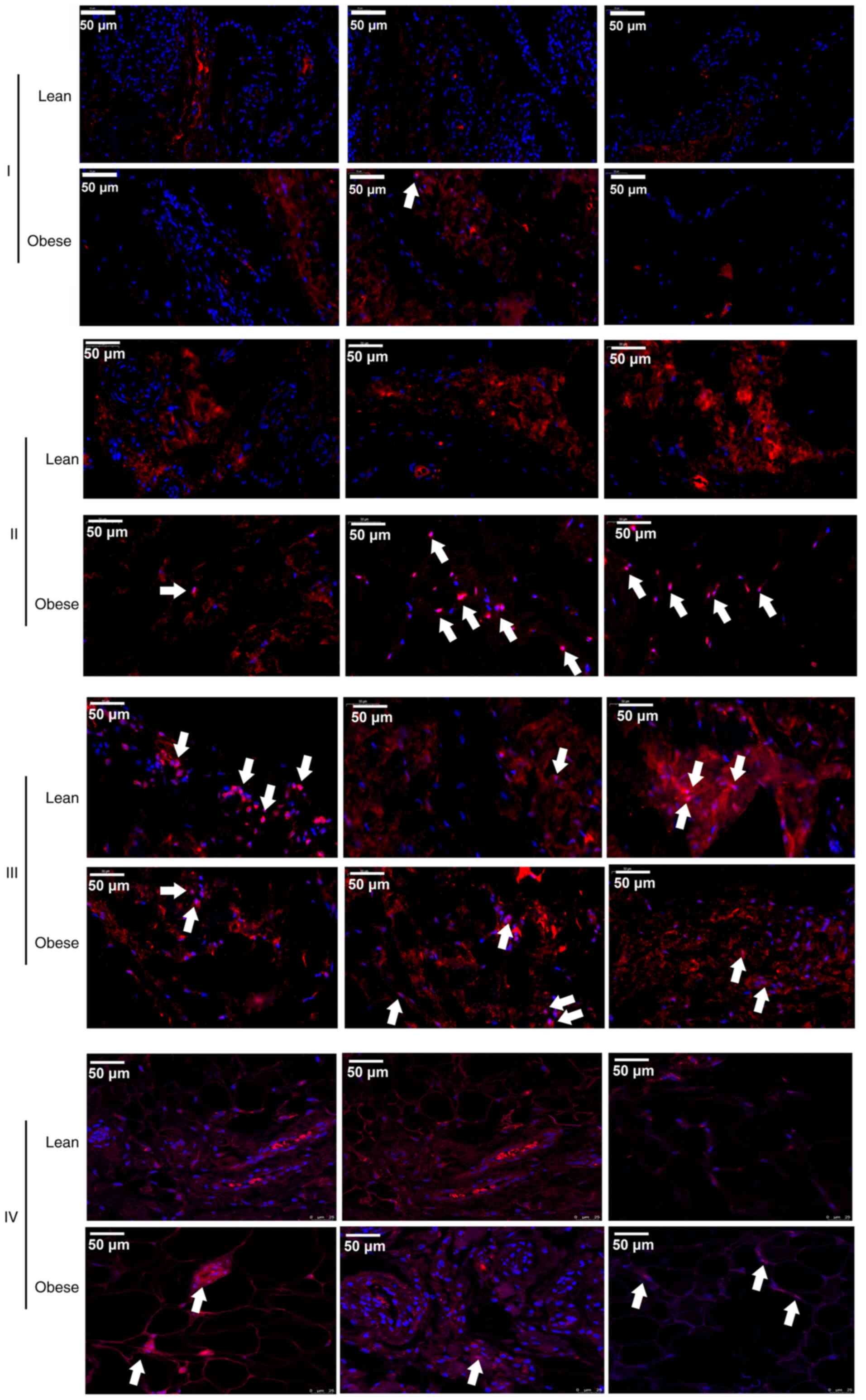
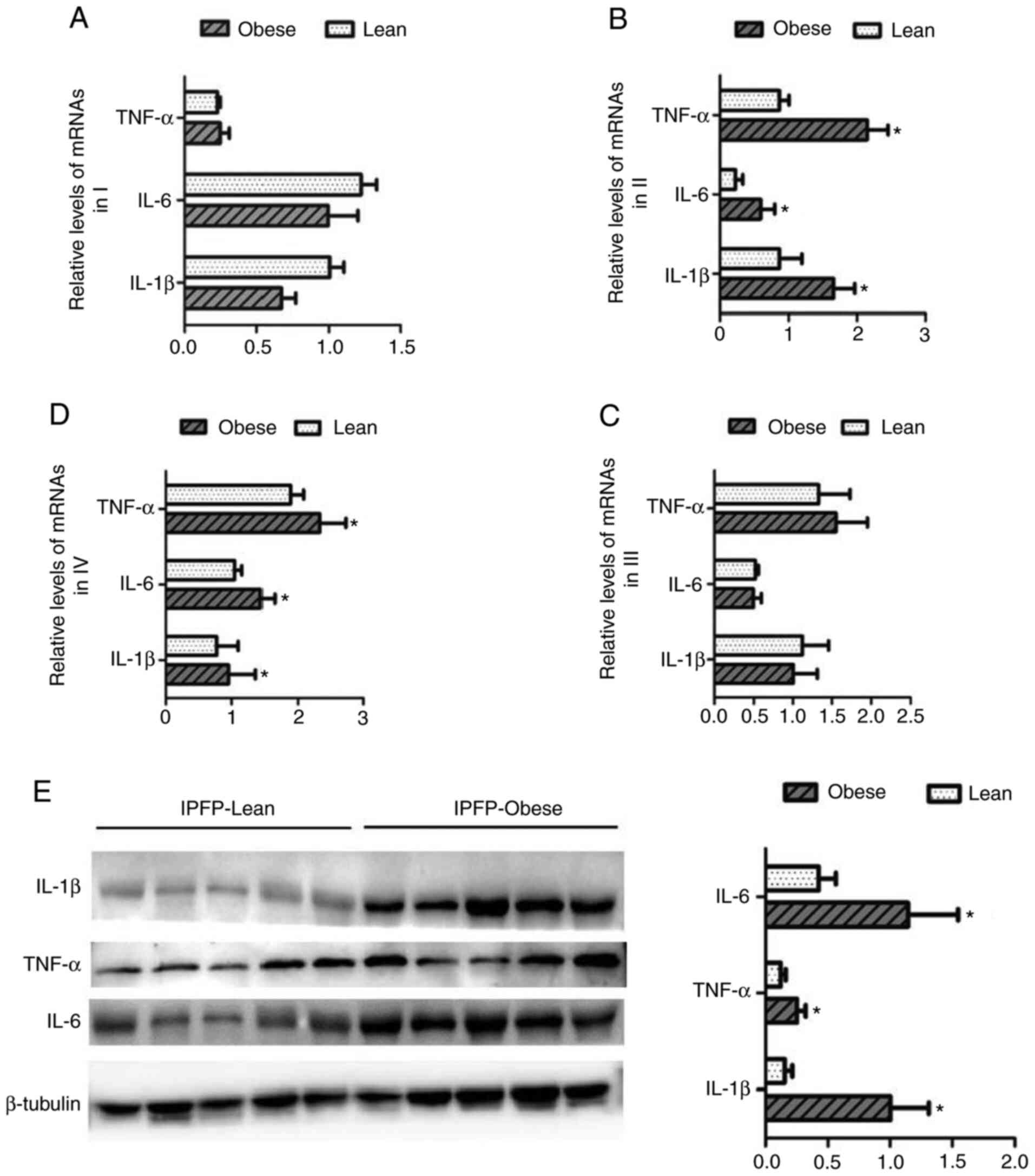
|
1
|
Oliveria SA, Felson DT, Cirillo PA, Reed
JI and Walker AM: Body weight, body mass index, and incident
symptomatic osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee.
Epidemiology. 10:161–166. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saltiel AR and Olefsky JM: Inflammatory
mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest.
127:1–4. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Eymard F and Chevalier X: Inflammation of
the infrapatellar fat pad. Joint Bone Spine. 83:389–393. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Griffin T: Biomechanical and metabolic
implications of obesity in OA. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 26(Suppl):
S12018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Francisco V, Pérez T, Pino J, López V,
Franco E, Alonso A, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Mera A, Lago F, Gómez R and
Gualillo O: Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of
adipokines: When the levee breaks. J Orthop Res. 36:595–604.
2018.
|
|
6
|
Van Beeck A, Clockaerts S, Somville J, Van
Heeswijk JH, Van Glabbeek F, Bos PK and Reijman M: Does
infrapatellar fat pad resection in total knee arthroplasty impair
clinical outcome? A systematic review. Knee. 20:226–231. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yoshimura N, Muraki S, Oka H, Tanaka S,
Kawaguchi H, Nakamura K and Akune T: Accumulation of metabolic risk
factors such as overweight, hypertension, dyslipidaemia, and
impaired glucose tolerance raises the risk of occurrence and
progression of knee osteoarthritis: A 3-year follow-up of the ROAD
study. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 20:1217–1226. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kanneganti TD and Dixit VD: Immunological
complications of obesity. Nat Immunol. 13:707–712. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Osborn O and Olefsky JM: The cellular and
signaling networks linking the immune system and metabolism in
disease. Nat Med. 18:363–374. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buchholz AL, Niesen MC, Gausden EB,
Sterken DG, Hetzel SJ, Baum SZ, Squire MW and Kaplan LD: Metabolic
activity of osteoarthritic knees correlates with BMI. Knee.
17:161–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jotanovic Z, Mihelic R, Sestan B and
Dembic Z: Role of inter-leukin-1 inhibitors in osteoarthritis: An
evidence-based review. Drugs Aging. 29:343–358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guarner V and Rubio-Ruiz ME: Low-grade
systemic inflammation connects aging, metabolic syndrome and
cardiovascular disease. Interdiscip Top Gerontol. 40:99–106. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Dalmas E, Venteclef N, Caer C, Poitou C,
Cremer I, Aron-Wisnewsky J, Lacroix-Desmazes S, Bayry J, Kaveri SV,
Clément K, et al: T cell-derived IL-22 amplifies IL-1β-driven
inflammation in human adipose tissue: Relevance to obesity and type
2 diabetes. Diabetes. 63:1966–1977. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Esser N, Legrand-Poels S, Piette J, Scheen
AJ and Paquot N: Inflammation as a link between obesity, metabolic
syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 105:141–150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eymard F, Pigenet A, Citadelle D, Tordjman
J, Foucher L, Rose C, Flouzat Lachaniette CH, Rouault C, Clément K,
Berenbaum F, et al: Knee and hip intra-articular adipose tissues
(IAATs) compared with autologous subcutaneous adipose tissue: A
specific phenotype for a central player in osteoarthritis. Ann
Rheum Dis. 76:1142–1148. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Distel E, Cadoudal T, Durant S, Poignard
A, Chevalier X and Benelli C: The infrapatellar fat pad in knee
osteoarthritis: An important source of interleukin-6 and its
soluble receptor. Arthritis Rheum. 60:3374–3377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Klein-Wieringa IR, Kloppenburg M,
Bastiaansen-Jenniskens YM, Yusuf E, Kwekkeboom JC, El-Bannoudi H,
Nelissen RG, Zuurmond A, Stojanovic-Susulic V, Van Osch GJ, et al:
The infrapatellar fat pad of patients with osteoarthritis has an
inflammatory phenotype. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:851–857. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Eymard F, Pigenet A, Citadelle D,
Flouzat-Lachaniette CH, Poignard A, Benelli C, Berenbaum F,
Chevalier X and Houard X: Induction of an inflammatory and
prodegradative phenotype in autologous fibroblast-like synoviocytes
by the infrapatellar fat pad from patients with knee
osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:2165–2174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iwata M, Ochi H, Hara Y, Tagawa M, Koga D,
Okawa A and Asou Y: Initial responses of articular tissues in a
murine high-fat diet-induced osteoarthritis model: Pivotal role of
the IPFP as a cytokine fountain. PLoS One. 8:e607062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bastiaansen-Jenniskens YM, Wei W, Feijt C,
Waarsing JH, Verhaar JA, Zuurmond AM, Hanemaaijer R, Stoop R and
van Osch GJ: Stimulation of fibrotic processes by the infrapatellar
fat pad in cultured synoviocytes from patients with osteoarthritis:
A possible role for prostaglandin f2α. Arthritis Rheum.
65:2070–2080. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma B and Hottiger MO: Crosstalk between
Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathway during inflammation.
Front Immunol. 7:3782016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liao S, Zhou K, Li D, Xie X, Fang J and
Wang J: Schisantherin A suppresses interleukin-1β-induced
inflammation in human chondrocytes via inhibition of NF-κB and
MAPKs activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 780:65–70. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Olivotto E, Otero M, Marcu KB and Goldring
MB: Pathophysiology of osteoarthritis: Canonical
NF-κB/IKKβ-dependent and kinase-independent effects of IKKα in
cartilage degradation and chondrocyte differentiation. RMD Open.
1(Suppl 1): e0000612015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kulkarni K, Karssiens T, Kumar V and
Pandit H: Obesity and osteoarthritis. Maturitas. 89:22–28. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang L, Rong J, Wang Y, Hu F, Bao C, Li X
and Zhao Y: The relationship between body mass index and hip
osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint Bone
Spine. 78:150–155. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang L, Tian W, Wang Y, Rong J, Bao C,
Liu Y, Zhao Y and Wang C: Body mass index and susceptibility to
knee osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Joint
Bone Spine. 79:291–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Hunter D, Xu J and Ding C:
Metabolic triggered inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 23:22–30. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Apostolopoulos V, de Courten MP,
Stojanovska L, Blatch GL, Tangalakis K and de Courten B: The
complex immunological and inflammatory network of adipose tissue in
obesity. Mol Nutr Food Res. 60:43–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Iliopoulos D, Malizos KN, Oikonomou P and
Tsezou A: Integrative MicroRNA and proteomic approaches identify
novel osteoarthritis genes and their collaborative metabolic and
inflammatory networks. PLoS One. 3:e37402008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gandhi R, Takahashi M, Virtanen C, Syed K,
Davey JR and Mahomed NN: Microarray analysis of the infrapatellar
fat pad in knee osteoarthritis: Relationship with joint
inflammation. J Rheumatol. 38:1966–1972. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lübbeke A, Finckh A, Puskas GJ, Suva D,
Lädermann A, Bas S, Fritschy D, Gabay C and Hoffmeyer P: Do
synovial leptin levels correlate with pain in end stage arthritis?
Int Orthopaedics. 37:2071–2079. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Francisco V, Pino J, Gonzalez-Gay MA, Mera
A, Lago F, Gómez R, Mobasheri A and Gualillo O: Adipokines and
inflammation: Is it a question of weight? Br J Pharmacol.
175:1569–1579. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Afif H, Benderdour M, Mfuna-Endam L,
Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Duval N and Fahmi H: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma 1 expression is diminished in
human osteoarthritis cartilage and is downregulated by
interleukin-1beta in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther.
9:R312007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tu C, He J, Wu B, Wang W and Li Z: An
extensive review regarding the adipokines in the pathogenesis and
progression of osteoarthritis. Cytokine. 113:1–12. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Springer BD, Carter JT, McLawhorn AS,
Scharf K, Roslin M, Kallies KJ, Morton JM and Kothari SN: Obesity
and the role of bariatric surgery in the surgical management of
osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: A review of the literature.
Surg Obes Relat Dis. 13:111–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee WJ, Wu CS, Lin H, Lee IT, Wu CM, Tseng
JJ, Chou MM and Sheu WH: Visfatin-induced expression of
inflammatory mediators in human endothelial cells through the
NF-kappaB pathway. Int J Obes (Lond). 33:465–472. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Simopoulou T, Malizos K, Iliopoulos D,
Stefanou N, Papatheodorou L, Ioannou M and Tsezou A: Differential
expression of leptin and leptin's receptor isoform (Ob-Rb) mRNA
between advanced and minimally affected osteoarthritic cartilage;
effect on cartilage metabolism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
15:872–883. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gross JB, Guillaume C, Gegout-Pottie P,
Reboul P, Jouzeau JY, Mainard D and Presle N: The infrapatellar fat
pad induces inflammatory and degradative effects in articular cells
but not through leptin or adiponectin. Clin Exp Rheumatol.
35:53–60. 2017.
|
|
40
|
Kontny E, Plebanczyk M, Lisowska B,
Olszewska M, Maldyk P and Maslinski W: Comparison of rheumatoid
articular adipose and synovial tissue reactivity to proinflammatory
stimuli: Contribution to adipocytokine network. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:262–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Koskinen A, Vuolteenaho K, Nieminen R,
Moilanen T and Moilanen E: Leptin enhances MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13
production in human osteoarthritic cartilage and correlates with
MMP-1 and MMP-3 in synovial fluid from OA patients. Clin Exp
Rheumatol. 29:57–64. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Wang S, Zhu J, Li C, Zhang T, Liu
H, Xu Q, Ye X, Zhou L and Ye L: Effect of atmospheric PM2.5 on
expression levels of NF-κB genes and inflammatory cytokines
regulated by NF-κB in human macrophage. Inflammation. 41:784–794.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li QY, Chen L, Yan MM, Shi XJ and Zhong
MK: Tectorigenin regulates adipogenic differentiation and
adipocytokines secretion via PPARγ and IKK/NF-κB signaling. Pharm
Biol. 53:1567–1575. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hui W, Litherland GJ, Elias MS, Kitson GI,
Cawston TE, Rowan AD and Young DA: Leptin produced by joint white
adipose tissue induces cartilage degradation via upregulation and
activation of matrix metalloproteinases. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:455–462.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|