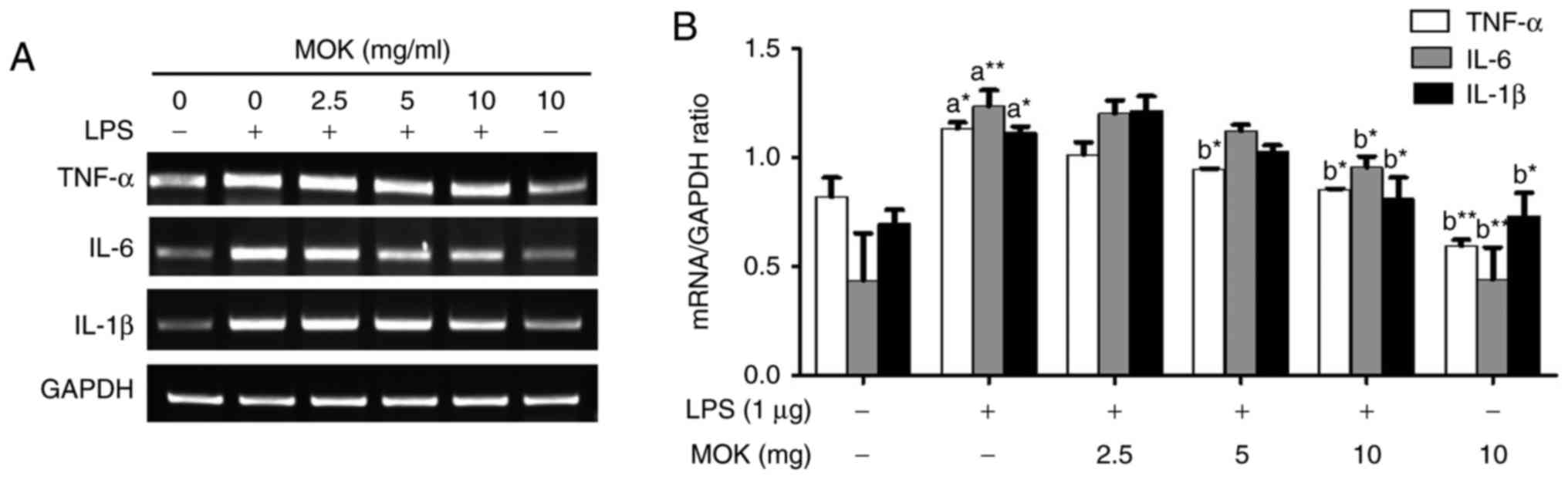
|
1
|
Liu Z, Tang L, Zou P, Zhang Y, Wang Z,
Fang Q, Jiang L, Chen G, Xu Z, Zhang H and Liang G: Synthesis and
biological evaluation of allylated and prenylated mono-carbonyl
analogs of curcumin as anti-inflammatory agents. Eur J Med Chem.
74:671–682. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Zhang L and Wang CC: Inflammatory response
of macrophages in infection. Hepastobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
13:138–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cho SY, Yang SB, Shin HS, Lee SH, Koh JS,
Kwon S, Jung WS, Moon SK, Park JM, Ko CN and Park SU:
Anti-inflammatory and immune regulatory effects of acupuncture
after craniotomy: Study protocol for a parallel-group randomized
controlled trial. Trials. 18:4812017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zijlstra FJ, van den Berg-de Lange I,
Huygen FJ and Klein J: Anti-inflammatory actions of acupuncture.
Mediators Inflamm. 12:59–69. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lisboa MR, Gondim DV, Ervolino E, Vale ML,
Frota NP, Nunes NL, Mariguela VC, Taba M Jr, Messora MR and
Furlaneto FA: Effects of electroacupuncture on experimental
periodontitis in rats. J Periodontol. 86:801–811. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McDonald JL, Cripps AW, Smith PK, Smith
CA, Xue CC and Golianu B: The anti-inflammatory effects of
acupuncture and their relevance to allergic rhinitis: A narrative
review and proposed model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013.591796:2013.
|
|
8
|
Song Q, Hu S, Wang H, Lv Y, Shi X, Sheng Z
and Sheng W: Electroacupuncturing at Zusanli point (ST36)
attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine release and organ dysfunction
by activating cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in rat with
endotoxin challenge. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med.
11:469–474. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wei Y, Dong M, Zhang H, Lv Y, Liu J, Wei
K, Luo Q, Sun J, Liu F, Xu F and Dong J: Acupuncture attenuated
inflammation and inhibited Th17 and treg activity in experimental
asthma. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015.340126:2015.
|
|
10
|
Jung C, Jung JH and Lee MS: A Clinical
Study of Immune Pharmacopuncturology. Kyungrak Medical Publishing
Co.; Chungnam: 2011, In Korean.
|
|
11
|
Hwang JH: A case report of Hwa-byeong with
MOK herbal acupuncture therapy. J Immuno-Pharmacopuncture. 2:43–55.
2013.In Korean.
|
|
12
|
Ha TD and Jung C: A case report on severe
tension-type headache treated with pharmacopuncture (Yakchim). J
Immuno-Pharmacopuncture. 5:37–45. 2016.In Korean.
|
|
13
|
Kim MJ, Kim SK, Ko SJ and Park JW: A case
study of MOK and V Yakchim on functional dyspepsia. J
Immuno-Pharmacopuncture. 3:41–49. 2014.In Korean.
|
|
14
|
Kim HJ, Gwan R, Han JW, Jung C and Park
KH: Analysis of physioactivities on MOK Yakchim. J
Immuno-Pharmacopuncture. 2:17–25. 2013.In Korean.
|
|
15
|
Hwang JH, Kang SY, Kang AN, Jung HW, Jung
C, Jeong JH and Park YK: MOK, a pharmacopuncture medicine,
regulates thyroid dysfunction in L-thyroxin-induced hyperthyroidism
in rats through the regulation of oxidation and the TRPV1 ion
channel. BMC Complement Altern Med. 17:5352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang JH, Jung HW, Kang SY, Kang AN, Ma
JN, Meng XL, Hwang MS and Park YK: Therapeutic effects of
acupuncture with MOK, a polyherbal medicine, on PTU-induced
hypothyroidism in rats. Exp Ther Med. 16:310–320. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hwang JH, Hwang MS and Park YK: MOK, a
pharmacopuncture medicine, reduces inflammatory response through
inhibiting the proinflammatory cytokine production in
LPS-stimulated mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Acupunct Res.
34:11–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Raschke WC, Baird S, RalpH P and Nakoinz
I: Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia
virus. Cell. 15:261–267. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Xiong H and Liu L: Effects of
taraxasterol on inflammatory responses in
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Ethnopharmacol.
141:206–211. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Choi HS, Seo HS, Kim SR, Choi YK, Shin YC
and Ko SG: Anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative effect of
herbal medicines (APR) in RAW264.7 cells. Mol Med Rep. 9:1569–1574.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li T, Gao D, Du M, Cheng X and Mao X:
Casein glycomacropeptide hydrolysates inhibit PGE2
production and COX2 expression in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7
macrophage cells via Akt mediated NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Food
Funct. 9:2524–2532. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yang X, Kang MC, Li Y, Kim EA, Kang SM and
Jeon YJ: Anti-inflammatory activity of questinol isolated from
marine-derived fungus Eurotium amstelodami in
lipopoly-saccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. J Microbiol
Biotechnol. 24:1346–1353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim HJ, Tsoyi K, Heo JM, Kang YJ, Park MK,
Lee YS, Lee JH, Seo HG, Choi HS and Chang KC: Regulation of
lipopolysaccha-ride-induced inducible nitric-oxide synthase
expression through the nuclear factor-κB pathway and
interferon-β/tyrosine kinase 2/Janus tyrosine kinase 2-signal
transducer and activator of transcription-1 signaling cascades by
2-naphthylethyl-6, 7-dihydroxy-1, 2, 3, 4-tetrahydroisoquinoline
(THI 53), a new synthetic isoquino-line alkaloid. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 320:782–789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gong HM, Jun SA, Lee HJ and Kim JS: A case
report of Herpes zoster patient treated with additional CS, V
pharmacopuncture. J Immuno-Pharmacopuncture. 1:27–36. 2016.
|
|
25
|
De D, Datta Chakraborty P, Mitra J, Sharma
K, Mandal S, Das A, Chakrabarti S and Bhattacharyya D:
Ubiquitin-like protein from human placental extract exhibits
collagenase activity. PLoS One. 8:e595852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng Y, Siu K, Wang N, Ng KM, Tsao SW,
Nagamatsu T and Tong Y: Bear bile: Dilemma of traditional medicinal
use and animal protection. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 5:22009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang SY, Park JW, Bu Y, Kang JO and Kim J:
Protective effects of hominis placenta hydrolysates on radiation
enteropathy in mice. Nat Prod Res. 25:1988–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li X, Xu Y, Zhang C, Deng L, Chang M, Yu Z
and Liu D: Protective effect of calculus bovis sativus on dextran
sulphate sodium-induced uicerative colitis in mice. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2015.469506:2015.
|
|
29
|
The National College of Oriental Medicine
Herbology Classroom: Herbology: Youngrimsa, Seoul. 2016.In
Korean.
|
|
30
|
Park SY, Phark S, Lee M, Lim JY and Sul D:
Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory activities of placental
extracts in benzo[a] pyrene-exposed rats. Placenta. 31:873–879.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park JY, Lee J, Jeong M, Min S, Kim SY,
Lee H, Lim Y and Park HJ: Effect of Hominis Placenta on cutaneous
wound healing in normal and diabetic mice. Nutr Res Pract.
8:404–409. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thevis M, Schänzer W, Geyer H, Thieme D,
Grosse J, Rautenberg C, Flenker U, Beuck S, Thomas A, Holland R and
Dvorak J: Traditional Chinese medicine and sports drug testing:
Identification of natural steroid administration in doping control
urine samples resulting from musk (pod) extracts. Br J Sports Med.
47:109–114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Okin D and Medzhitov R: Evolution of
inflammatory diseases. Curr Biol. 22:R733–R740. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Monaco C, Andreakos E, Kiriakidis S,
Feldmann M and Paleolog E: T-cell-mediated signalling in immune,
inflammatory and angiogenic processes: the cascade of events
leading to inflammatory diseases. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm
Allergy. 3:35–42. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yamamoto Y and Gaynor RB: IkappaB kinases:
Key regulators of the NF-kappaB pathway. Trends Biochem Sci.
29:72–79. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Adib-Conquy M, Scott-Algara D, Cavaillon
JM and Souza- Fonseca-Guimaraes F: TLR-mediated activation of NK
cells and their role in bacterial/viral immune responses in
mammals. Immunol Cell Biol. 92:256–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Korhonen R, Lahti A, Kankaanranta H and
Moilanen E: Nitric oxide production and signaling in inflammation.
Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:471–479. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sweet MJ and Hume DA: Endotoxin signal
transduction in macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 60:8–26. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Davies KJ: Oxidative stress: The paradox
of aerobic life. Biochem Soc Symp. 61:1–31. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Thalhamer T, McGrath MA and Harnett MM:
MAPKs and their relevance to arthritis and inflammation. Rheumatol
(Oxford). 47:409–414. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chang LY, Wan HC, Lai YL, Chou IC, Chen YT
and Hung SL: Areca nut extracts increased the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2, prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-1α in
human immune cells via oxidative stress. Arch Oral Biol.
58:1523–1531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Satoh M, Minami Y, Takahashi Y and
Nakamura M: Immune modulation: Role of theinflammatory cytokine
cascade in the failing human heart. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 5:69–74.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang L, Xu Ml, Liu J, Wang Y, Hu JH and
Wang MH: Sonchus asper extract inhibits 7 macrophages. Nutr Res
Pract. 9:579–585. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jin Y, Yang J, Lin L, Lin Y and Zheng C:
The attenuation of scutellariae radix extract on oxidative stress
for colon injury in lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 Cell and
2,4,6-trinitro-benzene sulfonic acid-induced ulcerative colitis
rats. Pharmacogn Mag. 12:153–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Broom OJ, Widjaya B, Troelsen J, Olsen J
and Nielsen OH: Mitogen activated protein kinases: A role in
inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 158:272–280. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shan J, Fu J, Zhao Z, Kong X, Huang H, Luo
L and Yin Z: Chlorogenic acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression in RAW264.7 cells through suppressing
NF-kappaB and JNK/AP-1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol.
9:1042–1048. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|