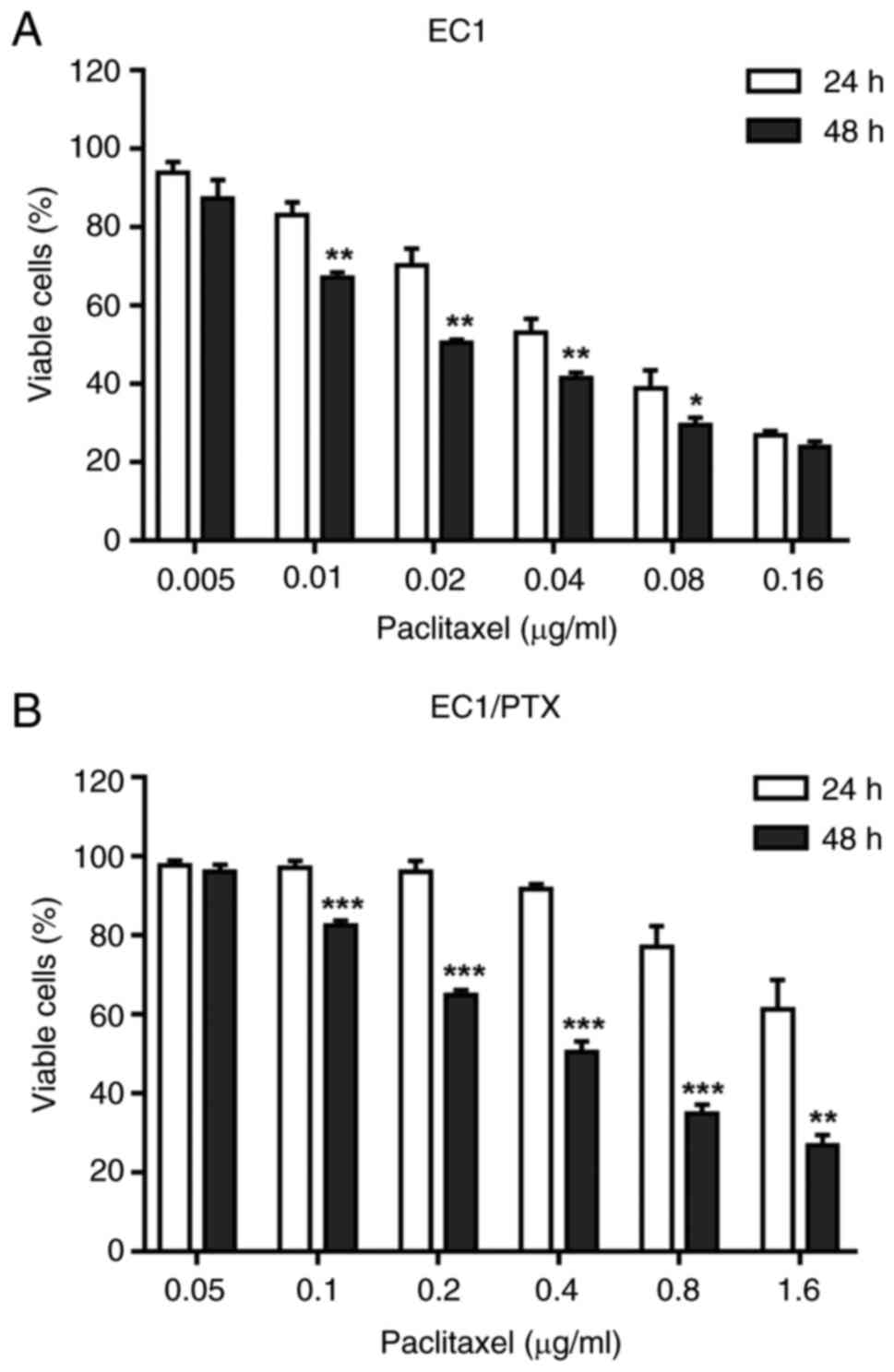
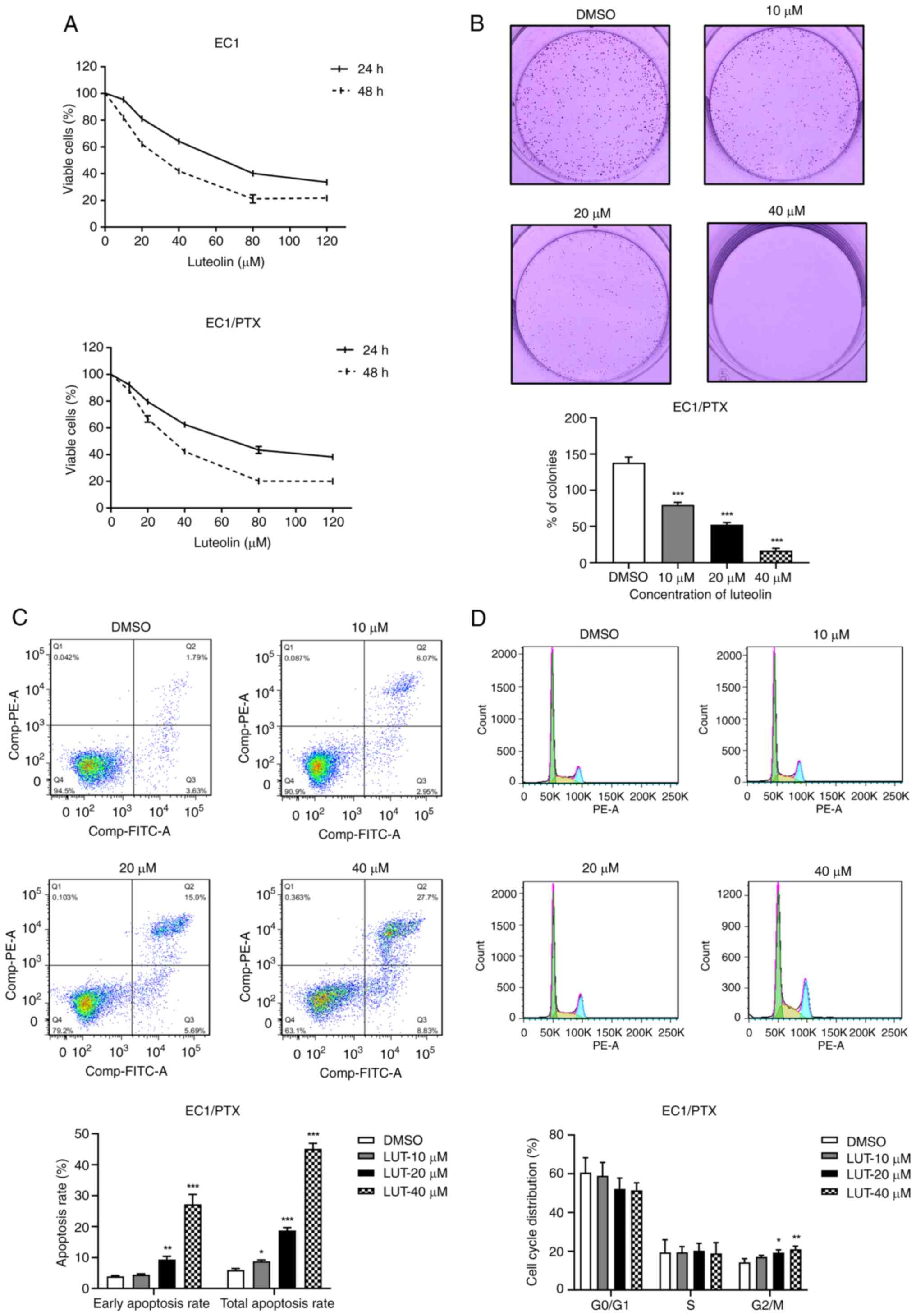
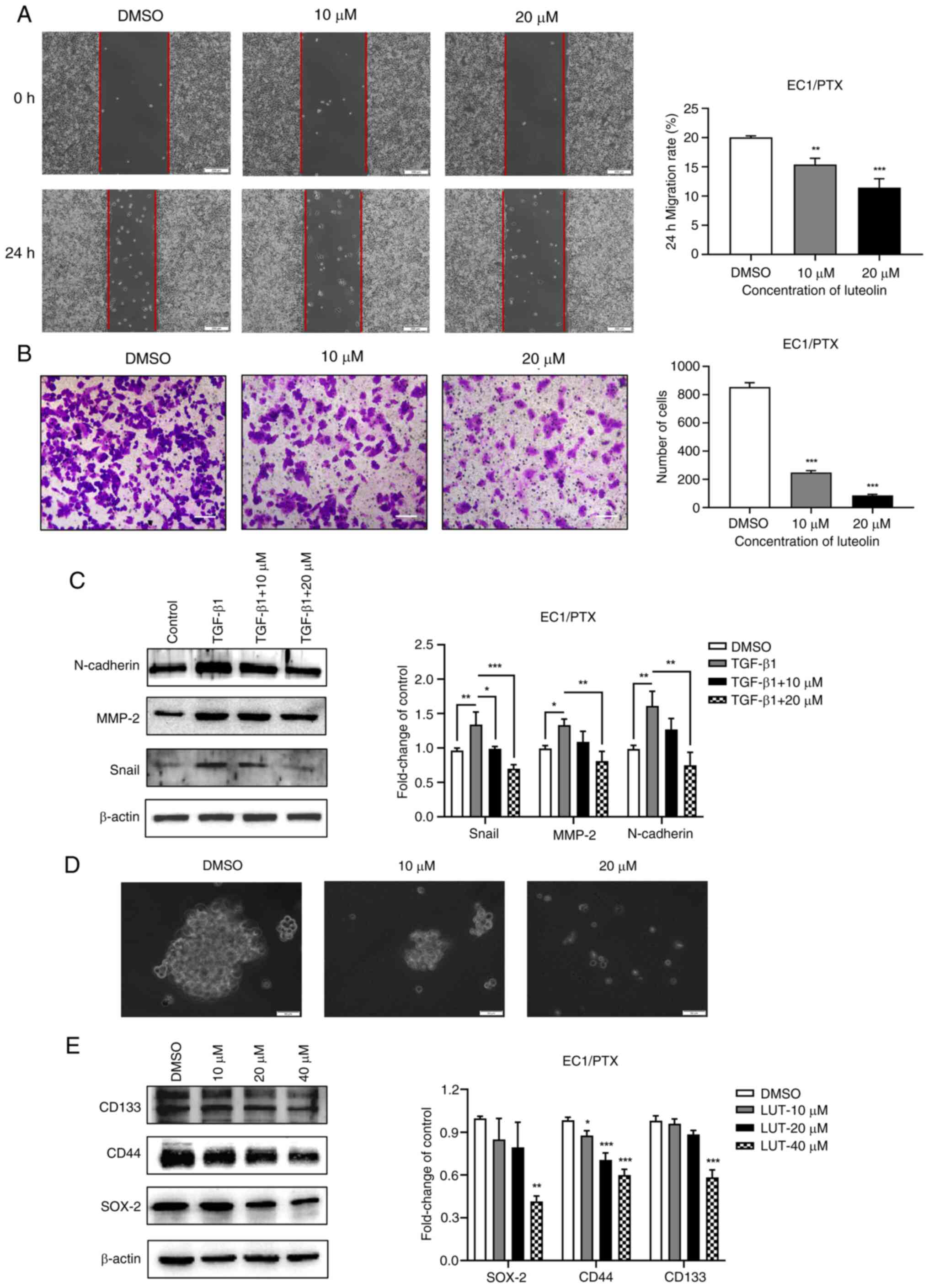
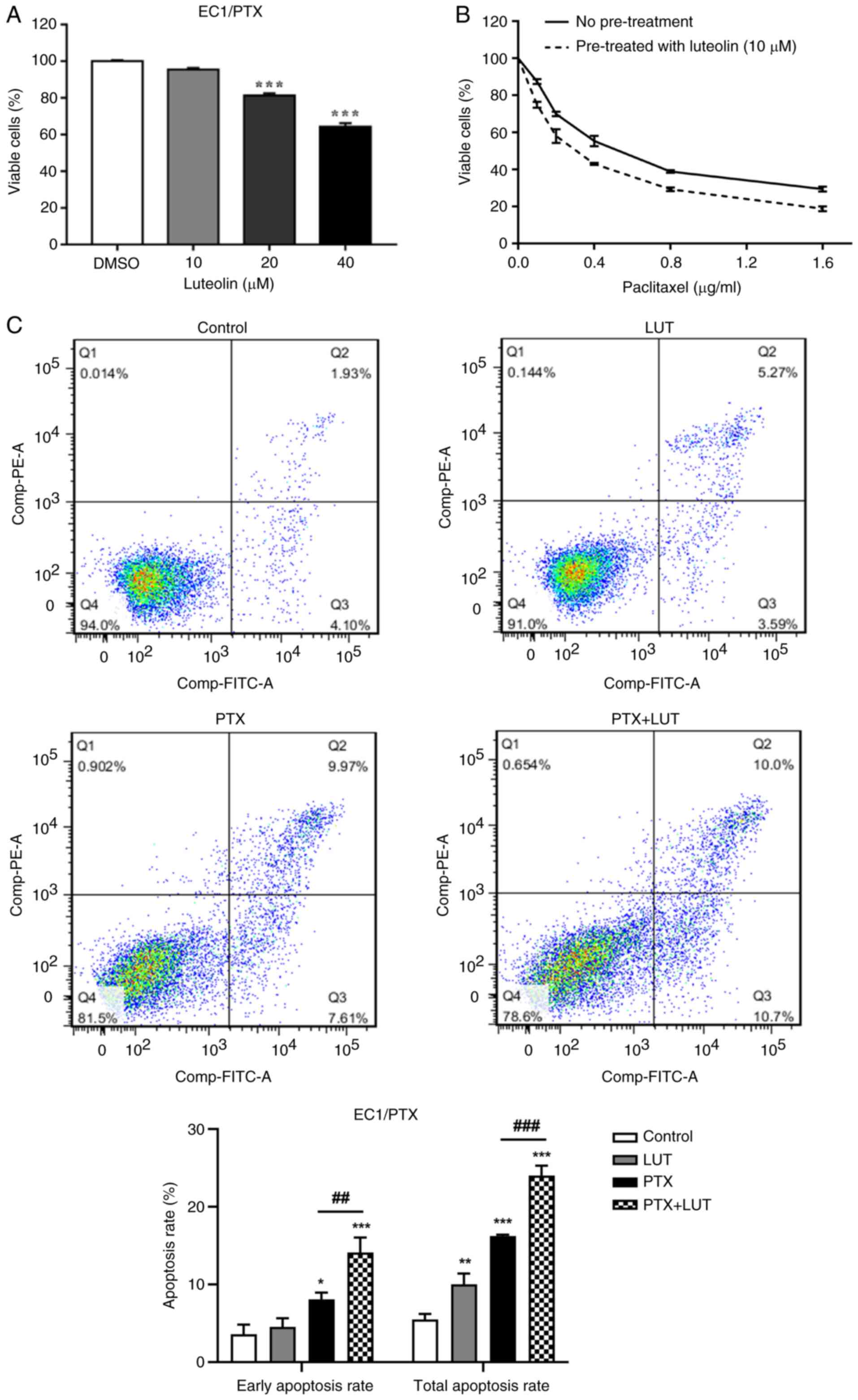
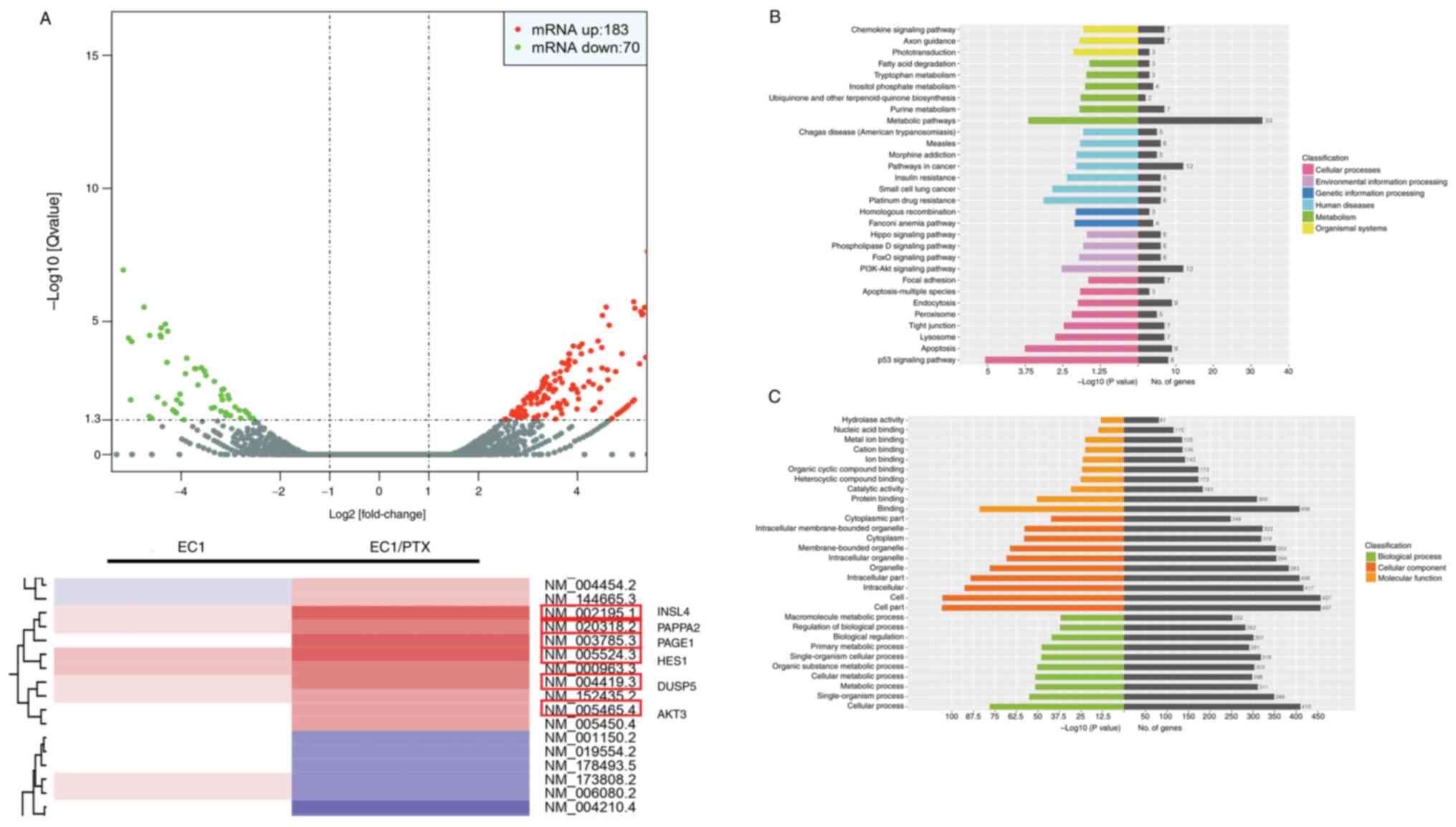
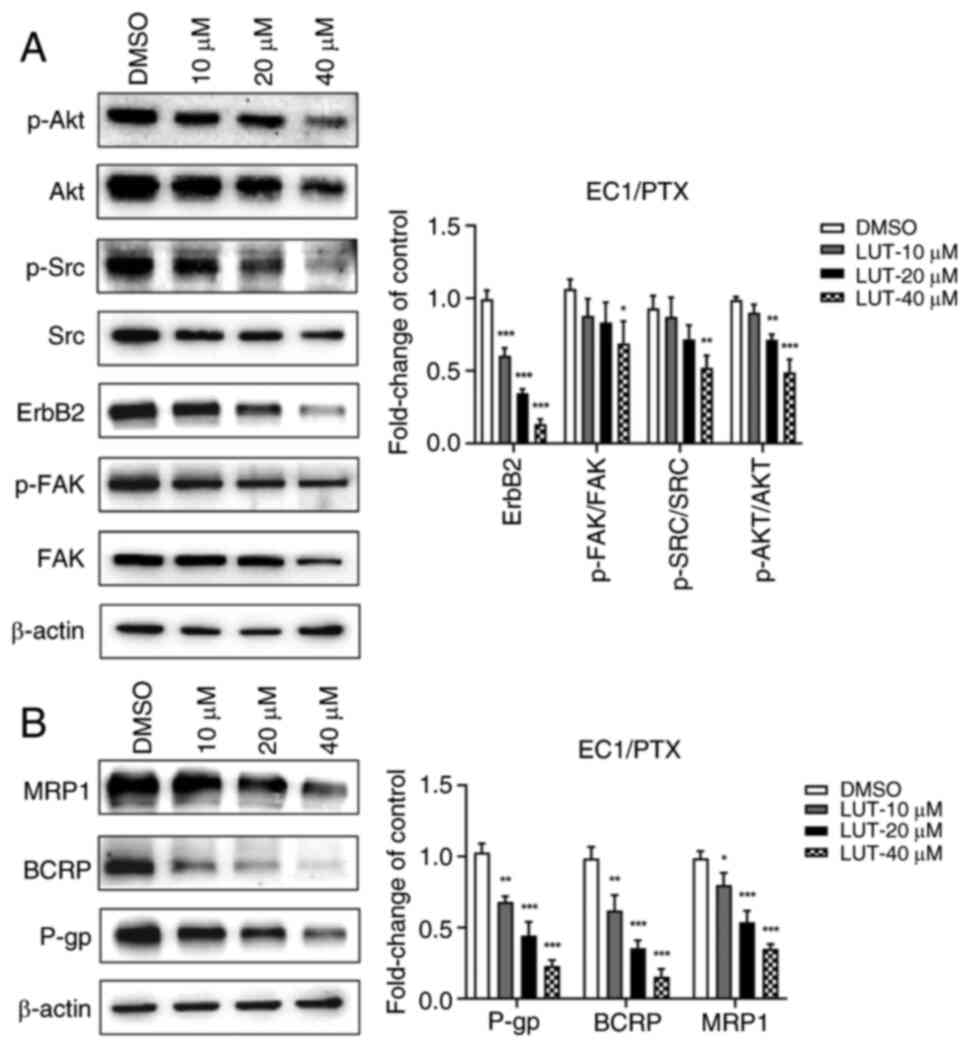
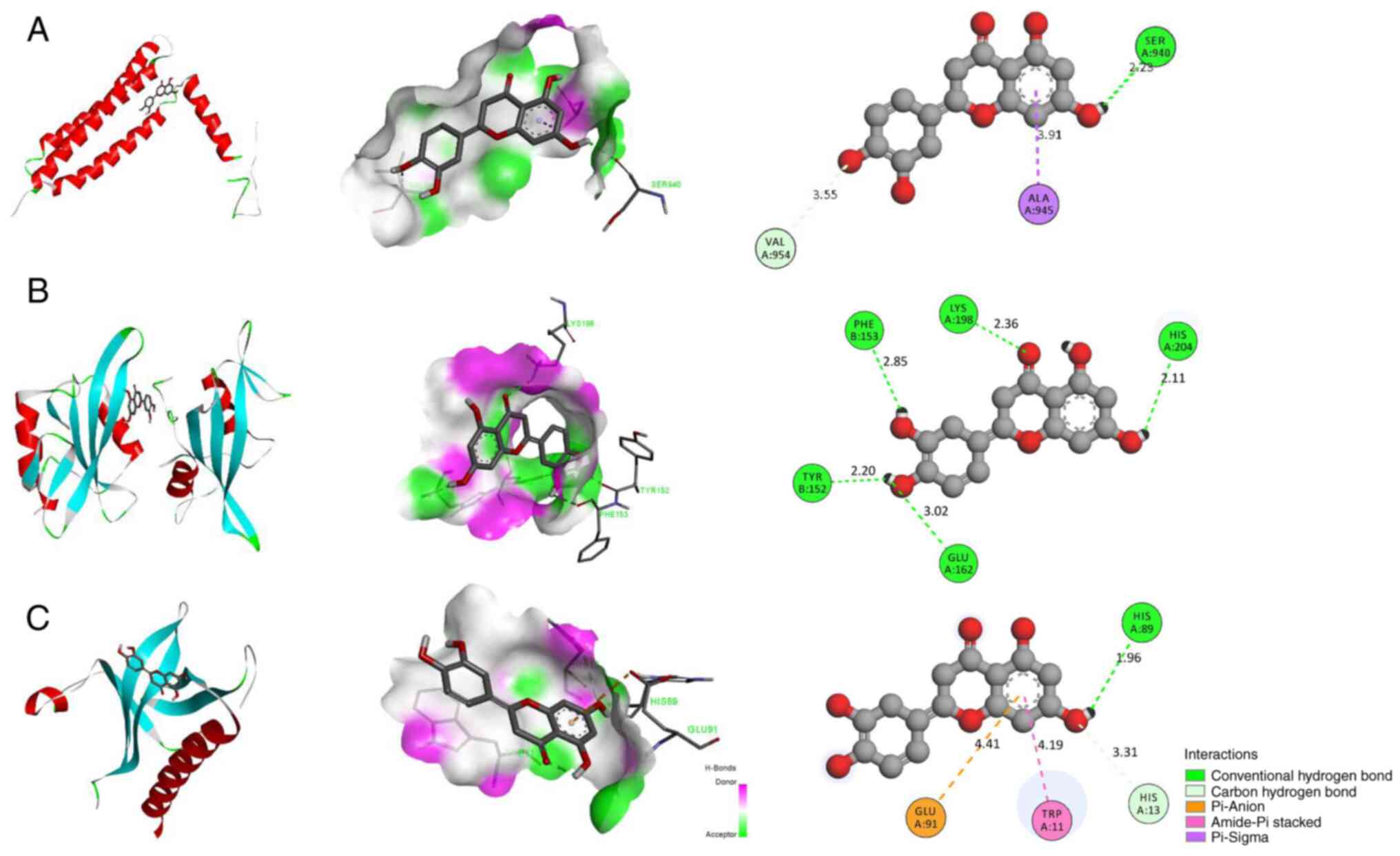
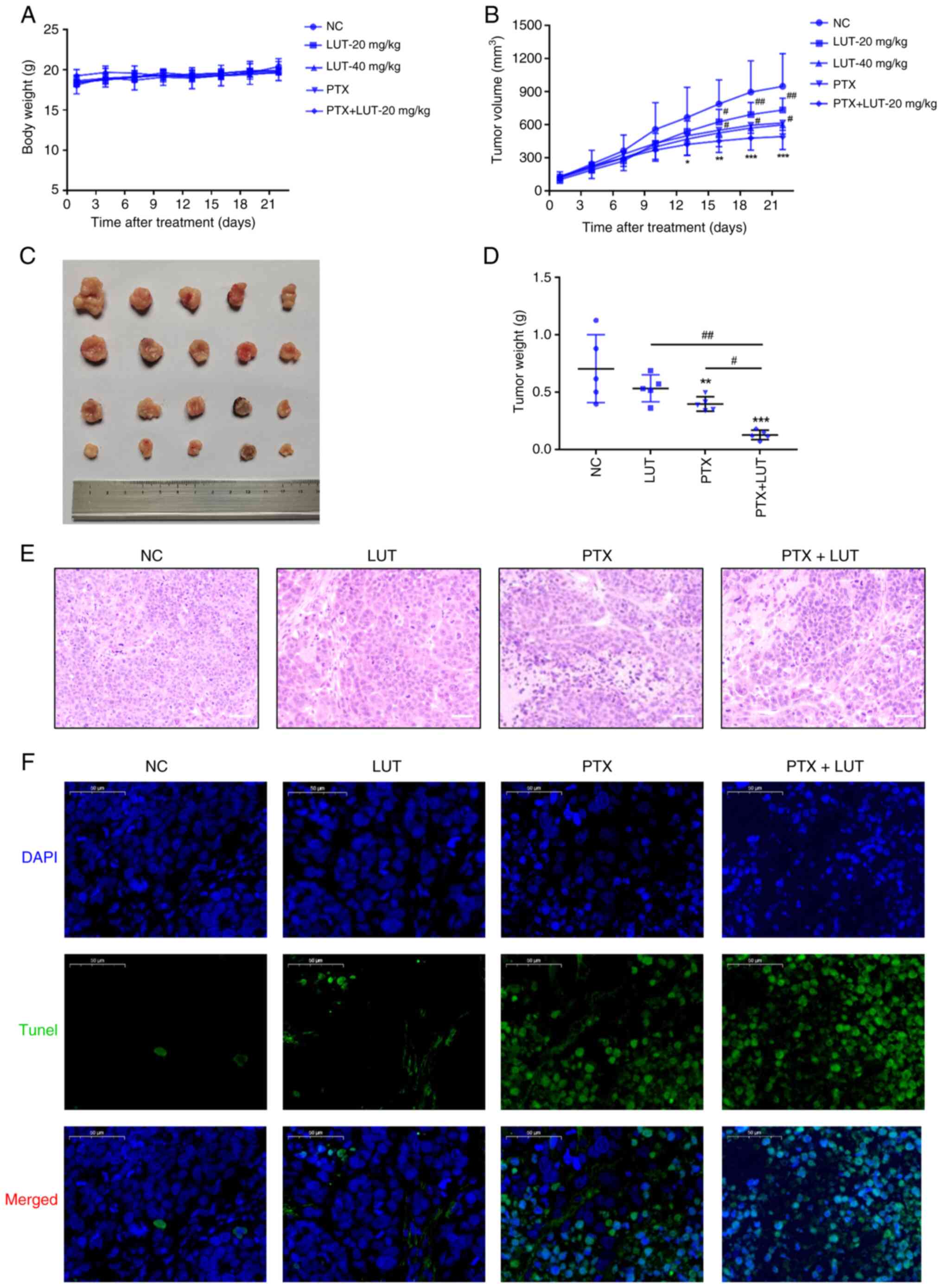
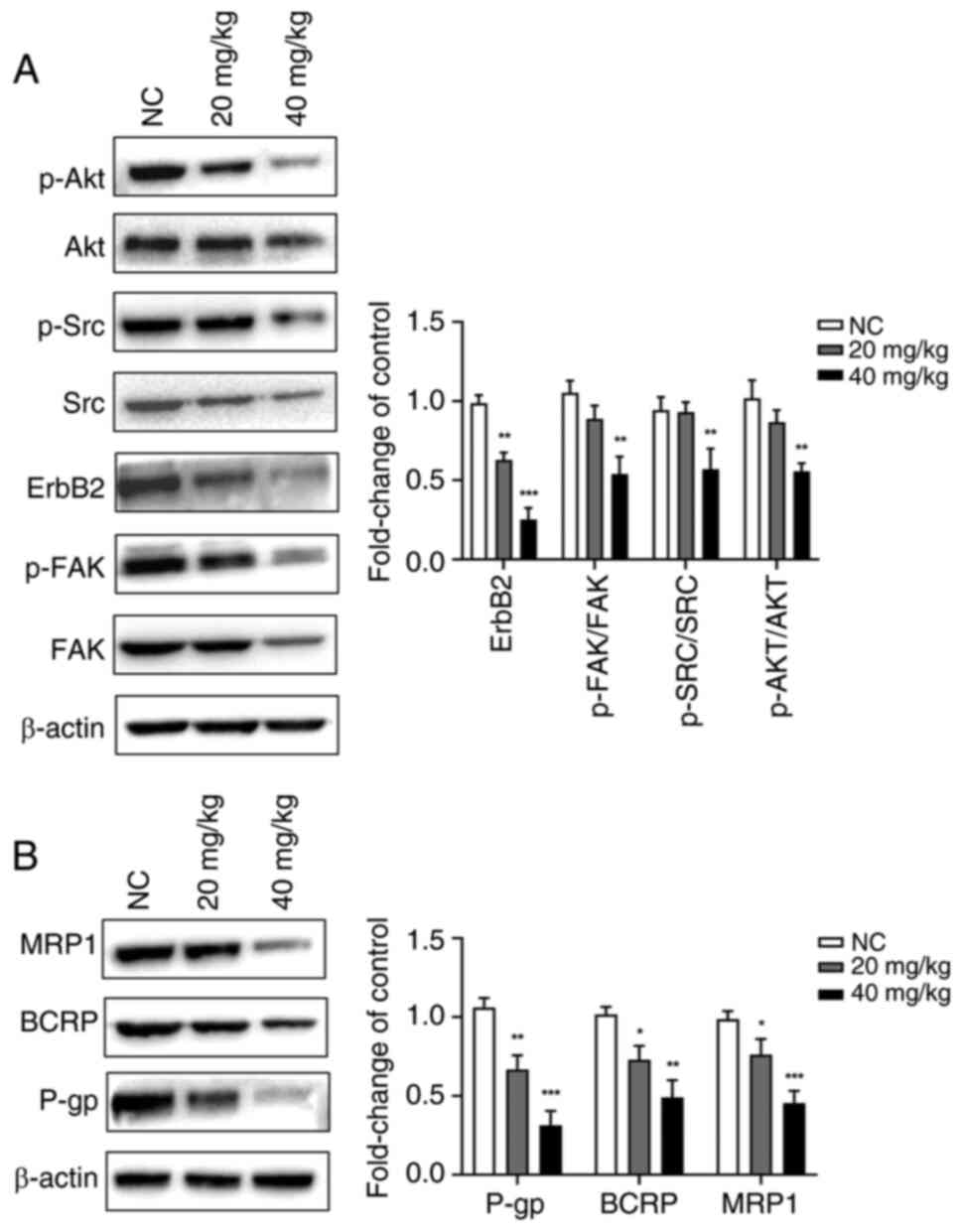
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 19:5598–5606. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Abnet CC, Arnold M and Wei WQ:
Epidemiology of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 154:360–373. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin Y, Totsuka Y, He Y, Kikuchi S, Qiao Y,
Ueda J, Wei W, Inoue M and Tanaka H: Epidemiology of esophageal
cancer in Japan and China. J Epidemiol. 23:233–242. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hiripi E, Jansen L, Gondos A, Emrich K,
Holleczek B, Katalinic A, Luttmann S, Nennecke A and Brenner H;
Gekid Cancer Survival Working Group: Survival of stomach and
esophagus cancer patients in Germany in the early 21st century.
Acta Oncol. 51:906–914. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ,
Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ,
Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al: Preoperative
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J
Med. 366:2074–2084. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gebski V, Burmeister B, Smithers BM, Foo
K, Zalcberg J and Simes J; Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials
Group: Survival benefits from neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or
chemotherapy in oesophageal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 8:226–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ando N, Kato H, Igaki H, Shinoda M, Ozawa
S, Shimizu H, Nakamura T, Yabusaki H, Aoyama N, Kurita A, et al: A
randomized trial comparing postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy with
cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil versus preoperative chemotherapy for
localized advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic
esophagus (JCOG9907). Ann Surg Oncol. 19:68–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu Y, Ren Z, Yuan L, Xu S, Yao Z, Qiao L
and Li K: Paclitaxel plus cisplatin vs. 5-fluorouracil plus
cisplatin as first-line treatment for patients with advanced
squamous cell esophageal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2345–2350.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hummel R, Sie C, Watson DI, Wang T, Ansar
A, Michael MZ, Van der Hoek M, Haier J and Hussey DJ: MicroRNA
signatures in chemotherapy resistant esophageal cancer cell lines.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:14904–1412. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Limtrakul P, Anuchapreeda S and Buddhasukh
D: Modulation of human multidrug-resistance MDR-1 gene by natural
curcuminoids. BMC Cancer. 4:132004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lopez-Lazaro M: Distribution and
biological activities of the flavonoid luteolin. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:31–59. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shi R, Huang Q, Zhu X, Ong YB, Zhao B, Lu
J, Ong CN and Shen HM: Luteolin sensitizes the anticancer effect of
cisplatin via c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated p53
phosphorylation and stabilization. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:1338–1347.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chian S, Li YY, Wang XJ and Tang XW:
Luteolin sensitizes two oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer
cell lines to chemotherapeutic drugs via inhibition of the Nrf2
pathway. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:2911–2916. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pandurangan AK, Dharmalingam P, Sadagopan
SK and Ganapasam S: Luteolin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 9
and 2 in azoxymethane-induced colon carcinogenesis. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 33:1176–1185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Carsten VF and Cardinale PJ: The
overdenture-a review. N Y State Dent J. 44:331–334. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu YT, Chen L, Tan ZB, Fan HJ, Xie LP,
Zhang WT, Chen HM, Li J, Liu B and Zhou YC: Luteolin inhibits
vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by
inhibiting TGFBR1 signaling. Front Pharmacol. 9:10592018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsai KJ, Tsai HY, Tsai CC, Chen TY, Hsieh
TH, Chen CL, Mbuyisa L, Huang YB and Lin MW: Luteolin inhibits
breast cancer stemness and enhances chemosensitivity through the
Nrf2-mediated pathway. Molecules. 26:64522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma J, Chen X, Zhu X, Pan Z, Hao W, Li D,
Zheng Q and Tang X: Luteolin potentiates low-dose
oxaliplatin-induced inhibitory effects on cell proliferation in
gastric cancer by inducing G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
Oncol Lett. 23:162022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lee BY, Timpson P, Horvath LG and Daly RJ:
FAK signaling in human cancer as a target for therapeutics.
Pharmacol Ther. 146:132–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Seguin L, Desgrosellier JS, Weis SM and
Cheresh DA: Integrins and cancer: Regulators of cancer stemness,
metastasis and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 25:234–240. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vadlamudi RK, Sahin AA, Adam L, Wang RA
and Kumar R: Heregulin and HER2 signaling selectively activates
c-Src phosphorylation at tyrosine 215. FEBS Lett. 543:76–80. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu D and Hung MC: Overexpression of ErbB2
in cancer and ErbB2-targeting strategies. Oncogene. 19:6115–6121.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|