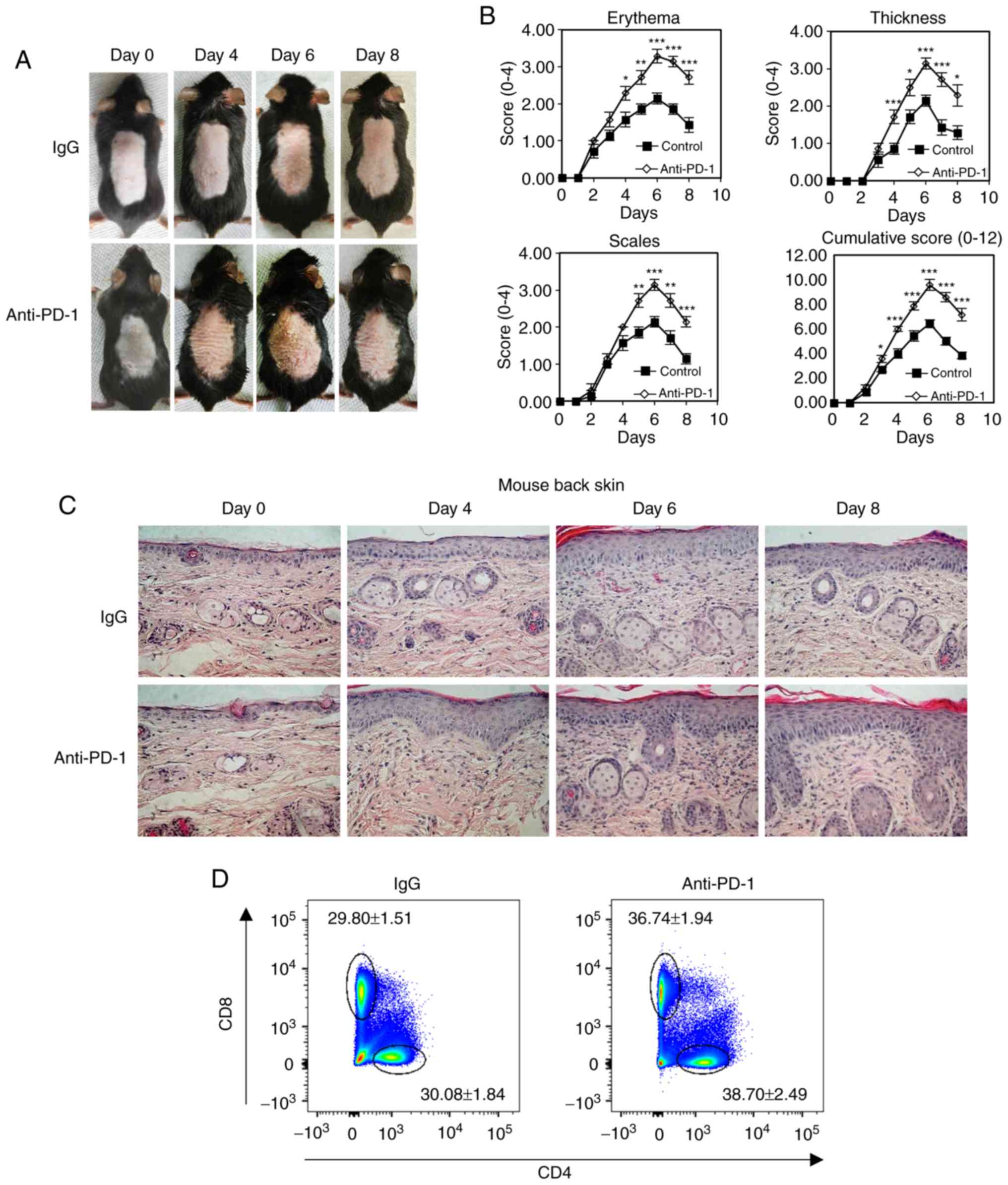
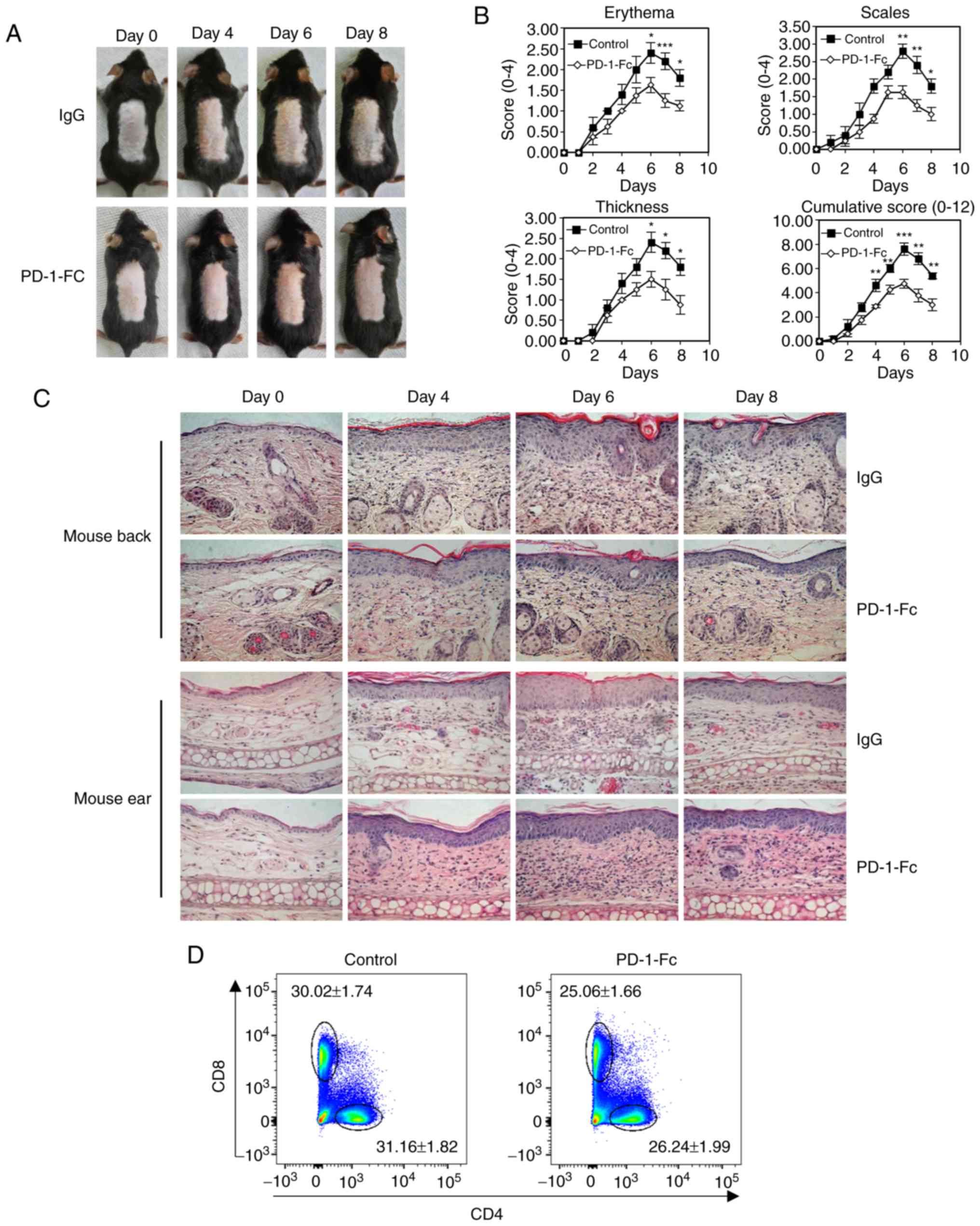
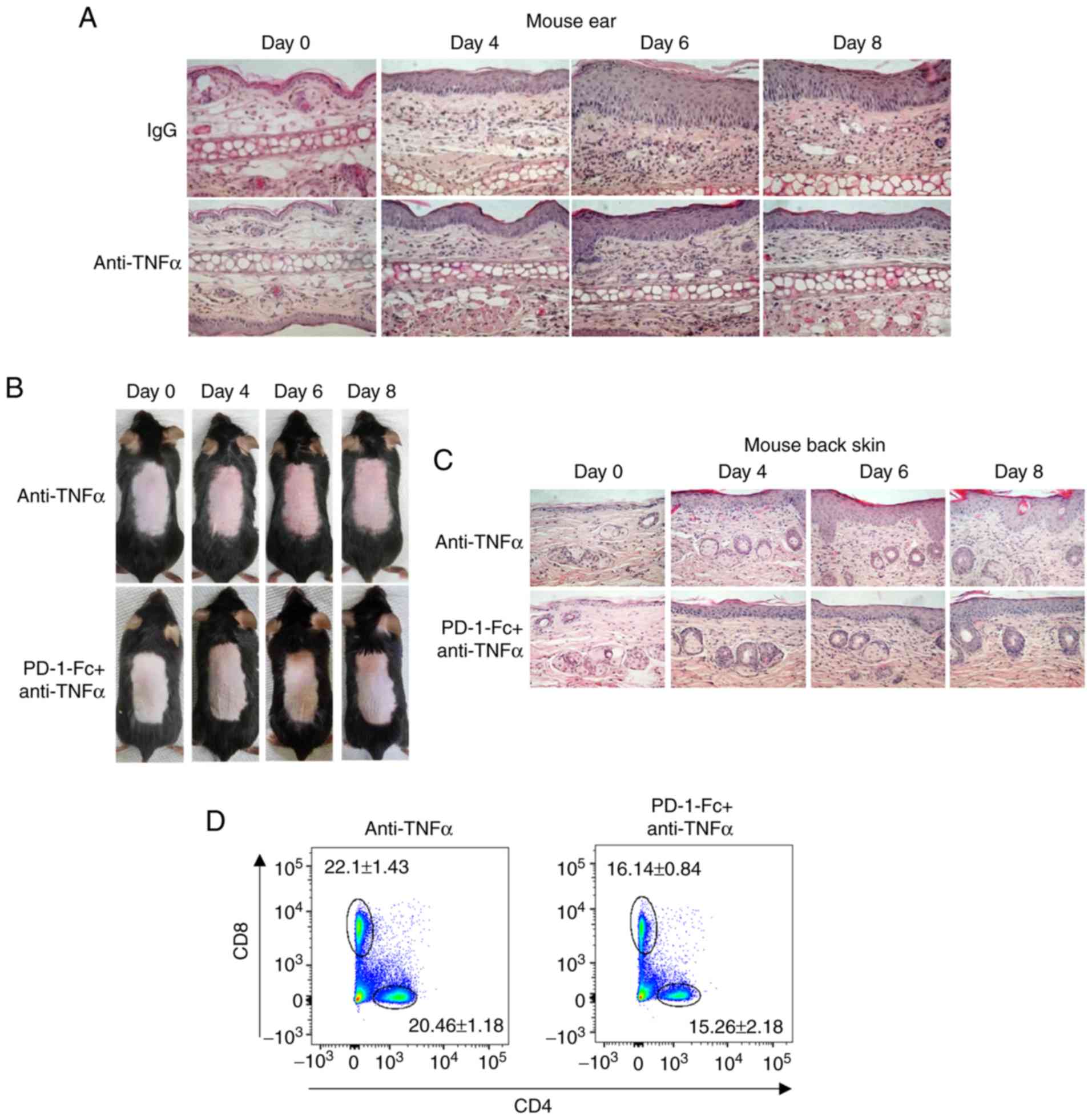
|
1
|
Bowcock AM and Krueger JG: Getting under
the skin: The immunogenetics of psoriasis. Nat Rev Immunol.
5:699–711. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gottlieb AB: Psoriasis: emerging
therapeutic strategies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 4:19–34. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nickoloff BJ, Bonish B, Huang BB and
Porcelli SA: Characterization of a T cell line bearing natural
killer receptors and capable of creating psoriasis in a SCID mouse
model system. j Dermatol Sci. 24:212–225. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang JC, Smith LR, Froning KJ, Schwabe
BJ, Laxer JA, Caralli LL, Kurland HH, Karasek MA, Wilkinson DI,
Carlo DJ, et al: CD8+ T cells in psoriatic lesions
preferentially use T-cell receptor V beta 3 and/or V beta 13.1
genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:9282–9286. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Prinz JC, Vollmer S, Boehncke WH, Menssen
A, Laisney I and Trommler P: Selection of conserved TCR VDJ
rearrangements in chronic psoriatic plaques indicates a common
antigen in psoriasis vulgaris. Eur J Immunol. 29:3360–3368. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vollmer S, Menssen A and Prinz JC:
Dominant lesional T cell receptor rearrangements persist in
relapsing psoriasis but are absent from nonlesional skin: evidence
for a stable antigen-specific pathogenic T cell response in
psoriasis vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 117:1296–1301. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K and Honjo
T: Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin
gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 11:3887–3895.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Riley JL: PD-1 signaling in primary T
cells. Immunol Rev. 229:114–125. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K,
Chernova T, Nishimura H, Fitz LJ, Malenkovich N, Okazaki T, Byrne
MC, et al: Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a
novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary
D, Borde M, Chernova I, Iwai Y, Long AJ, Brown JA, nunes R, et al:
PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sun X, Roudi R, Dai T, Chen S, Fan B, Li
H, Zhou Y, Zhou M, Zhu B, Yin C, et al: Immune-related adverse
events associated with programmed cell death protein-1 and
programmed cell death ligand 1 inhibitors for non-small cell lung
cancer: A PRISMA systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
19:5582019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ and Sharpe
AH: PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 26:677–704. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nishimura H, Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Sato M,
Imamura S, Minato N, Yagita H, Nakano T and Honjo T:
Developmentally regulated expression of the PD-1 protein on the
surface of double-negative (CD4-CD8-) thymocytes. Int Immunol.
8:773–780. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida
Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H and Honjo T: expression of the PD-1 antigen
on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int
Immunol. 8:765–772. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iwai Y, Ishida M, Tanaka Y, okazaki T,
Honjo T and Minato N: Involvement of PD-L1 on tumor cells in the
escape from host immune system and tumor immunotherapy by PD-L1
blockade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:12293–12297. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Okazaki T, Chikuma S, Iwai Y, Fagarasan S
and Honjo T: A rheostat for immune responses: The unique properties
of PD-1 and their advantages for clinical application. Nat Immunol.
14:1212–1218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fourcade J, Sun Z, Benallaoua M, Guillaume
P, Luescher IF, Sander C, Kirkwood JM, Kuchroo V and Zarour HM:
upregulation of Tim-3 and PD-1 expression is associated with tumor
antigen-specific CD8+ T cell dysfunction in melanoma
patients. J Exp Med. 207:2175–2186. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ott PA, Hodi FS and Robert C: CTLA-4 and
PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: new immunotherapeutic modalities with durable
clinical benefit in melanoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5300–5309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR,
Gettinger SN, Smith DC, McDermott DF, Powderly JD, Carvajal RD,
Sosman JA, Atkins MB, et al: Safety, activity, and immune
correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in cancer. New Engl J Med.
366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brahmer JR, Tykodi SS, Chow LG, Hwu WJ,
Topalian SL, Hwu P, Drake CG, Camacho LH, Kauh J, odunsi K, et al:
Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with
advanced cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2455–2465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang P and Wu MX: A clinical review of
phototherapy for psoriasis. Lasers Med Sci. 33:173–180. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Saurat JH, Stingl G, Dubertret L, Papp K,
Langley RG, ortonne JP, Unnebrink K, Kaul M and Camez A; CHAMPIon
Study Investigators: Efficacy and safety results from the
randomized controlled comparative study of adalimumab vs.
methotrexate vs placebo in patients with psoriasis (CHAMPIon). Br J
Dermatol. 158:558–566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Francisco LM, Sage PT and Sharpe AH: The
PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunol Rev.
236:219–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Imai Y, Ayithan N, Wu X, yuan Y, Wang L
and Hwang ST: Cutting edge: PD-1 regulates imiquimod-induced
psoriasiform dermatitis through inhibition of IL-17A expression by
innate gammadelta-low T cells. J Immunol. 195:421–425. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim JH, Choi YJ, Lee BH, Song My, Ban CY,
Kim J, Park J, Kim Se, Kim TG, Park SH, et al: Programmed cell
death ligand 1 alleviates psoriatic inflammation by suppressing
IL-17A production from programmed cell death 1-high T cells. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 137:1466–1476.e3. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Langley RG and Ellis CN: evaluating
psoriasis with psoriasis area and severity index, psoriasis global
assessment, and lattice system physician's global assessment. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 51:563–569. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JS,
Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, Cornelissen F, Mus AM, Florencia E, Prens
EP and Lubberts E: Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin
inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J
Immunol. 182:5836–5845. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu B, Zhang M, Williams EM, Keller C,
Mansoor A and Davie JK: TBX2 represses PTEN in rhabdomyosarcoma and
skeletal muscle. Oncogene. 35:4212–4224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Cui R, Widlund HR, Feige E, Lin JY,
Wilensky DL, Igras VE, D'orazio J, Fung CY, Schanbacher CF, Granter
SR and Fisher DE: Central role of p53 in the suntan response and
pathologic hyperpigmentation. Cell. 128:853–864. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
D'orazio JA, nobuhisa T, Cui R, Arya M,
Spry M, Wakamatsu K, Igras V, Kunisada T, granter SR, Nishimura EK,
et al: Topical drug rescue strategy and skin protection based on
the role of Mc1r in UV-induced tanning. Nature. 443:340–344. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Works MG, Yin F, Yin CC, Yiu Y, Shew K,
Tran TT, Dunlap N, Lam J, Mitchell T, Reader J, et al: Inhibition
of TYK2 and JAK1 ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like
dermatitis by inhibiting IL-22 and the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J Immunol.
193:3278–3287. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lubrano E, Scriffignano S and Perrotta FM:
TNF-alpha inhibitors for the six treatment targets of psoriatic
arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 15:1303–1312. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ronholt K and Iversen L: old and new
biological therapies for psoriasis. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E22972017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sibaud V: Dermatologic reactions to immune
checkpoint inhibitors: Skin toxicities and immunotherapy. Am J Clin
Dermatol. 19:345–361. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Muenst S, Soysal SD, Tzankov A and Hoeller
S: The PD-1/ PD-L1 pathway: Biological background and clinical
relevance of an emerging treatment target in immunotherapy. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 19:201–211. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Okazaki T and Honjo T: The PD-1-PD-L
pathway in immunological tolerance. Trends Immunol. 27:195–201.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li X, Xiang Y, Li F, yin C, Li B and Ke X:
WnT/β-catenin signaling pathway regulating T cell-inflammation in
the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. 10:22932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Voudouri D, Nikolaou V, Laschos K,
Charpidou A, Soupos N, Triantafyllopoulou I, Panoutsopoulou I,
Aravantinos G, Syrigos K and Stratigos A: Anti-PD1/PDL1 induced
psoriasis. Curr Probl Cancer. 41:407–412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
De Bock M, Hulstaert E, Kruse V and
Brochez L: Psoriasis vulgaris exacerbation during treatment with a
PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor: Case report and literature review. Case
Rep Dermatol. 10:190–197. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
He J, Hu Y, Hu M and Li B: Development of
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in tumor immune microenvironment and treatment
for non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep. 5:131102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Karunarathne DS, Horne-Debets JM, Huang
JX, Faleiro R, Leow CY, Amante F, Watkins TS, Miles JJ, Dwyer PJ,
Stacey KJ, et al: Programmed death-1 ligand 2-mediated regulation
of the PD-L1 to PD-1 axis is essential for establishing CD4(+) T
Cell Immunity. Immunity. 45:333–345. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ellis JS, guloglu FB, Tartar DM, Hoeman
CM, Haymaker CL, Cascio JA, Wan X, Dhakal M, VanMorlan A, Yahng SH
and Zaghouani H: APCs expressing high levels of programmed death
ligand 2 sustain the development of CD4 T cell memory. J Immunol.
185:3149–3157. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Versteven M, Van den Bergh JMJ, Marcq E,
Smits ELJ, Van Tendeloo VFI, Hobo W and Lion E: Dendritic cells and
programmed death-1 blockade: A joint venture to combat cancer.
Front Immunol. 9:3942018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ritprajak P and Azuma M: Intrinsic and
extrinsic control of expression of the immunoregulatory molecule
PD-L1 in epithelial cells and squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol.
51:221–228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pulko V, Liu X, Krco CJ, Harris KJ,
Frigola X, Kwon ED and Dong H: TLR3-stimulated dendritic cells
up-regulate B7-H1 expression and influence the magnitude of CD8 T
cell responses to tumor vaccination. J Immunol. 183:3634–3641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Diskin B, Adam S, Cassini MF, Sanchez G,
Liria M, Aykut B, Buttar C, Li E, Sundberg B, Salas RD, et al:
PD-L1 engagement on T cells promotes self-tolerance and suppression
of neighboring macrophages and effector T cells in cancer. Nat
Immunol. 21:442–454. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Balak DM and Hajdarbegovic E: Drug-induced
psoriasis: Clinical perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl). 7:87–94.
2017.
|
|
48
|
Trafford AM, Parisi R, Kontopantelis E,
Griffiths CEM and Ashcroft DM: Association of psoriasis with the
risk of developing or dying of cancer: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Abrams JR, Lebwohl MG, Guzzo CA, Jegasothy
BV, Goldfarb MT, Goffe BS, Menter A, Lowe NJ, Krueger G, Brown MJ,
et al: CTLA4Ig-mediated blockade of T-cell costimulation in
patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Clin Invest. 103:1243–1252.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
El Malki K, Karbach SH, Huppert J, Zayoud
M, Reissig S, Schüler R, Nikolaev A, Karram K, Münzel T, Kuhlmann
CR, et al: An alternative pathway of imiquimod-induced
psoriasis-like skin inflammation in the absence of interleukin-17
receptor a signaling. J Invest Dermatol. 133:441–451. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|