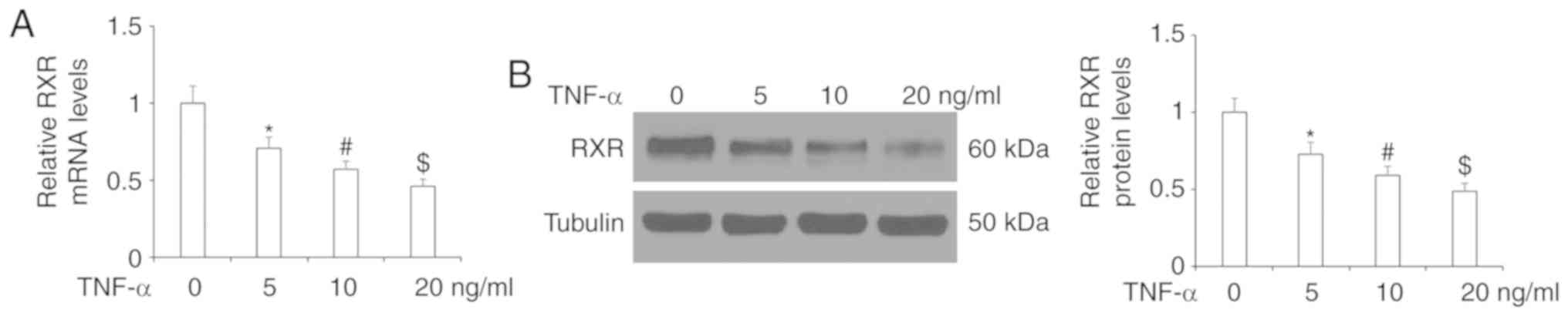
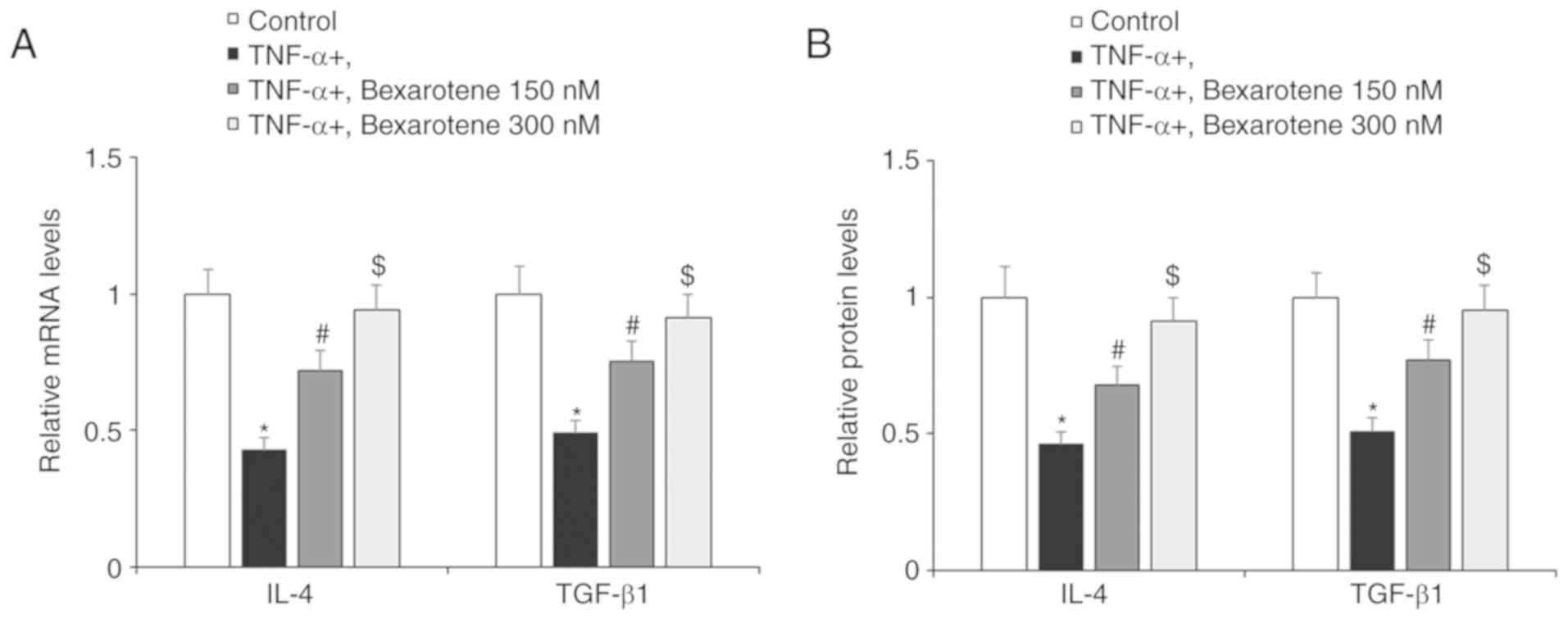
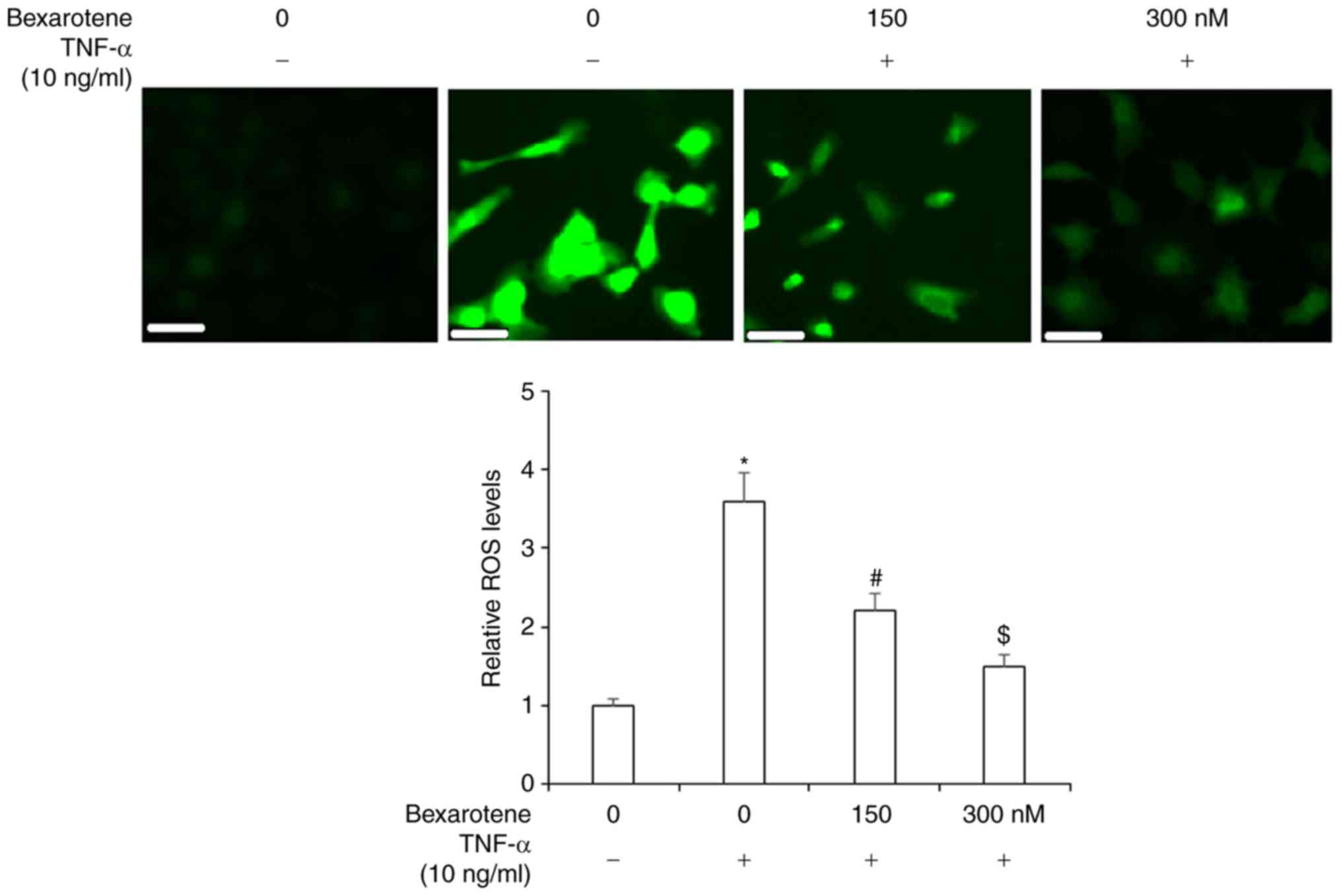
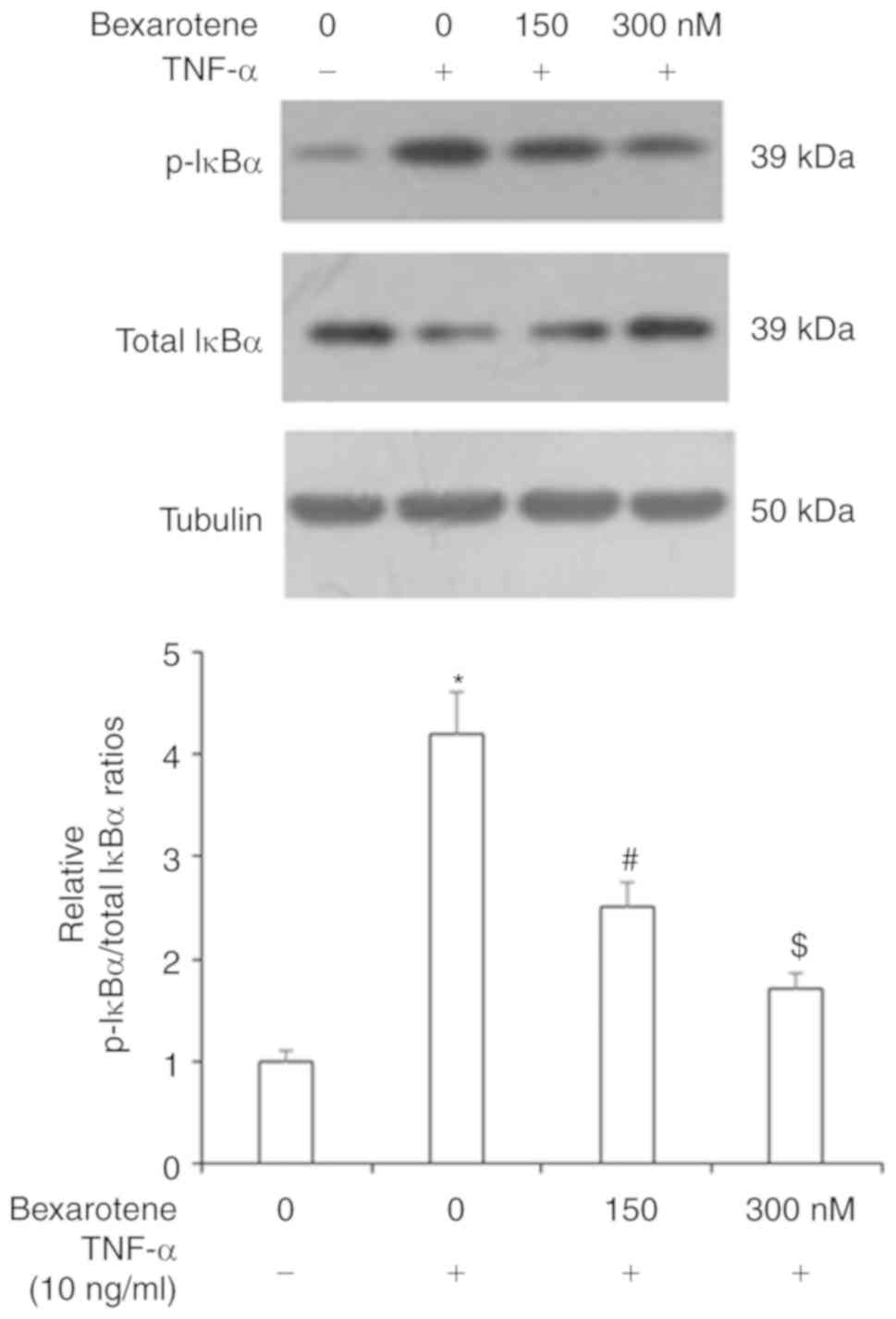
|
1
|
Sweeney SE and Firestein GS: Rheumatoid
arthritis: Regulation of synovial inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 36:372–378. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pap T and Korb-Pap A: Cartilage damage in
osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis-two unequal siblings. Nat
Rev Rheumatol. 11:606–615. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bresnihan B: Pathogenesis of joint damage
in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 26:717–719. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nanki T, Nagasaka K, Hayashida K, Saita Y
and Miyasaka N: Chemokines regulate IL-6 and IL-8 production by
fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. J Immunol. 167:5381–5385. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Georganas C, Liu H, Perlman H, Hoffmann A,
Thimmapaya B and Pope RM: Regulation of IL-6 and IL-8 expression in
rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts: The dominant role for
NF-kappa B but not C/EBP beta or c-Jun. J Immunol. 165:7199–7206.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yokota K, Miyazaki T, Hirano M, Akiyama Y
and Mimura T: Simvastatin inhibits production of interleukin 6
(IL-6) and IL-8 and cell proliferation induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 33:463–471. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harigai M, Hara M, Yoshimura T, Leonard
EJ, Inoue K and Kashiwazaki S: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
(MCP-1) in inflammatory joint diseases and its involvement in the
cytokine network of rheumatoid synovium. Clin Immunol Immunopathol.
69:83–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Green MJ, Gough AK, Devlin J, Smith J,
Astin P, Taylor D and Emery P: Serum MMP-3 and MMP-1 and
progression of joint damage in early rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 42:83–88. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Agere SA, Akhtar N, Watson JM and Ahmed S:
RANTES/CCL5 induces collagen degradation by activating MMP-1 and
MMP-13 expression in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial
fibroblasts. Front Immunol. 8:13412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lubberts E, Joosten LA, Chabaud M, van den
Bersselaar L, Oppers B, Coenen-de Roo CJ, Richards CD, Miossec P
and van den Berg WB: IL-4 gene therapy for collagen arthritis
suppresses synovial IL-17 and osteoprotegerin ligand and prevents
bone erosion. J Clin Invest. 105:1697–1710. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chemel M, Brion R, Segaliny A, Lamora A,
Charrier C, Brulin B, Maugars Y, Le Goff B, Heymann D and
Verrecchia F: Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and transforming growth
factor-β1 inhibit the expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokine
IL-34 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Am J Pathol.
187:156–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sugiura Y, Niimi T, Sato S, Yoshinouchi T,
Banno S, Naniwa T, Maeda H, Shimizu S and Ueda R: Transforming
growth factor β1 gene polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 61:826–828. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mateen S, Zafar A, Moin S, Khan AQ and
Zubair S: Understanding the role of cytokines in the pathogenesis
of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 455:161–171. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kageyama Y, Takahashi M, Ichikawa T,
Torikai E and Nagano A: Reduction of oxidative stress marker levels
by anti-TNF-alpha antibody, infliximab, in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 26:73–80. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Charles P, Elliott MJ, Davis D, Potter A,
Kalden JR, Antoni C, Breedveld FC, Smolen JS, Eberl G, deWoody K,
et al: Regulation of cytokines, cytokine inhibitors, and
acute-phase proteins following anti-TNF-alpha therapy in rheumatoid
arthritis. J Immunol. 163:1521–1528. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gottenberg JE, Brocq O, Perdriger A,
Lassoued S, Berthelot JM, Wendling D, Euller-Ziegler L, Soubrier M,
Richez C, Fautrel B, et al: Non-TNF-targeted biologic vs. a second
anti-TNF drug to treat rheumatoid arthritis in patients with
insufficient response to a first anti-TNF drug: A randomized
clinical trial. JAMA. 316:1172–1180. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li L, Liu Y, Wang J, Chen L, Zhang W and
Yan X: Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of bexarotene
nanocrystals with surface modification by folate-chitosan
conjugates. Drug Deliv. 23:79–87. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yen WC, Prudente RY, Corpuz MR,
Negro-Vilar A and Lamph WW: A selective retinoid X receptor agonist
bexarotene (LGD1069, targretin) inhibits angiogenesis and
metastasis in solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 94:654–660. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamanishi Y, Boyle DL, Green DR, Keystone
EC, Connor A, Zollman S and Firestein GS: P53 tumor suppressor gene
mutations in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from erosion synovium and
non-erosion synovium in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
7:R12–R18. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Terraneo L, Bianciardi P, Malavalli A,
Mkrtchyan G, Spann SN, Lohman J, Samaja M and Vandegriff KD:
Hemoglobin extravasation in the brain of rats exchange-transfused
with hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 45:710–716. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ma S, Bai Z, Wu H and Wang W: The DPP-4
inhibitor saxagliptin ameliorates ox-LDL-induced endothelial
dysfunction by regulating AP-1 and NF-κB. Eur J Pharmacol.
851:186–193. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schett G, Zwerina J and Firestein G: The
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway in rheumatoid
arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 67:909–916. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mitchell JP and Carmody RJ: NF-κB and the
transcriptional control of inflammation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol.
335:41–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Noack M and Miossec P: Selected cytokine
pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 39:365–383.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Emdad L, Das SK, Hu B, Kegelman T, Kang
DC, Lee SG, Sarkar D and Fisher PB: AEG-1/MTDH/LYRIC: A promiscuous
protein partner critical in cancer, obesity, and CNS diseases. Adv
Cancer Res. 131:97–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiazza F and Collino M: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in glucose control. Mol
Nutri Diabetes. 105–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Vincenti MP, Clark IM and Brinckerhoff CE:
Using inhibitors of metalloproteinases to treat arthritis. Easier
said than done? Arthritis Rheum. 37:1115–1126. 1994.
|
|
30
|
Mosquera N, Rodriguez-Trillo A,
Mera-Varela A, Gonzalez A and Conde C: Uncovering Cellular retinoic
acid-binding protein 2 as a potential target for rheumatoid
arthritis synovial hyper-plasia. Sci Rep. 8:87312018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Uray IP and Brown PH: Chemoprevention of
hormone receptor-negative breast cancer: New approaches needed.
Recent Results Cancer Res. 188:147–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang D, Leal AS, Carapellucci S, Zydeck
K, Chaaban N, Sporn MB, Wagner CE and Liby KT: Comparison of the
rexinoids Bexarotene and Pyrimidine-Bexarotene in a preclinical
model of lung carcinogenesis. FASEB J. 31(Suppl 1): S671–S616.
2017.
|
|
33
|
Zhong J, Cheng C, Liu H, Huang Z, Wu Y,
Teng Z, He J, Zhang H, Wu J, Cao F, et al: Bexarotene protects
against traumatic brain injury in mice partially through
apolipoprotein E. Neuroscience. 343:434–448. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tunctan B, Kucukkavruk SP, Temiz-Resitoglu
M, Guden DS, Sari AN and Sahan-Firat S: Bexarotene, a selective
RXRα agonist, reverses hypotension associated with inflammation and
tissue injury in a rat model of septic shock. Inflammation.
41:337–355. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kim DH, Lee GC, Kim CH, Oh SW, Han KH and
Han SY: Anti-inflammatory effect of combination therapy with
rosiglitazone and all-trans retinoic acid on high glucose-induced
MCP-1 response in rat mesangial cells. Biomed Res. 28:463–467.
2017.
|
|
36
|
Escudero P, Martinez de Marañón A, Collado
A, Gonzalez- Navarro H, Hermenegildo C, Peiró C, Piqueras L and
Sanz MJ: Combined sub-optimal doses of rosuvastatin and bexarotene
impair angiotensin II-induced arterial mononuclear cell adhesion
through inhibition of Nox5 signaling pathways and increased
RXR/PPARα and RXR/PPARγ interactions. Antioxid Redox Signal.
22:901–920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Niu X, Xiao S and Ma H: Retinoic
acid ameliorates photo-aged skin through RAR-mediated pathway in
mice. Mol Med Rep. 16:6240–6247. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Westra J and Limburg PC: p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in rheumatoid arthritis.
Mini Rev Med Chem. 6:867–874. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Desreumaux P, Dubuquoy L, Nutten S,
Peuchmaur M, Englaro W, Schoonjans K, Derijard B, Desvergne B,
Wahli W, Chambon P, et al: Attenuation of colon inflammation
through activators of the retinoid X receptor (RXR)/peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) heterodimer: A
basis for new therapeutic strategies. J Exp Med. 193:827–838. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fan Y, Wang J, Wei L, He B, Wang C and
Wang B: Iron deficiency activates pro-inflammatory signaling in
macrophages and foam cells via the p38 MAPK-NF-κB pathway. Int J
Cardiol. 152:49–55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|