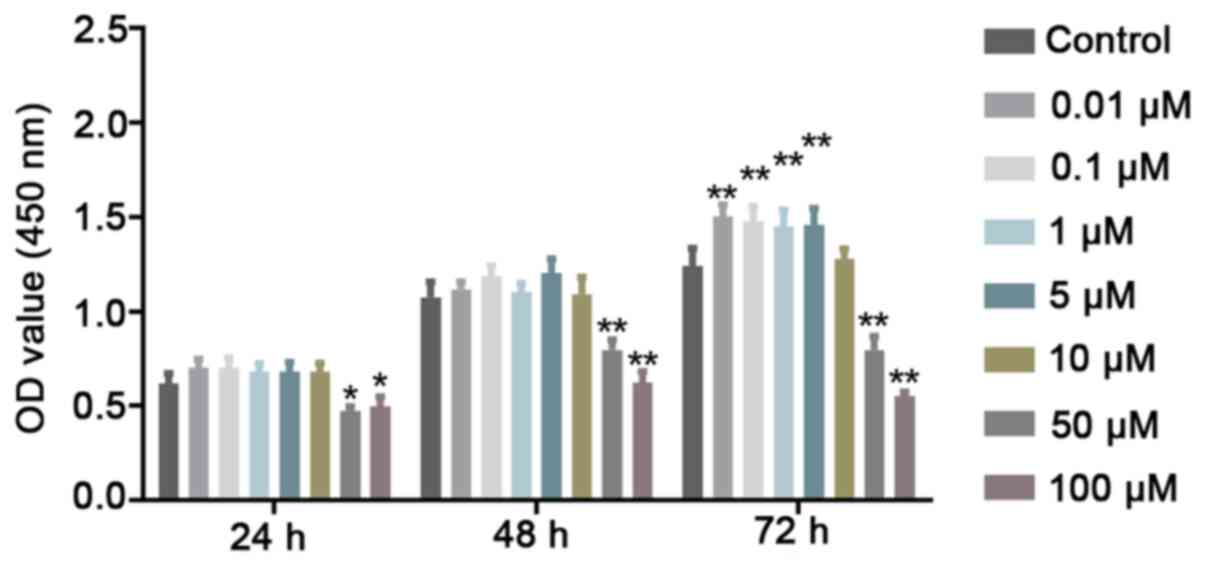
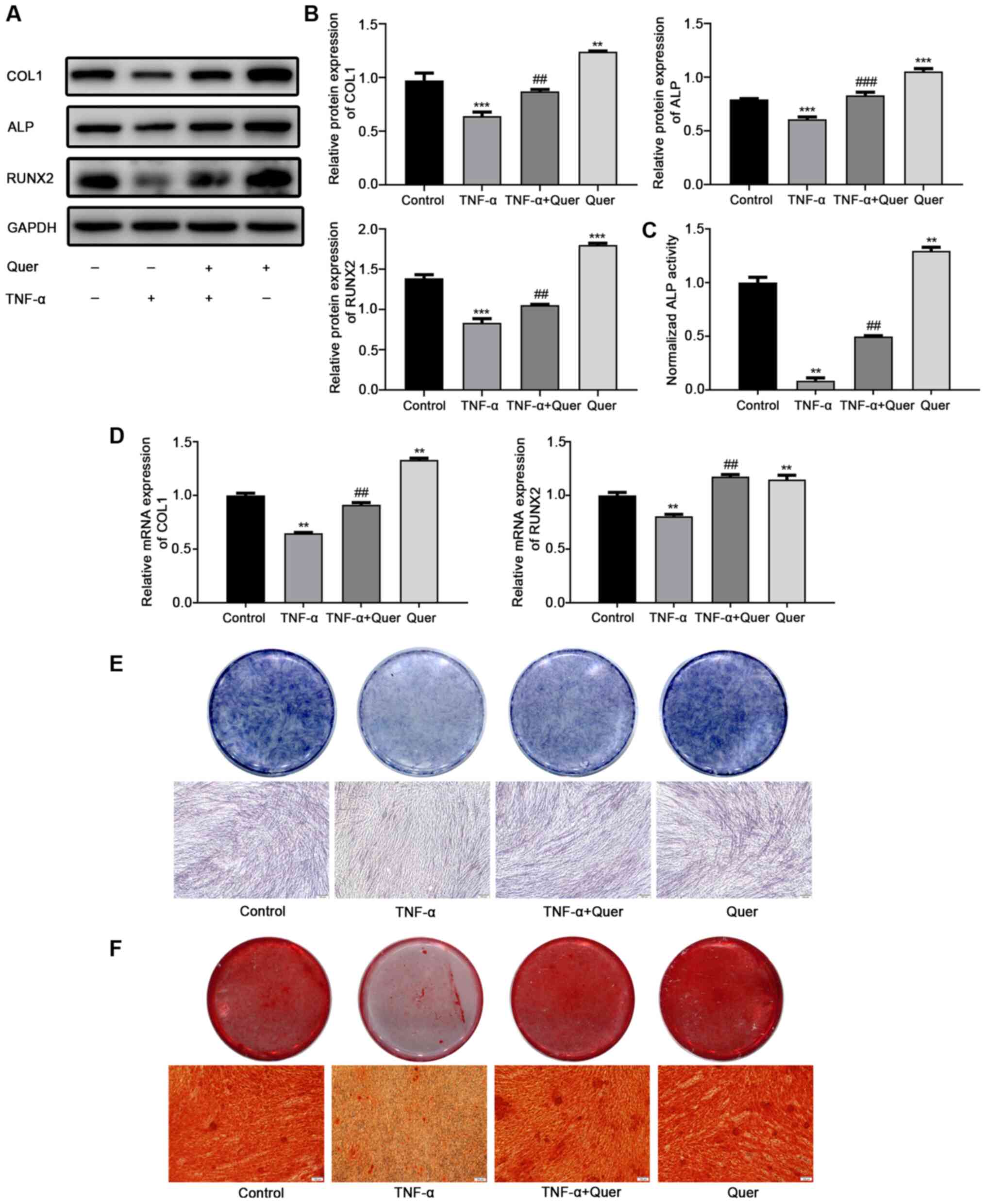
|
1
|
Bartold PM and Van Dyke TE: Periodontitis:
A host-mediated disruption of microbial homeostasis. Unlearning
learned concepts. Periodontol 2000. 62:203–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gao F, Chiu SM, Motan DA, Zhang Z, Chen L,
Ji HL, Tse HF, Fu QL and Lian Q: Mesenchymal stem cells and
immunomodulation: Current status and future prospects. Cell Death
Dis. 7:e20622016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moradi SL, Golchin A, Hajishafieeha Z,
Khani MM and Ardeshirylajimi A: Bone tissue engineering: Adult stem
cells in combination with electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds. J Cell
Physiol. 233:6509–6522. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ouchi T and Nakagawa T: Mesenchymal stem
cell-based tissue regeneration therapies for periodontitis. Regen
Ther. 14:72–78. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xia Y, Tang HN, Wu RX, Yu Y, Gao LN and
Chen FM: Cell responses to conditioned media produced by
patient-matched stem cells derived from healthy and inflamed
periodontal ligament tissues. J Periodontol. 87:e53–e63. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bright R, Hynes K, Gronthos S and Bartold
PM: Periodontal ligament-derived cells for periodontal regeneration
in animal models: A systematic review. J Periodontal Res.
50:160–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhang Y, Xing Y, Jia L, Ji Y, Zhao B, Wen
Y and Xu X: An in vitro comparative study of multisource derived
human mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Stem
Cells Dev. 27:1634–1645. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trubiani O, Pizzicannella J, Caputi S,
Marchisio M, Mazzon E, Paganelli R, Paganelli A and Diomede F:
Periodontal ligament stem cells: Current knowledge and future
perspectives. Stem Cells Dev. 28:995–1003. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Winning L, El Karim IA and Lundy FT: A
Comparative analysis of the osteogenic potential of dental
mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 28:1050–1058. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xu XY, He XT, Wang J, Li X, Xia Y, Tan YZ
and Chen FM: Role of the P2X7 receptor in inflammation-mediated
changes in the osteogenesis of periodontal ligament stem cells.
Cell Death Dis. 10:202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bartold PM, Cantley MD and Haynes DR:
Mechanisms and control of pathologic bone loss in periodontitis.
Periodontol 2000. 53:55–69. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abbas S, Zhang YH, Clohisy JC and Abu-Amer
Y: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits pre-osteoblast
differentiation through its type-1 receptor. Cytokine. 22:33–41.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang H, Zhao N, Xu X, Xu Y, Li S, Zhang J
and Yang P: Dose-specific effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha on
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Prolif.
44:420–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A,
Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks
BG, Fitzgerald KA, et al: Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating
pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3
inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol.
183:787–791. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guo H, Callaway JB and Ting JP:
Inflammasomes: Mechanism of action, role in disease, and
therapeutics. Nat Med. 21:677–687. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schroder K and Tschopp J: The
inflammasomes. Cell. 140:821–832. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yi X, Zhang L, Lu W, Tan X, Yue J, Wang P,
Xu W, Ye L and Huang D: The effect of NLRP inflammasome on the
regulation of AGEs-induced inflammatory response in human
periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 54:681–689. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang L, Chen K, Wan X, Wang F, Guo Z and
Mo Z: NLRP3 inflammasome activation in mesenchymal stem cells
inhibits osteogenic differentiation and enhances adipogenic
differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 484:871–877. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu L, Zhang L, Wang Z, Li C, Li S, Li L,
Fan Q and Zheng L: Melatonin suppresses estrogen deficiency-induced
osteoporosis and promotes osteoblastogenesis by inactivating the
NLRP3 inflammasome. Calcif Tissue Int. 103:400–410. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
de Alencar JB, Zacarias JMV, Tsuneto PY,
Souza VH, Silva COE, Visentainer JEL and Sell AM: Influence of
inflammasome NLRP3, and IL1B and IL2 gene polymorphisms in
periodontitis susceptibility. PLoS One. 15:e02279052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Isaza-Guzmán DM, Medina-Piedrahíta VM,
Gutiérrez-Henao C and Tobón-Arroyave SI: Salivary levels of NLRP3
inflammasome-related proteins as potential biomarkers of
periodontal clinical status. J Periodontol. 88:1329–1338. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Yao J, Han C, Yang J, Chaudhry MT,
Wang S, Liu H and Yin Y: Quercetin, inflammation and immunity.
Nutrients. 8:1672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng WC, Huang RY, Chiang CY, Chen JK,
Liu CH, Chu CL and Fu E: Ameliorative effect of quercetin on the
destruction caused by experimental periodontitis in rats. J
Periodontal Res. 45:788–795. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan Z, Min J, Zhao Y, Cheng Q, Wang K,
Lin S, Luo J and Liu H: Quercetin rescued TNF-alpha-induced
impairments in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell
osteogenesis and improved osteoporosis in rats. Am J Transl Res.
10:4313–4321. 2018.
|
|
25
|
Guo C, Yang RJ, Jang K, Zhou XL and Liu
YZ: Protective effects of pretreatment with quercetin against
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and the inhibition of
osteoblast differentiation via the MAPK and Wnt/β-Catenin pathways
in MC3T3-E1 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 43:1547–1561. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim HR, Kim BM, Won JY, Lee KA, Ko HM,
Kang YS, Lee SH and Kim KW: Quercetin, a plant polyphenol, has
potential for the prevention of bone destruction in rheumatoid
arthritis. J Med Food. 22:152–161. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zendedel A, Johann S, Mehrabi S, Joghataei
MT, Hassanzadeh G, Kipp M and Beyer C: Activation and regulation of
NLRP3 inflammasome by intrathecal application of SDF-1a in a spinal
cord injury model. Mol Neurobiol. 53:3063–3075. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jiang W, Huang Y, Han N, He F, Li M, Bian
Z, Liu J, Sun T and Zhu L: Quercetin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome
activation and attenuates histopathology in a rat model of spinal
cord injury. Spinal Cord. 54:592–596. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Xu X, Li Y, Kou J, Huang F, Liu B
and Liu K: Quercetin, luteolin and epigallocatechin gallate
alleviate TXNIP and NLRP3-mediated inflammation and apoptosis with
regulation of AMPK in endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
745:59–68. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Qu X, Gao H, Zhai J, Tao L, Sun
J, Song Y and Zhang J: Quercetin attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome
activation and apoptosis to protect INH-induced liver injury via
regulating SIRT1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 85:1066342020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao B, Zhang Y, Xiong Y and Xu X: Rutin
promotes the formation and osteogenic differentiation of human
periodontal ligament stem cell sheets in vitro. Int J Mol Med.
44:2289–2297. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bosshardt DD: The periodontal pocket:
Pathogenesis, histopathology and consequences. Periodontol 2000.
76:43–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Huang J, Liu L, Jin S, Zhang Y, Zhang L,
Li S, Song A and Yang P: Proanthocyanidins promote osteogenic
differentiation of human periodontal ligament fibroblasts in
inflammatory environment via suppressing NF-κB signal pathway.
Inflammation. 43:892–902. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yue H, Xu X, Liu Q, Li X, Xiao Y and Hu B:
Effects of non-surgical periodontal therapy on systemic
inflammation and metabolic markers in patients undergoing
haemodialysis and/or peritoneal dialysis: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMC Oral Health. 20:182020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Romero-Castro NS, Vázquez-Villamar M,
Muñoz-Valle JF, Reyes-Fernández S, Serna-Radilla VO,
García-Arellano S and Castro-Alarcón N: Relationship between TNF-α,
MMP-8, and MMP-9 levels in gingival crevicular fluid and the
subgingival microbiota in periodontal disease. Odontology.
108:25–33. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ohori F, Kitaura H, Ogawa S, Shen WR, Qi
J, Noguchi T, Marahleh A, Nara Y, Pramusita A and Mizoguchi I:
IL-33 inhibits TNF-α-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone
resorption. Int J Mol Sci. 21:11302020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tan J, Zhou L, Xue P, An Y, Luo L, Zhang
R, Wu G, Wang Y, Zhu H and Wang Q: Tumor necrosis factor-α
attenuates the osteogenic differentiation capacity of periodontal
ligament stem cells by activating PERK signaling. J Periodontol.
87:e159–e171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qin Z, Fang Z, Zhao L, Chen J, Li Y and
Liu G: High dose of TNF-α suppressed osteogenic differentiation of
human dental pulp stem cells by activating the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling. J Mol Histol. 46:409–420. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Casado-Diaz A, Anter J, Dorado G and
Quesada-Gómez JM: Effects of quercetin, a natural phenolic
compound, in the differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells
(MSC) into adipocytes and osteoblasts. J Nutr Biochem. 32:151–162.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Noh MK, Jung M, Kim SH, Lee SR, Park KH,
Kim DH, Kim HH and Park YG: Assessment of IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α
levels in the gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis. Exp
Ther Med. 6:847–851. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Marchesan JT: Inflammasomes as
contributors to periodontal disease. J Periodontol. 91(Suppl 1):
S6–S11. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pang XG, Cong Y, Bao NR, Li YG and Zhao
JN: Quercetin stimulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell
differentiation through an estrogen receptor-mediated pathway.
Biomed Res Int. 2018:41780212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen X, Hu C, Wang G, Li L, Kong X, Ding Y
and Jin Y: Nuclear factor-κB modulates osteogenesis of periodontal
ligament stem cells through competition with β-catenin signaling in
inflammatory microenvironments. Cell Death Dis. 4:e5102013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang LM, Zhao N, Zhang J, Sun QF, Yang CZ
and Yang PS: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibits osteogenic
differentiation of pre-osteoblasts by downregulation of EphB4
signaling via activated nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. J
Periodontal Res. 53:66–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li T, Li F, Liu X, Liu J and Li D:
Synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of quercetin and catechin via
inhibiting activation of TLR4-MyD88-mediated NF-κB and MAPK
signaling pathways. Phytother Res. 33:756–767. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Y, Yu C, Ji K, Wang X, Li X, Xie H,
Wang Y, Huang Y, Qi D and Fan H: Quercetin reduces TNF-α-induced
mesangial cell proliferation and inhibits PTX3 production:
Involvement of NF-κB signaling pathway. Phytother Res.
33:2401–2408. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Hu T, Lu XY, Shi JJ, Liu XQ, Chen QB, Wang
Q, Chen YB and Zhang SJ: Quercetin protects against diabetic
encephalopathy via SIRT1/NLRP3 pathway in db/db mice. J Cell Mol
Med. 24:3449–3459. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|