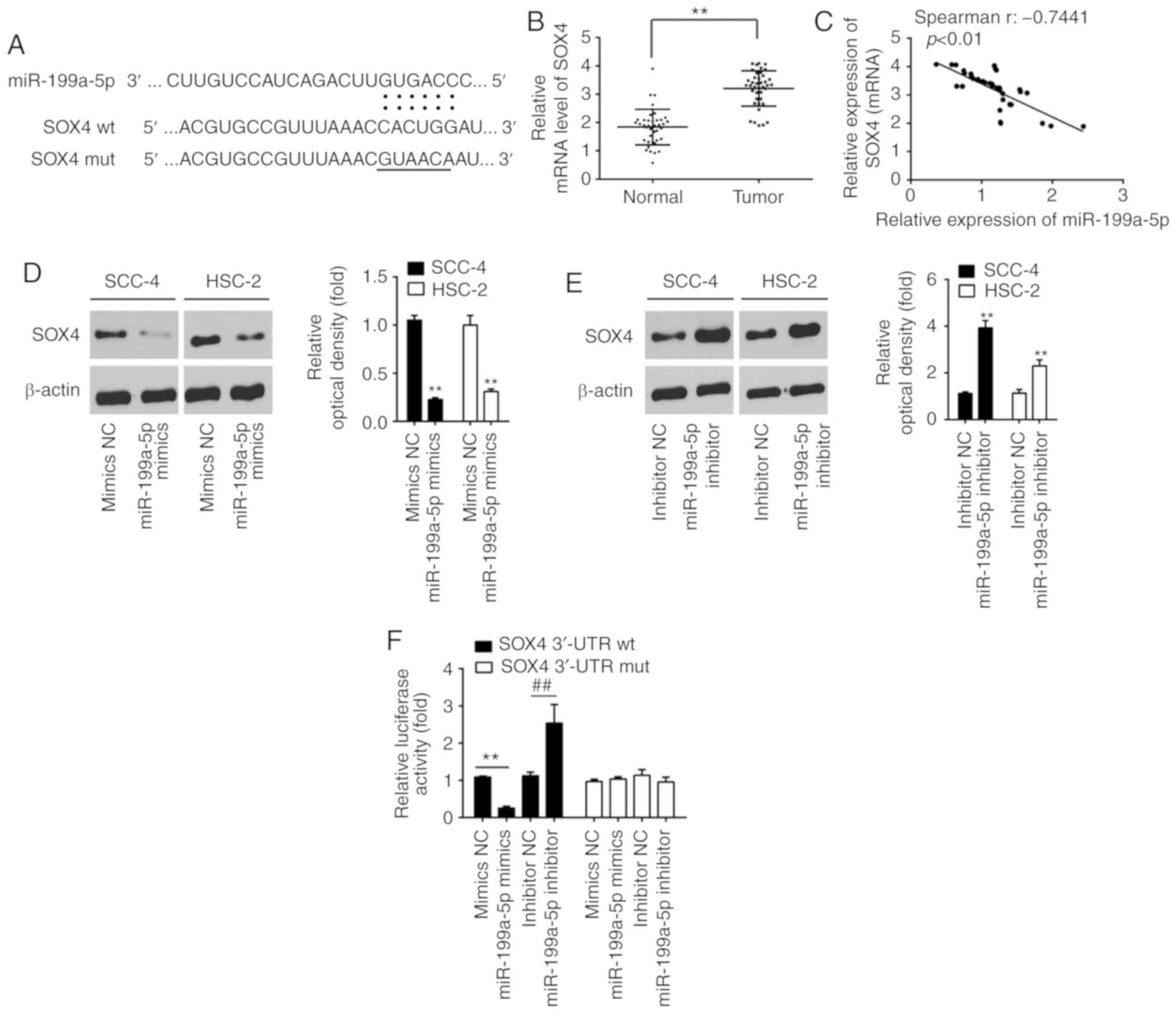
|
1
|
Andersen CL, Christensen LL, Thorsen K,
Schepeler T, Sørensen FB, Verspaget HW, Simon R, Kruhøffer M,
Aaltonen LA, Laurberg S and Ørntoft TF: Dysregulation of the
transcription factors SOX4, CBFB and SMARCC1 correlates with
outcome of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:511–523. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Min R, Zun Z, Siyi L, Wenjun Y, Lizheng W
and Chenping Z: Increased expression of Toll-like receptor-9 has
close relation with tumour cell proliferation in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Arch Oral Biol. 56:877–884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang H, Xia J, Wang K and Zhang J: Serum
autoantibodies in the early detection of esophageal cancer: A
systematic review. Tumour Biol. 36:95–109. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Genden EM, Ferlito A, Bradley PJ, Rinaldo
A and Scully C: Neck disease and distant metastases. Oral Oncol.
39:207–212. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu F, Min J, Cao X, Liu L, Ge Z, Hu J and
Li X: MiR-363-3p inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
and suppresses metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting Sox4.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:35–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Penzo-Méndez AI: Critical roles for SoxC
transcription factors in development and cancer. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 42:425–428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Lee CJ, Appleby VJ, Orme AT, Chan WI and
Scotting PJ: Differential expression of SOX4 and SOX11 in
medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol. 57:201–214. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Castillo SD, Matheu A, Mariani N,
Carretero J, Lopez-Rios F, Lovell-Badge R and Sanchez-Cespedes M:
Novel transcriptional targets of the SRY-HMG box transcription
factor SOX4 link its expression to the development of small cell
lung cancer. Cancer Res. 72:176–186. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu P, Ramachandran S, Ali Seyed M,
Scharer CD, Laycock N, Dalton WB, Williams H, Karanam S, Datta MW,
Jaye DL and Moreno CS: Sex-determining region Y box 4 is a
transforming oncogene in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:4011–4019. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liao YL, Sun YM, Chau GY, Chau YP, Lai TC,
Wang JL, Horng JT, Hsiao M and Tsou AP: Identification of SOX4
target genes using phylogenetic footprinting-based prediction from
expression microarrays suggests that overexpression of SOX4
potentiates metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene.
27:5578–5589. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Medina PP, Castillo SD, Blanco S,
Sanz-Garcia M, Largo C, Alvarez S, Yokota J, Gonzalez-Neira A,
Benitez J, Clevers HC, et al: The SRY-HMG box gene, SOX4, is a
target of gene amplification at chromosome 6p in lung cancer. Hum
Mol Genet. 18:1343–1352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Koumangoye RB, Andl T, Taubenslag KJ,
Zilberman ST, Taylor CJ, Loomans HA and Andl CD: SOX4 interacts
with EZH2 and HDAC3 to suppress microRNA-31 in invasive esophageal
cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 14:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tiwari N, Tiwari VK, Waldmeier L, Balwierz
PJ, Arnold P, Pachkov M, Meyer-Schaller N, Schübeler D, van
Nimwegen E and Christofori G: Sox4 is a master regulator of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition by controlling Ezh2 expression
and epigenetic reprogramming. Cancer Cell. 23:768–783. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kang Y and Massagué J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: Twist in development and
metastasis. Cell. 118:277–279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Croce CM: Causes and consequences of
microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet. 10:704–714. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Zeng Y, Wu S, Zhong J, Wang Y and Xu
J: MiR-204, down-regulated in retinoblastoma, regulates
proliferation and invasion of human retinoblastoma cells by
targeting CyclinD2 and MMP-9. FEBS Lett. 589:645–650. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Voorhoeve PM: MicroRNAs: Oncogenes, tumor
suppressors or master regulators of cancer heterogeneity? Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1805:72–86. 2010.
|
|
19
|
Wu BH, Luo M, Zhang DH and Zhou X:
Deformation control and chatter suppression in 5-Axis milling of
thin-walled blade. Adv Mater Res. 188:314–318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shen Q, Cicinnati VR, Zhang X, Iacob S,
Weber F, Sotiropoulos GC, Radtke A, Lu M, Paul A, Gerken G and
Beckebaum S: Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor
1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol Cancer.
9:2272010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, Kim H, Kim YT, Kim
JH, Kim JW and Kim S: MicroRNA expression profiles in serous
ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:2690–2695. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He XJ, Ma YY, Yu S, Jiang XT, Lu YD, Tao
L, Wang HP, Hu ZM and Tao HQ: Up-regulated miR-199a-5p in gastric
cancer functions as an oncogene and targets klotho. BMC Cancer.
14:2182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Worley LA, Long MD, Onken MD and Harbour
JW: Micro-RNAs associated with metastasis in uveal melanoma
identified by multiplexed microarray profiling. Melanoma Res.
18:184–190. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhong J, Huang R, Su Z, Zhang M, Xu M,
Gong J, Chen N, Zeng H, Chen X and Zhou Q: Downregulation of
miR-199a-5p promotes prostate adenocarcinoma progression through
loss of its inhibition of HIF-1α. Oncotarget. 8:83523–83538. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Arai
T, Okato A, Kurozumi A, Kato M, Katada K, Okamoto Y and Seki N:
Regulation of ITGA3 by the anti-tumor miR-199 family inhibits
cancer cell migration and invasion in head and neck cancer. Cancer
Sci. 108:1681–1692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kim SY, Nam SY, Choi SH, Cho KJ and Roh
JL: Prognostic value of lymph node density in node-positive
patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.
18:2310–2317. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH,
Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z and
Hanahan D: Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic
switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2:737–744. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Natalwala A, Spychal R and Tselepis C:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition mediated tumourigenesis in the
gastrointestinal tract. World J Gastroenterol. 14:3792–3797. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Shahryari
V, Hashimoto Y, Bhat NS, Shiina M, Deng G, Saini S, Tabatabai ZL,
et al: MicroRNA-203 inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR and
regulates tumorigenesis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
17:1061–1069. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Imani S, Wei C, Cheng J, Khan MA, Fu S,
Yang L, Tania M, Zhang X, Xiao X, Zhang X and Fu J: MicroRNA-34a
targets epithelial to mesenchymal transition-inducing transcription
factors (EMT-TFs) and inhibits breast cancer cell migration and
invasion. Oncotarget. 8:21362–21379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ko YH, Kim EJ, Sun DS, Won HS and Ahn YH:
Abstract 1466: QKI, a miRNA-200 target gene, suppresses
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell
carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 77:14662017.
|
|
33
|
Kim BK, Yoo HI, Kim I, Park J and Kim Yoon
S: FZD6 expression is negatively regulated by miR-199a-5p in human
colorectal cancer. BMB Rep. 48:360–366. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsukigi M, Bilim V, Yuuki K, Ugolkov A,
Naito S, Nagaoka A, Kato T, Motoyama T and Tomita Y: Re-expression
of miR-199a suppresses renal cancer cell proliferation and survival
by targeting GSK-3β. Cancer Lett. 315:189–197. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huang L, Lin JX, Yu YH, Zhang MY, Wang HY
and Zheng M: Downregulation of six MicroRNAs is associated with
advanced stage, lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in small
cell carcinoma of the cervix. PLoS One. 7:e337622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen J, Shin VY, Siu MT, Ho JC, Cheuk I
and Kwong A: miR-199a-5p confers tumor-suppressive role in
triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:8872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nauseef JT and Henry MD:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer: Paradigm
or puzzle? Nat Rev Urol. 8:428–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao X, He L, Li T, Lu Y, Miao Y, Liang S,
Guo H, Bai M, Xie H, Luo G, et al: SRF expedites metastasis and
modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition by regulating
miR-199a-5p expression in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Differ.
21:1900–1913. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu Y, Liu J, Jiang B, Chen J, Fu Z, Bai F,
Jiang J and Tang Z: MiR-199a-5p loss up-regulated DDR1 aggravated
colorectal cancer by activating epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition related signaling. Dig Dis Sci. 59:2163–2172. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kang M, Li Y, Liu W, Wang R, Tang A, Hao
H, Liu Z and Ou H: miR-129-2 suppresses proliferation and migration
of esophageal carcinoma cells through downregulation of SOX4
expression. Int J Mol Med. 32:51–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huang YW, Liu JC, Deatherage DE, Luo J,
Mutch DG, Goodfellow PJ, Miller DS and Huang TH: Epigenetic
repression of microRNA-129-2 leads to overexpression of SOX4
oncogene in endometrial cancer. Cancer Res. 69:9038–9046. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou X, Li L, Su J and Zhang G: Decreased
miR-204 in H. pylori-associated gastric cancer promotes cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting SOX4. PLoS One.
9:e1014572014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yeh YM, Chuang CM, Chao KC and Wang LH:
MicroRNA-138 suppresses ovarian cancer cell invasion and metastasis
by targeting SOX4 and HIF-1α. Int J Cancer. 133:867–878. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang J, Xu G, Shen F and Kang Y: miR-132
targeting cyclin E1 suppresses cell proliferation in osteosarcoma
cells. Tumour Biol. 35:4859–4865. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li S, Qin X, Li Y, Zhang X, Niu R, Zhang
H, Cui A, An W and Wang X: MiR-133a suppresses the migration and
invasion of esophageal cancer cells by targeting the EMT regulator
SOX4. Am J Transl Res. 7:1390–1403. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|