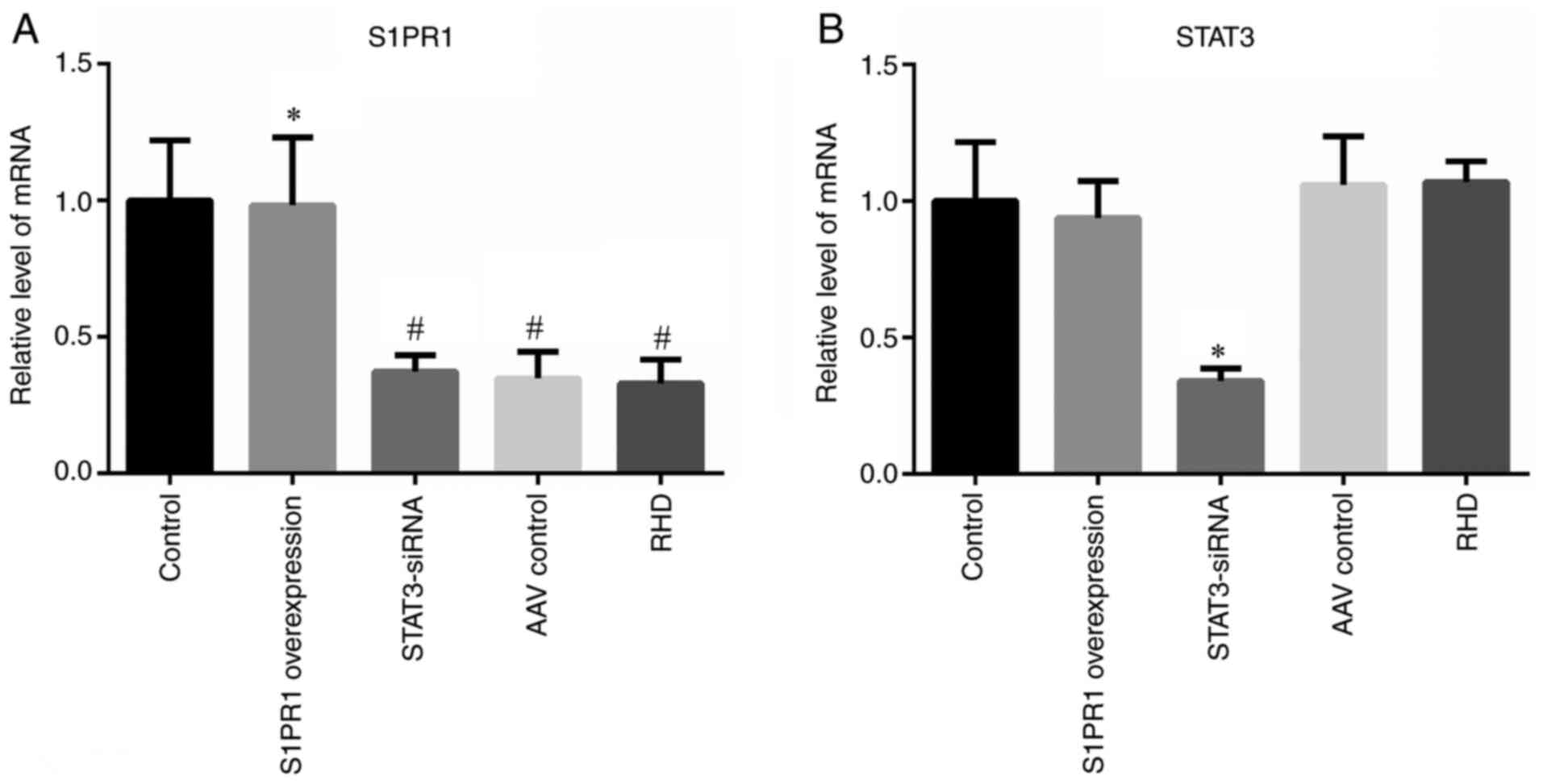
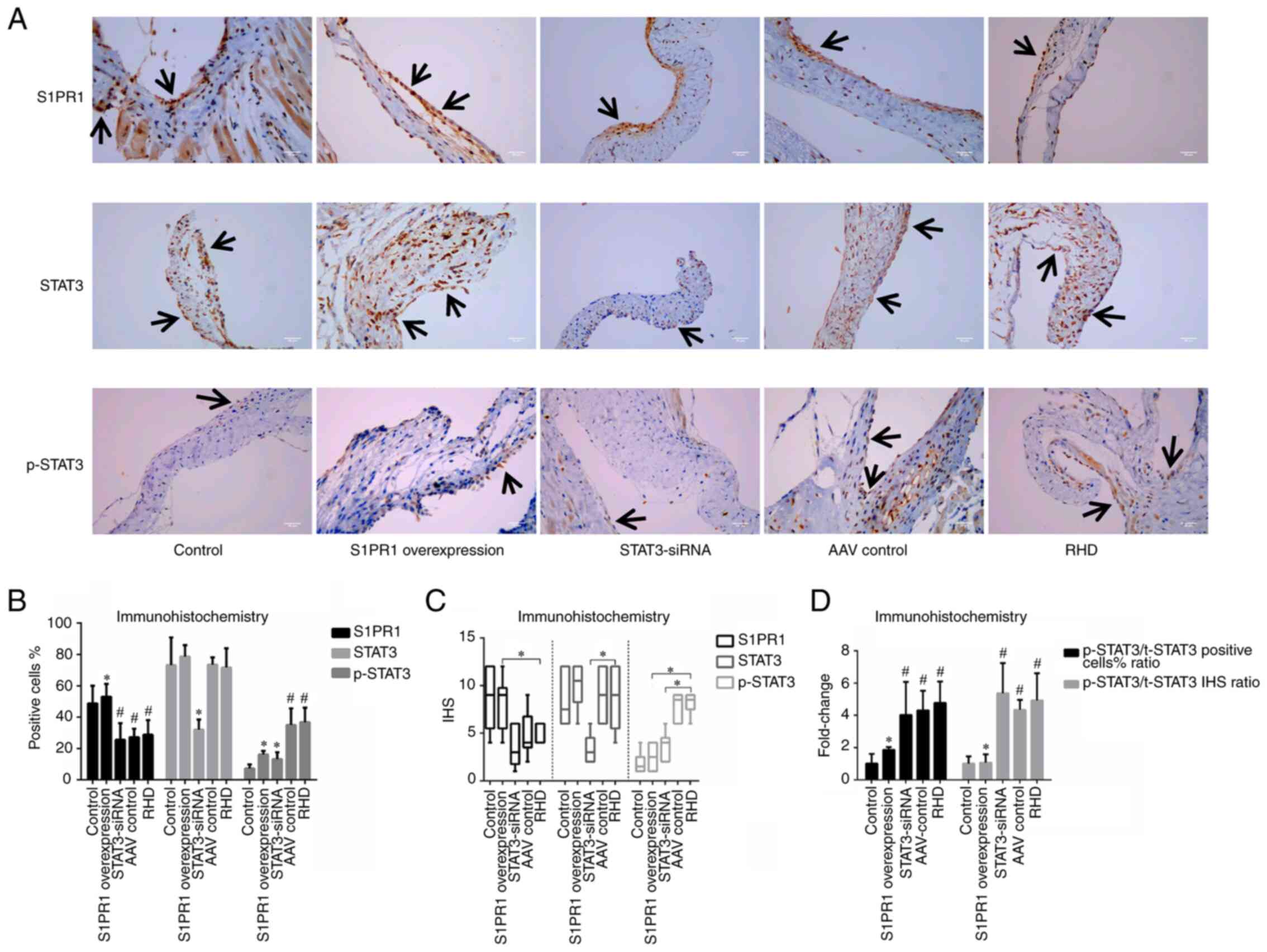
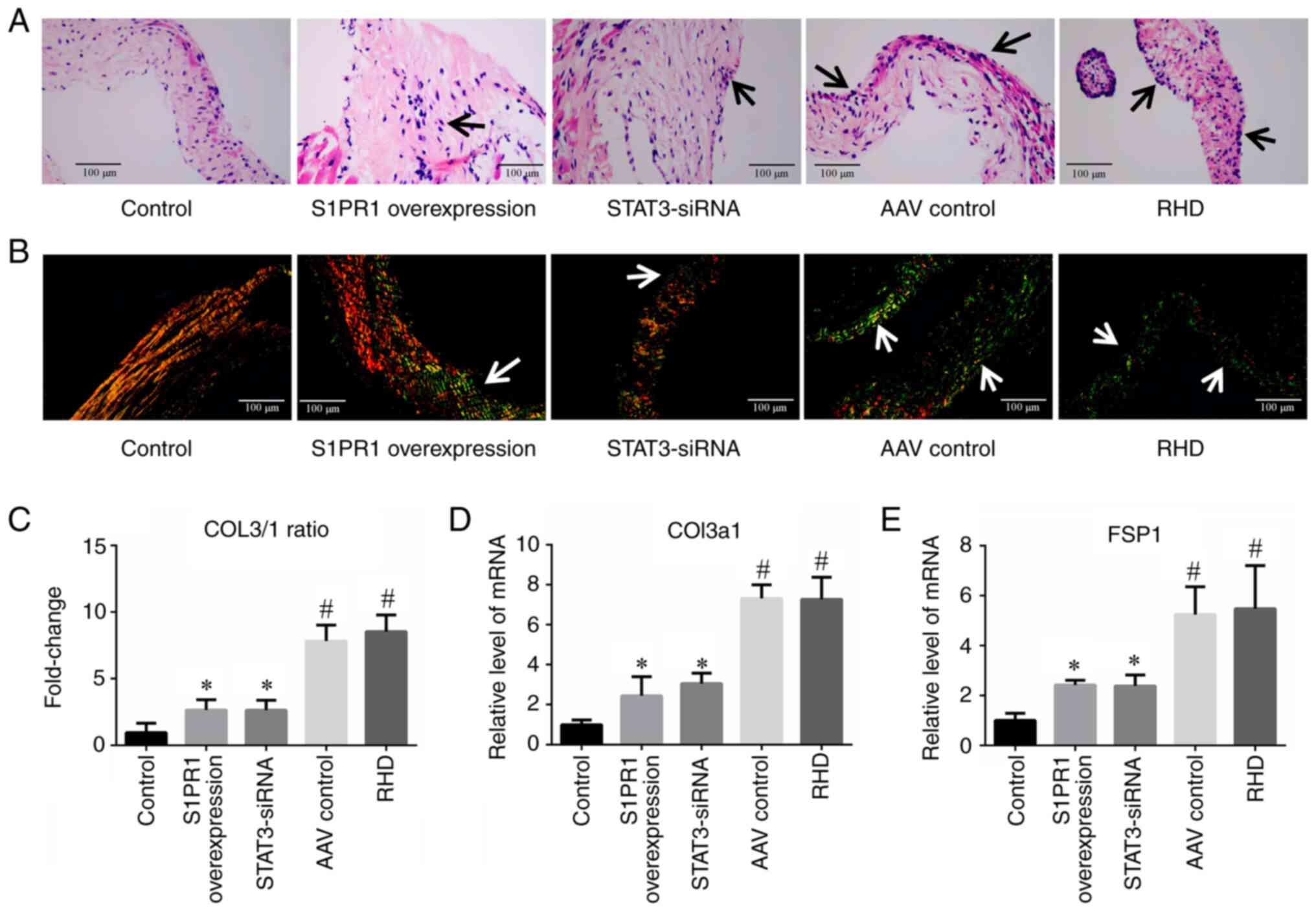
|
1
|
Watkins DA, Johnson CO, Colquhoun SM,
Karthikeyan G, Beaton A, Bukhman G, Forouzanfar MH, Longenecker CT,
Mayosi BM, Mensah GA, et al: Global, regional, and national burden
of rheumatic heart disease, 1990-2015. N Engl J Med. 377:713–722.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Leal MT, Passos LS, Guarçoni FV, Aguiar
JM, Silva RB, Paula TM, Santos RF, Nassif MC, Gomes NF, Tan TC and
Nunes MC: Rheumatic heart disease in the modern era: Recent
developments and current challenges. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop.
52:e201800412019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mirabel M, Narayanan K, Jouven X and
Marijon E: Cardiology patient page. Prevention of acute rheumatic
fever and rheumatic heart disease. Circulation. 130:e35–e37. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhao Z, He D, Ling F, Chu T, Huang D, Wu H
and Ge J: CD4+ T cells and TGFβ1/MAPK signal pathway
involved in the valvular hyperblastosis and fibrosis in patients
with rheumatic heart disease. Exp Mol Pathol. 114:1044022020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Messias-Reason IJ, Schafranski MD,
Kremsner PG and Kun JF: Ficolin 2 (FCN2) functional polymorphisms
and the risk of rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease. Clin
Exp Immunol. 157:395–399. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li M, Xu S, Geng Y, Sun L, Wang R, Yan Y,
Wang H, Li Y, Yi Q, Zhang Y, et al: The protective effects of
L-carnitine on myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury in patients
with rheumatic valvular heart disease undergoing CPB surgery are
associated with the suppression of NF-κB pathway and the activation
of Nrf2 pathway. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 46:1001–1012. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Aoki M, Aoki H, Ramanathan R, Hait NC and
Takabe K: Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling in immune cells and
inflammation: Roles and therapeutic potential. Mediators Inflamm.
2016:86068782016.
|
|
8
|
Jozefczuk E, Guzik TJ and Siedlinski M:
Significance of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiovascular
physiology and pathology. Pharmacol Res. 156:1047932020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Deng S, Zhou X, Ge Z, Song Y, Wang H, Liu
X and Zhang D: Exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
ameliorate cardiac damage after myocardial infarction by activating
S1P/SK1/S1PR1 signaling and promoting macrophage M2 polarization.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 114:1055642019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu X, Wu J, Zhu C, Liu J, Chen X, Zhuang
T, Kuang Y, Wang Y, Hu H, Yu P, et al: Endothelial S1pr1 regulates
pressure overload-induced cardiac remodelling through AKT-eNOS
pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 24:2013–2026. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Y, Zhi Y, Song H, Zong M, Yi J, Mao G,
Chen L and Huang G: S1PR1 promotes proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through activating
STAT3 pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3692019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen YZ, Wang F, Wang HJ and Liu HB:
Sphingosine 1 phosphate receptor-1 (S1PR1) signaling protects
cardiac function by inhibiting cardiomyocyte autophagy. J Geriatr
Cardiol. 15:334–345. 2018.
|
|
13
|
Garris CS, Wu L, Acharya S, Arac A, Blaho
VA, Huang Y, Moon BS, Axtell RC, Ho PP, Steinberg GK, et al:
Defective sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1) phosphorylation
exacerbates TH17-mediated autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat
Immunol. 14:1166–1172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wu XD, Zeng ZY, Gong DP, Wen JL and Huang
F: Potential involvement of S1PR1/STAT3 signaling pathway in
cardiac valve damage due to rheumatic heart disease. Biotech
Histochem. 94:398–403. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hu YS, Han X and Liu XH: STAT3: A
potential drug target for tumor and inflammation. Curr Top Med
Chem. 19:1305–1317. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu X, Hu H, Fan H, Zuo D, Shou Z, Liao Y,
Nan Z and Tang Q: The role of STAT3 and AhR in the differentiation
of CD4+ T cells into Th17 and Treg cells. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e66152017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gaffen SL, Jain R, Garg AV and Cua DJ: The
IL-23-IL-17 immune axis: From mechanisms to therapeutic testing.
Nat Rev Immunol. 14:585–600. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Whibley N, Tritto E, Traggiai E, Kolbinger
F, Moulin P, Brees D, Coleman BM, Mamo AJ, Garg AV, Jaycox JR, et
al: Antibody blockade of IL-17 family cytokines in immunity to
acute murine oral mucosal candidiasis. J Leukoc Biol. 99:1153–1164.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Y, Shao Z, Zhang X, Jia X, Xia Y,
Zhang Y, Xin N, Guo M, Chen J, Zheng S, et al: TIPE2 play a
negative role in TLR4-mediated autoimmune T helper 17 cell
responses in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Neuroimmune
Pharmacol. 10:635–644. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bas HD, Baser K, Yavuz E, Bolayir HA,
Yaman B, Unlu S, Cengel A, Bagriacik EU and Yalcin R: A shift in
the balance of regulatory T and T helper 17 cells in rheumatic
heart disease. J Investig Med. 62:78–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wen Y, Zeng Z, Gui C, Li L and Li W:
Changes in the expression of Th17 cell-associated cytokines in the
development of rheumatic heart disease. Cardiovasc Pathol.
24:382–387. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lankadasari MB, Aparna JS, Mohammed S,
James S, Aoki K, Binu VS, Nair S and Harikumar KB: Targeting
S1PR1/STAT3 loop abrogates desmoplasia and chemosensitizes
pancreatic cancer to gemcitabine. Theranostics. 8:3824–3840. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lin Q, Ren L, Jian M, Xu P, Li J, Zheng P,
Feng Q, Yang L, Ji M, Wei Y and Xu J: The mechanism of the
premetastatic niche facilitating colorectal cancer liver metastasis
generated from myeloid-derived suppressor cells induced by the
S1P1STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 10:6932019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee H, Deng J, Kujawski M, Yang C, Liu Y,
Herrmann A, Kortylewski M, Horne D, Somlo G, Forman S, et al:
STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3
activation in tumors. Nat Med. 16:1421–1428. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Deng J, Liu Y, Lee H, Herrmann A, Zhang W,
Zhang C, Shen S, Priceman SJ, Kujawski M, Pal SK, et al:
S1PR1-STAT3 signaling is crucial for myeloid cell colonization at
future metastatic sites. Cancer Cell. 21:642–654. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen A, Wen J, Lu C, Lin B, Xian S, Huang
F, Wu Y and Zeng Z: Inhibition of miR-155-5p attenuates the
valvular damage induced by rheumatic heart disease. Int J Mol Med.
45:429–440. 2020.
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Guendisch U, Weiss J, Ecoeur F, Riker JC,
Kaupmann K, Kallen J, Hintermann S, Orain D, Dawson J, Billich A
and Guntermann C: Pharmacological inhibition of RORγt suppresses
the Th17 pathway and alleviates arthritis in vivo. PLoS One.
12:e01883912017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Friedrichs K, Gluba S, Eidtmann H and
Jonat W: Overexpression of p53 and prognosis in breast cancer.
Cancer. 72:3641–3647. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Purushothaman KR, Purushothaman M,
Turnbull IC, Adams DH, Anyanwu A, Krishnan P, Kini A, Sharma SK,
O'Connor WN and Moreno PR: Association of altered collagen content
and lysyl oxidase expression in degenerative mitral valve disease.
Cardiovasc Pathol. 29:11–18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
GBD 2015 Mortality and Causes of Death
Collaborators: global, regional, and national life expectancy,
all-cause mortality, and cause-specific mortality for 249 causes of
death, 1980-2015: A systematic analysis for the global burden of
disease study 2015. Lancet. 388:1459–1544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators:
global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264
causes of death, 1980-2016: A systematic analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2016. Lancet. 390:1151–1210. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators:
global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282
causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: A
systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017.
Lancet. 392:1736–1788. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang F, Xia Y, Yan W, Zhang H, Zhou F,
Zhao S, Wang W, Zhu D, Xin C, Lee Y, et al: Sphingosine 1-phosphate
signaling contributes to cardiac inflammation, dysfunction, and
remodeling following myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 310:H250–H261. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Edmonds Y, Milstien S and Spiegel S:
Development of small-molecule inhibitors of sphingosine-1-phosphate
signaling. Pharmacol Ther. 132:352–360. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cartier A, Leigh T, Liu CH and Hla T:
Endothelial sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors promote vascular
normalization and antitumor therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:3157–3166. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Abarca-Zabalía J, García MI, Lozano Ros A,
Marín-Jiménez I, Martínez-Ginés ML, López-Cauce B, Martín-Barbero
ML, Salvador-Martín S, Sanjurjo-Saez M, García-Domínguez JM and
López Fernández LA: Differential expression of SMAD genes and S1PR1
on circulating CD4+ T cells in multiple sclerosis and Crohn's
disease. Int J Mol Sci. 21:6762020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang C, Shen J, Kong S, Zhang M, Zhang Q,
Zhou J, Zhen X, Kang N, Jiang Y, Ding L, et al: MicroRNA-181a
promotes follicular granulosa cell apoptosis via
sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 expression downregulation†. Biol
Reprod. 101:975–985. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Silva VR, Micheletti TO, Katashima CK,
Lenhare L, Morari J, Moura-Assis A, de Lima-Júnior JC, Camargo JA,
Passos GR, Gaspar RS, et al: Exercise activates the hypothalamic
S1PR1-STAT3 axis through the central action of interleukin 6 in
mice. J Cell Physiol. 233:9426–9436. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Camporeale A, Marino F, Papageorgiou A,
Carai P, Fornero S, Fletcher S, Page BD, Gunning P, Forni M,
Chiarle R, et al: STAT3 activity is necessary and sufficient for
the development of immune-mediated myocarditis in mice and promotes
progression to dilated cardiomyopathy. EMBO Mol Med. 5:572–590.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yuan J, Yu M, Lin QW, Cao AL, Yu X, Dong
JH, Wang JP, Zhang JH, Wang M, Guo HP, et al: Th17 cells contribute
to viral replication in coxsackievirus B3-induced acute viral
myocarditis. J Immunol. 185:4004–4010. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kurdi M, Zgheib C and Booz GW: Recent
developments on the crosstalk Between STAT3 and inflammation in
heart function and disease. Front Immunol. 9:30292018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Turkson J and Jove R: STAT proteins: Novel
molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene.
19:6613–6626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang Y, Wang Y, Che X, Hou K, Wu J, Zheng
C, Cheng Y, Liu Y, Hu X and Zhang J: Integrin α5 promotes migration
and invasion through the FAK/STAT3/AKT signaling pathway in
icotinib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Lett.
22:5562021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hu X, Jiao F, Zhang L and Jiang Y:
Dihydrotanshinone Inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma by suppressing
the JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:6549862021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Liu X, Zhou F, Wang W, Chen G, Zhang Q, Lv
R, Zhao Z, Li X, Yu Q, Meves JM, et al: IL-9-triggered lncRNA
Gm13568 regulates Notch1 in astrocytes through interaction with
CBP/P300: Contribute to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation. 18:1082021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Camporeale A and Poli V: IL-6, IL-17 and
STAT3: A holy trinity in auto-immunity? Front Biosci (Landmark Ed).
17:2306–2326. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wu J, Niu P, Zhao Y, Cheng Y, Chen W, Lin
L, Lu J, Cheng X and Xu Z: Impact of miR-223-3p and miR-2909 on
inflammatory factors IL-6, IL-1ß, and TNF-α, and the
TLR4/TLR2/NF-κB/STAT3 signaling pathway induced by
lipopolysaccharide in human adipose stem cells. PLoS One.
14:e02120632019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Bonetto A, Aydogdu T, Jin X, Zhang Z, Zhan
R, Puzis L, Koniaris LG and Zimmers TA: JAK/STAT3 pathway
inhibition blocks skeletal muscle wasting downstream of IL-6 and in
experimental cancer cachexia. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
303:E410–E421. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Damasceno LE, Prado DS, Veras FP, Fonseca
MM, Toller-Kawahisa JE, Rosa MH, Públio GA, Martins TV, Ramalho FS,
Waisman A, et al: PKM2 promotes Th17 cell differentiation and
autoimmune inflammation by fine-tuning STAT3 activation. J Exp Med.
217:e201906132020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shui X, Chen S, Lin J, Kong J, Zhou C and
Wu J: Knockdown of lncRNA NEAT1 inhibits Th17/CD4+ T cell
differentiation through reducing the STAT3 protein level. J Cell
Physiol. 234:22477–22484. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Jiang L, Wei XF, Yi DH, Xu P, Liu H, Chang
Q, Yang SM, Li ZF, Gao HB and Hao GJ: Synergistic effects of cyclic
strain and Th1-like cytokines on tenascin-C production by rheumatic
aortic valve interstitial cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 155:216–223.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li M, Yi XIN, Ma L and Zhou Y: Hepatocyte
growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor regulate atrial
fibrosis in patients with atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart
disease via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Exp Ther Med. 6:1121–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang P, Wang W, Wang X, Wang X, Song Y,
Zhang J and Zhao H: Focal adhesion kinase mediates atrial fibrosis
via the AKT/S6K signaling pathway in chronic atrial fibrillation
patients with rheumatic mitral valve disease. Int J Cardiol.
168:3200–3207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Zhang L, Zhang N, Tang X, Liu F, Luo S and
Xiao H: Increased α-actinin-2 expression in the atrial myocardium
of patients with atrial fibrillation related to rheumatic heart
disease. Cardiology. 135:151–159. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Guo F, Yi X, Li M, Fu J and Li S: Snail1
is positively correlated with atrial fibrosis in patients with
atrial fibrillation and rheumatic heart disease. Exp Ther Med.
14:4231–4237. 2017.
|
|
57
|
Wu Y, Xu M, Bao H and Zhang JH:
Sitagliptin inhibits EndMT in vitro and improves cardiac function
of diabetic rats through the SDF-1α/PKA pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:841–848. 2019.
|
|
58
|
Remenyi B, ElGuindy A, Smith SC Jr, Yacoub
M and Holmes DR Jr: Valvular aspects of rheumatic heart disease.
Lancet. 387:1335–1346. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|