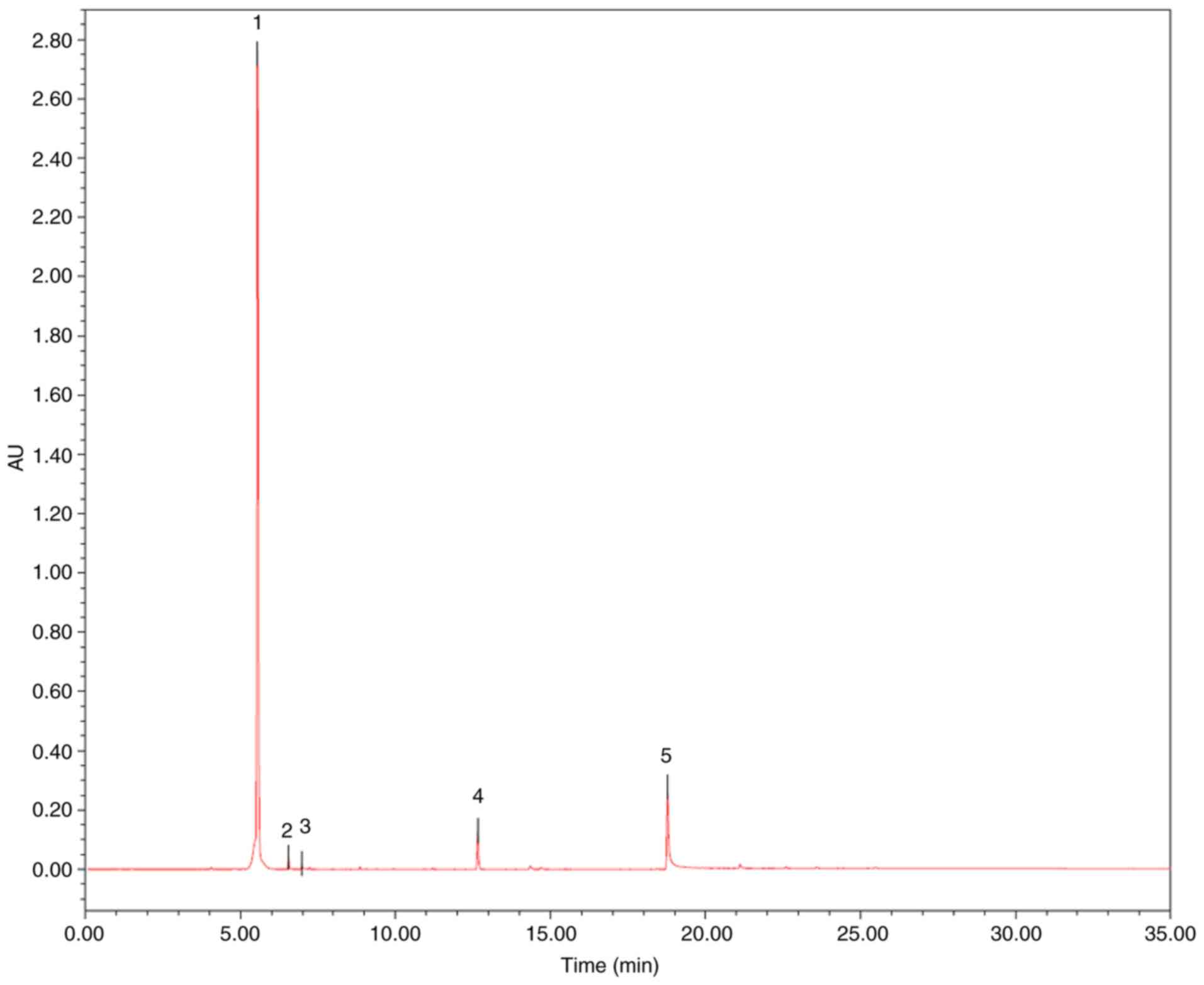
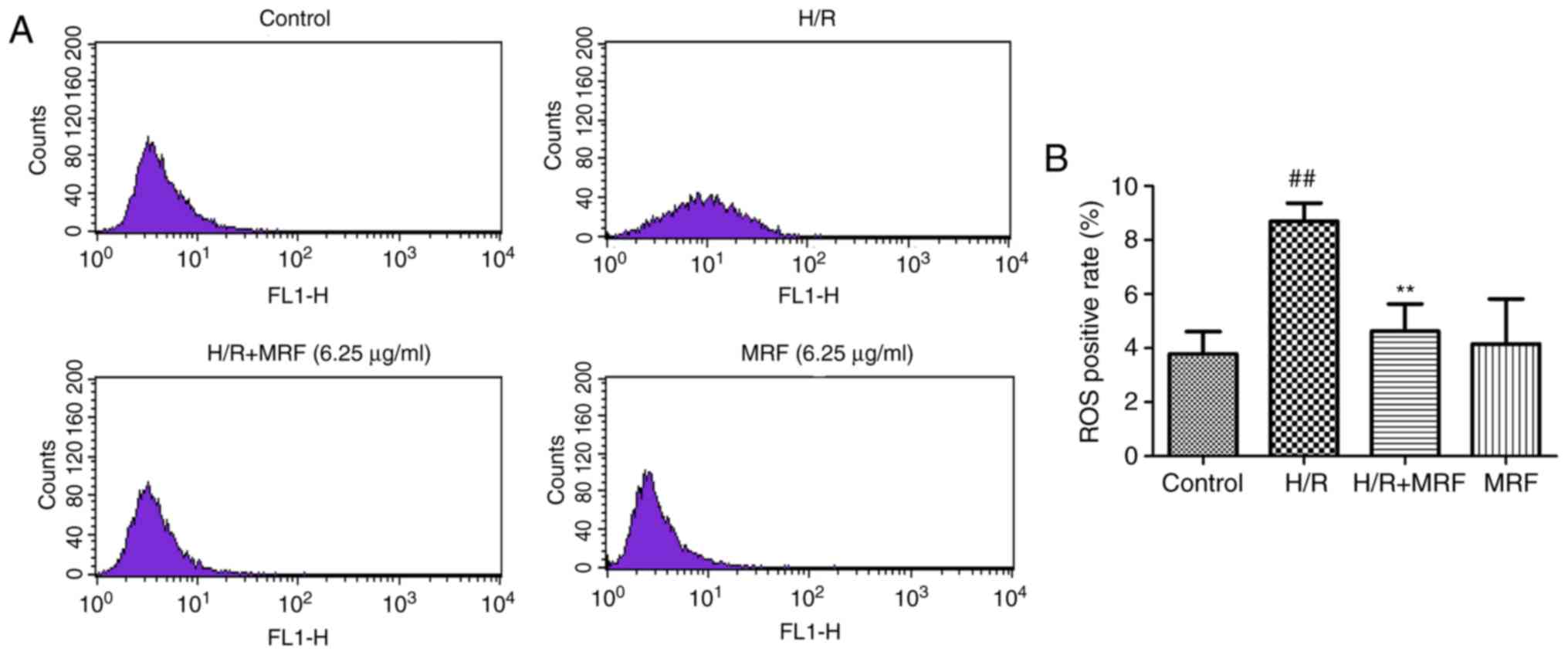
|
1
|
Moran AE, Roth GA, Narula J and Mensah GA:
1990-2010 Global cardiovascular disease atlas. Glob Heart. 9:3–16.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharma V, Bell RM and Yellon DM: Targeting
reperfusion injury in acute myocardial infarction: A review of
reperfusion injury pharmacotherapy. Expert Opin Pharmacother.
13:1153–1175. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kalogeris T, Baines CP, Krenz M and
Korthuis RJ: Cell biology of ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int Rev
Cell Mol Biol. 298:229–317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gerczuk PZ and Kloner RA: An update on
cardioprotection: A review of the latest adjunctive therapies to
limit myocardial infarction size in clinical trials. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 59:969–978. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Marczin N, El-Habashi N, Hoare GS, Bundy
RE and Yacoub M: Antioxidants in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury: Therapeutic potential and basic mechanisms. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 420:222–236. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fu Y, Qiao L, Cao Y, Zhou X, Liu Y and Ye
X: Structural elucidation and antioxidant activities of
proanthocyanidins from Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et
Zucc.) leaves. PLoS One. 9:e961622014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Qi X, Cao S and Li P: Protective
effect of flavonoid extract from Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra
Sieb. et Zucc.) fruit on alcoholic liver oxidative injury in mice.
J Nat Med. 68:521–529. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feng C, Chen M, Xu CJ, Bai L, Yin XR, Li
X, Allan AC, Ferguson IB and Chen KS: Transcriptomic analysis of
Chinese bayberry (Myrica rubra) fruit development and ripening
using RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics. 13:192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dai GH, Meng GM, Tong YL, Chen X, Ren ZM,
Wang K and Yang F: Growth-inhibiting and apoptosis-inducing
activities of Myricanol from the bark of Myrica rubra in human lung
adeno-carcinoma A549 cells. Phytomedicine. 21:1490–1496. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sun C, Huang H, Xu C, Li X and Chen K:
Biological activities of extracts from Chinese bayberry (Myrica
rubra Sieb. et Zucc.): A review. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 68:97–106.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tao J, Morikawa T, Toguchida I, Ando S,
Matsuda H and Yoshikawa M: Inhibitors of nitric oxide production
from the bark of Myrica rubra: Structures of new biphenyl type
diaryl-heptanoid glycosides and taraxerane type triterpene. Bioorg
Med Chem. 10:4005–4012. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsuda H, Morikawa T, Tao J, Ueda K and
Yoshikawa M: Bioactive constituents of Chinese natural medicines.
VII. Inhibitors of degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells and absolute
stereo-structures of three new diarylheptanoid glycosides from the
bark of Myrica rubra. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 50:208–215. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hobbs CA, Swartz C, Maronpot R, Davis J,
Recio L, Koyanagi M and Hayashi SM: Genotoxicity evaluation of the
flavonoid, myricitrin, and its aglycone, myricetin. Food Chem
Toxicol. 83:283–292. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He K, Li X, Xiao Y, Yong Y, Zhang Z, Li S,
Zhou T, Yang D, Gao P and Xin X: Hypolipidemic effects of Myrica
rubra extracts and main compounds in C57BL/6j mice. Food Funct.
7:3505–3515. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Chen S, Wei C, Gong H, Li L and
Ye X: Chemical and cellular assays combined with in vitro digestion
to determine the antioxidant activity of flavonoids from Chinese
Bayberry (Myrica rubra Sieb. et Zucc.) leaves. PLoS One.
11:e01674842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin W, Sun G, Pan R, Shen S and Wang T:
Protective effects of myricetin against injury induced by
H2O2 in vascular endothelial cells. Modern
Chinese Med. 17:443–447. 2015.
|
|
17
|
Wang M, Meng XB, Yu YL, Sun GB, Xu XD,
Zhang XP, Dong X, Ye JX, Xu HB, Sun YF and Sun XB: Elatoside C
protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in H9c2
cardiomyocytes through the reduction of endoplasmic reticulum
stress partially depending on STAT3 activation. Apoptosis.
19:1727–1735. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun J, Sun G, Meng X, Wang H, Wang M, Qin
M, Ma B, Luo Y, Yu Y, Chen R, et al: Ginsenoside RK3 prevents
hypoxia-reoxygenation induced apoptosis in H9c2 cardiomyocytes via
AKT and MAPK pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6901902013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang M, Sun GB, Sun X, Wang HW, Meng XB,
Qin M, Sun J, Luo Y and Sun XB: Cardioprotective effect of
salvianolic acid B against arsenic trioxide-induced injury in
cardiac H9c2 cells via the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Toxicol Lett.
216:100–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sun GB, Sun X, Wang M, Ye JX, Si JY, Xu
HB, Meng XB, Qin M, Sun J, Wang HW and Sun XB: Oxidative stress
suppression by luteolin-induced heme oxygenase-1 expression.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 265:229–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li W, Wu Y, Liu X, Yan C, Liu D, Pan Y,
Yang G, Yin F, Weng Z, Zhao D, et al: Antioxidant properties of
cis-Z, Z'-3a.7a',7a.3a'-dihydroxyligustilide on human umbilical
vein endothelial cells in vitro. Molecules. 18:520–534. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun X, Sun GB, Wang M, Xiao J and Sun XB:
Protective effects of cynaroside against
H2O2-induced apoptosis in H9c2
cardio-myoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 112:2019–2029. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rodrigo R, Libuy M, Feliu F and Hasson D:
Oxidative stress-related biomarkers in essential hypertension and
ischemia-reperfusion myocardial damage. Dis Markers. 35:773–790.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hu Y, Li L, Yin W, Shen L, You B and Gao
H: Protective effect of proanthocyanidins on anoxia-reoxygenation
injury of myocardial cells mediated by the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta
pathway and mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Mol Med
Rep. 10:2051–2058. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Panche AN, Diwan AD and Chandra SR:
Flavonoids: An overview. J Nutr Sci. 5:e472016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Mahady GB: Ginkgo biloba for the
prevention and treatment of cardiovascular disease: A review of the
literature. J Cardiovasc Nurs. 16:21–32. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim HH, Kim DH, Kim MH, Oh MH, Kim SR,
Park KJ and Lee MW: Flavonoid constituents in the leaves of Myrica
rubra sieb. et zucc. with anti-inflammatory activity. Arch Pharm
Res. 36:1533–1540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun GB, Qin M, Ye JX, Pan RL, Meng XB,
Wang M, Luo Y, Li ZY, Wang HW and Sun XB: Inhibitory effects of
myricitrin on oxidative stress-induced endothelial damage and early
atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
271:114–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qin M, Luo Y, Meng XB, Wang M, Wang HW,
Song SY, Ye JX, Pan RL, Yao F, Wu P, et al: Myricitrin attenuates
endothelial cell apoptosis to prevent atherosclerosis: An insight
into PI3K/Akt activation and STAT3 signaling pathways. Vascul
Pharmacol. 70:23–34. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang M, Sun GB, Du YY, Tian Y, Liao P, Liu
XS, Ye JX and Sun XB: Myricitrin protects cardiomyocytes from
hypoxia/reoxygenation injury: Involvement of heat shock protein 90.
Front Pharmacol. 8:3532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Choi JS, Bae JY, Kim DS, Li J, Kim JL, Lee
YJ and Kang YH: Dietary compound quercitrin dampens VEGF induction
and PPARgamma activation in oxidized LDL-exposed murine
macrophages: Association with scavenger receptor CD36. J Agric Food
Chem. 58:1333–1341. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
van Empel VP, Bertrand AT, Hofstra L,
Crijns HJ, Doevendans PA and De Windt LJ: Myocyte apoptosis in
heart failure. Cardiovasc Res. 67:21–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB and Sil PC:
Oxidative stress: The mitochondria-dependent and
mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol.
87:1157–1180. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaushal GP, Liu L, Kaushal V, Hong X,
Melnyk O, Seth R, Safirstein R and Shah SV: Regulation of caspase-3
and -9 activation in oxidant stress to RTE by forkhead
transcription factors, Bcl-2 proteins, and MAP kinases. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 287:F1258–F1268. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lu D, Bai XC, Gui L, Su YC, Deng F, Liu B,
Li XM, Zeng WS, Cheng BL and Luo SQ: Hydrogen peroxide in the
Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Raji provides protection against
arsenic trioxide-induced apoptosis via the phosphoinositide-3
kinase signalling pathway. Br J Haematol. 125:512–520. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu CW, Yang F, Cheng SZ, Liu Y, Wan LH
and Cong HL: Rosuvastatin postconditioning protects isolated hearts
against ischemia-reperfusion injury: The role of radical oxygen
species, PI3K-Akt-GSK-3beta pathway, and mitochondrial permeability
transition pore. Cardiovasc Ther. 35:3–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Martin M, Rehani K, Jope RS and Michalek
SM: Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is
differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nat
Immunol. 6:777–784. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu T, Fang Y, Liu S, Yu X, Zhang H, Liang
M and Ding X: Limb ischemic preconditioning protects against
contrast-induced acute kidney injury in rats via phosphorylation of
GSK-3beta. Free Radic Biol Med. 81:170–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|