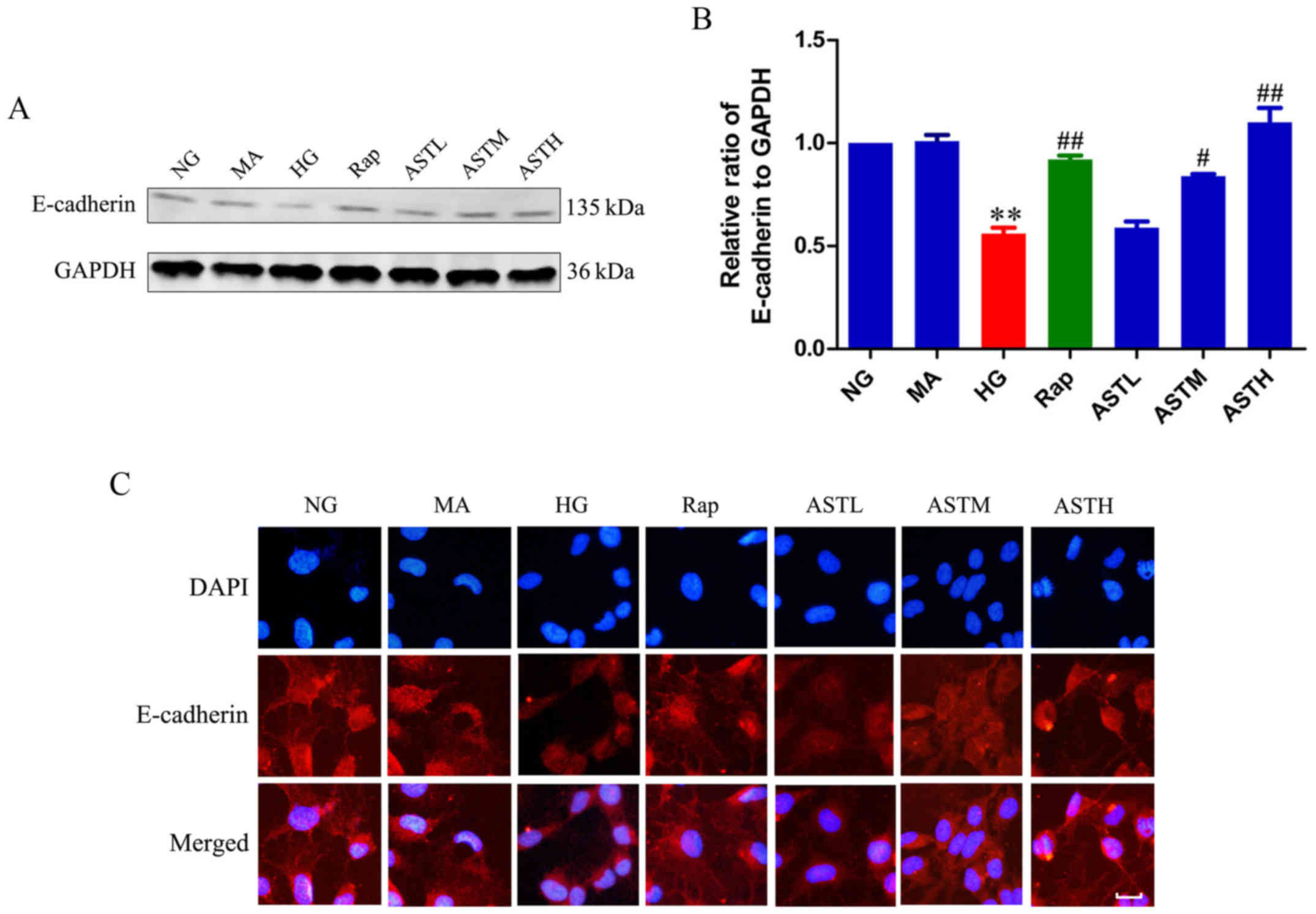
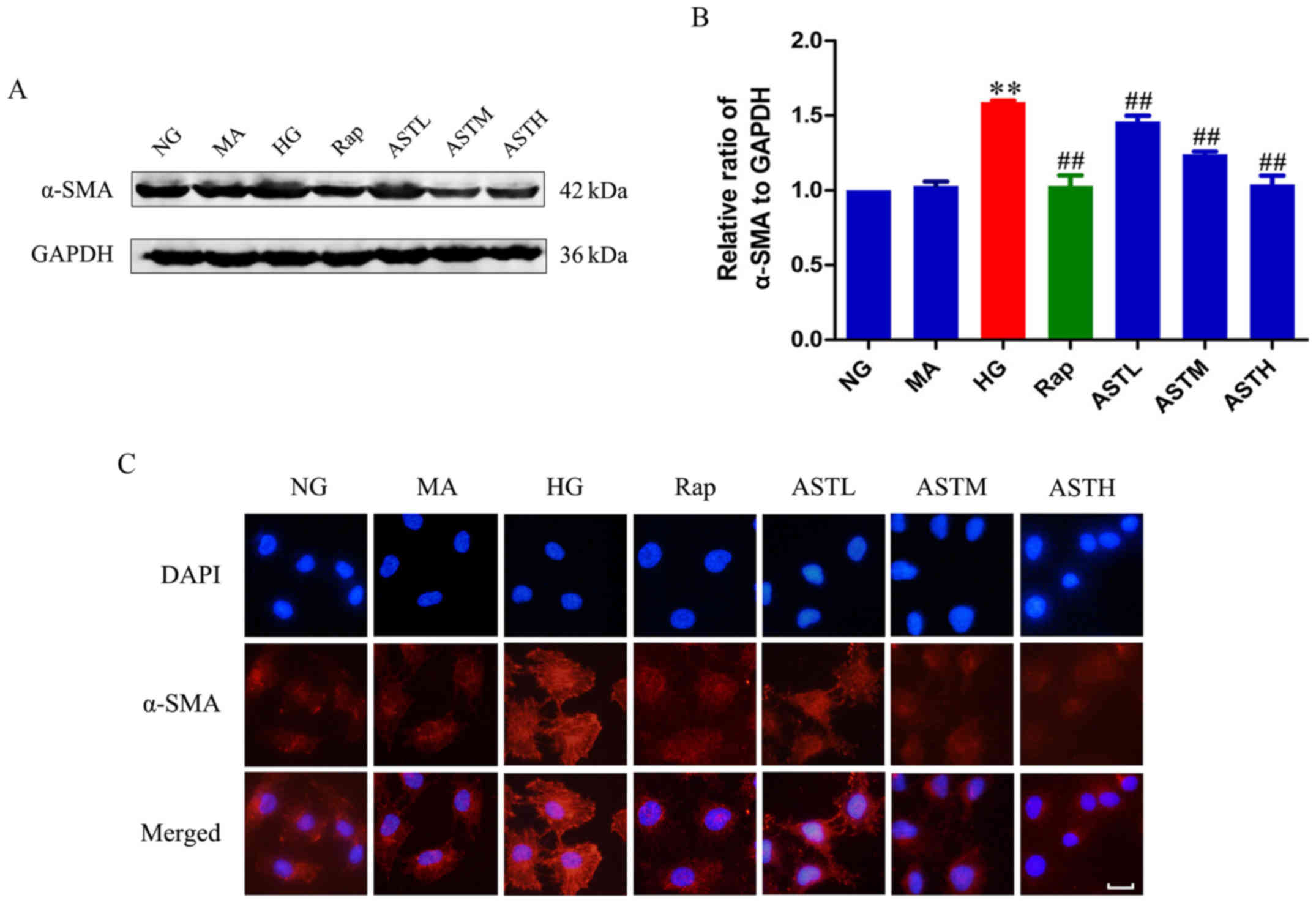
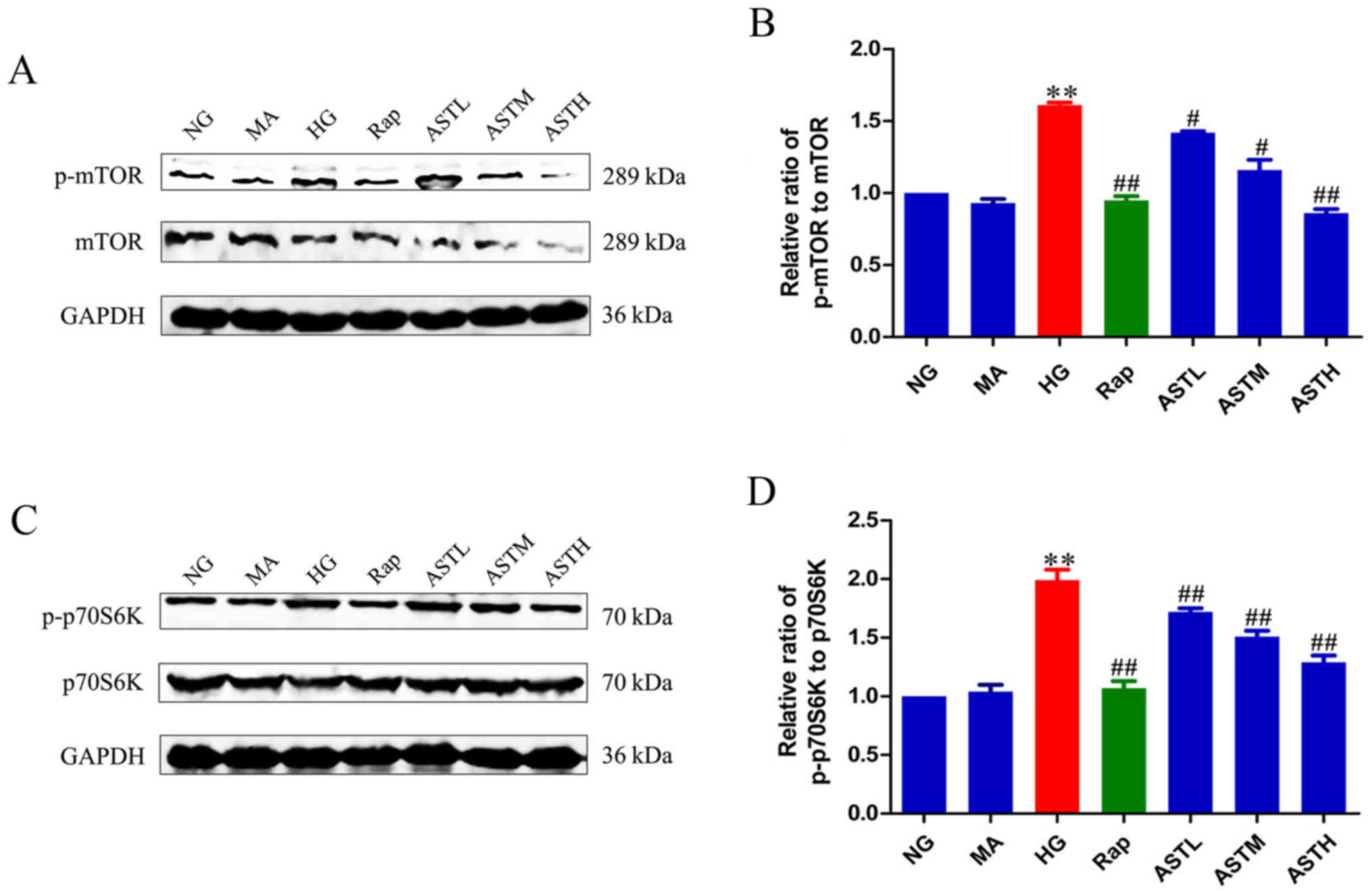
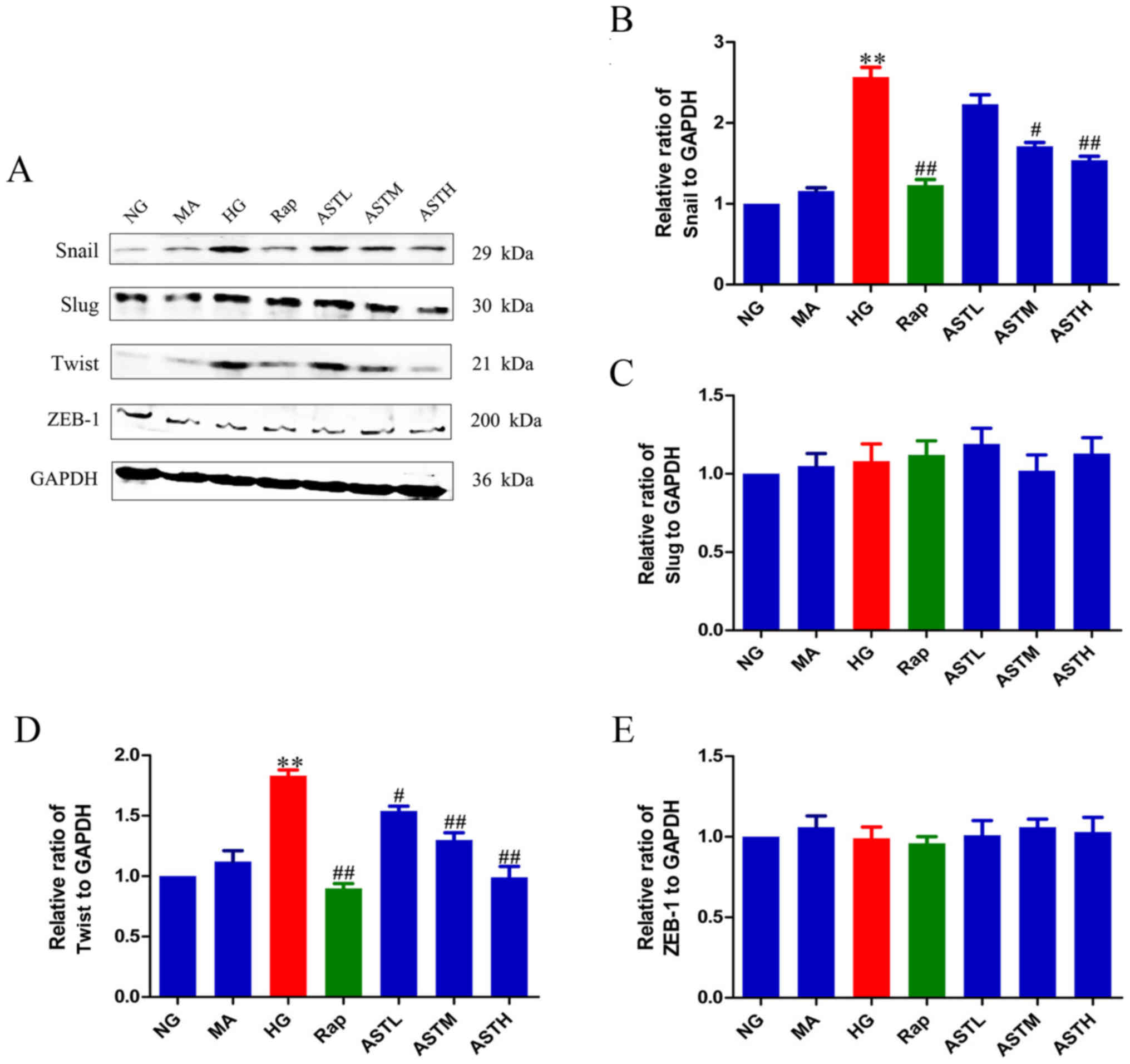
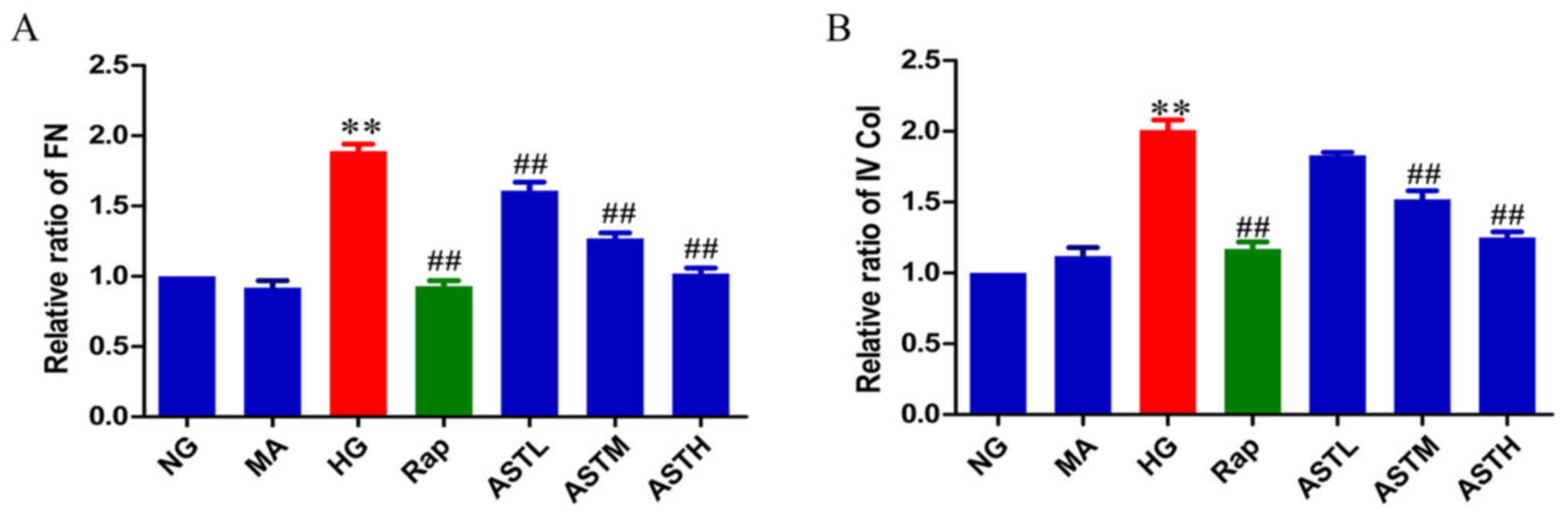
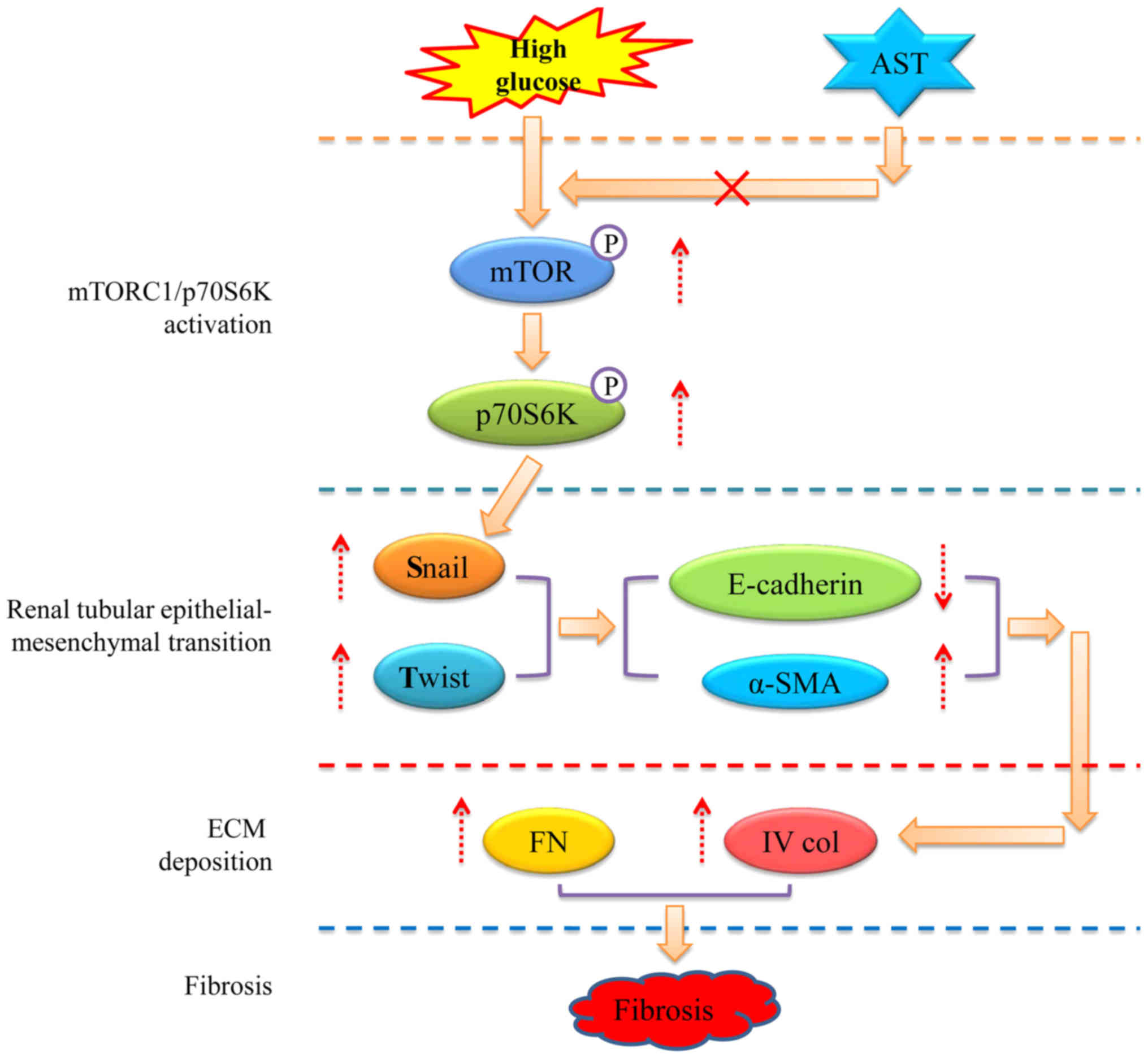
|
1
|
Dixit P, Ghaskadbi S, Mohan H and
Devasagayam TP: Antioxidant properties of germinated fenugreek
seeds. Phytother Res. 19:977–983. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roberts KT: The potential of fenugreek
(Trigonella foenum-graecum) as a functional food and nutraceutical
and its effects on glycemia and lipidemia. J Med Food.
14:1485–1489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kashihara N, Haruna Y, Kondeti VK and
Kanwar YS: Oxidative stress in diabetic nephropathy. Curr Med Chem.
17:4256–4269. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Collins AJ, Foley RN, Herzog C, Chavers B,
Gilbertson D, Ishani A, Kasiske B, Liu J, Mau LW, McBean M, et al:
US Renal Data System 2010 Annual Data Report. Am J Kidney Dis.
57(Suppl 1): A8e1–e526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Reutens AT and Atkins RC: Epidemiology of
diabetic nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 170:1–7. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brosius FC, Khoury CC, Buller CL and Chen
S: Abnormalities in signaling pathways in diabetic nephropathy.
Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. 5:51–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Steffes MW, Osterby R, Chavers B and Mauer
SM: Mesangial expansion as a central mechanism for loss of kidney
function in diabetic patients. Diabetes. 38:1077–1081. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ziyadeh FN: The extracellular matrix in
diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 22:736–744. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Valcourt U, Kowanetz M, Niimi H, Heldin CH
and Moustakas A: TGF-beta and the Smad signaling pathway support
tran-scriptomic reprogramming during epithelial-mesenchymal cell
transition. Mol Biol Cell. 16:1987–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Badid C, Desmouliere A, Babici D,
Hadj-Aissa A, McGregor B, Lefrancois N, Touraine JL and Laville M:
Interstitial expression of alpha-SMA: An early marker of chronic
renal allograft dysfunction. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 17:1993–1998.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hills CE and Squires PE: The role of TGF-β
and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:131–139. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nieto MA: The snail superfamily of
zinc-finger transcription factors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:155–166. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I,
Locascio A, Blanco MJ, del Barrio MG, Portillo F and Nieto MA: The
transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hajra KM, Chen DY and Fearon ER: The SLUG
zinc-finger protein represses E-cadherin in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 62:1613–1618. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu Q, Ji XJ, Zhou YX, Yao XQ, Liu YQ,
Zhang F and Yin XX: Quercetin inhibits the mTORC1/p70S6K
signaling-mediated renal tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Pharmacol Res.
99:237–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma XM and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms
of mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu W, Hu W, Han WB, Liu YL, Tu Y, Yang HM,
Fang QJ, Zhou MY, Wan ZY, Tang RM, et al: Inhibition of
Akt/mTOR/p70S6K Signaling Activity With Huangkui Capsule Alleviates
the Early Glomerular Pathological Changes in Diabetic Nephropathy.
Front Pharmacol. 9:4432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li M, Qu YZ, Zhao ZW, Wu SX, Liu YY, Wei
XY, Gao L and Gao GD: Astragaloside IV protects against focal
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury correlating to suppression of
neutrophils adhesion-related molecules. Neurochem Int. 60:458–465.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Luo Y, Qin Z, Hong Z, Zhang X, Ding D, Fu
JH, Zhang WD and Chen J: Astragaloside IV protects against ischemic
brain injury in a murine model of transient focal ischemia.
Neurosci Lett. 363:218–223. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Du Q, Zhang S, Li A, Mohammad IS, Liu B
and Li Y: Astragaloside IV: Astragaloside IV Inhibits Adipose
Lipolysis and Reduces Hepatic Glucose Production via Akt Dependent
PDE3B Expression in HFD-Fed Mice. Front Physiol. 9:152018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li C, Yang F, Liu F, Li D and Yang T:
NRF2/HO-1 activation via ERK pathway involved in the
anti-neuroinflammatory effect of Astragaloside IV in LPS induced
microglial cells. Neurosci Lett. 666:104–110. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tang B, Zhang JG, Tan HY and Wei XQ:
Astragaloside IV inhibits ventricular remodeling and improves fatty
acid utili-zation in rats with chronic heart failure. Biosci Rep.
38:382018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang S, Li J, Huang H, Gao W, Zhuang C, Li
B, Zhou P and Kong D: Anti-hepatitis B virus activities of
astragaloside IV isolated from radix Astragali. Biol Pharm Bull.
32:132–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu J and Wen K: Astragaloside IV inhibits
TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through inhibition
of the PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in gastric cancer cells. Phytother
Res. 32:1289–1296. 2018. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Brownlee M: The pathobiology of diabetic
complications: A unifying mechanism. Diabetes. 54:1615–1625. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010–2030. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu ZH: Nephrology in china. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 9:523–528. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Afkarian M, Zelnick LR, Hall YN, Heagerty
PJ, Tuttle K, Weiss NS and de Boer IH: Clinical Manifestations of
Kidney Disease Among US Adults With Diabetes, 1988–2014. JAMA.
316:602–610. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
de Boer IH: A new chapter for diabetic
kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 377:885–887. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Penno G, Garofolo M and Del Prato S:
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibition in chronic kidney disease and
potential for protection against diabetes-related renal injury.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 26:361–373. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang D, Zhang G, Chen X, Wei T, Liu C,
Chen C, Gong Y and Wei Q: Sitagliptin ameliorates diabetic
nephropathy by blocking TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 41:2784–2792. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang GY, Wang DD, Cao Z, Wei T, Liu CX
and Wei QL: Sitagliptin ameliorates high glucose-induced cell
proliferation and expression of the extracellular matrix in
glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Ther Med. 14:3862–3867. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett
D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC
and Zinman B: Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 375:323–334. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D,
Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ,
et al: Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in
type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 373:2117–2128. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Muskiet MHA, Tonneijck L, Smits MM, van
Baar MJB, Kramer MHH, Hoorn EJ, Joles JA and van Raalte DH: GLP-1
and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in
diabetes. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:605–628. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matkovic Z, Zivkovic V, Korica M, Plavec
D, Pecanic S and Tudoric N: Efficacy and safety of Astragalus
membranaceus in the treatment of patients with seasonal allergic
rhinitis. Phytother Res. 24:175–181. 2010.
|
|
41
|
Li SQ, Yuan RX and Gao H: Clinical
observation on the treatment of ischemic heart disease with
Astragalus membranaceus. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
15:77–80. 1995.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang C, Zhu C, Ling Y, Zhou X, Dong C,
Luo J and Liu Y: The clinical value of Huangqi injection in the
treatment of leucopenia: A meta-analysis of clinical controlled
trials. PLoS One. 8:e831232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li M, Wang W, Xue J, Gu Y and Lin S:
Meta-analysis of the clinical value of Astragalus membranaceus in
diabetic nephropathy. J Ethnopharmacol. 133:412–419. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qiao Y, Fan CL and Tang MK: Astragaloside
IV protects rat retinal capillary endothelial cells against high
glucose-induced oxidative injury. Drug Des Devel Ther.
11:3567–3577. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen X, Wang DD, Wei T, He SM, Zhang GY
and Wei QL: Effects of astragalosides from Radix Astragali on high
glucose-induced proliferation and extracellular matrix accumulation
in glomerular mesangial cells. Exp Ther Med. 11:2561–2566. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nieto MA: Epithelial-Mesenchymal
Transitions in development and disease: Old views and new
perspectives. Int J Dev Biol. 53:1541–1547. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gonzalez J, Klein J, Chauhan SD, Neau E,
Calise D, Nevoit C, Chaaya R, Miravete M, Delage C, Bascands JL, et
al: Delayed treatment with plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 decoys
reduces tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
234:1511–1518. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang JY, Yin XX, Wu YM, Tang DQ, Gao YY,
Wan MR, Hou XY and Zhang B: Ginkgo biloba extract suppresses
hypertrophy and extracellular matrix accumulation in rat mesangial
cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:1222–1230. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu W, Shao X, Tian L, Gu L, Zhang M, Wang
Q, Wu B, Wang L, Yao J, Xu X, et al: Astragaloside IV ameliorates
renal fibrosis via the inhibition of mitogen-activated protein
kinases and antiapoptosis in vivo and in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 350:552–562. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li Y, Kang YS, Dai C, Kiss LP, Wen X and
Liu Y: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a potential pathway
leading to podocyte dysfunction and proteinuria. Am J Pathol.
172:299–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|