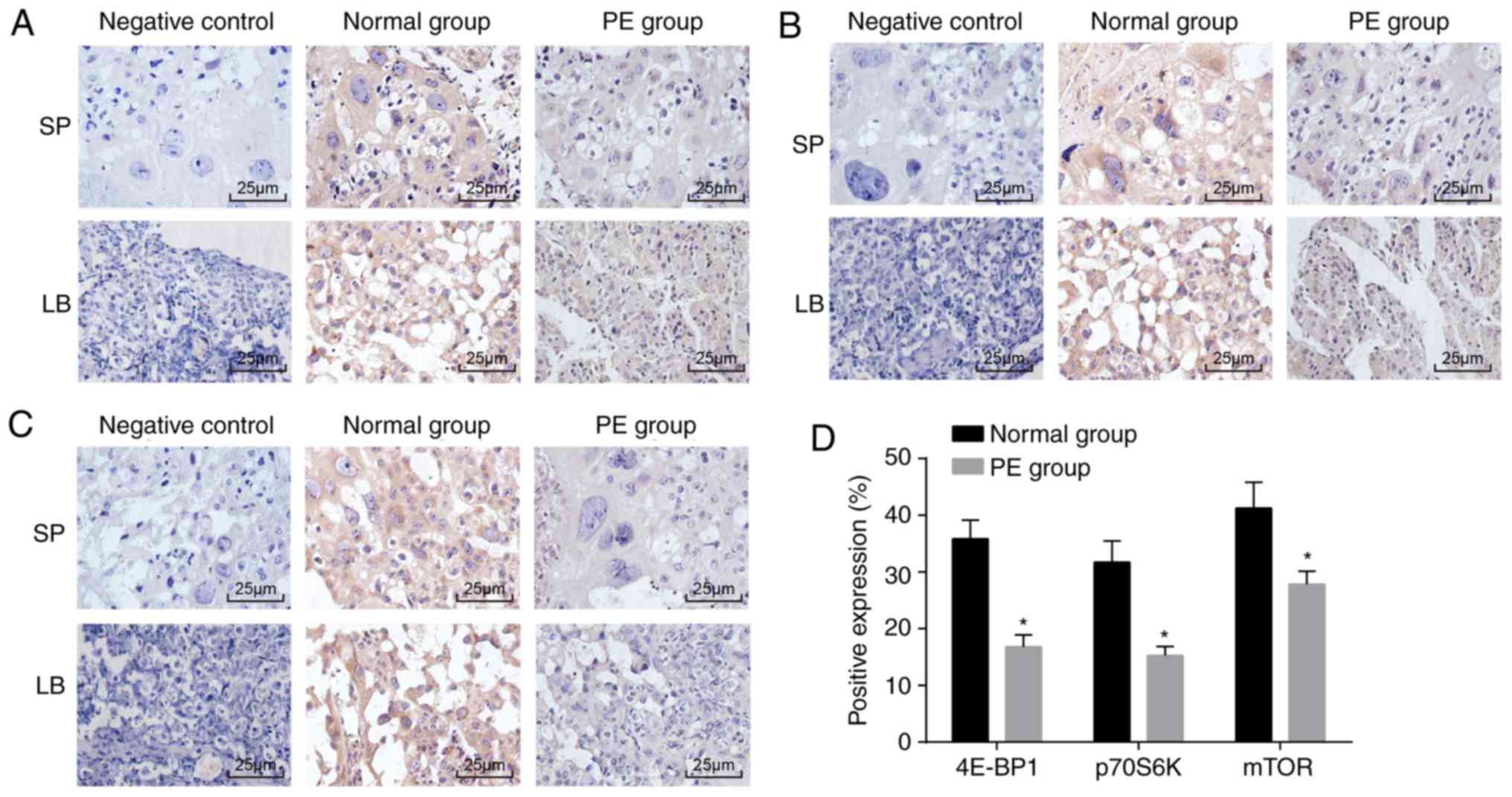
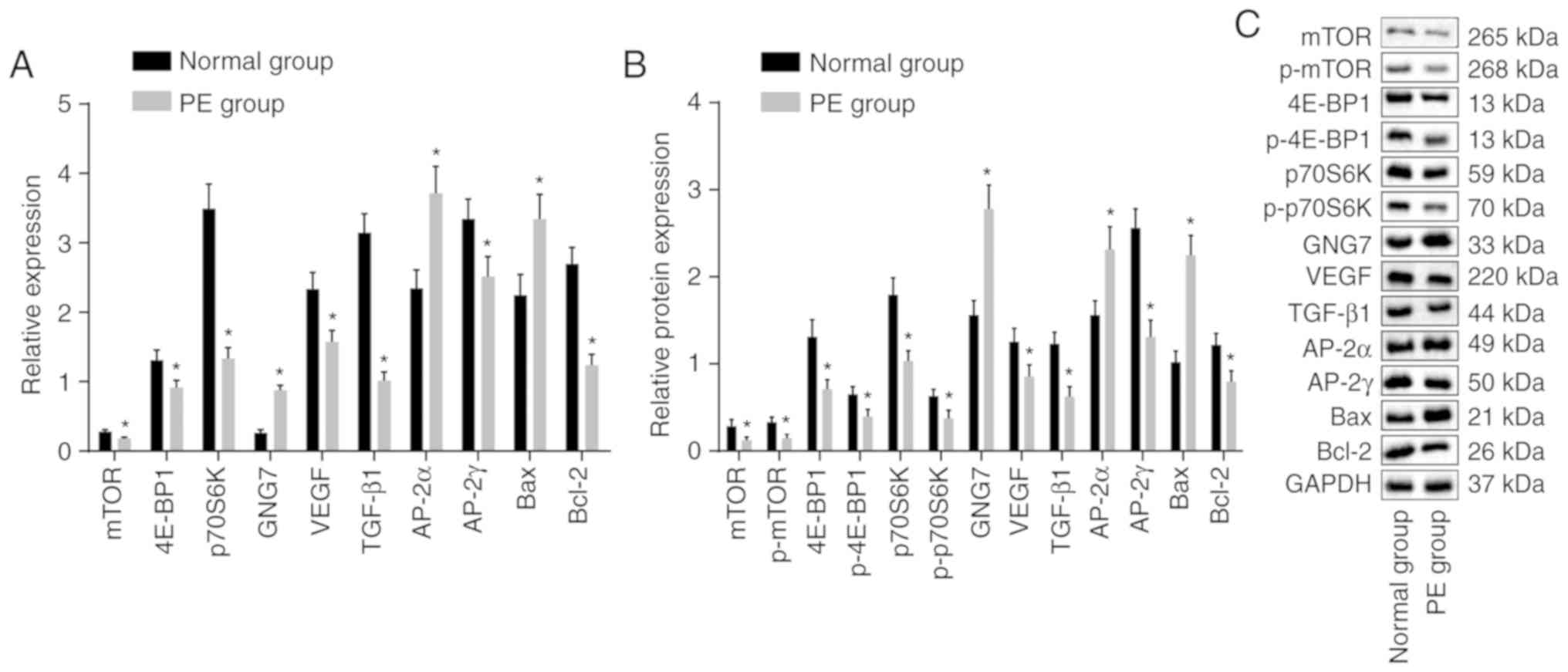
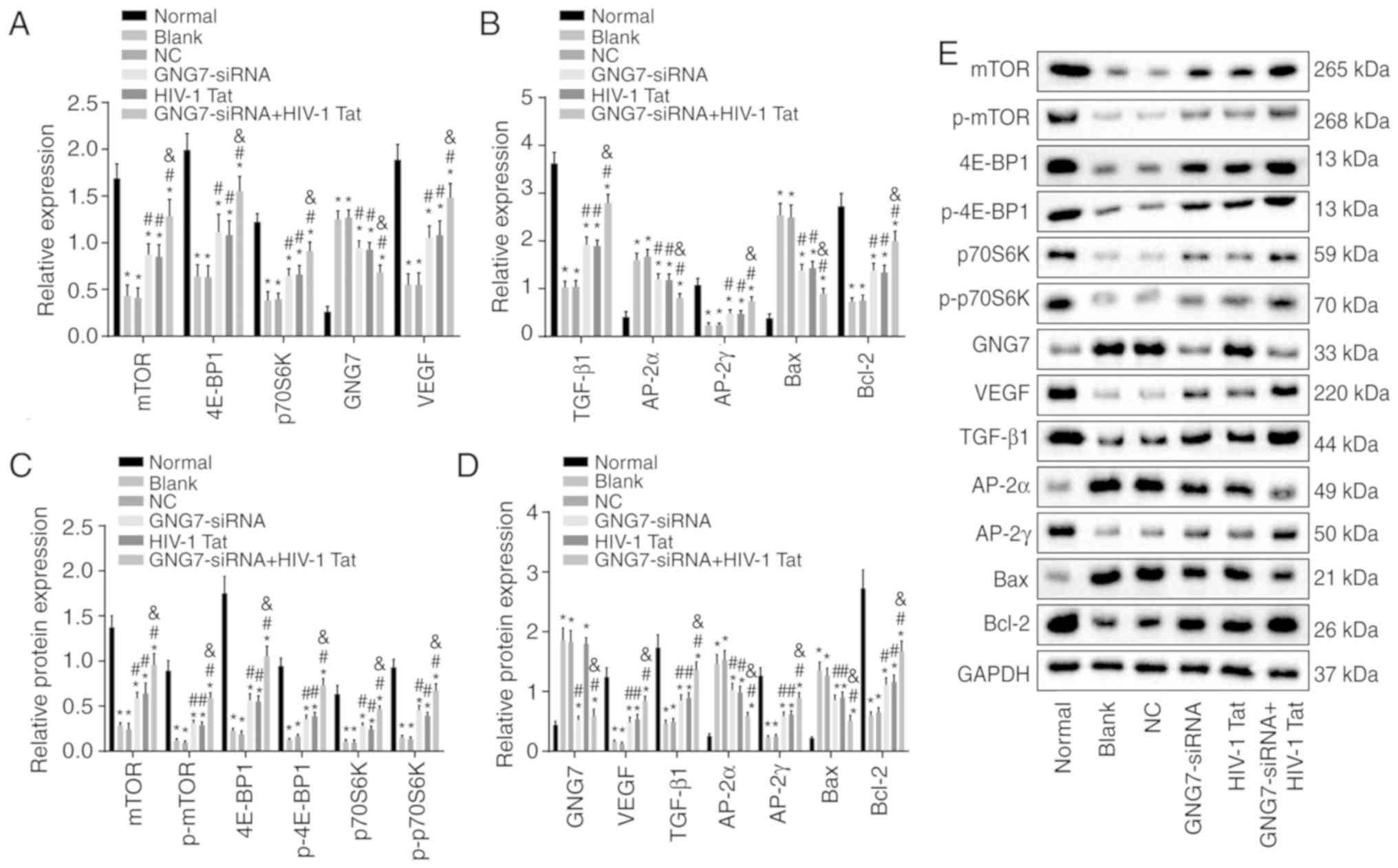
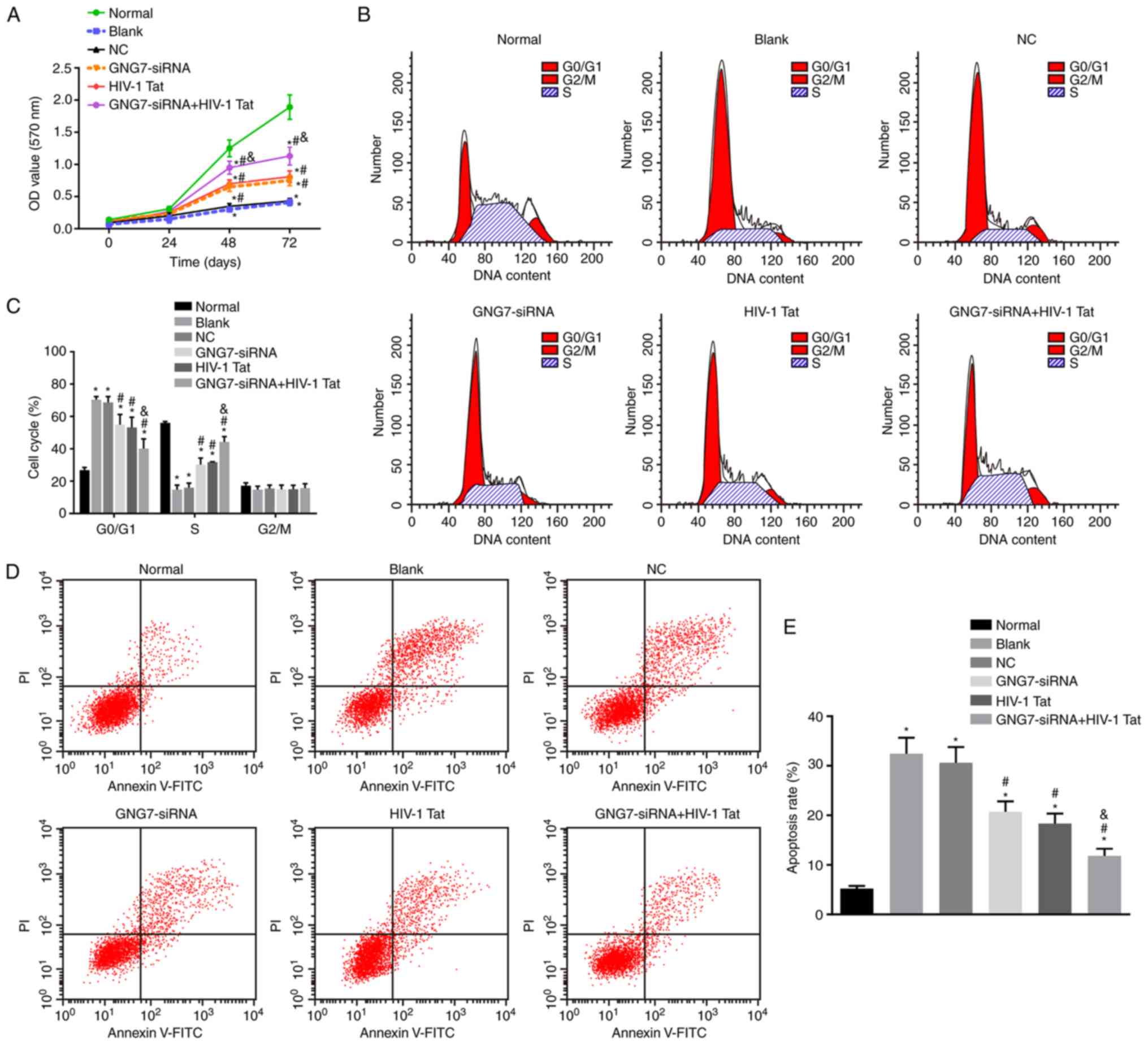
|
1
|
Ghulmiyyah L and Sibai B: Maternal
mortality from preeclampsia/eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 36:56–59.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Phipps E, Prasanna D, Brima W and Jim B:
Preeclampsia: Updates in pathogenesis, definitions, and guidelines.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:1102–1113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Staff AC, Benton SJ, von Dadelszen P,
Roberts JM, Taylor RN, Powers RW, Charnock-Jones DC and Redman CW:
Redefining preeclampsia using placenta-derived biomarkers.
Hypertension. 61:932–942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burwick RM and Feinberg BB: Eculizumab for
the treatment of preeclampsia/HELLP syndrome. Placenta. 34:201–203.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hansson SR, Gram M and Akerstrom B: Fetal
hemoglobin in preeclampsia: A new causative factor, a tool for
prediction/diagnosis and a potential target for therapy. Curr Opin
Obstet Gynecol. 25:448–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu J, Ji X, Li Z, Yang X, Wang W and
Zhang X: G protein gamma subunit 7 induces autophagy and inhibits
cell division. Oncotarget. 7:24832–24847. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hartmann S, Szaumkessel M, Salaverria I,
Simon R, Sauter G, Kiwerska K, Gawecki W, Bodnar M, Marszalek A,
Richter J, et al: Loss of protein expression and recurrent DNA
hypermethylation of the GNG7 gene in squamous cell carcinoma of the
head and neck. J Appl Genet. 53:167–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Kvehaugen AS, Melien O, Holmen OL,
Laivuori H, Oian P, Andersgaard AB, Dechend R and Staff AC: Single
nucleotide polymorphisms in G protein signaling pathway genes in
preeclampsia. Hypertension. 61:655–661. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Populo H, Lopes JM and Soares P: The mTOR
signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1886–1918.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gomez-Pinillos A and Ferrari AC: mTOR
signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 26:483–505. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeng X, Huang Z, Mao X, Wang J, Wu G and
Qiao S: N-carbamylglutamate enhances pregnancy outcome in rats
through activation of the PI3K/PKB/mTOR signaling pathway. PLoS
One. 7:e411922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu D, Hong H, Huang X, Huang L, He Z, Fang
Q and Luo Y: CXCR2 is decreased in preeclamptic placentas and
promotes human trophoblast invasion through the Akt signaling
pathway. Placenta. 43:17–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Amaral LM, Cornelius DC, Harmon A, Moseley
J, Martin JN Jr and LaMarca B: 17-hydroxyprogesterone caproate
significantly improves clinical characteristics of preeclampsia in
the reduced uterine perfusion pressure rat model. Hypertension.
65:225–231. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Serman L, Vlahovic M, Sijan M, Bulic-Jakus
F, Serman A, Sincic N, Matijevic R, Juric-Lekic G and Katusic A:
The impact of 5-azacytidine on placental weight, glycoprotein
pattern and proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in rat
placenta. Placenta. 28:803–811. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bergmann A, Ahmad S, Cudmore M, Gruber AD,
Wittschen P, Lindenmaier W, Christofori G, Gross V, Gonzalves ACh
Grone HJ, et al: Reduction of circulating soluble Flt-1 alleviates
preeclampsia-like symptoms in a mouse model. J Cell Mol Med.
14:1857–1867. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Grotegut CA: Prevention of preeclampsia. J
Clin Invest. 126:4396–4398. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Velicky P, Windsperger K, Petroczi K, Pils
S, Reiter B, Weiss T, Vondra S, Ristl R, Dekan S, Fiala C, et al:
Pregnancy-associated diamine oxidase originates from extravillous
trophoblasts and is decreased in early-onset preeclampsia. Sci Rep.
8:63422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang M, Gong B, Li Y and Wang Y: Human
G-protein gamma 7 in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its
clinicopathological significance. Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Ther.
3:66–70. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Giguere V: Canonical signaling and nuclear
activity of mTOR-a teamwork effort to regulate metabolism and cell
growth. FEBS J. 285:1572–1588. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aiko Y, Askew DJ, Aramaki S, Myoga M,
Tomonaga C, Hachisuga T, Suga R, Kawamoto T, Tsuji M and Shibata E:
Differential levels of amino acid transporters System L and ASCT2,
and the mTOR protein in placenta of preeclampsia and IUGR. BMC
Pregnancy Childbirth. 14:1812014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou K, Fan YD, Wu PF, Duysenbi S, Feng
ZH, Du GJ and Zhang TR: MicroRNA-145 inhibits the activation of the
mTOR signaling pathway to suppress the proliferation and invasion
of invasive pituitary adenoma cells by targeting AKT3 in vivo and
in vitro. Onco Targets Ther. 10:1625–1635. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang G, Liu M, Wang H, Yu S, Jiang Z, Sun
J, Han K, Shen J, Zhu M, Lin Z, et al: Centrosomal protein of 55
regulates glucose metabolism, proliferation and apoptosis of glioma
cells via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. J Cancer. 7:1431–1440.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Orso F, Penna E, Cimino D, Astanina E,
Maione F, Valdembri D, Giraudo E, Serini G, Sismondi P, De Bortoli
M and Taverna D: AP-2alpha and AP-2gamma regulate tumor progression
via specific genetic programs. FASEB J. 22:2702–2714. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Biadasiewicz K, Sonderegger S, Haslinger
P, Haider S, Saleh L, Fiala C, Pollheimer J and Knofler M:
Transcription factor AP-2α promotes EGF-dependent invasion of human
trophoblast. Endocrinology. 152:1458–1469. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Jia L, Cui S, Shi Y, Chang A,
Wang P and Zhang Z: AP-2alpha-dependent regulation of Bcl-2/Bax
expression affects apoptosis in the trophoblast. J Mol Histol.
43:681–689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang A, Liu Q, Zhang J and Zheng R:
Berberine alleviates preeclampsia possibly by regulating the
expression of interleukin-2/interleukin-10 and Bcl-2/Bax. Int J
Clin Exp Med. 8:16301–16307. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schneider HA, Gembruch U, Fimmers R,
Schmitz J and Muller AM: Expression of AP-2γ in placentas of
patients with preeclampsia and of smokers. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
291:1015–1021. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hu LY, Sun ZG, Wen YM, Cheng GZ, Wang SL,
Zhao HB and Zhang XR: ATP-mediated protein kinase B Akt/mammalian
target of rapamycin mTOR/p70 ribosomal S6 protein p70S6 kinase
signaling pathway activation promotes improvement of locomotor
function after spinal cord injury in rats. Neuroscience.
169:1046–1062. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wahl EA, Schenck TL, Machens HG and
Balmayor ER: VEGF released by deferoxamine preconditioned
mesenchymal stem cells seeded on collagen-GAG substrates enhances
neovascularization. Sci Rep. 6:368792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Escudero C, Bertoglia P, Hernadez M, Celis
C, Gonzalez M, Aguayo C and Acurio J: Impaired A2A adenosine
receptor/nitric oxide/VEGF signaling pathway in fetal endothelium
during late- and early-onset preeclampsia. Purinergic Signal.
9:215–226. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Khanabdali R, Shakouri-Motlagh A,
Wilkinson S, Murthi P, Georgiou HM, Brennecke SP and Kalionis B:
Low-dose aspirin treatment enhances the adhesion of preeclamptic
decidual mesenchymal stem/stromal cells and reduces their
production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Mol Med (Berl).
96:1215–1225. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kintiraki E, Papakatsika S, Kotronis G,
Goulis DG and Kotsis V: Pregnancy-induced hypertension. Hormones
(Athens). 14:211–223. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lu F, Longo M, Tamayo E, Maner W, Al-Hendy
A, Anderson GD, Hankins GD and Saade GR: The effect of
over-expression of sFlt-1 on blood pressure and the occurrence of
other manifestations of preeclampsia in unrestrained conscious
pregnant mice. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 196. pp. 396 e391–397;
discussion 396 e397. 2007, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Maynard SE, Min JY, Merchan J, Lim KH, Li
J, Mondal S, Libermann TA, Morgan JP, Sellke FW, Stillman IE, et
al: Excess placental soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFlt1) may
contribute to endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and
proteinuria in preeclampsia. J Clin Invest. 111:649–658. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ohkuchi A, Hirashima C, Suzuki H,
Takahashi K, Yoshida M, Matsubara S and Suzuki M: Evaluation of a
new and automated electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for plasma
sFlt-1 and PlGF levels in women with preeclampsia. Hypertens Res.
33:422–427. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Venkatesha S, Toporsian M, Lam C, Hanai J,
Mammoto T, Kim YM, Bdolah Y, Lim KH, Yuan HT, Libermann TA, et al:
Soluble endoglin contributes to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia.
Nat Med. 12:642–649. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|