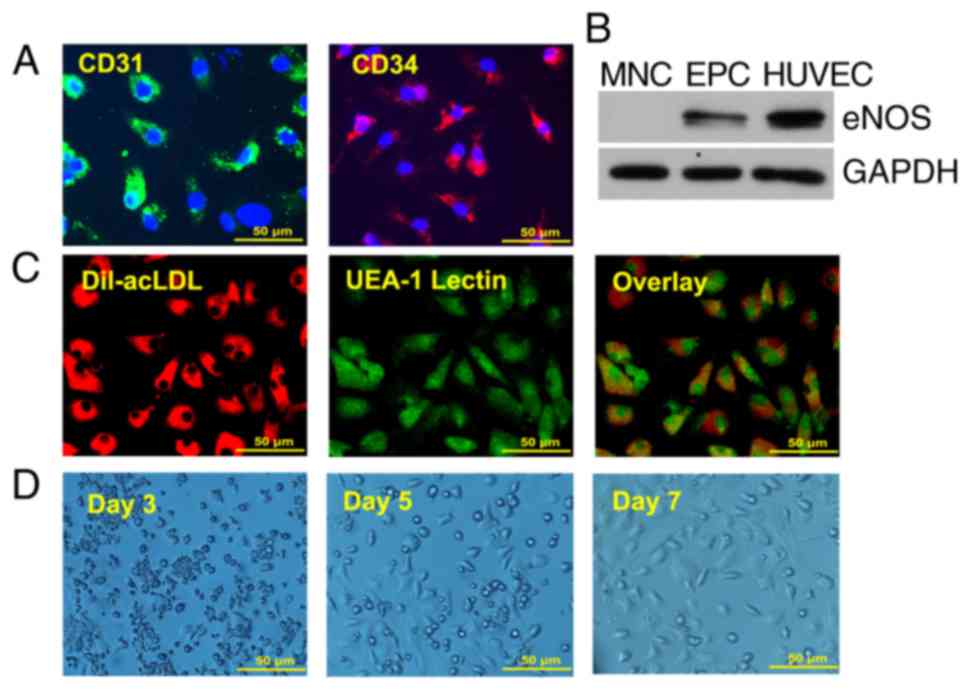
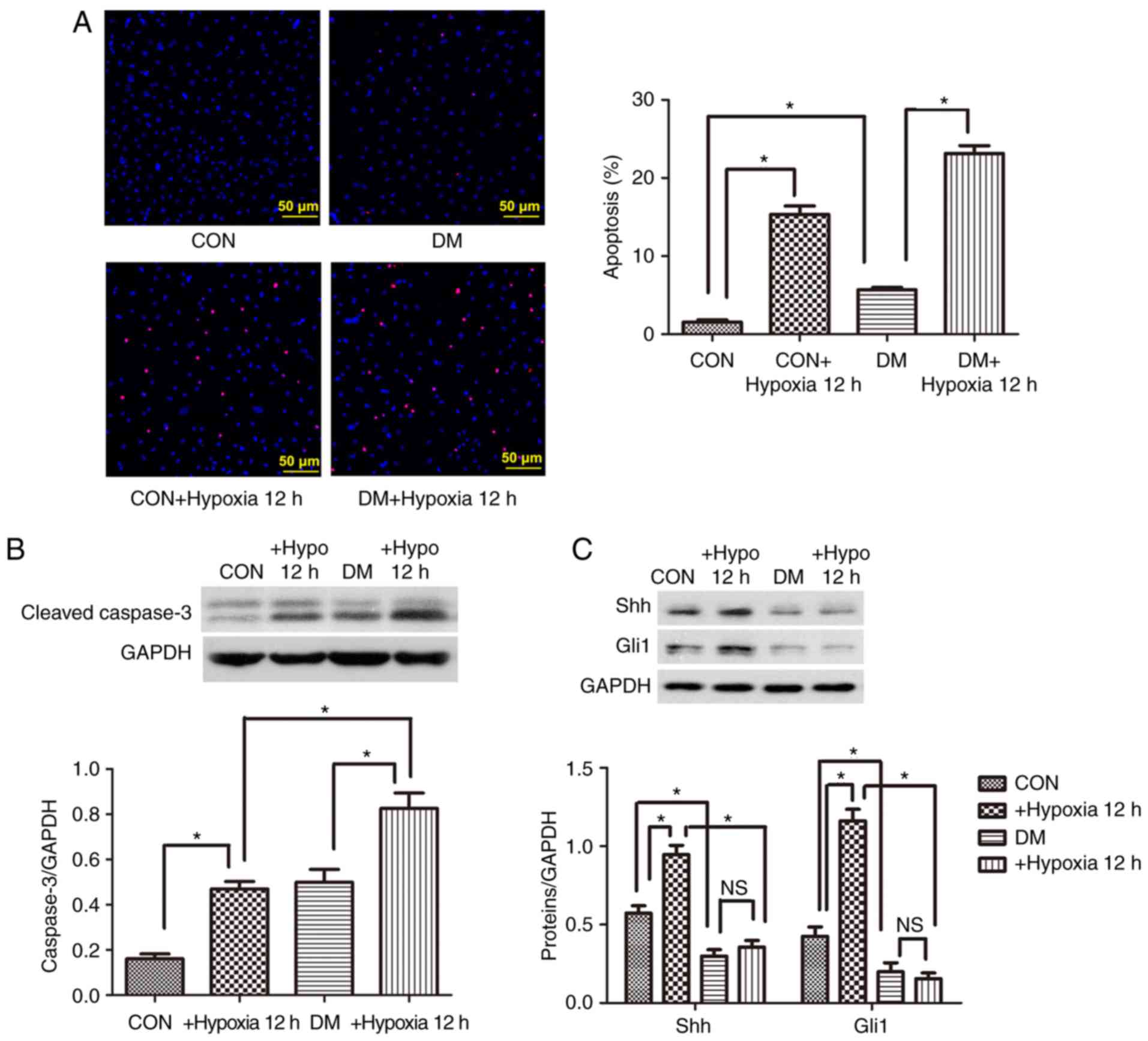
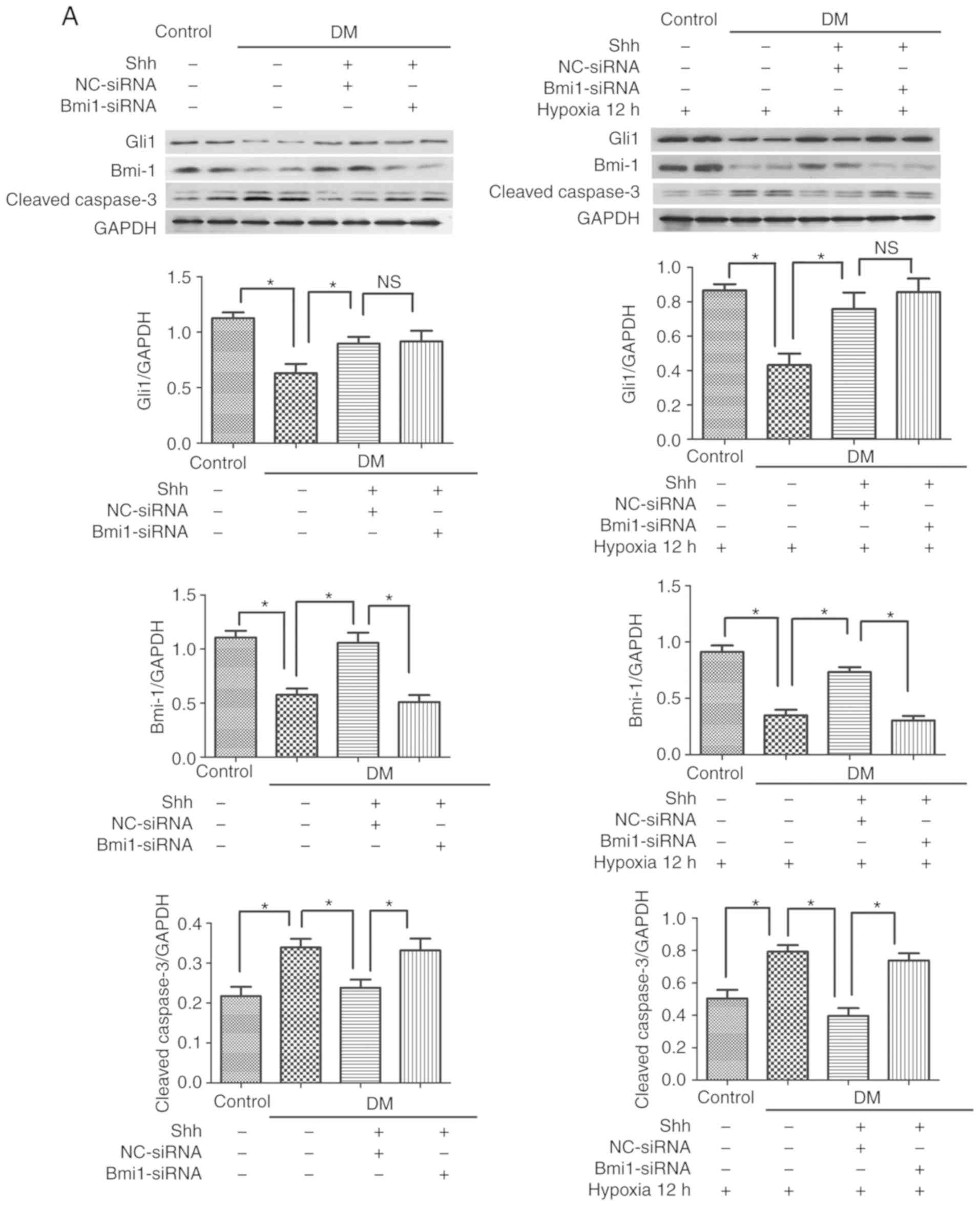
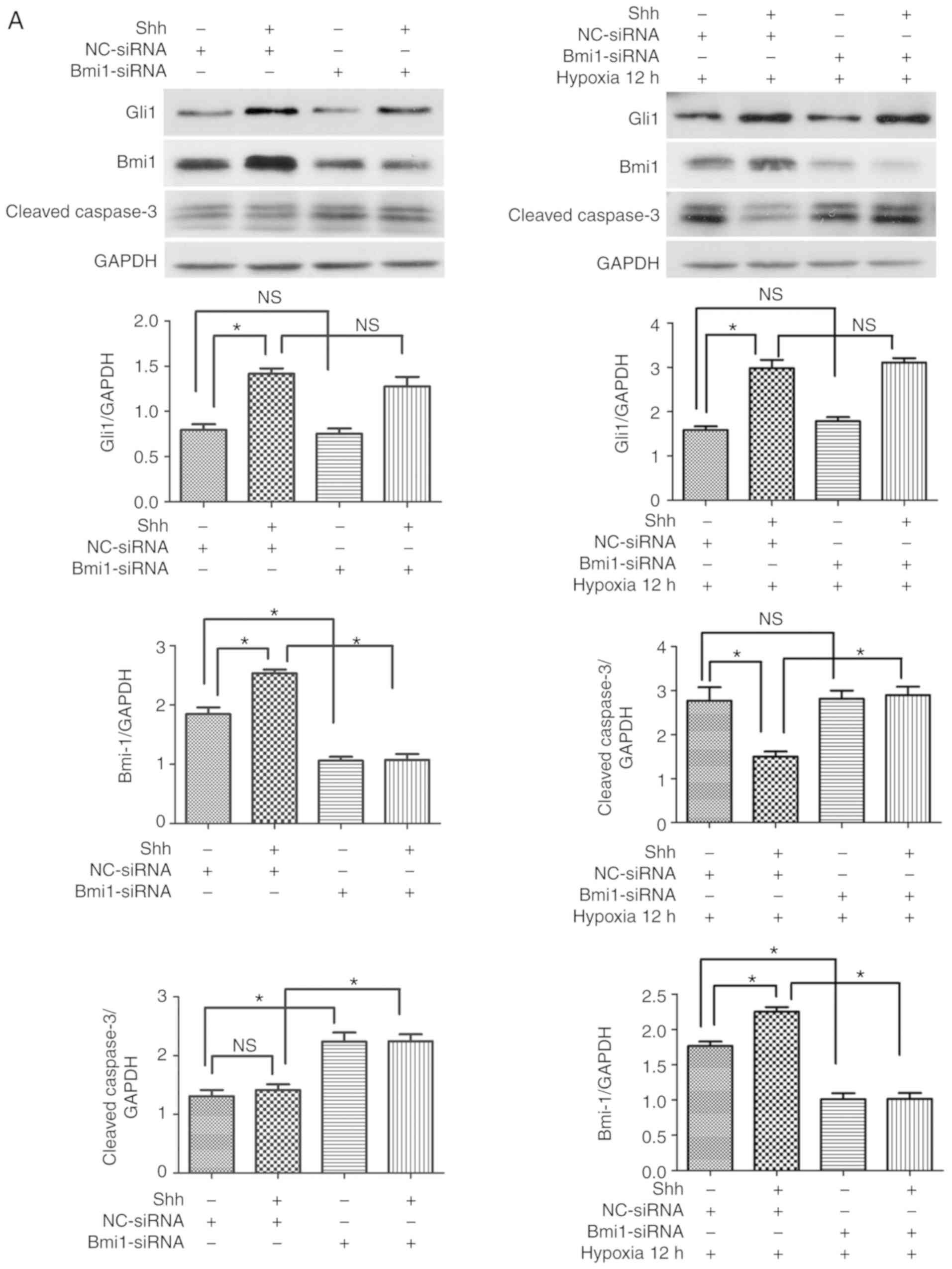
|
1
|
Patel NB and Balady GJ: Diagnostic and
prognostic testing to evaluate coronary artery disease in patients
with diabetes mellitus. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 11:11–20. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng R and Ma J: Angiogenesis in diabetes
and obesity. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 16:67–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Howangyin KY and Silvestre JS: Diabetes
mellitus and ischemic diseases: Molecular mechanisms of vascular
repair dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:1126–1135.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Co M, Tay E, Lee CH, Poh KK, Low A, Lim J,
Lim IH, Lim YT and Tan HC: Use of endothelial progenitor cell
capture stent (Genous Bio-Engineered R Stent) during primary
percutaneous coronary intervention in acute myocardial infarction:
Intermediate- to long-term clinical follow-up. Am Heart J.
155:128–132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhu J, Song J, Yu L, Zheng H, Zhou B, Weng
S and Fu G: Safety and efficacy of autologous thymosin β4
pre-treated endothelial progenitor cell transplantation in patients
with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction: A pilot
study. Cytotherapy. 18:1037–1042. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Georgescu A, Alexandru N, Constantinescu
A, Titorencu I and Popov D: The promise of EPC-based therapies on
vascular dysfunction in diabetes. Eur J Pharmacol. 669:1–6. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ling L, Shen Y, Wang K, Jiang C, Fang C,
Ferro A, Kang L and Xu B: Worse clinical outcomes in acute
myocardial infarction patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus:
Relevance to impaired endothelial progenitor cells mobilization.
PLoS One. 7:pp. e507392012, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
António N, Fernandes R, Ribeiro CF and
Providência LA: Challenges in vascular repair by endothelial
progenitor cells in diabetic patients. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord
Drug Targets. 10:161–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Briscoe J and Thérond PP: The mechanisms
of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:416–429. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Álvarez-Buylla A and Ihrie RA: Sonic
hedgehog signaling in the postnatal brain. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
33:105–111. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lopez-Rios J: The many lives of SHH in
limb development and evolution. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 49:116–124.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rimkus TK, Carpenter RL, Qasem S, Chan M
and Lo HW: Targeting the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway: Review
of smoothened and gli inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 8. pp. E222016,
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Xiao Q, Hou N, Wang YP, He LS, He YH,
Zhang GP, Yi Q, Liu SM, Chen MS and Luo JD: Impaired sonic hedgehog
pathway contributes to cardiac dysfunction in type 1 diabetic mice
with myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. 95:507–516. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiao Q, Yang YA, Zhao XY, He LS, Qin Y, He
YH, Zhang GP and Luo JD: Oxidative stress contributes to the
impaired sonic hedgehog pathway in type 1 diabetic mice with
myocardial infarction. Exp Ther Med. 10:1750–1758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Qin Y, He YH, Hou N, Zhang GS, Cai Y,
Zhang GP, Xiao Q, He LS, Li SJ, Yi Q and Luo JD: Sonic hedgehog
improves ischemia-induced neovascularization by enhancing
endothelial progenitor cell function in type 1 diabetes. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 423:30–39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Gao M, Ma MM, Tang YB, Zhou JG,
Wang GL, Du YH and Guan YY: Endophilin A2 protects H2O2-induced
apoptosis by blockade of Bax translocation in rat basilar artery
smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 92:122–133. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Marrotte EJ, Chen DD, Hakim JS and Chen
AF: Manganese superoxide dismutase expression in endothelial
progenitor cells accelerates wound healing in diabetic mice. J Clin
Invest. 120:4207–4219. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Krishnamurthy P, Thal M, Verma S, Hoxha E,
Lambers E, Ramirez V, Qin G, Losordo D and Kishore R: IL-10
deficiency impairs bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell
(EPC) survival and function in ischemic myocardium. Circ Res.
109:1280–1289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun YY, Bai WW, Wang B, Lu XT, Xing YF,
Cheng W, Liu XQ and Zhao YX: Period 2 is essential to maintain
early endothelial progenitor cell function in vitro and
angiogenesis after myocardial infarction in mice. J Cell Mol Med.
18:907–918. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang H, He Y, Zhang G, Li X, Yan S, Hou
N, Xiao Q, Huang Y, Luo M, Zhang G, et al: HDAC2 is required by the
physiological concentration of glucocorticoid to inhibit
inflammation in cardiac fibroblasts. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
95:1030–1038. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cao L, Bombard J, Cintron K, Sheedy J,
Weetall ML and Davis TW: BMI1 as a novel target for drug discovery
in cancer. J Cell Biochem. 112:2729–2741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shahi MH, Farheen S, Mariyath MP and
Castresana JS: Potential role of Shh-Gli1-BMI1 signaling pathway
nexus in glioma chemoresistance. Tumour Biol. 37:15107–15114. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Venugopal C, Manoranjan B,
McFarlane N, O'Farrell E, Nolte S, Gunnarsson T, Hollenberg R,
Kwiecien J, Northcott P, et al: Sonic hedgehog regulates Bmi1 in
human medulloblastoma brain tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene.
31:187–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Subkhankulova T, Zhang X, Leung C and
Marino S: Bmi1 directly represses p21Waf1/Cip1 in Shh-induced
proliferation of cerebellar granule cell progenitors. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 45:151–162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Savvatis K, Westermann D, Schultheiss HP
and Tschöpe C: Kinins in cardiac inflammation and regeneration:
Insights from ischemic and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Neuropeptides.
44:119–125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Aragona CO, Imbalzano E, Mamone F, Cairo
V, Lo Gullo A, D'Ascola A, Sardo MA, Scuruchi M, Basile G, Saitta A
and Mandraffino G: Endothelial progenitor cells for diagnosis and
prognosis in cardiovascular disease. Stem Cells Int.
2016:80437922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
António N, Fernandes R, Soares A, Soares
F, Lopes A, Carvalheiro T, Paiva A, Pêgo GM, Providência LA,
Gonçalves L and Ribeiro CF: Reduced levels of circulating
endothelial progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction
patients with diabetes or pre-diabetes: Accompanying the glycemic
continuum. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 13:1012014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fu JR, Liu WL, Zhou JF, Sun HY, Xu HZ, Luo
L, Zhang H and Zhou YF: Sonic hedgehog protein promotes bone
marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cell proliferation, migration
and VEGF production via PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathways. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 27:685–693. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanaya K, Ii M, Okazaki T, Nakamura T,
Horii-Komatsu M, Alev C, Akimaru H, Kawamoto A, Akashi H, Tanaka H,
et al: Sonic Hedgehog signaling regulates vascular differentiation
and function in human CD34 positive cells: Vasculogenic CD34(+)
cells with Sonic Hedgehog. Stem Cell Res. 14:165–176. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kusano KF, Pola RT, Murayama T, Curry C,
Kawamoto A, Iwakura A, Shintani S, Ii M, Asai J, Tkebuchava T, et
al: Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: Tissue repair through
transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med.
11:1197–1204. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahmed RP, Haider KH, Shujia J, Afzal MR
and Ashraf M: Sonic Hedgehog gene delivery to the rodent heart
promotes angiogenesis via iNOS/netrin-1/PKC pathway. PLoS One.
5:pp. e85762010, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiao Q, Yang Y, Qin Y, He YH, Chen KX, Zhu
JW, Zhang GP and Luo JD: AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent
autophagy mediated the protective effect of sonic hedgehog pathway
on oxygen glucose deprivation-induced injury of cardiomyocytes.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:419–425. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Roncalli J, Renault MA, Tongers J, Misener
S, Thorne T, Kamide C, Jujo K, Tanaka T, Ii M, Klyachko E and
Losordo DW: Sonic hedgehog-induced functional recovery after
myocardial infarction is enhanced by AMD3100-mediated
progenitor-cell mobilization. J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:2444–2452.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu Z, Tu K, Wang Y, Yao B, Li Q, Wang L,
Dou C, Liu Q and Zheng X: Hypoxia accelerates aggressiveness of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells involving oxidative stress,
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and non-canonical hedgehog
signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1856–1868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hung YH, Chang SH, Huang CT, Yin JH, Hwang
CS, Yang LY and Yang DI: Inhibitor of differentiation-1 and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediate sonic hedgehog induction by
amyloid beta-peptide in rat cortical neurons. Mol Neurobiol.
53:793–809. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Spivak-Kroizman TR, Hostetter G, Posner R,
Aziz M, Hu C, Demeure MJ, Von Hoff D, Hingorani SR, Palculict TB,
Izzo J, et al: Hypoxia triggers hedgehog-mediated tumor-stromal
interactions in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 73:3235–3247. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Onishi H, Kai M, Odate S, Iwasaki H,
Morifuji Y, Ogino T, Morisaki T, Nakashima Y and Katano M: Hypoxia
activates the hedgehog signaling pathway in a ligand-independent
manner by upregulation of Smo transcription in pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Sci. 102:1144–1150. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bijlsma MF, Groot AP, Oduro JP, Franken
RJ, Schoenmakers SH, Peppelenbosch MP and Spek CA: Hypoxia induces
a hedgehog response mediated by HIF-1alpha. J Cell Mol Med.
13:2053–2060. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Marfella R, D'Amico M, Di Filippo C,
Piegari E, Nappo F, Esposito K, Berrino L, Rossi F and Giugliano D:
Myocardial infarction in diabetic rats: Role of hyperglycaemia on
infarct size and early expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
Diabetologia. 45:1172–1181. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ceriello A, Quagliaro L, D'Amico M, Di
Filippo C, Marfella R, Nappo F, Berrino L, Rossi F and Giugliano D:
Acute hyperglycemia induces nitrotyrosine formation and apoptosis
in perfused heart from rat. Diabetes. 51:1076–1082. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Banerjee Mustafi S, Aznar N, Dwivedi SK,
Chakraborty PK, Basak R, Mukherjee P, Ghosh P and Bhattacharya R:
Mitochondrial BMI1 maintains bioenergetic homeostasis in cells.
FASEB J. 30:4042–4055. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin X, Ojo D, Wei F, Wong N, Gu Y and Tang
D: A novel aspect of tumorigenesis—BMI1 functions in regulating dna
damage response. Biomolecules. 5:3396–3415. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Allegra E, Trapasso S, Pisani D and Puzzo
L: The role of BMI1 as a biomarker of cancer stem cells in head and
neck cancer: A review. Oncology. 86:199–205. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ren H, Du P, Ge Z, Jin Y, Ding D, Liu X
and Zou Q: TWIST1 and BMI1 in cancer metastasis and
chemoresistance. J Cancer. 7:1074–1080. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yao D, Wang Y, Xue L, Wang H, Zhang J and
Zhang X: Different expression pattern and significance of
p14ARF-Mdm2-p53 pathway and Bmi-1 exist between gastric cardia and
distal gastric adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 44:844–851. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xu XH, Liu Y, Li DJ, Hu J, Su J, Huang Q,
Lu MQ, Yi F, Bao D and Fu YZ: Effect of shRNA-mediated gene
silencing of Bmi-1 expression on chemosensitivity of CD44+
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cancer stem-like cells. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 15:NP27–NP39. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kundu N, Domingues CC, Chou C, Ahmadi N,
Houston S, Jerry DJ and Sen S: Use of p53-silenced endothelial
progenitor cells to treat ischemia in diabetic peripheral vascular
disease. J Am Heart Assoc. 6:pp. e0051462017, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Brownlee M: Biochemistry and molecular
cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature. 414:813–820. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Feldman EL: Oxidative stress and diabetic
neuropathy: A new understanding of an old problem. J Clin Invest.
111:431–433. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kim WK, Meliton V, Bourquard N, Hahn TJ
and Parhami F: Hedgehog signaling and osteogenic differentiation in
multipotent bone marrow stromal cells are inhibited by oxidative
stress. J Cell Biochem. 111:1199–1209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Larrick JW and Mendelsohn A: Applied
healthspan engineering. Rejuvenation Res. 13:265–280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen X, Gu M, Zhao X, Zheng X, Qin Y and
You X: Deterioration of cardiac function after acute myocardial
infarction is prevented by transplantation of modified endothelial
progenitor cells over-expressing endothelial NO synthases. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 31:355–365. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bianconi V, Sahebkar A, Kovanen P,
Bagaglia F, Ricciuti B, Calabrò P, Patti G and Pirro M: Endothelial
and cardiac progenitor cells for cardiovascular repair: A
controversial paradigm in cell therapy. Pharmacol Ther.
181:156–168. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|