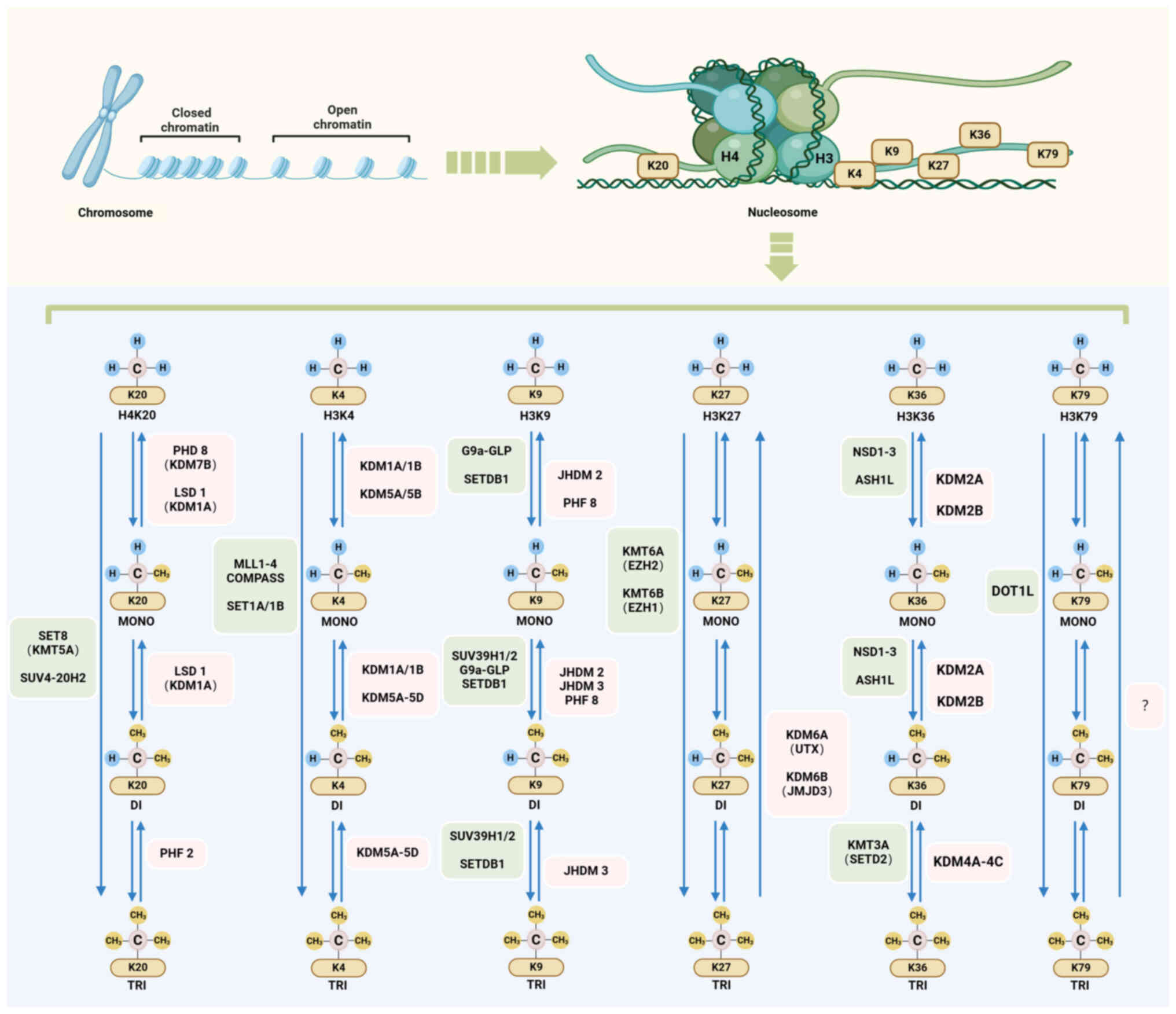
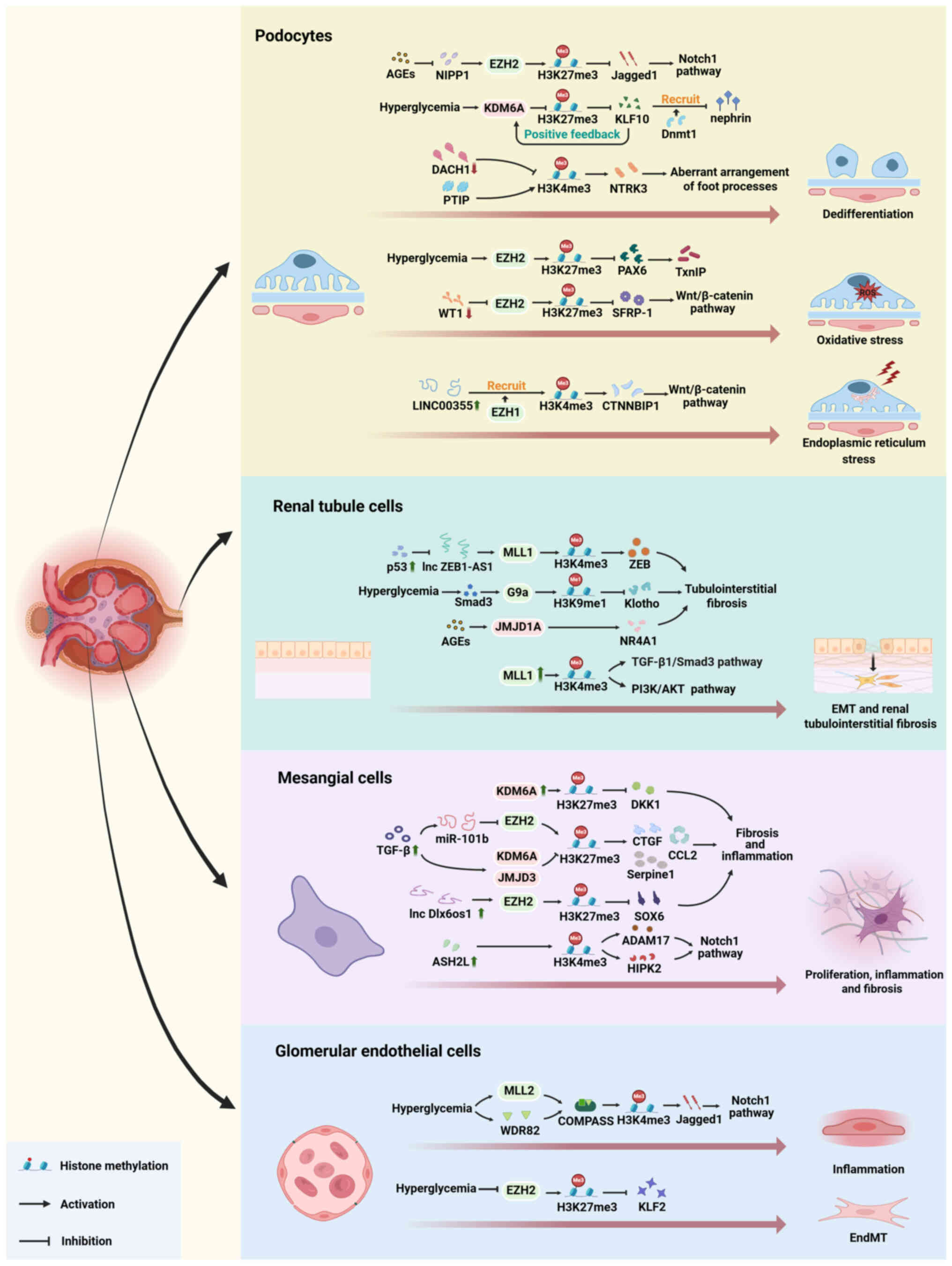
|
1
|
Thomas MC, Brownlee M, Susztak K, Sharma
K, Jandeleit-Dahm KA, Zoungas S, Rossing P, Groop PH and Cooper ME:
Diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150182015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Johansen KL, Chertow GM, Foley RN,
Gilbertson DT, Herzog CA, Ishani A, Israni AK, Ku E, Kurella Tamura
M, Li S, et al: US renal data system 2020 annual data report:
Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney
Dis. 77(4 Suppl 1): A7–A8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Anders HJ, Huber TB, Isermann B and
Schiffer M: CKD in diabetes: Diabetic kidney disease versus
nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 14:361–377. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thomas MC, Weekes AJ, Broadley OJ, Cooper
ME and Mathew TH: The burden of chronic kidney disease in
Australian patients with type 2 diabetes (the NEFRON study). Med J
Aust. 185:140–144. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scilletta S, Di Marco M, Miano N,
Filippello A, Di Mauro S, Scamporrino A, Musmeci M, Coppolino G, Di
Giacomo Barbagallo F, Bosco G, et al: Update on diabetic kidney
disease (DKD): Focus on Non-Albuminuric DKD and cardiovascular
risk. Biomolecules. 13:7522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Parving HH, Hommel E, Jensen BR and Hansen
HP: Long-term beneficial effect of ACE inhibition on diabetic
nephropathy in normotensive type 1 diabetic patients. Kidney Int.
60:228–234. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zou H, Zhou B and Xu G: SGLT2 inhibitors:
A novel choice for the combination therapy in diabetic kidney
disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Barrera-Chimal J, Lima-Posada I, Bakris GL
and Jaisser F: Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in diabetic
kidney disease-mechanistic and therapeutic effects. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 18:56–70. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang R, Wang Q, Li Y, Li Q, Zhou X, Chen
X and Dong Z: A new perspective on proteinuria and drug therapy for
diabetic kidney disease. Front Pharmacol. 15:13490222024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang N and Zhang C: Recent advances in the
management of diabetic kidney disease: Slowing progression. Int J
Mol Sci. 25:30862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forst T, Mathieu C, Giorgino F, Wheeler
DC, Papanas N, Schmieder RE, Halabi A, Schnell O, Streckbein M and
Tuttle KR: New strategies to improve clinical outcomes for diabetic
kidney disease. BMC Med. 20:3372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Regele F, Jelencsics K, Shiffman D, Paré
G, McQueen MJ, Mann JF and Oberbauer R: Genome-wide studies to
identify risk factors for kidney disease with a focus on patients
with diabetes. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30(Suppl 4): iv26–iv34.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cowie CC, Port FK, Wolfe RA, Savage PJ,
Moll PP and Hawthorne VM: Disparities in incidence of diabetic
end-stage renal disease according to race and type of diabetes. N
Engl J Med. 321:1074–1079. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cefalu WT, Buse JB, Tuomilehto J, Fleming
GA, Ferrannini E, Gerstein HC, Bennett PH, Ramachandran A, Raz I,
Rosenstock J and Kahn SE: Update and next steps for real-world
translation of interventions for type 2 diabetes prevention:
Reflections from a diabetes care editors' expert forum. Diabetes
Care. 39:1186–1201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tervaert TW, Mooyaart AL, Amann K, Cohen
AH, Cook HT, Drachenberg CB, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Haas M, de Heer
E, et al: Pathologic classification of diabetic nephropathy. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 21:556–563. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caramori ML, Parks A and Mauer M: Renal
lesions predict progression of diabetic nephropathy in type 1
diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:1175–1181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mohandes S, Doke T, Hu H, Mukhi D, Dhillon
P and Susztak K: Molecular pathways that drive diabetic kidney
disease. J Clin Invest. 133:e1656542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Ge K, Li T, Cai R and Chen Y: The
engagement of histone lysine methyltransferases with nucleosomes:
Structural basis, regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic
implications. Protein Cell. 14:165–179. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Greer EL and Shi Y: Histone methylation: A
dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet.
13:343–357. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Millán-Zambrano G, Burton A, Bannister AJ
and Schneider R: Histone post-translational modifications-cause and
consequence of genome function. Nat Rev Genet. 23:563–580. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Keating ST, van Diepen JA, Riksen NP and
El-Osta A: Epigenetics in diabetic nephropathy immunity and
metabolism. Diabetologia. 61:6–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lefevre GM, Patel SR, Kim D, Tessarollo L
and Dressler GR: Altering a histone H3K4 methylation pathway in
glomerular podocytes promotes a chronic disease phenotype. PLoS
Genet. 6:e10011422010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sayyed SG, Gaikwad AB, Lichtnekert J,
Kulkarni O, Eulberg D, Klussmann S, Tikoo K and Anders HJ:
Progressive glomerulosclerosis in type 2 diabetes is associated
with renal histone H3K9 and H3K23 acetylation, H3K4 dimethylation
and phosphorylation at serine 10. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
25:1811–1817. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Husmann D and Gozani O: Histone lysine
methyltransferases in biology and disease. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
26:880–889. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Martin C and Zhang Y: The diverse
functions of histone lysine methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
6:838–849. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hyun K, Jeon J, Park K and Kim J: Writing,
erasing and reading histone lysine methylations. Exp Mol Med.
49:e3242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gong F and Miller KM: Histone methylation
and the DNA damage response. Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 780:37–47.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Black JC, Van Rechem C and Whetstine JR:
Histone lysine methylation dynamics: Establishment, regulation, and
biological impact. Mol Cell. 48:491–507. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mohan M, Herz HM and Shilatifard A:
SnapShot: Histone lysine methylase complexes. Cell. 149:498–498.e1.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Højfeldt JW, Agger K and Helin K: Histone
lysine demethylases as targets for anticancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 12:917–930. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schwartz-Orbach L, Zhang C, Sidoli S, Amin
R, Kaur D, Zhebrun A, Ni J and Gu SG: Caenorhabditis elegans
nuclear RNAi factor SET-32 deposits the transgenerational histone
modification, H3K23me3. Elife. 9:e543092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen Y, Mevius DEHF, Caliandro R,
Carrozzini B, Roh Y, Kim J, Kim S, Ha SC, Morishita M and di Luccio
E: Set7 Is a H3K37 methyltransferase in schizosaccharomyces pombe
and is required for proper gametogenesis. Structure. 27:631–638.e8.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zong Y, Weiss N, Wang K, Pagano AE,
Heissel S, Perveen S and Huang J: Development of complementary
photo-arginine/lysine to promote discovery of Arg/Lys hPTMs
Interactomes. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23075262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Feng X, Wang AH, Juan AH, Ko KD, Jiang K,
Riparini G, Ciuffoli V, Kaba A, Lopez C, Naz F, et al: Polycomb
Ezh1 maintains murine muscle stem cell quiescence through
non-canonical regulation of Notch signaling. Dev Cell.
58:1052–1070.e10. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Z and Liu H: Roles of lysine
methylation in glucose and lipid metabolism: Functions, regulatory
mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. Biomolecules. 14:8622024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Aziz N, Hong YH, Kim HG, Kim JH and Cho
JY: Tumor-suppressive functions of protein lysine
methyltransferases. Exp Mol Med. 55:2475–2497. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu BC, Tang TT, Lv LL and Lan HY: Renal
tubule injury: A driving force toward chronic kidney disease.
Kidney Int. 93:568–579. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Cheng Y, Chen Y, Wang G, Liu P, Xie G,
Jing H, Chen H, Fan Y, Wang M and Zhou J: Protein methylation in
diabetic kidney disease. Front Med (Lausanne). 9:7360062022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Allis CD, Bowen JK, Abraham GN, Glover CV
and Gorovsky MA: Proteolytic processing of histone H3 in chromatin:
A physiologically regulated event in Tetrahymena micronuclei. Cell.
20:55–64. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, Mulligan P,
Whetstine JR, Cole PA, Casero RA and Shi Y: Histone demethylation
mediated by the nuclear amine oxidase homolog LSD1. Cell.
119:941–953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Di Nisio E, Manzini V, Licursi V and Negri
R: To Erase or not to erase: non-canonical catalytic functions and
non-catalytic functions of members of histone lysine demethylase
families. Int J Mol Sci. 25:69002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang J, Hu Y, Zhang B, Liang X and Li X:
The JMJD family histone demethylases in crosstalk between
inflammation and cancer. Front Immunol. 13:8813962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim W, Kim R, Park G, Park JW and Kim JE:
Deficiency of H3K79 histone methyltransferase Dot1-like protein
(DOT1L) inhibits cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 287:5588–5599.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
44
|
Feng Q, Wang H, Ng HH, Erdjument-Bromage
H, Tempst P, Struhl K and Zhang Y: Methylation of H3-lysine 79 is
mediated by a new family of HMTases without a SET domain. Curr
Biol. 12:1052–1058. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee YH, Ren D, Jeon B and Liu HW:
S-Adenosylmethionine: More than just a methyl donor. Nat Prod Rep.
40:1521–1549. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gou D, Liu R, Shan X, Deng H, Chen C,
Xiang J, Liu Y, Gao Q, Li Z, Huang A, et al: Gluconeogenic enzyme
PCK1 supports S-adenosylmethionine biosynthesis and promotes
H3K9me3 modification to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma
progression. J Clin Invest. 133:e1617132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lim CY, Lin HT, Kumsta C, Lu TC, Wang FY,
Kang YH, Hansen M, Ching TT and Hsu AL: SAMS-1 coordinates
HLH-30/TFEB and PHA-4/FOXA activities through histone methylation
to mediate dietary restriction-induced autophagy and longevity.
Autophagy. 19:224–240. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
48
|
Cenik BK and Shilatifard A: COMPASS and
SWI/SNF complexes in development and disease. Nat Rev Genet.
22:38–58. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Xue H, Yao T, Cao M, Zhu G, Li Y, Yuan G,
Chen Y, Lei M and Huang J: Structural basis of nucleosome
recognition and modification by MLL methyltransferases. Nature.
573:445–449. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mitchell K, Sprowls SA, Arora S, Shakya S,
Silver DJ, Goins CM, Wallace L, Roversi G, Schafer RE, Kay K, et
al: WDR5 represents a therapeutically exploitable target for cancer
stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 37:86–102. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao Z, Rendleman EJ, Szczepanski AP,
Morgan MA, Wang L and Shilatifard A: CARM1-mediated methylation of
ASXL2 impairs tumor-suppressive function of MLL3/COMPASS. Sci Adv.
8:eadd33392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lu J, Huang Y, Zhang X, Xu Y and Nie S:
Noncoding RNAs involved in DNA methylation and histone methylation,
and acetylation in diabetic vascular complications. Pharmacol Res.
170:1055202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee JS, Smith E and Shilatifard A: The
language of histone crosstalk. Cell. 142:682–685. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Stirpe A, Guidotti N, Northall SJ, Kilic
S, Hainard A, Vadas O, Fierz B and Schalch T: SUV39 SET domains
mediate crosstalk of heterochromatic histone marks. Elife.
10:e626822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Segelle A, Núñez-Álvarez Y, Oldfield AJ,
Webb KM, Voigt P and Luco RF: Histone marks regulate the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition via alternative splicing. Cell
Rep. 38:1103572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hogg SJ, Motorna O, Cluse LA, Johanson TM,
Coughlan HD, Raviram R, Myers RM, Costacurta M, Todorovski I,
Pijpers L, et al: Targeting histone acetylation dynamics and
oncogenic transcription by catalytic P300/CBP inhibition. Mol Cell.
81:2183–2200.e13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He F, Yu Q, Wang M, Wang R, Gong X, Ge F,
Yu X and Li S: SESAME-catalyzed H3T11 phosphorylation inhibits
Dot1-catalyzed H3K79me3 to regulate autophagy and telomere
silencing. Nat Commun. 13:75262022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Metzker ML: Sequencing technologies-the
next generation. Nat Rev Genet. 11:31–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Pulecio J, Verma N, Mejía-Ramírez E,
Huangfu D and Raya A: CRISPR/Cas9-Based engineering of the
epigenome. Cell Stem Cell. 21:431–447. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Peng X, Peng Q and Zhong L: Targeting
H3K36 methyltransferases NSDs: A promising strategy for tumor
targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:2202021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Basavarajappa BS and Subbanna S: Histone
methylation regulation in neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:46542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Komers R, Mar D, Denisenko O, Xu B, Oyama
TT and Bomsztyk K: Epigenetic changes in renal genes dysregulated
in mouse and rat models of type 1 diabetes. Lab Invest. 93:543–552.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tao S, Yang L, Wu C, Hu Y, Guo F, Ren Q,
Ma L and Fu P: Gambogenic acid alleviates kidney fibrosis via
epigenetic inhibition of EZH2 to regulate Smad7-dependent
mechanism. Phytomedicine. 106:1543902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Majumder S, Thieme K, Batchu SN, Alghamdi
TA, Bowskill BB, Kabir MG, Liu Y, Advani SL, White KE, Geldenhuys
L, et al: Shifts in podocyte histone H3K27me3 regulate mouse and
human glomerular disease. J Clin Invest. 128:483–499. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
65
|
Paneni F, Costantino S, Battista R,
Castello L, Capretti G, Chiandotto S, Scavone G, Villano A, Pitocco
D, Lanza G, et al: Adverse epigenetic signatures by histone
methyltransferase Set7 contribute to vascular dysfunction in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
8:150–158. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Siddiqi FS, Majumder S, Thai K, Abdalla M,
Hu P, Advani SL, White KE, Bowskill BB, Guarna G, Dos Santos CC, et
al: The histone methyltransferase enzyme enhancer of zeste homolog
2 protects against podocyte oxidative stress and renal injury in
diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:2021–2034. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
67
|
Pavenstädt H, Kriz W and Kretzler M: Cell
biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev. 83:253–307. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Nagata M: Podocyte injury and its
consequences. Kidney Int. 89:1221–1230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Reidy K, Kang HM, Hostetter T and Susztak
K: Molecular mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease. J Clin Invest.
124:2333–2340. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shankland SJ: The podocyte's response to
injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int.
69:2131–2147. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ying Q and Wu G: Molecular mechanisms
involved in podocyte EMT and concomitant diabetic kidney diseases:
An update. Ren Fail. 39:474–483. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
May CJ, Saleem M and Welsh GI: Podocyte
dedifferentiation: a specialized process for a specialized cell.
Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 5:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Guo Y, Xiong Z and Guo X: Histone
demethylase KDM6B regulates human podocyte differentiation in
vitro. Biochem J. 476:1741–1751. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Wan J, Hou X, Zhou Z, Geng J, Tian J, Bai
X and Nie J: WT1 ameliorates podocyte injury via repression of
EZH2/β-catenin pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Free Radic Biol
Med. 108:280–299. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nishad R, Meshram P, Singh AK, Reddy GB
and Pasupulati AK: Activation of Notch1 signaling in podocytes by
glucose-derived AGEs contributes to proteinuria. BMJ Open Diabetes
Res Care. 8:e0012032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liebisch M and Wolf G: AGE-Induced
Suppression of EZH2 mediates injury of podocytes by reducing
H3K27me3. Am J Nephrol. 51:676–692. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lin CL, Hsu YC, Huang YT, Shih YH, Wang
CJ, Chiang WC and Chang PJ: A KDM6A-KLF10 reinforcing feedback
mechanism aggravates diabetic podocyte dysfunction. EMBO Mol Med.
11:e98282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Muñoz IM and Rouse J: Control of histone
methylation and genome stability by PTIP. EMBO Rep. 10:239–245.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Patel SR, Kim D, Levitan I and Dressler
GR: The BRCT-domain containing protein PTIP links PAX2 to a histone
H3, lysine 4 methyltransferase complex. Dev Cell. 13:580–592. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Cao A, Li J, Asadi M, Basgen JM, Zhu B, Yi
Z, Jiang S, Doke T, El Shamy O, Patel N, et al: DACH1 protects
podocytes from experimental diabetic injury and modulates
PTIP-H3K4Me3 activity. J Clin Invest. 131:e1412792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Xu H, Lan J, Feng Z,
Huang R, Geng J, Chi H and Bai X: LINC00355 Mediates CTNNBIP1
promoter methylation and promotes endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 39:225–240. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Qi R and Yang C: Renal tubular epithelial
cells: The neglected mediator of tubulointerstitial fibrosis after
injury. Cell Death Dis. 9:11262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Legouis D, Ricksten SE, Faivre A,
Verissimo T, Gariani K, Verney C, Galichon P, Berchtold L, Feraille
E, Fernandez M, et al: Altered proximal tubular cell glucose
metabolism during acute kidney injury is associated with mortality.
Nat Metab. 2:732–743. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Edwards A, Palm F and Layton AT: A model
of mitochondrial O(2) consumption and ATP generation in rat
proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 318:F248–F259.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Wang Y, Jin M, Cheng CK and Li Q: Tubular
injury in diabetic kidney disease: Molecular mechanisms and
potential therapeutic perspectives. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
14:12389272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Liu Y: Cellular and molecular mechanisms
of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 7:684–696. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sun L, Liu L, Jiang J, Liu K, Zhu J, Wu L,
Lu X, Huang Z, Yuan Y, Crowley SD, et al: Transcription factor
Twist1 drives fibroblast activation to promote kidney fibrosis via
signaling proteins Prrx1/TNC. Kidney Int. Aug 22–2024.Epub ahead of
print. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bai M, Xu S, Jiang M, Guo Y, Hu D, He J,
Wang T, Zhang Y, Guo Y, Zhang Y, et al: Meis1 targets protein
tyrosine phosphatase receptor J in fibroblast to retard chronic
kidney disease progression. Adv Sci (Weinh). Aug 20–2024.Epub ahead
of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kim DH, Sung M, Park MS, Sun EG, Yoon S,
Yoo KH, Radhakrishnan K, Jung SY, Bae WK, Cho SH and Chung IJ:
Galectin 3-binding protein (LGALS3BP) depletion attenuates hepatic
fibrosis by reducing transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)
availability and inhibits hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Commun
(Lond). Jul 28–2024.Epub ahead of print. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Fesneau O, Thevin V, Pinet V, Goldsmith C,
Vieille B, M'Homa Soudja S, Lattanzio R, Hahne M, Dardalhon V,
Hernandez-Vargas H, et al: An intestinal T(H)17 cell-derived subset
can initiate cancer. Nat Immunol. 25:1637–1649. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gifford CC, Tang J, Costello A, Khakoo NS,
Nguyen TQ, Goldschmeding R, Higgins PJ and Samarakoon R: Negative
regulators of TGF-β1 signaling in renal fibrosis; pathological
mechanisms and novel therapeutic opportunities. Clin Sci (Lond).
135:275–303. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
You JB, Cao Y, You QY, Liu ZY, Wang XC,
Ling H, Sha JM and Tao H: The landscape of histone modification in
organ fibrosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 977:1767482024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zou J, Yu C, Zhang C, Guan Y, Zhang Y,
Tolbert E, Zhang W, Zhao T, Bayliss G, Li X, et al: Inhibition of
MLL1-menin interaction attenuates renal fibrosis in obstructive
nephropathy. FASEB J. 37:e227122023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wang J, Pan J, Li H, Long J, Fang F, Chen
J, Zhu X, Xiang X and Zhang D: lncRNA ZEB1-AS1 was suppressed by
p53 for renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 12:741–750. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Irifuku T, Doi S, Sasaki K, Doi T,
Nakashima A, Ueno T, Yamada K, Arihiro K, Kohno N and Masaki T:
Inhibition of H3K9 histone methyltransferase G9a attenuates renal
fibrosis and retains klotho expression. Kidney Int. 89:147–157.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Ike T, Doi S, Nakashima A, Sasaki K,
Ishiuchi N, Asano T and Masaki T: The hypoxia-inducible factor-α
prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor FG4592 ameliorates renal fibrosis by
inducing the H3K9 demethylase JMJD1A. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
323:F539–F552. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Wang S, Zuo A, Jiang W, Xie J, Lin H, Sun
W, Zhao M, Xia J, Shao J, Zhao X, et al: JMJD1A/NR4A1 signaling
regulates the procession of renal tubular epithelial interstitial
fibrosis induced by AGEs in HK-2. Front Med (Lausanne).
8:8076942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Han X and Sun Z: Epigenetic Regulation of
KL (Klotho) via H3K27me3 (Histone 3 Lysine [K] 27 Trimethylation)
in renal tubule cells. Hypertension. 75:1233–1241. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Niculae A, Gherghina ME, Peride I, Tiglis
M, Nechita AM and Checherita IA: Pathway from acute kidney injury
to chronic kidney disease: Molecules involved in renal fibrosis.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:140192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Cohen C, Mhaidly R, Croizer H, Kieffer Y,
Leclere R, Vincent-Salomon A, Robley C, Anglicheau D, Rabant M,
Sannier A, et al: WNT-dependent interaction between inflammatory
fibroblasts and FOLR2+ macrophages promotes fibrosis in chronic
kidney disease. Nat Commun. 15:7432024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Huang R, Fu P and Ma L: Kidney fibrosis:
From mechanisms to therapeutic medicines. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 8:1292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Liu Y: New insights into
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in kidney fibrosis. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 21:212–222. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Hewitson TD, Holt SG, Tan SJ, Wigg B,
Samuel CS and Smith ER: Epigenetic modifications to H3K9 in renal
tubulointerstitial cells after unilateral ureteric obstruction and
TGF-β1 Stimulation. Front Pharmacol. 8:3072017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Zhou X, Zang X, Ponnusamy M, Masucci MV,
Tolbert E, Gong R, Zhao TC, Liu N, Bayliss G, Dworkin LD and Zhuang
S: Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 inhibition attenuates renal fibrosis
by maintaining Smad7 and phosphatase and tensin homolog expression.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:2092–2108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
106
|
An C, Jiao B, Du H, Tran M, Song B, Wang
P, Zhou D and Wang Y: Jumonji domain-containing protein-3 (JMJD3)
promotes myeloid fibroblast activation and macrophage polarization
in kidney fibrosis. Br J Pharmacol. 180:2250–2265. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Steffes MW, Osterby R, Chavers B and Mauer
SM: Mesangial expansion as a central mechanism for loss of kidney
function in diabetic patients. Diabetes. 38:1077–1081. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Thomas HY and Ford Versypt AN:
Pathophysiology of mesangial expansion in diabetic nephropathy:
Mesangial structure, glomerular biomechanics, and biochemical
signaling and regulation. J Biol Eng. 16:192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kriz W: Maintenance and breakdown of
glomerular tuft architecture. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:1075–1077. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Avraham S, Korin B, Chung JJ, Oxburgh L
and Shaw AS: The Mesangial cell-the glomerular stromal cell. Nat
Rev Nephrol. 17:855–864. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Alicic RZ, Rooney MT and Tuttle KR:
Diabetic kidney disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities.
Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 12:2032–2045. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Baccora MH, Cortes P, Hassett C, Taube DW
and Yee J: Effects of long-term elevated glucose on collagen
formation by mesangial cells. Kidney Int. 72:1216–1225. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wu P, Ren Y, Ma Y, Wang Y, Jiang H,
Chaudhari S, Davis ME, Zuckerman JE and Ma R: Negative regulation
of Smad1 pathway and collagen IV expression by store-operated
Ca(2+) entry in glomerular mesangial cells. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 312:F1090–F1100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kuo FC, Chao CT and Lin SH: The dynamics
and plasticity of epigenetics in diabetic kidney disease:
therapeutic applications Vis-à-Vis. Int J Mol Sci. 23:8432022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Boi R, Ebefors K and Nyström J: The role
of the mesangium in glomerular function. Acta Physiol (Oxf).
239:e140452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Zhong W, Hong C, Dong Y, Li Y, Xiao C and
Liu X: ASH2L aggravates fibrosis and inflammation through HIPK2 in
high glucose-induced glomerular mesangial cells. Genes (Basel).
13:22442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhong W, Hong C, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xiao C and
Liu X: ASH2L-mediated H3K4me3 drives diabetic nephropathy through
HIPK2 and Notch1 pathway. Transl Res. 264:85–96. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Chen YX, Zhu SY, Huang C, Xu CY, Fang XD
and Tu WP: LncRNA Dlx6os1 accelerates diabetic nephropathy
progression by epigenetically repressing SOX6 via Recruiting EZH2.
Kidney Blood Press Res. 47:177–184. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Hung PH, Hsu YC, Chen TH, Ho C and Lin CL:
The histone demethylase inhibitor GSK-J4 Is a therapeutic target
for the kidney fibrosis of diabetic kidney disease via DKK1
Modulation. Int J Mol Sci. 23:94072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Chen H, Huang Y, Zhu X, Liu C, Yuan Y, Su
H, Zhang C, Liu C, Xiong M, Qu Y, et al: Histone demethylase UTX is
a therapeutic target for diabetic kidney disease. J Physiol.
597:1643–1660. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
121
|
Jia Y, Reddy MA, Das S, Oh HJ, Abdollahi
M, Yuan H, Zhang E, Lanting L, Wang M and Natarajan R:
Dysregulation of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation in
transforming growth factor-β1-induced gene expression in mesangial
cells and diabetic kidney. J Biol Chem. 294:12695–12707. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Satchell SC and Braet F: Glomerular
endothelial cell fenestrations: An integral component of the
glomerular filtration barrier. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
296:F947–F956. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Savage CO: The biology of the glomerulus:
endothelial cells. Kidney Int. 45:314–319. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lassén E and Daehn IS: Molecular
mechanisms in early diabetic kidney disease: Glomerular endothelial
cell dysfunction. Int J Mol Sci. 21:94562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Thakar S, Katakia YT, Ramakrishnan SK,
Pandya Thakkar N and Majumder S: Intermittent high glucose elevates
nuclear localization of EZH2 to Cause H3K27me3-dependent repression
of KLF2 leading to endothelial inflammation. Cells. 10:25482021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Takizawa F, Mizutani S, Ogawa Y and Sawada
N: Glucose-independent persistence of PAI-1 gene expression and
H3K4 tri-methylation in type 1 diabetic mouse endothelium:
implication in metabolic memory. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
433:66–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Huang T, Li X, Wang F, Lu L, Hou W, Zhu M
and Miao C: The CREB/KMT5A complex regulates PTP1B to modulate high
glucose-induced endothelial inflammatory factor levels in diabetic
nephropathy. Cell Death Dis. 12:3332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Alvandi Z and Bischoff J:
Endothelial-Mesenchymal transition in cardiovascular disease.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 41:2357–2369. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Glaser SF, Heumüller AW, Tombor L, Hofmann
P, Muhly-Reinholz M, Fischer A, Günther S, Kokot KE, Hassel D,
Kumar S, et al: The histone demethylase JMJD2B regulates
endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:4180–4187. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Pandya Thakkar N, Pereira BMV, Katakia YT,
Ramakrishnan SK, Thakar S, Sakhuja A, Rajeev G, Soorya S, Thieme K
and Majumder S: Elevated H3K4me3 Through MLL2-WDR82 upon
hyperglycemia causes jagged ligand dependent notch activation to
interplay with differentiation state of endothelial cells. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 10:8391092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Vastenhouw NL and Schier AF: Bivalent
histone modifications in early embryogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
24:374–386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Conway E, Healy E and Bracken AP: PRC2
mediated H3K27 methylations in cellular identity and cancer. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 37:42–48. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Miller SA, Damle M, Kim J and Kingston RE:
Full methylation of H3K27 by PRC2 is dispensable for initial
embryoid body formation but required to maintain differentiated
cell identity. Development. 148:dev1963292021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Lavarone E, Barbieri CM and Pasini D:
Dissecting the role of H3K27 acetylation and methylation in PRC2
mediated control of cellular identity. Nat Commun. 10:16792019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Soofi A, Kutschat AP, Azam M, Laszczyk AM
and Dressler GR: Regeneration after acute kidney injury requires
PTIP-mediated epigenetic modifications. JCI insight. 5:e1302042020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
El-Dahr SS and Saifudeen Z: Epigenetic
regulation of renal development. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 91:111–118.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Jin J, Liu XM, Shao W and Meng XM: Nucleic
acid and protein methylation modification in renal diseases. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 45:661–673. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Yu C and Zhuang S: Histone
methyltransferases as therapeutic targets for kidney diseases.
Front Pharmacol. 10:13932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Ho TCS, Chan AHY and Ganesan A: Thirty
Years of HDAC Inhibitors: 2020 insight and hindsight. J Med Chem.
63:12460–12484. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Bhat KP, Ümit Kaniskan H, Jin J and Gozani
O: Epigenetics and beyond: Targeting writers of protein lysine
methylation to treat disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:265–286.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Kourtidou C and Tziomalos K: The role of
histone modifications in the pathogenesis of diabetic kidney
disease. Int J Mol Sci. 24:60072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Jones PA, Issa JP and Baylin S: Targeting
the cancer epigenome for therapy. Nat Rev Genet. 17:630–641. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Zhang Q, Chen X, Cao J, Yang W, Wan G,
Feng Q, Zhou S, Yang H, Wang N, Liu Z, et al: Discovery of a Novel
Covalent EZH2 inhibitor based on tazemetostat scaffold for the
treatment of ovarian cancer. J Med Chem. 66:1725–1741. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Vejmelkova K, Pokorna P, Noskova K,
Faustmannova A, Drabova K, Pavelka Z, Bajciova V, Broz M, Tinka P,
Jezova M, et al: Tazemetostat in the therapy of pediatric
INI1-negative malignant rhabdoid tumors. Sci Rep. 13:216232023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ni J, Hou X, Wang X, Shi Y, Xu L, Zheng X,
Liu N, Qiu A and Zhuang S: 3-deazaneplanocin A protects against
cisplatin-induced renal tubular cell apoptosis and acute kidney
injury by restoration of E-cadherin expression. Cell Death Dis.
10:3552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Tellez CS, Picchi MA, Juri D, Do K, Desai
DH, Amin SG, Hutt JA, Filipczak PT and Belinsky SA: Chromatin
remodeling by the histone methyltransferase EZH2 drives lung
pre-malignancy and is a target for cancer prevention. Clin
Epigenetics. 13:442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
De La Rosa J, Urdiciain A, Zazpe I, Zelaya
MV, Meléndez B, Rey JA, Idoate MA and Castresana JS: The
synergistic effect of DZ-NEP, panobinostat and temozolomide reduces
clonogenicity and induces apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Int J
Oncol. 56:283–300. 2020.
|
|
148
|
Li Y, Ren Y, Wang Y, Tan Y, Wang Q, Cai J,
Zhou J, Yang C, Zhao K, Yi K, et al: A Compound AC1Q3QWB
Selectively Disrupts HOTAIR-Mediated Recruitment of PRC2 and
Enhances Cancer Therapy of DZNep. Theranostics. 9:4608–4623. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Miranda TB, Cortez CC, Yoo CB, Liang G,
Abe M, Kelly TK, Marquez VE and Jones PA: DZNep is a global histone
methylation inhibitor that reactivates developmental genes not
silenced by DNA methylation. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:1579–1588. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Gounder M, Schöffski P, Jones RL, Agulnik
M, Cote GM, Villalobos VM, Attia S, Chugh R, Chen TW, Jahan T, et
al: Tazemetostat in advanced epithelioid sarcoma with loss of
INI1/SMARCB1: An international, open-label, phase 2 basket study.
Lancet Oncol. 21:1423–1432. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Dalpatraj N, Naik A and Thakur N: GSK-J4:
An H3K27 histone demethylase inhibitor, as a potential anti-cancer
agent. Int J Cancer. 153:1130–1138. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Chang Y, Zhang X, Horton JR, Upadhyay AK,
Spannhoff A, Liu J, Snyder JP, Bedford MT and Cheng X: Structural
basis for G9a-like protein lysine methyltransferase inhibition by
BIX-01294. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:312–317. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Chae YC, Kim JY, Park JW, Kim KB, Oh H,
Lee KH and Seo SB: FOXO1 degradation via G9a-mediated methylation
promotes cell proliferation in colon cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:1692–1705. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
154
|
Kim Y, Kim YS, Kim DE, Lee JS, Song JH,
Kim HG, Cho DH, Jeong SY, Jin DH, Jang SJ, et al: BIX-01294 induces
autophagy-associated cell death via EHMT2/G9a dysfunction and
intracellular reactive oxygen species production. Autophagy.
9:2126–2139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Yokoyama A and Cleary ML: Menin critically
links MLL proteins with LEDGF on cancer-associated target genes.
Cancer Cell. 14:36–46. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Caslini C, Yang Z, El-Osta M, Milne TA,
Slany RK and Hess JL: Interaction of MLL amino terminal sequences
with menin is required for transformation. Cancer Res.
67:7275–7283. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the nearly four decades from 01/1981
to 09/2019. J Nat Prod. 83:770–803. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Sasaki K, Doi S, Nakashima A, Irifuku T,
Yamada K, Kokoroishi K, Ueno T, Doi T, Hida E, Arihiro K, et al:
Inhibition of SET domain-containing lysine methyltransferase 7/9
ameliorates renal fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:203–215. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Yu X, Zhao Q and Zhang H, Fan C, Zhang X,
Xie Q, Xu C, Liu Y, Wu X, Han Q and Zhang H: Gambogenic acid
inhibits LPS-simulated inflammatory response by suppressing NF-κB
and MAPK in macrophages. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai).
48:454–461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chen X, Zhang X, Cai H, Yang W, Lei H, Xu
H, Wang W, Zhu Q, Kang J, Yin T, et al: Targeting USP9x/SOX2 axis
contributes to the anti-osteosarcoma effect of neogambogic acid.
Cancer Lett. 469:277–286. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Xu L, Meng X, Xu N, Fu W, Tan H, Zhang L,
Zhou Q, Qian J, Tu S, Li X, et al: Gambogenic acid inhibits
fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway in
erlotinib-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer and suppresses
patient-derived xenograft growth. Cell Death Dis. 9:2622018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|