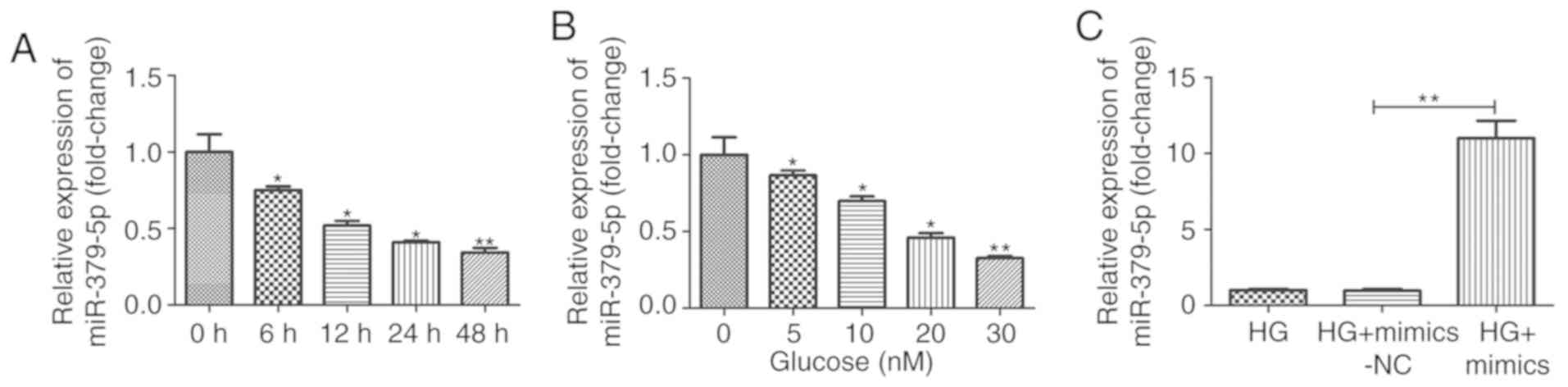
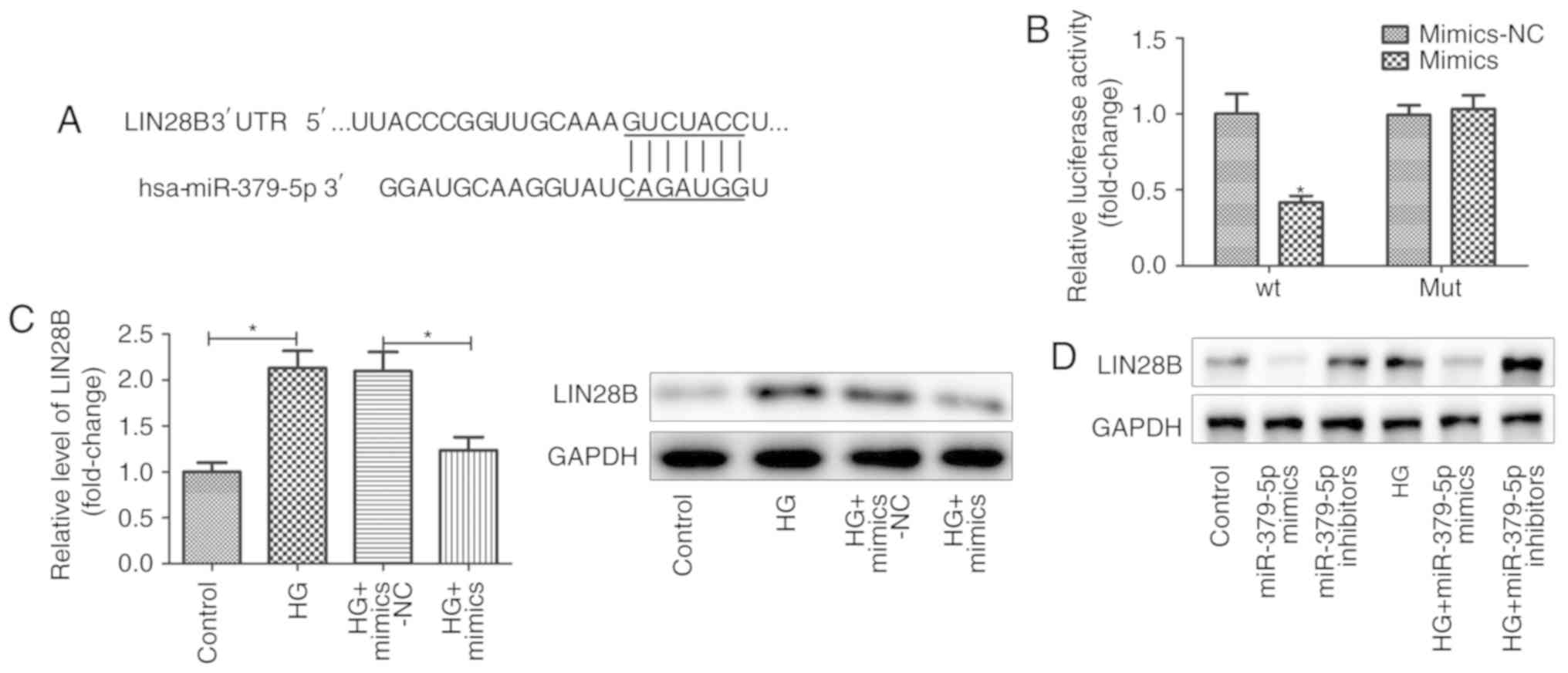
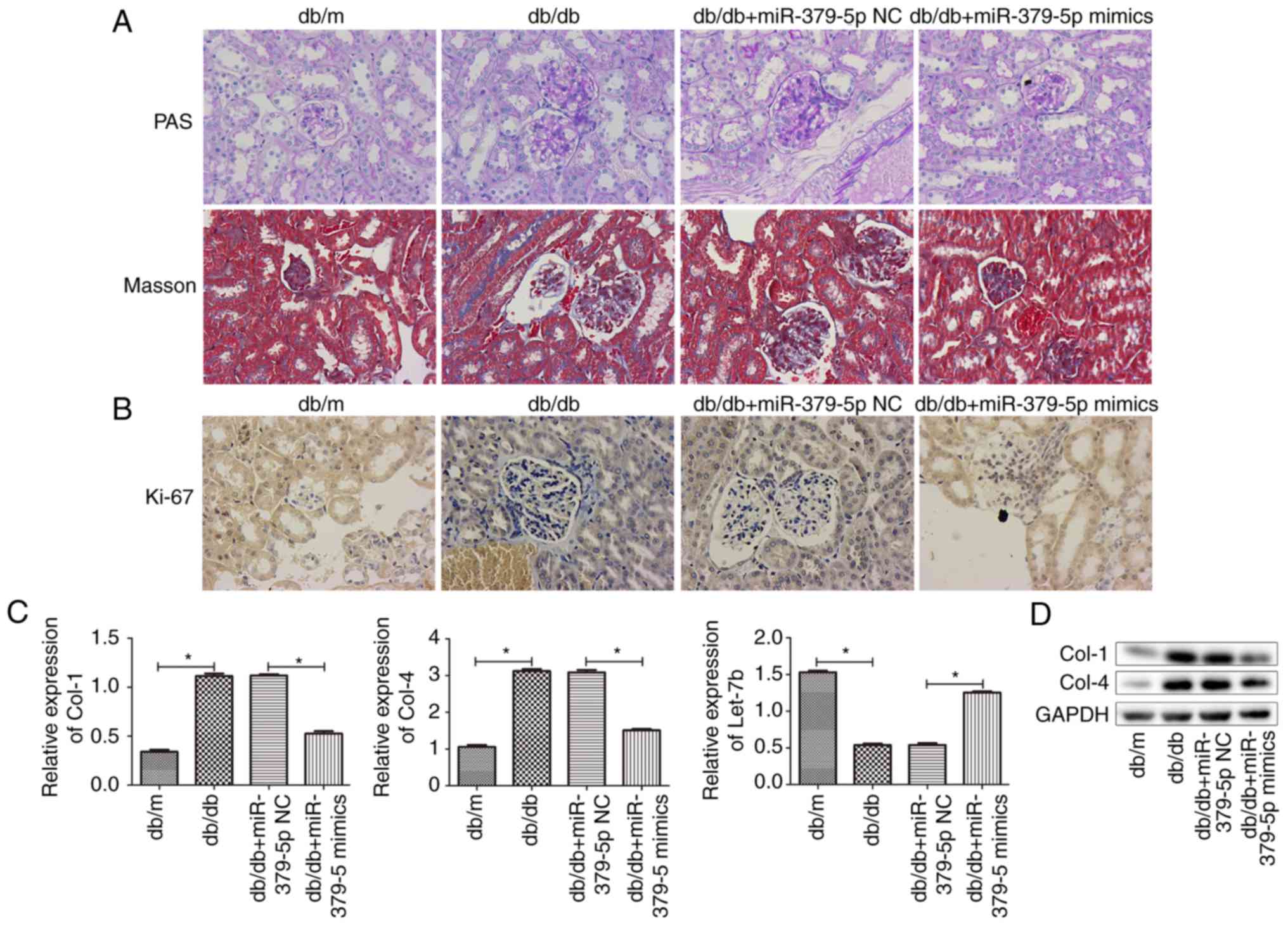
|
1
|
Incidence and prevalence of ESRD: United
States Renal Data System. Am J Kidney Dis. 32(2 Suppl 1): pp.
S38–S49. 1998, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun YM, Su Y, Li J and Wang LF: Recent
advances in understanding the biochemical and molecular mechanism
of diabetic nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 433:359–361.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbach N: Pathogenesis of diabetes
mellitus and diabetic complications. Studies on diabetic mouse
models. Pathologe. 33(Suppl 2): pp. S318–S324. 2012, In German.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gholaminejad A, Abdul Tehrani H and
Gholami Fesharaki M: Identification of candidate microRNA
biomarkers in diabetic nephropathy: A meta-analysis of profiling
studies. J Nephrol. 31:813–831. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Allison SJ: Diabetic nephropathy: A lncRNA
and miRNA mega-cluster in diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:7132016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Alvarez ML and DiStefano JK: Towards
microRNA-based therapeutics for diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia.
56:444–456. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cardenas-Gonzalez M, Srivastava A,
Pavkovic M, Bijol V, Rennke HG, Stillman IE, Zhang X, Parikh S,
Rovin BH, Afkarian M, et al: Identification, confirmation, and
replication of novel urinary MicroRNA biomarkers in lupus nephritis
and diabetic nephropathy. Clin Chem. 63:1515–1526. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu F, Zhang ZP, Xin GD, Guo LH, Jiang Q
and Wang ZX: miR-192 prevents renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis in
diabetic nephropathy by targeting Egr1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:4252–4260. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Peng J, Wu Y, Deng Z, Zhou Y, Song T, Yang
Y, Zhang X, Xu T, Xia M, Cai A, et al: miR-377 promotes white
adipose tissue inflammation and decreases insulin sensitivity in
obesity via suppression of sirtuin-1 (SIRT1). Oncotarget.
8:70550–70563. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu Wu J, Ding J, Zhu Y, Lu M, Zhou K, Xie
J, Xu X, Shen Y, Chen XY, et al: miR-455-3p suppresses renal
fibrosis through repression of ROCK2 expression in diabetic
nephropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 503:977–983. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu X, Zhang C, Fan Q, Liu X, Yang G,
Jiang Y and Wang L: Inhibiting microRNA-503 and microRNA-181d with
losartan ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in KKAy mice. Med Sci
Monit. 22:3902–3909. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Balzeau J, Menezes MR, Cao S and Hagan JP:
The LIN28/let-7 pathway in cancer. Front Genet. 8:312017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Park JT, Kato M, Lanting L, Castro N, Nam
BY, Wang M, Kang SW and Natarajan R: Repression of let-7 by
transforming growth factor-β1-induced Lin28 up-regulates collagen
expression in glomerular mesangial cells under diabetic conditions.
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 307:F1390–F1403. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim YS, Reddy MA, Lanting L, Adler SG and
Natarajan R: Differential behavior of mesangial cells derived from
12/15-lipoxygenase knockout mice relative to control mice. Kidney
Int. 64:1702–1714. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shao Y, Lv C, Wu C, Zhou Y and Wang Q:
Mir-217 promotes inflammation and fibrosis in high glucose cultured
rat glomerular mesangial cells via Sirt1/HIF-1α signaling pathway.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 32:534–543. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang Y, Wang S, Qian W, Ji D, Wang Q,
Zhang Z, Wang S, Ji B, Fu Z and Sun Y: uc.338 targets p21 and
cyclin D1 via PI3K/AKT pathway activation to promote cell
proliferation in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 40:1119–1128.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kolset SO, Reinholt FP and Jenssen T:
Diabetic nephropathy and extracellular matrix. J Histochem
Cytochem. 60:976–986. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou SX, Huo DM, He XY, Yu P, Xiao YH, Ou
CL, Jiang RM, Li D and Li H: High glucose/lysophosphatidylcholine
levels stimulate extracellular matrix deposition in diabetic
nephropathy via plateletactivating factor receptor. Mol Med Rep.
17:2366–2372. 2018.
|
|
21
|
McWhorter ES, West RC, Russ JE, Ali A,
Winger QA and Bouma GJ: LIN28B regulates androgen receptor in human
trophoblast cells through Let-7c. Mol Reprod Dev. Jun 19–2019, Epub
ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : 2019, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim CW, Vo MT, Kim HK, Lee HH, Yoon NA,
Lee BJ, Min YJ, Joo WD, Cha HJ, Park JW and Cho WJ: Ectopic
over-expression of tristetraprolin in human cancer cells promotes
biogenesis of let-7 by down-regulation of Lin28. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:3856–3869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bera A, Das F, Ghosh-Choudhury N,
Mariappan MM, Kasinath BS and Ghosh Choudhury G: Reciprocal
regulation of miR-214 and PTEN by high glucose regulates renal
glomerular mesangial and proximal tubular epithelial cell
hypertrophy and matrix expansion. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
313:C430–C447. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen D, Li Y, Mei Y, Geng W, Yang J, Hong
Q, Feng Z, Cai G, Zhu H, Shi S, et al: miR-34a regulates mesangial
cell proliferation via the PDGFR-β/Ras-MAPK signaling pathway. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 71:4027–4042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jee YH, Wang J, Yue S, Jennings M, Clokie
SJ, Nilsson O, Lui JC and Baron J: Mir-374-5p, mir-379-5p, and
mir-503-5p regulate proliferation and hypertrophic differentiation
of growth plate chondrocytes in male rats. Endocrinology.
159:1469–1478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liang Y, Zhao G, Tang L, Zhang J, Li T and
Liu Z: miR-1003p and miR-8773pregulate overproduction of IL-8 and
IL-1β in mesangial cells activated by secretory IgA from IgA
nephropathy patients. Exp Cell Res. 347:312–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sun T, Yang J, Dong W, Wang R, Ma P, Kang
P, Zhang H, Xie C, Du J and Zhao L: Down-regulated miR-15a mediates
the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular epithelial
cells promoted by high glucose. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
78:1363–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang B, Yao K, Wise AF, Lau R, Shen HH,
Tesch GH and Ricardo SD: miR-378 reduces mesangial hypertrophy and
kidney tubular fibrosis via MAPK signalling. Clin Sci (Lond).
131:411–423. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang X, Shen E, Wang Y, Jiang Z, Gui D,
Cheng D, Chen T and Wang N: miR-196a regulates high glucose-induced
mesangial cell hypertrophy by targeting p27kip1. J Lab Autom.
20:491–499. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Du B, Ma LM, Huang MB, Zhou H, Huang HL,
Shao P, Chen YQ and Qu LH: High glucose down-regulates miR-29a to
increase collagen IV production in HK-2 cells. FEBS Lett.
584:811–816. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu H, Zhao J and Lv J: Inhibitory effects
of miR-101 overexpression on cervical cancer SiHa cells. Eur J
Gynaecol Oncol. 38:236–240. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Laddha SV, Nayak S, Paul D, Reddy R,
Sharma C, Jha P, Hariharan M, Agrawal A, Chowdhury S, Sarkar C and
Mukhopadhyay A: Genome-wide analysis reveals downregulation of
miR-379/miR-656 cluster in human cancers. Biol Direct. 8:102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Khan S, Brougham CL, Ryan J, Sahrudin A,
O'Neill G, Wall D, Curran C, Newell J, Kerin MJ and Dwyer RM:
miR-379 regulates cyclin B1 expression and is decreased in breast
cancer. PLoS One. 8:pp. e687532013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nayak S, Aich M, Kumar A, Sengupta S,
Bajad P, Dhapola P, Paul D, Narta K, Purkrait S, Mehani B, et al:
Novel internal regulators and candidate miRNAs within
miR-379/miR-656 miRNA cluster can alter cellular phenotype of human
glioblastoma. Sci Rep. 8:76732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Huang DJ, Huang JZ, Yang J, Li YH, Luo YC,
He HY and Huang HJ: Bioinformatic identification of IGF1 as a hub
gene in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and in-vitro analysis of the
chemosensitizing effect of miR-379 via suppressing the IGF1/IGF1R
signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:5098–5106.
2016.
|
|
36
|
Hao GJ, Hao HJ, Ding YH, Wen H, Li XF,
Wang QR and Zhang BB: Suppression of EIF4G2 by miR-379 potentiates
the cisplatin chemosensitivity in nonsmall cell lung cancer cells.
FEBS Lett. 591:636–645. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yi J and An Y: Circulating miR-379 as a
potential novel biomarker for diagnosis of acute myocardial
infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:540–546. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xu Z, Han Y, Liu J, Jiang F, Hu H, Wang Y,
Liu Q, Gong Y and Li X: miR-135b-5p and miR-499a-3ppromote cell
proliferation and migration in atherosclerosis by directly
targeting MEF2C. Sci Rep. 5:122762015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Cheng SW, Tsai HW, Lin YJ, Cheng PN, Chang
YC, Yen CJ, Huang HP, Chuang YP, Chang TT, Lee CT, et al: Lin28B is
an oncofetal circulating cancer stem cell-like marker associated
with recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 8:pp.
e800532013, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
King CE, Cuatrecasas M, Castells A,
Sepulveda AR, Lee JS and Rustgi AK: LIN28B promotes colon cancer
progression and metastasis. Cancer Res. 71:4260–4268. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alajez NM, Shi W, Wong D, Lenarduzzi M,
Waldron J, Weinreb I and Liu FF: Lin28b promotes head and neck
cancer progression via modulation of the insulin-like growth factor
survival pathway. Oncotarget. 3:1641–1652. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kugel S, Sebastian C, Fitamant J, Ross KN,
Saha SK, Jain E, Gladden A, Arora KS, Kato Y, Rivera MN, et al:
SIRT6 suppresses pancreatic cancer through control of lin28b. Cell.
165:1401–1415. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Piskounova E, Polytarchou C, Thornton JE,
LaPierre RJ, Pothoulakis C, Hagan JP, Iliopoulos D and Gregory RI:
Lin28A and Lin28B inhibit let-7 microRNA biogenesis by distinct
mechanisms. Cell. 147:1066–1079. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
McDaniel K, Huang L, Sato K, Wu N, Annable
T, Zhou T, Ramos-Lorenzo S, Wan Y, Huang Q, Francis H, et al: The
let-7/Lin28 axis regulates activation of hepatic stellate cells in
alcoholic liver injury. J Biol Chem. 292:11336–11347. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liang H, Liu S, Chen Y, Bai X, Liu L, Dong
Y, Hu M, Su X, Chen Y, Huangfu L, et al: miR-26a suppresses EMT by
disrupting the Lin28B/let-7d axis: Potential cross-talks among
miRNAs in IPF. J Mol Med (Berl). 94:pp. 655–665. 2016, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hills CE and Squires PE: TGF-beta1-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and therapeutic intervention
in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 31:68–74. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhu H, Shyh-Chang N, Segre AV, Shinoda G,
Shah SP, Einhorn WS, Takeuchi A, Engreitz JM, Hagan JP, Kharas MG,
et al: The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism. Cell.
147:81–94. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Frost RJ and Olson EN: Control of glucose
homeostasis and insulin sensitivity by the Let-7 family of
microRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:21075–21080. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ji J, Tao P and He L: Kangxianling
decoction prevents renal fibrosis in rats with 5/6 nephrectomy and
inhibits Ang II-induced ECM production in glomerular mesangial
cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 139:367–372. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee EJ, Kang MK, Kim DY, Kim YH, Oh H and
Kang YH: Chrysin inhibits advanced glycation end products-induced
kidney fibrosis in renal mesangial cells and diabetic kidneys.
Nutrients. 10:E8822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|