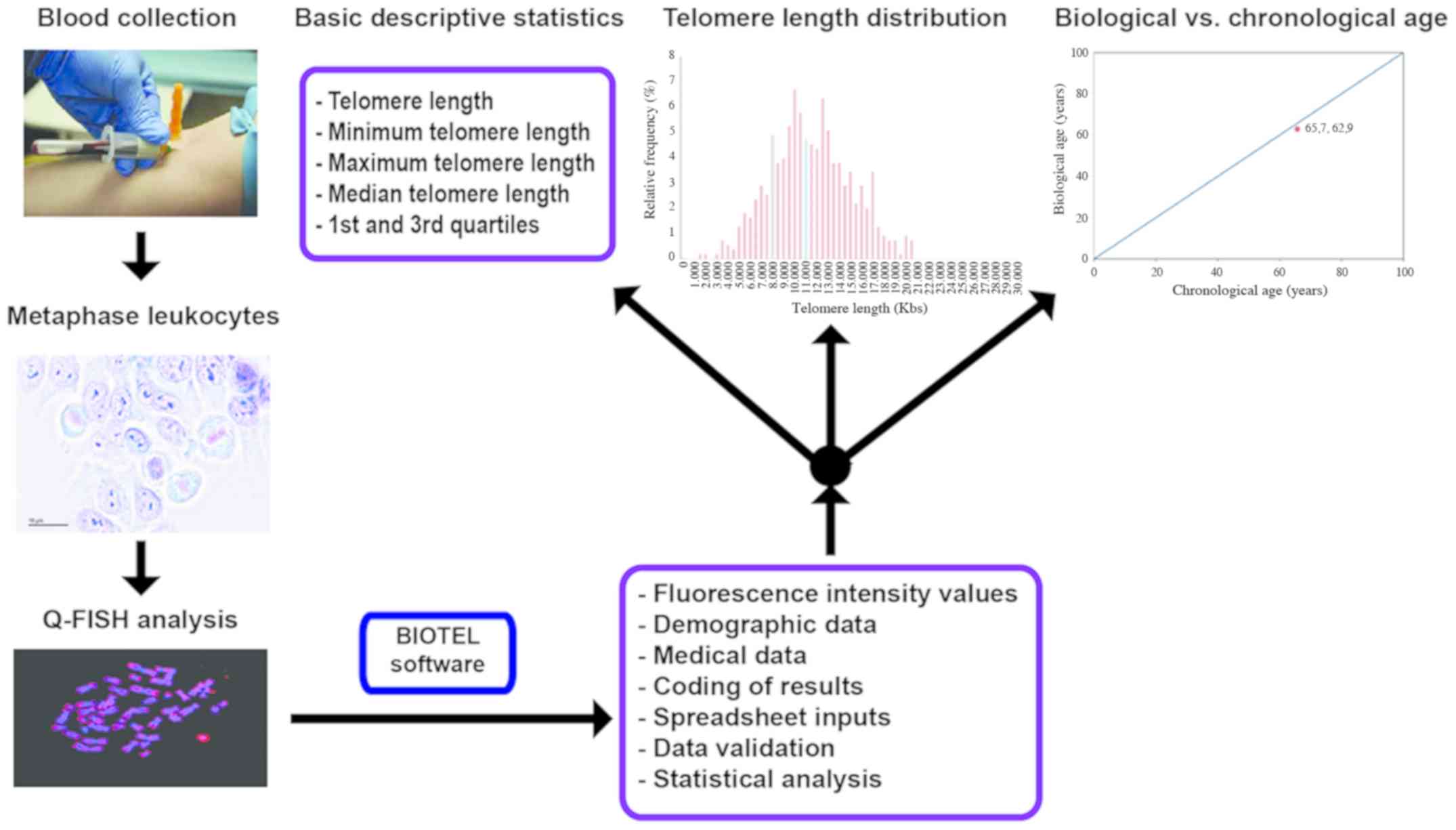
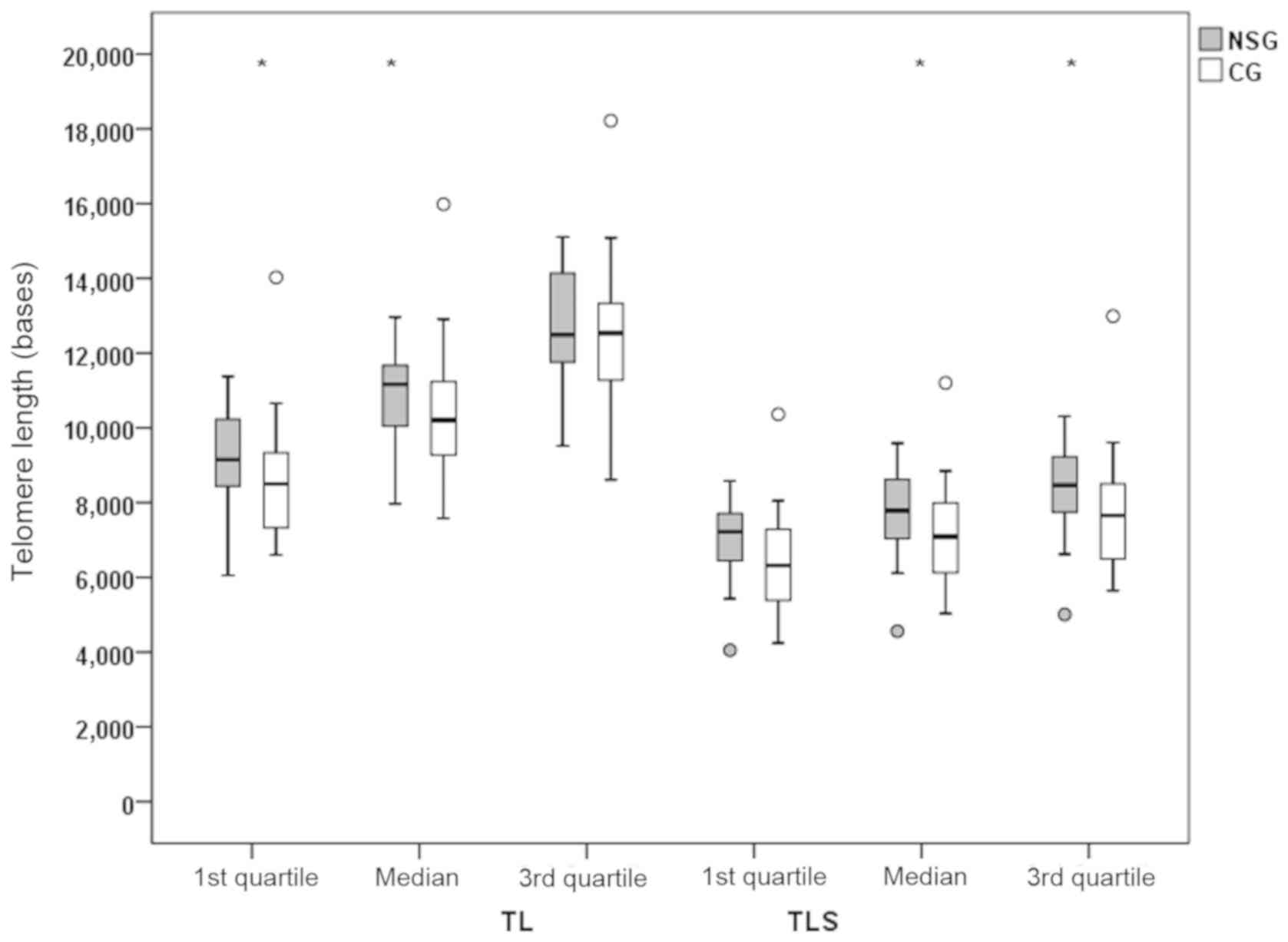
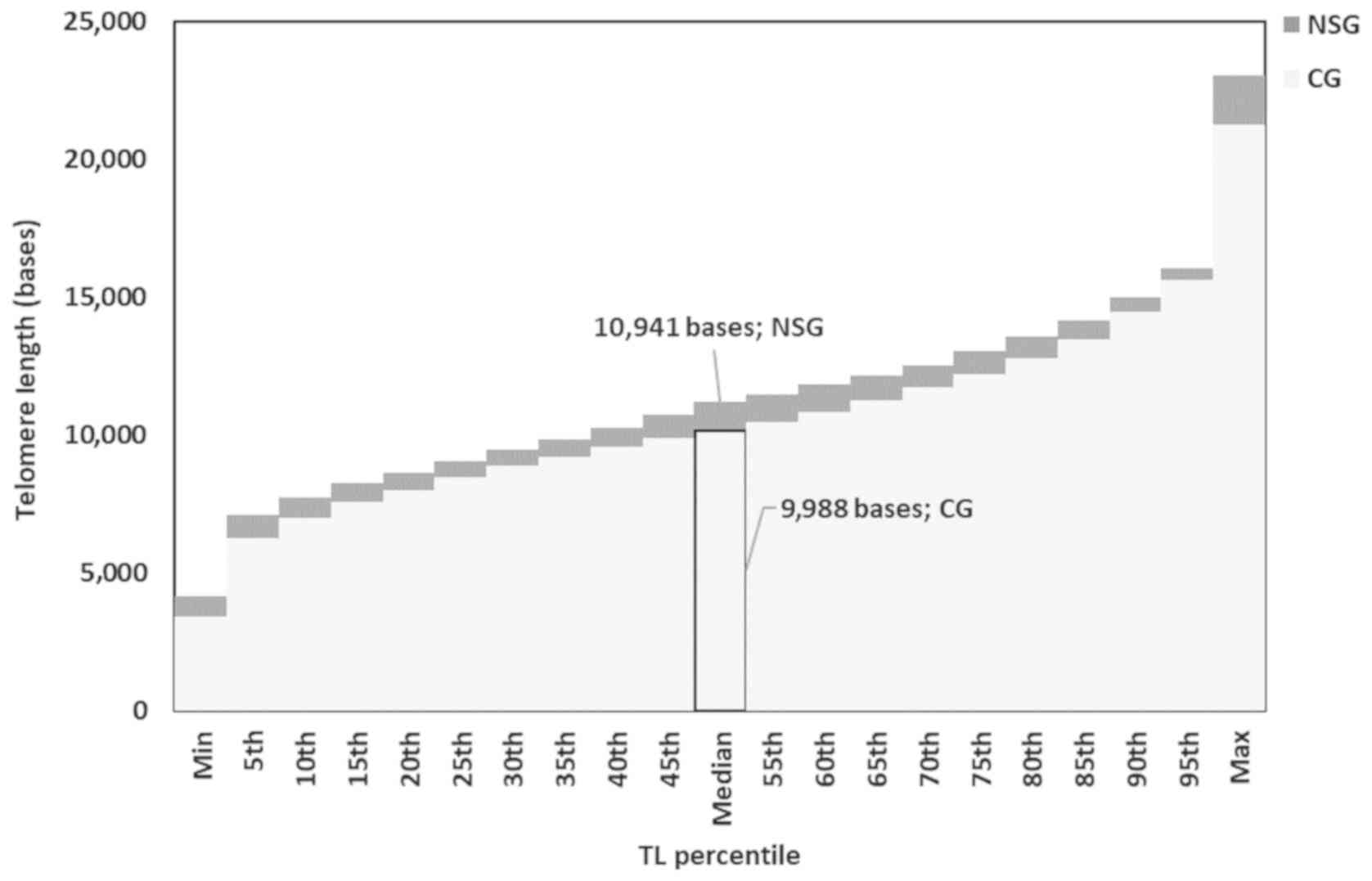
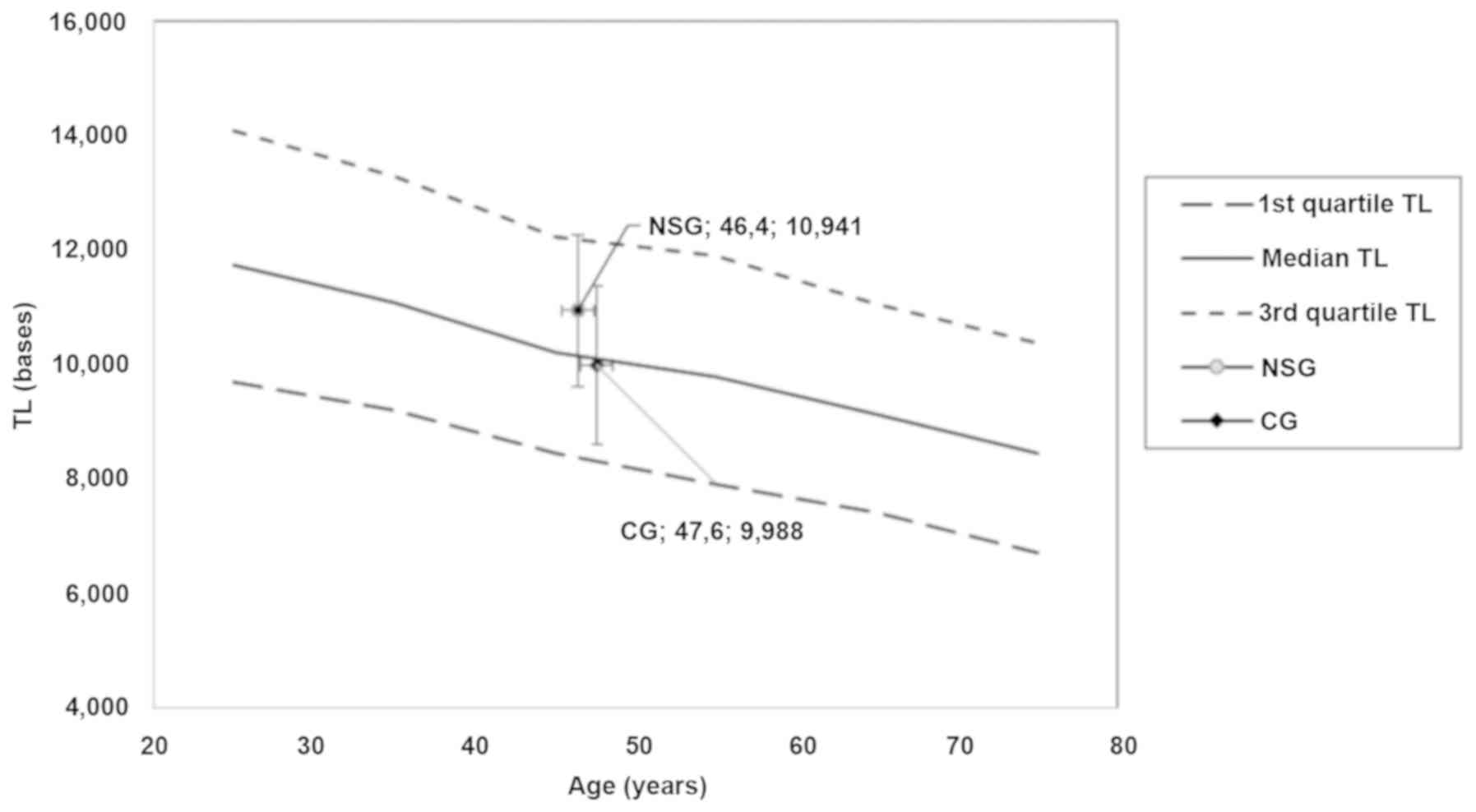
|
1
|
Starkweather AR, Alhaeeri AA, Montpetit A,
Brumelle J, Filler K, Montpetit M, Mohanraj L, Lyon DE and
Jackson-Cook CK: An integrative review of factors associated with
telomere length and implications for biobehavioral research. Nurs
Res. 63. pp. 36–50. 2014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blackburn EH, Chan S, Chang J, Fulton TB,
Krauskopf A, McEachern M, Prescott J, Roy J, Smith C and Wang H:
Molecular manifestations and molecular determinants of telomere
capping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 65:253–263. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Beyne-Rauzy O, Prade-Houdellier N, Demur
C, Recher C, Ayel J, Laurent G and Mansat-De Mas V: Tumor necrosis
factor- alpha inhibits hTERT gene expression in human myeloid
normal and leukemic cells. Blood. 106:3200–3205. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Westin ER, Aykin-Burns N, Buckingham EM,
Spitz DR, Goldman FD and Klingelhutz AJ: The p53/p21(WAF/CIP)
pathway mediates oxidative stress and senescence in dyskeratosis
congenita cells with telomerase insufficiency. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 14:985–997. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
5
|
Fragkiadaki P, Tsoukalas D, Fragkiadoulaki
I, Psycharakis C, Nikitovic D, Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM:
Telomerase activity in pregnancy complications (Review). Mol Med
Rep. 14:16–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujii H, Shao L, Colmegna I, Goronzy JJ
and Weyand CM: Telomerase insufficiency in rheumatoid arthritis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:4360–4365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vakonaki E, Tsiminikaki K, Plaitis S,
Fragkiadaki P, Tsoukalas D, Katsikantami I, Vaki G, Tzatzarakis MN,
Spandidos DA and Tsatsakis AM: Common mental disorders and
association with telomere length. Biomed Rep. 8:111–116.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu X, Amos CI, Zhu Y, Zhao H, Grossman BH,
Shay JW, Luo S, Hong WK and Spitz MR: Telomere dysfunction: A
potential cancer predisposition factor. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95. pp.
1211–1218. 2003, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Willeit P, Raschenberger J, Heydon EE,
Tsimikas S, Haun M, Mayr A, Weger S, Witztum JL, Butterworth AS,
Willeit J, et al: Leucocyte telomere length and risk of type 2
diabetes mellitus: New prospective cohort study and
literature-based meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e112483. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Calado RT and Young NS: Telomere diseases.
N Engl J Med. 361:2353–2365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Turner KJ, Vasu V and Griffin DK: Telomere
biology and human phenotype. Cells. 8:E732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sanders JL and Newman AB: Telomere length
in epidemiology: A biomarker of aging, age-related disease, both,
or neither? Epidemiol Rev. 35:112–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vera E, Bernardes de Jesus B, Foronda M,
Flores JM and Blasco MA: The rate of increase of short telomeres
predicts longevity in mammals. Cell Rep. 2:732–737. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vakonaki E, Tzatzarakis M, Tsiminikaki K,
Nathena D, Fragkiadaki P, Kalliantasi K, Kanaki K, Vaki G, Plaitis
S, Tsoukalas D, et al: Effect of chronic and heavy drug abuse on
biological aging. World Acad Sci. 1:67–73. 2019.
|
|
15
|
Tsatsakis A, Tsoukalas D, Fragkiadaki P,
Vakonaki E, Tzatzarakis M, Sarandi E, Nikitovic D, Tsilimidos G and
Alegakis AK: Developing BIOTEL: A semi-automated spreadsheet for
estimating telomere length and biological age. Front Genet.
10:842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Hallmarks of
telomeres in ageing research. J Pathol. 211:114–123. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muraki K, Nyhan K, Han L and Murnane JP:
Mechanisms of telomere loss and their consequences for chromosome
instability. Front Oncol. 2:1352012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hemann MT, Strong MA, Hao LY and Greider
CW: The shortest telomere, not average telomere length, is critical
for cell viability and chromosome stability. Cell. 107:67–77. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hao LY, Armanios M, Strong MA, Karim B,
Feldser DM, Huso D and Greider CW: Short telomeres, even in the
presence of telomerase, limit tissue renewal capacity. Cell.
123:1121–1131. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baltzis D, Meimeti E, Grammatikopoulou MG,
Roustit M, Mavrogonatou E, Kletsas D, Efraimidou S, Manes C,
Nikolouzakis TK, Tsiaoussis J, et al: Assessment of telomerase
activity in leukocytes of type 2 diabetes mellitus patients having
or not foot ulcer: Possible correlation with other clinical
parameters. Exp Ther Med. 15:3420–3424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nikolouzakis TK, Vassilopoulou L,
Fragkiadaki P, Mariolis Sapsakos T, Papadakis GZ, Spandidos DA,
Tsatsakis AM and Tsiaoussis J: Improving diagnosis, prognosis and
prediction by using biomarkers in CRC patients (Review). Oncol Rep.
39:2455–2472. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haycock PC, Heydon EE, Kaptoge S,
Butterworth AS, Thompson A and Willeit P: Leucocyte telomere length
and risk of cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ. 349. pp. g42272014, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Goglin SE, Farzaneh-Far R, Epel ES, Lin J,
Blackburn EH and Whooley MA: Change in leukocyte telomere length
predicts mortality in patients with stable coronary heart; disease
from the heart and soul study. PLoS One. 11:e01607482016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
De Meyer T, Vandepitte K, Denil S, De
Buyzere ML, Rietzschel ER and Bekaert S: A non-genetic,
epigenetic-like mechanism of telomere length inheritance? Eur J Hum
Genet. 22:10–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Armanios M: Telomeres and age-related
disease: How telomere biology informs clinical paradigms. J Clin
Invest. 123:996–1002. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pusceddu I, Herrmann M, Kirsch SH, Werner
C, Hübner U, Bodis M, Laufs U, Wagenpfeil S, Geisel J and Herrmann
W: Prospective study of telomere length and LINE-1 methylation in
peripheral blood cells: The role of B vitamins supplementation. Eur
J Nutr. 55:1863–1873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pusceddu I, Herrmann M, Kirsch SH, Werner
C, Hübner U, Bodis M, Laufs U, Widmann T, Wagenpfeil S, Geisel J,
et al: One-carbon metabolites and telomere length in a prospective
and randomized study of B- and/or D-vitamin supplementation. Eur J
Nutr. 56:1887–1898. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Richards JB, Valdes AM, Gardner JP,
Paximadas D, Kimura M, Nessa A, Lu X, Surdulescu GL, Swaminathan R,
Spector TD, et al: Higher serum vitamin D concentrations are
associated with longer leukocyte telomere length in women. Am J
Clin Nutr. 86:1420–1425. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Moores CJ, Fenech M and O'Callaghan NJ:
Telomere dynamics: The influence of folate and DNA methylation. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1229:76–88. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Holick MF: Vitamin D deficiency. N Engl J
Med. 357:266–281. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nazki FH, Sameer AS and Ganaie BA: Folate:
Metabolism, genes, polymorphisms and the associated diseases. Gene.
533:11–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Barden A, O'Callaghan N, Burke V, Mas E,
Beilin LJ, Fenech M, Irish AB, Watts GF, Puddey IB, Huang RC, et
al: n-3 fatty acid supplementation and leukocyte telomere length in
patients with chronic kidney disease. Nutrients. 8:1752016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calder PC: Polyunsaturated fatty acids and
inflammation. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:423–427. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Belury MA, Andridge R,
Malarkey WB and Glaser R: Omega- 3 supplementation lowers
inflammation and anxiety in medical students: A randomized
controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun. 25:1725–1734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nälsén C, Vessby B, Berglund L, Uusitupa
M, Hermansen K, Riccardi G, Rivellese A, Storlien L, Erkkilä A,
Ylä-Herttuala S, et al: Dietary (n-3) fatty acids reduce plasma
F2-isoprostanes but not prostaglandin F2alpha in healthy humans. J
Nutr. 136:1222–1228. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Rane G, Dai X, Shanmugam MK,
Arfuso F, Samy RP, Lai MK, Kappei D, Kumar AP and Sethi G: Ageing
and the telomere connection: An intimate relationship with
inflammation. Ageing Res Rev. 25:55–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shen J, Gammon MD, Terry MB, Wang Q,
Bradshaw P, Teitelbaum SL, Neugut AI and Santella RM: Telomere
length, oxidative damage, antioxidants and breast cancer risk. Int
J Cancer. 124:1637–1643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Furumoto K, Inoue E, Nagao N, Hiyama E and
Miwa N: Age-dependent telomere shortening is slowed down by
enrichment of intracellular vitamin C via suppression of oxidative
stress. Life Sci. 63:935–948. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yokoo S, Furumoto K, Hiyama E and Miwa N:
Slow- down of age-dependent telomere shortening is executed in
human skin keratinocytes by hormesis-like-effects of trace hydrogen
peroxide or by anti-oxidative effects of pro-vitamin C in common
concurrently with reduction of intracellular oxidative stress. J
Cell Biochem. 93:588–597. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kashino G, Kodama S, Nakayama Y, Suzuki K,
Fukase K, Goto M and Watanabe M: Relief of oxidative stress by
ascorbic acid delays cellular senescence of normal human and Werner
syndrome fibroblast cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 35:438–443. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tanaka Y, Moritoh Y and Miwa N: Age-
dependent telomere- shortening is repressed by phosphorylated
alpha-tocopherol together with cellular longevity and intracellular
oxidative-stress reduction in human brain microvascular
endotheliocytes. J Cell Biochem. 102:689–703. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsoukalas D, Fragkiadaki P, Docea AO,
Alegakis AK, Sarandi E, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis A, Razgonova MP and
Calina D: Discovering novel telomerase activators. Mol Med Rep. In
press.
|
|
43
|
Bailey RL, West KP Jr and Black RE: The
epidemiology of global micronutrient deficiencies. Ann Nutr Metab.
66(Suppl 2): 22–33. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fairfield KM and Fletcher RH: Vitamins for
chronic disease prevention in adults: Scientific review. JAMA.
287:3116–3126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
McIlrath J, Bouffler SD, Samper E,
Cuthbert A, Wojcik A, Szumiel I, Bryant PE, Riches AC, Thompson A,
Blasco MA, et al: Telomere length abnormalities in mammalian
radiosensitive cells. Cancer Res. 61:912–915. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lindqvist D, Epel ES, Mellon SH, Penninx
BW, Révész D, Verhoeven JE, Reus VI, Lin J, Mahan L, Hough CM, et
al: Psychiatric disorders and leukocyte telomere length: Underlying
mechanisms linking mental illness with cellular aging. Neurosci
Biobehav Rev. 55:333–364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Masi S, Salpea KD, Li K, Parkar M, Nibali
L, Donos N, Patel K, Taddei S, Deanfield JE, D'Aiuto F, et al:
Oxidative stress, chronic inflammation, and telomere length in
patients with periodontitis. Free Radic Biol Med. 50:730–735. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Watfa G, Dragonas C, Brosche T, Dittrich
R, Sieber CC, Alecu C, Benetos A and Nzietchueng R: Study of
telomere length and different markers of oxidative stress in
patients with Parkinson's disease. J Nutr Health Aging. 15:277–281.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ma D, Zhu W, Hu S, Yu X and Yang Y:
Association between oxidative stress and telomere length in Type 1
and Type 2 diabetic patients. J Endocrinol Invest. 36:1032–1037.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
de Vos-Houben JM, Ottenheim NR, Kafatos A,
Buijsse B, Hageman GJ, Kromhout D and Giltay EJ: Telomere length,
oxidative stress, and antioxidant status in elderly men in Zutphen
and Crete. Mech Ageing Dev. 133:373–377. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Prasad KN, Wu M and Bondy SC: Telomere
shortening during aging: Attenuation by antioxidants and anti-
inflammatory agents. Mech Ageing Dev. 164:61–66. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Paul L: Diet, nutrition and telomere
length. J Nutr Biochem. 22:895–901. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Herrmann M, Pusceddu I, Marz W and
Herrmann W: Telomere biology and age- related diseases. Clin Chem
Lab Med. 56:1210–1222. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kiecolt-Glaser JK, Epel ES, Belury MA,
Andridge R, Lin J, Glaser R, Malarkey WB, Hwang BS and Blackburn E:
Omega- 3 fatty acids, oxidative stress, and leukocyte telomere
length: A randomized controlled trial. Brain Behav Immun. 28:16–24.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|