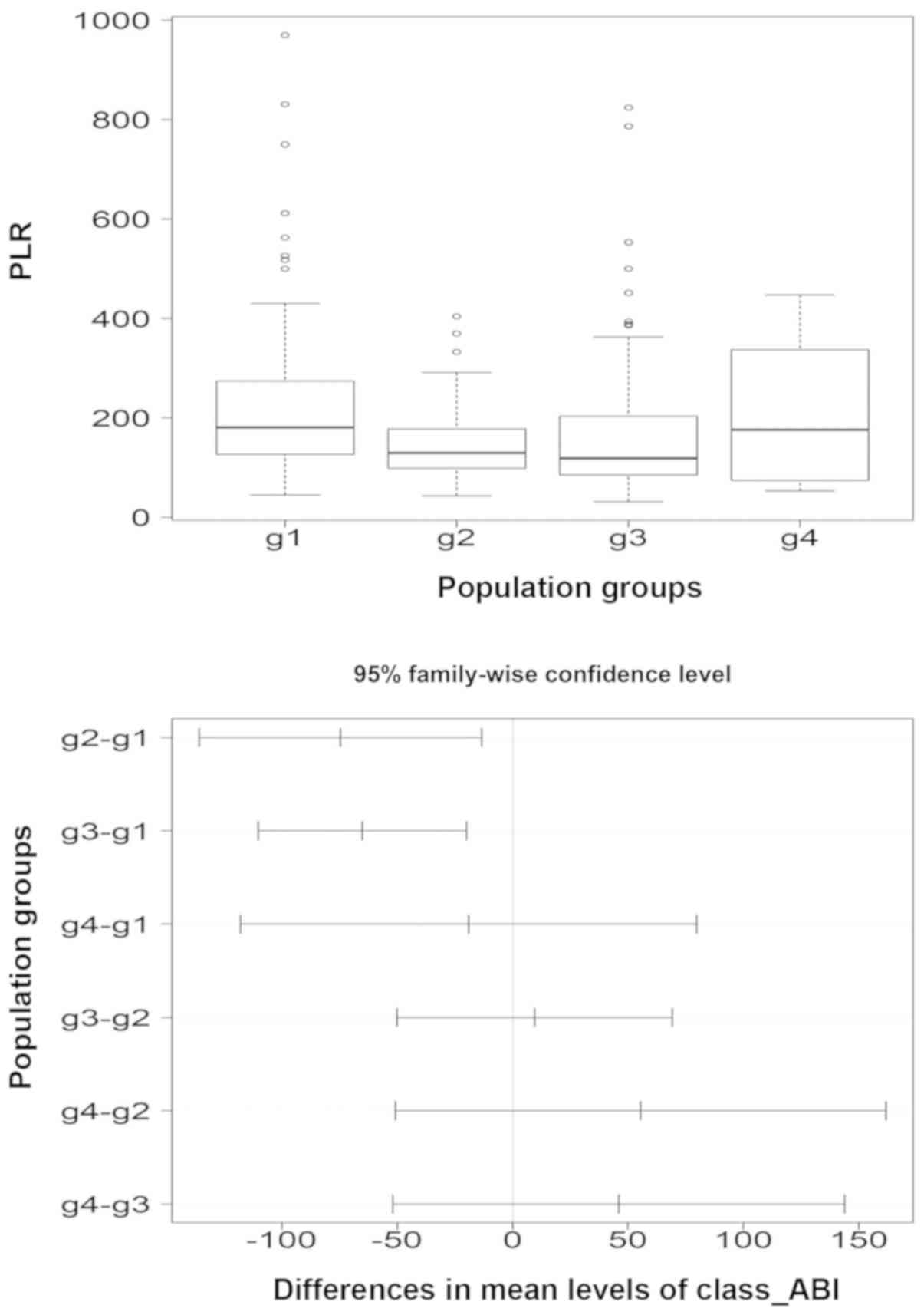
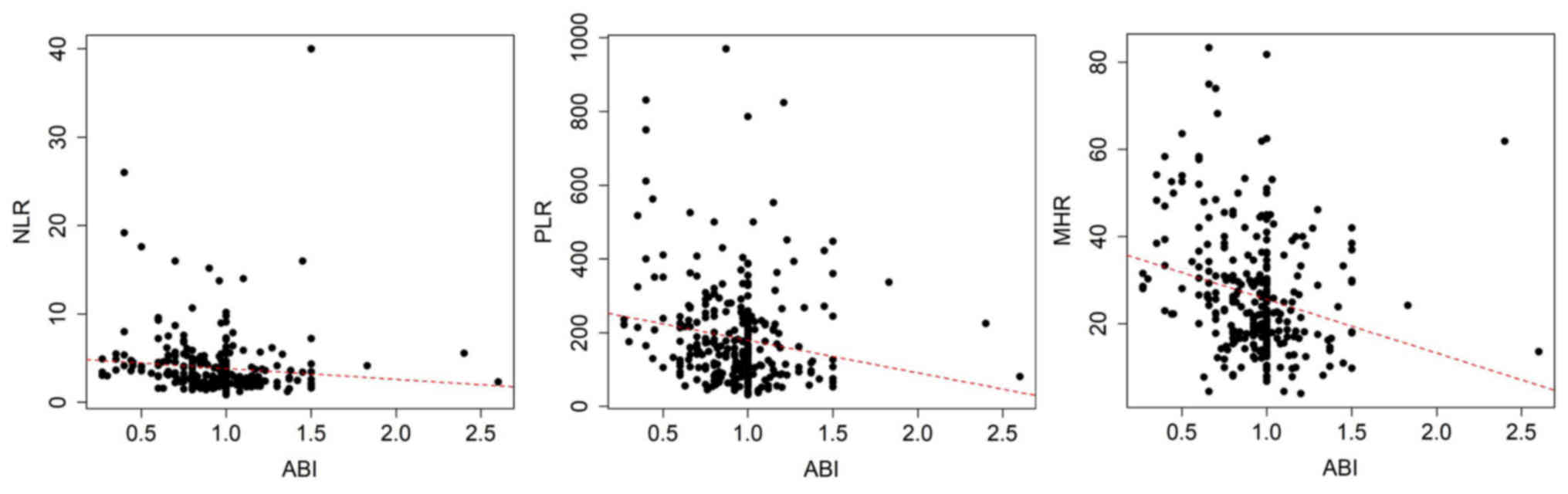
|
1
|
Writing group Members; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, Fullerton HJ, et al American Heart
Association Statistics Committee; Stroke Statistics Subcommittee:
Heart disease and stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the
American Heart Association. Circulation. 133:e38–360. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P,
Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M and Nichols M: Cardiovascular disease in
Europe: Epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J. 37:3232–3245.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Corrado E, Rizzo M, Muratori I, Coppola G
and Novo S: Older age and markers of inflammation are strong
predictors of clinical events in women with asymptomatic carotid
lesions. Menopause. 15:240–247. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Corrado E and Novo S: High sensitivity of
C-reactive protein in primary prevention. G Ital Cardiol (Rome).
8:327–334. 2007.In Italian.
|
|
5
|
Maresca G, Di Blasio A, Marchioli R and Di
Minno G: Measuring plasma fibrinogen to predict stroke and
myocardial infarction: An update. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
19:1368–1377. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wierzbicki AS: Homocysteine and
cardiovascular disease: A review of the evidence. Diab Vasc Dis
Res. 4:143–150. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Michaud M, Balardy L, Moulis G, Gaudin C,
Peyrot C, Vellas B, Cesari M and Nourhashemi F: Proinflammatory
cytokines, aging, and age-related diseases. J Am Med Dir Assoc.
14:877–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim NY, Chun DH, Kim SY, Kim NK, Baik SH,
Hong JH, Kim KS and Shin CS: Prognostic value of systemic
inflammatory indices, NLR, PLR, and MPV, for predicting 1-year
survival of patients undergoing cytoreductive surgery with HIPEC. J
Clin Med. 8:5892019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Kurtul A and Ornek E: Platelet to
lymphocyte ratio in cardiovascular diseases: A systematic review.
Angiology. 70:802–818. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ganjali S, Gotto AM Jr, Ruscica M, Atkin
SL, Butler AE, Banach M and Sahebkar A: Monocyte-to-HDL-cholesterol
ratio as a prognostic marker in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell
Physiol. 233:9237–9246. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Toor IS, Jaumdally RJ, Moss MS and Babu
SB: Preprocedural neutrophil count predicts outcome in patients
with advanced peripheral vascular disease undergoing percutaneous
trans-luminal angioplasty. J Vasc Surg. 48:1504–1508. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liang RF, Li M, Li JH, Zuo MR, Yang Y and
Liu YH: The significance of preoperative haematological
inflammatory markers in patients with meningiomas. Clin Neurol
Neurosurg. 182:1–4. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
American Diabetes Association: Standards
of medical care in diabetes - 2012. Diabetes Care. 35(Suppl 1):
S11–S63. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman
WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright
JT Jr, et al National High Blood Pressure Education Program
Coordinating Committee: The seventh report of the Joint Ntional
Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of
high blood pressure: The JNC 7 report. JAMA. 289:2560–2572. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB
Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC Jr and Stone
NJ; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American College of
Cardiology Foundation; American Heart Association: Implications of
recent clinical trials for the national cholesterol education
program adult treatment panel III guidelines. Circulation.
110:227–239. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Khan TH, Farooqui FA and Niazi K: Critical
review of the ankle brachial index. Curr Cardiol Rev. 4:101–106.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Balta S and Ozturk C: The
platelet-lymphocyte ratio: A simple, inexpensive and rapid
prognostic marker for cardiovascular events. Platelets. 26:680–681.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gary T, Pichler M, Belaj K, Hafner F,
Gerger A, Froehlich H, Eller P, Rief P, Hackl G, Pilger E, et al:
Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio: A novel marker for critical limb
ischemia in peripheral arterial occlusive disease patients. PLoS
One. 8:e676882013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Çiçek G, Açıkgoz SK, Bozbay M, Altay S,
Uğur M, Uluganyan M and Uyarel H: Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and
platelet-lymphocyte ratio combination can predict prognosis in
patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing
primary percutaneous coronary intervention. Angiology. 66:441–447.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Paquissi FC: The role of inflammation in
cardiovascular diseases: The predictive value of
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio as a marker in peripheral arterial
disease. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 12:851–860. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Belaj K, Pichler M, Hackl G, Rief P, Eller
P, Hafner F, Brodmann M and Gary T: Association of the derived
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio with critical limb ischemia. Angiology.
67:350–354. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tacke F, Alvarez D, Kaplan TJ, Jakubzick
C, Spanbroek R, Llodra J, Garin A, Liu J, Mack M, van Rooijen N, et
al: Monocyte subsets differentially employ CCR2, CCR5, and CX3CR1
to accumulate within atherosclerotic plaques. J Clin Invest.
117:185–194. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sala F, Cutuli L, Grigore L, Pirillo A,
Chiesa G, Catapano AL and Norata GD: Prevalence of classical
CD14++/CD16− but not of intermediate
CD14++/CD16+ monocytes in
hypoalphalipoproteinemia. Int J Cardiol. 168:2886–2889. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cetin MS, Ozcan Cetin EH, Kalender E,
Aydin S, Topaloglu S, Kisacik HL and Temizhan A: Monocyte to HDL
cholesterol ratio predicts coronary artery disease severity and
future major cardiovascular adverse events in acute coronary
syndrome. Heart Lung Circ. 25:1077–1086. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Criqui MH and Aboyans V: Epidemiology of
peripheral artery disease. Circ Res. 116:1509–1526. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xue G, Deng H and Zhang L:
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and platelet-lymphocyte ratio predict
severity and prognosis of lower limb arteriosclerosis obliterans.
Ann Vasc Surg. 64:221–227. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Signorelli SS, Malaponte G, Libra M, Di
Pino L, Celotta G, Bevelacqua V, Petrina M, Nicotra GS, Indelicato
M, Navolanic PM, et al: Plasma levels and zymographic activities of
matrix metal-loproteinases 2 and 9 in type II diabetics with
peripheral arterial disease. Vasc Med. 10:1–6. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Signorelli SS, Anzaldi M, Libra M,
Navolanic PM, Malaponte G, Mangano K, Quattrocchi C, Di Marco R,
Fiore V and Neri S: Plasma levels of Inflammatory Biomarkers in
Peripheral Arterial Disease: Results of a cohort study. Angiology.
67:870–874. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Signorelli SS, Mazzarino MC, Spandidos DA
and Malaponte G: Proinflammatory circulating molecules in
peripheral arterial disease. Int J Mol Med. 20:279–286.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|