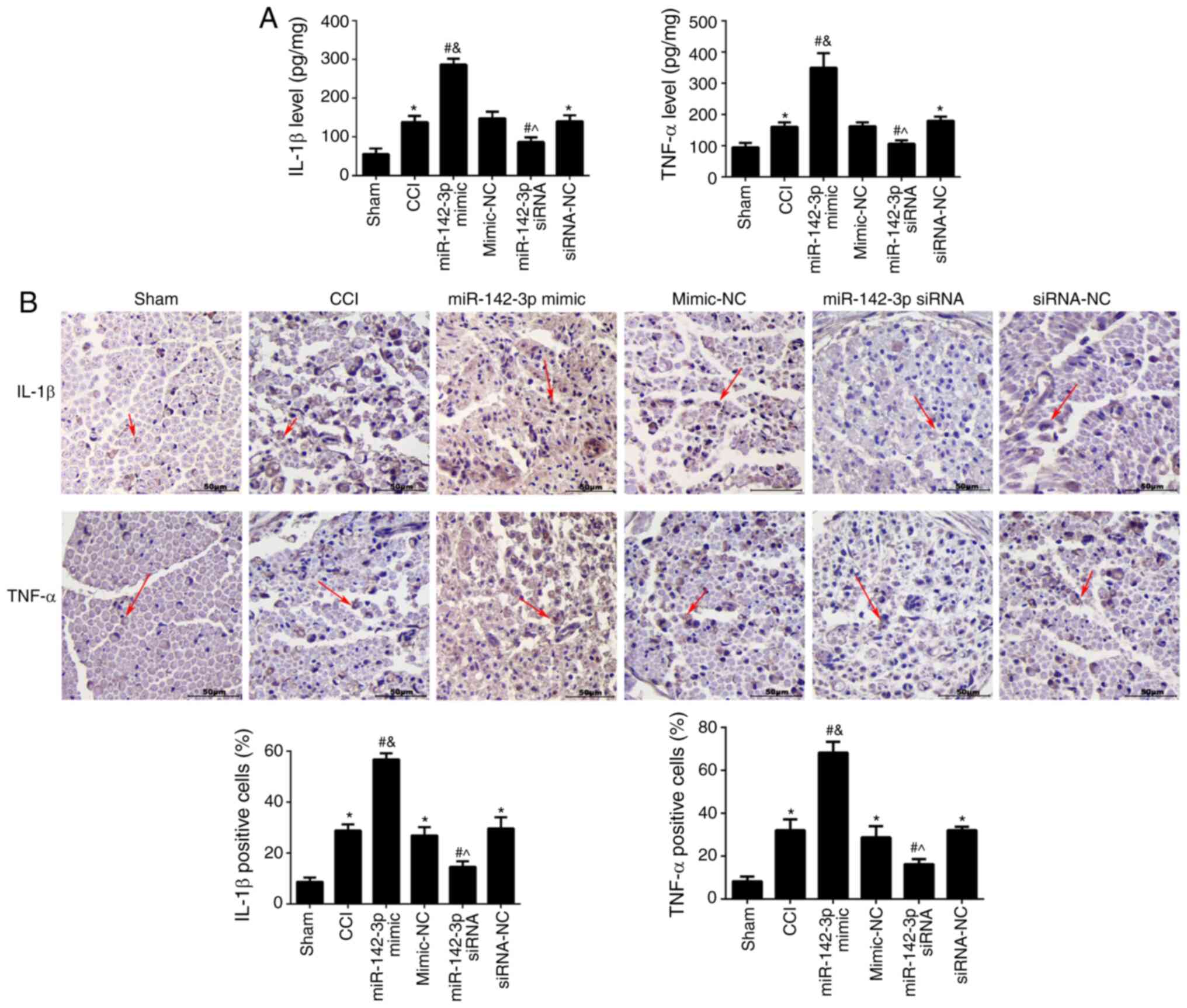
|
1
|
Baron R: Peripheral neuropathic pain: From
mechanisms to symptoms. Clin J Pain. 16(Suppl 2): S12–S20. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baron R: Mechanisms of disease:
Neuropathic pain-a clinical perspective. Nat Clin Pract Neurol.
2:95–106. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Connor AB and Dworkin RH: Treatment of
neuropathic pain: An overview of recent guidelines. Am J Med.
122(Suppl 10): S22–S32. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiangpan P, Qingsheng M, Zhiwen Y and Tao
Z: Emerging role of microRNA in neuropathic pain. Curr Drug Metab.
17:336–344. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lu X, Li X, He Q, Gao J, Gao Y, Liu B and
Liu F: miR-142-3p regulates the formation and differentiation of
hematopoietic stem cells in vertebrates. Cell Res. 23:1356–1368.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang T, Li B, Wang Z, Wang X, Xia Z, Ning
G, Wang X, Zhang Y, Cui L, Yu M, et al: Sorafenib promotes sensory
conduction function recovery via miR-142-3p/AC9/cAMP axis post
dorsal column injury. Neuropharmacology. 148:347–357. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ouyang B, Tang Z, Hou X, Chen D, Guo Q and
Weng Y: Trichostatin A suppresses up-regulation of histone
deacetylase 4 and reverses differential expressions of miRNAs in
the spinal cord of rats with chronic constrictive injury. Nan Fang
Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 39:1421–1426. 2019.In Chinese.
|
|
8
|
Tahamtan A, Teymoori-Rad M, Nakstad B and
Salimi V: Anti-inflammatory MicroRNAs and their potential for
inflammatory diseases treatment. Front Immunol. 9:13772018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ji RR, Nackley A, Huh Y, Terrando N and
Maixner W: Neuroinflammation and central sensitization in chronic
and widespread pain. Anesthesiology. 129:343–366. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sakaue G, Shimaoka M, Fukuoka T, Hiroi T,
Inoue T, Hashimoto N, Sakaguchi T, Sawa Y, Morishita R, Kiyono H,
et al: NF-kappa B decoy suppresses cytokine expression and thermal
hyperalgesia in a rat neuropathic pain model. Neuroreport.
12:2079–2084. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Scholz J and Woolf CJ: The neuropathic
pain triad: Neurons, immune cells and glia. Nat Neurosci.
10:1361–1368. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Price TJ and Dussor G: AMPK: An emerging
target for modification of injury-induced pain plasticity. Neurosci
Lett. 557:9–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu L, Pan C, Chen L, Hu L, Wang C, Han Y,
Yang Y, Cheng Z and Liu WT: AMPK activation by peri-sciatic nerve
administration of ozone attenuates CCI-induced neuropathic pain in
rats. J Mol Cell Biol. 9:132–143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Huang ZJ, Li HC, Cowan AA, Liu S, Zhang YK
and Song XJ: Chronic compression or acute dissociation of dorsal
root ganglion induces cAMP-dependent neuronal hyperexcitability
through activation of PAR2. Pain. 153:1426–1437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bennett GJ and Xie YK: A peripheral
mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation
like those seen in man. Pain. 33:87–107. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pan Z, Shan Q, Gu P, Wang XM, Tai LW, Sun
M, Luo X, Sun L and Cheung CW: miRNA-23a/CXCR4 regulates
neuropathic pain via directly targeting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome
axis. J Neuroinflammation. 15:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Aglah C, Gordon T and Posse de Chaves EI:
cAMP promotes neurite outgrowth and extension through protein
kinase A but independently of Erk activation in cultured rat
motoneurons. Neuropharmacology. 55:8–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C
and Joris J: A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal
nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 32:77–88. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shao H, Xue Q, Zhang F, Luo Y, Zhu H,
Zhang X, Zhang H, Ding W and Yu B: Spinal SIRT1 activation
attenuates neuropathic pain in mice. PLoS One. 9:e1009382014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tsuda M: Microglia in the spinal cord and
neuropathic pain. J Diabetes Investig. 7:17–26. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Andersen HH, Duroux M and Gazerani P:
MicroRNAs as modulators and biomarkers of inflammatory and
neuropathic pain conditions. Neurobiol Dis. 71:159–168. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Dai Z, Chu H, Ma J, Yan Y, Zhang X and
Liang Y: The regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential of
MicroRNAs: From chronic pain to morphine tolerance. Front Mol
Neurosci. 11:802018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shi G, Shi J, Liu K, Liu N, Wang Y, Fu Z,
Ding J, Jia L and Yuan W: Increased miR-195 aggravates neuropathic
pain by inhibiting autophagy following peripheral nerve injury.
Glia. 61:504–512. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Heyn J, Luchting B, Hinske LC, Hübner M,
Azad SC and Kreth S: miR-124a and miR-155 enhance differentiation
of regulatory T cells in patients with neuropathic pain. J
Neuroinflammation. 13:2482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia L, Zhang Y and Dong T: Inhibition of
MicroRNA-221 alleviates neuropathic pain through targeting
suppressor of cytokine signaling 1. J Mol Neurosci. 59:411–420.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang C, Jiang Q, Wang M and Li D: miR-19a
targets suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 to modulate the
progression of neuropathic pain. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10901–10907. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu Y, Cao DL, Jiang BC, Yang T and Gao YJ:
MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates neuropathic pain via suppressing TRAF6
signaling in the spinal cord. Brain Behav Immun. 49:119–129. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Leinders M, Üçeyler N, Pritchard RA,
Sommer C and Sorkin LS: Increased miR-132-3p expression is
associated with chronic neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol. 283:276–286.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Mou J, Cao L, Zhen S, Huang H and
Bao H: MicroRNA-142-3p relieves neuropathic pain by targeting high
mobility group box 1. Int J Mol Med. 41:501–510. 2018.
|
|
31
|
Xiang HC, Lin LX, Hu XF, Zhu H, Li HP,
Zhang RY, Hu L, Liu WT, Zhao YL, Shu Y, et al: AMPK activation
attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-kappaB
activation and IL-1beta expression. J Neuroinflammation. 16:342019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hasanvand A, Amini-Khoei H, Hadian MR,
Abdollahi A, Tavangar SM, Dehpour AR, Semiei E and Mehr SE:
Anti-inflammatory effect of AMPK signaling pathway in rat model of
diabetic neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology. 24:207–219. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|