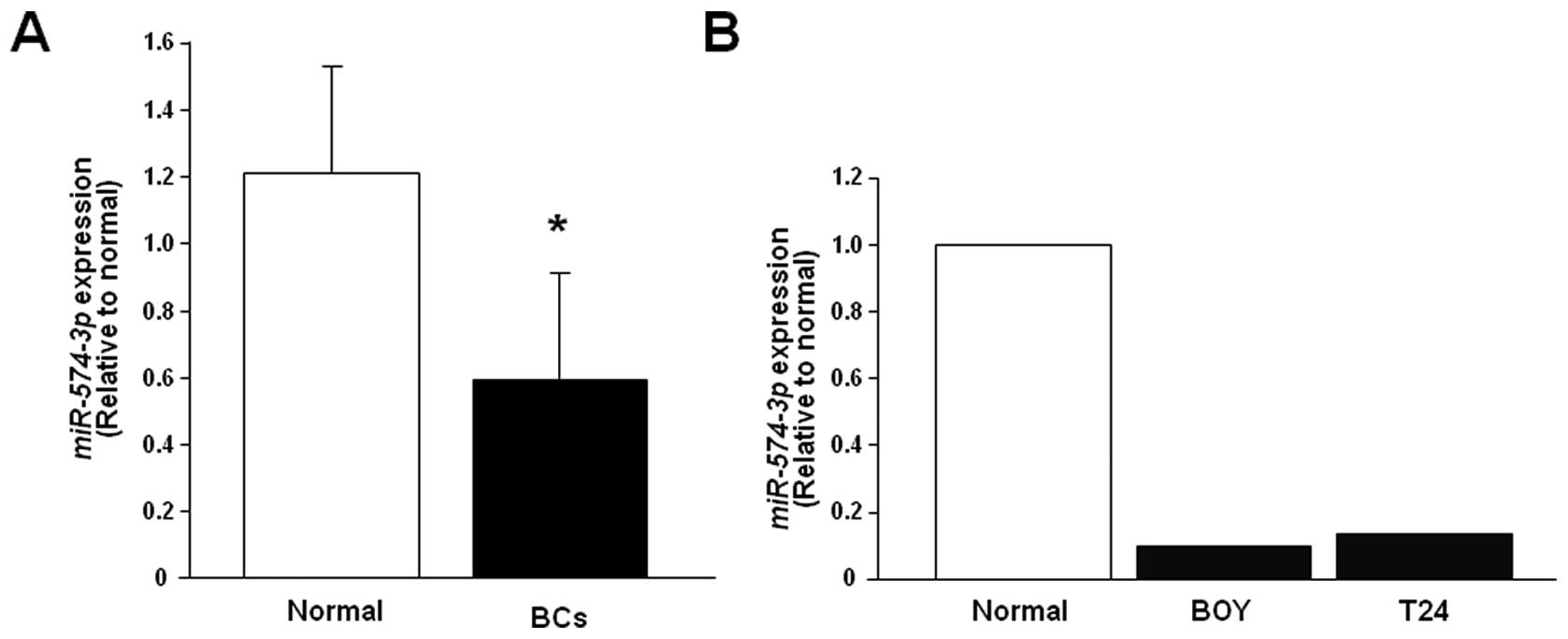
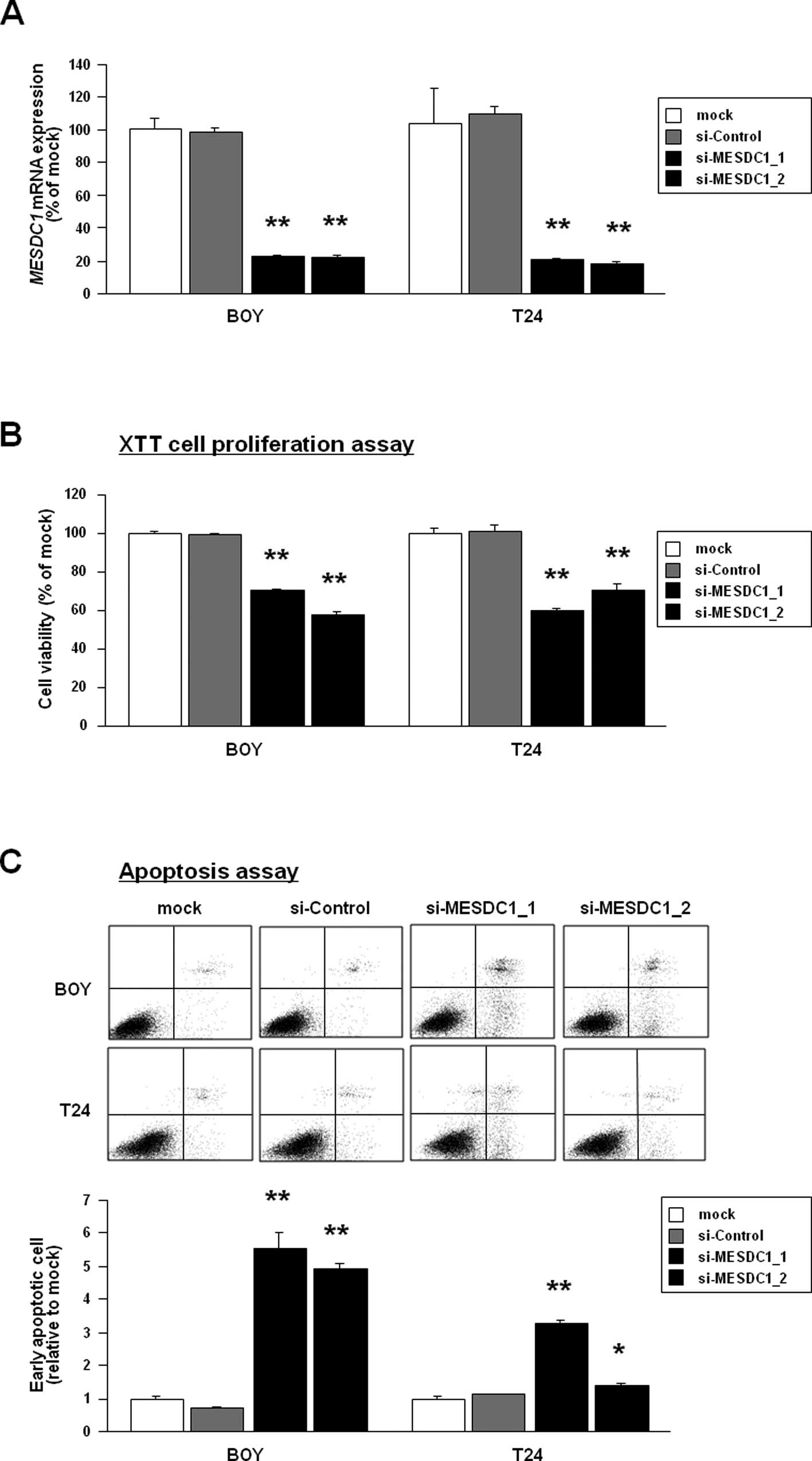
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Website of Center for Cancer Control and
Information Services. National Cancer Center; Japan: (http://ganjoho.jp/professional/statistics/statistics.html).
|
|
3
|
Herr H, Konety B, Stein J, et al:
Optimizing outcomes at every stage of bladder cancer: do we
practice it? Urol Oncol. 27:72–74. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zimmerman AL and Wu S: MicroRNAs, cancer
and cancer stem cells. Cancer Lett. 300:10–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fendler A, Stephan C, Yousef GM and Jung
K: MicroRNAs as regulators of signal transduction in urological
tumors. Clin Chem. 57:954–968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Esquela-Kerscher A and Slack FJ: Oncomirs
- microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:259–269. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gottardo F, Liu CG, Ferracin M, et al:
Micro-RNA profiling in kidney and bladder cancers. Urol Oncol.
25:387–392. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang H, Dinney CP, Ye Y, et al: Evaluation
of genetic variants in microRNA-related genes and high risk of
bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 68:2530–2537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ichimi T, Enokida H, Okuno Y, et al:
Identification of novel microRNA targets based on microRNA
signatures in bladder cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:345–352. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Catto JW, Miah S, Owen HC, et al: Distinct
microRNA alterations characterize high- and low-grade bladder
cancer. Cancer Res. 69:8472–8481. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Catto JW, Alcaraz A, Bjartell AS, et al:
MicroRNA in prostate, bladder, and kidney cancer: a systematic
review. Eur Urol. 59:671–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, et al: MicroRNA
expression signature of bladder cancer revealed by deep sequencing.
PLoS One. 6:e182862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Tatarano S, et al:
miR-145 and miR-133a function as tumor suppressors and directly
regulate FSCN1 expression in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:883–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kawakami K, et al:
Functional role of LASP1 in cell viability and its regulation by
microRNAs in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 2010.[Epub ahead of
print].
|
|
16
|
Yoshino H, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, et al:
The tumour-suppressive function of miR-1 and miR-133a targeting
TAGLN2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:808–818. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tatarano S, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, et
al: Mir-218 on the genomic loss region of chromosome 4p15.31
function as a tumor suppressor in bladder cancer. Int J Oncol.
39:13–21. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Matsuda R, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, et al:
LY6K is a novel molecular target in bladder cancer on basis of
integrate genome-wide profiling. Br J Cancer. 104:376–386. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshitomi T, Kawakami K, Enokida H, et al:
Restoration of miR-517a expression induces cell apoptosis in
bladder cancer cell lines. Oncol Rep. 24:1661–1668. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Takemoto M, Shirahama T, Miyauchi T, et
al: Metanestin, a glycoprotein with metastasis-associated
expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary bladder.
Int J Cancer. 74:7–14. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sobin LH and Wittekind C: TNM
Classification of Malignant Tumors International Union Against
Cancer (UICC). 6th edition. Wiley-Liss Publications; New York, NY:
pp. 199–202. 2002
|
|
22
|
Gui J, Tian Y, Wen X, et al: Serum
microRNA characterization identifies miR-885-5p as a potential
marker for detecting liver pathologies. Clin Sci. 120:183–193.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hawkins SM, Creighton CJ, Han DY, et al:
Functional microRNA involved in endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol.
25:821–832. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chiyomaru T, Tatarano S, Kawakami K, et
al: SWAP70, actin-binding protein, function as an oncogene
targeting tumor-suppressive miR-145 in prostate cancer. Prostate.
View Article : Google Scholar : 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kureishy N, Sapountzi V, Prag S, Anilkumar
N and Adams JC: Fascins, and their roles in cell structure and
function. Bioessays. 24:350–361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wines ME, Lee L, Katari MS, et al:
Identification of mesoderm development (mesd) candidate genes by
comparative mapping and genome sequence analysis. Genomics.
72:88–98. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gingras AR, Bate N, Goult BT, et al:
Central region of talin has a unique fold that binds vinculin and
actin. J Biol Chem. 285:29577–29587. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Uchida Y, Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, et al:
MiR-133a induces apoptosis through direct regulation of GSTP1 in
bladder cancer cell lines. Urol Oncol. 2011.[Epub ahead of
print].
|
|
29
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Tumor suppressive microRNA-375 regulates oncogene AEG-1/MTDH in
head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). J Hum Genet.
56:595–601. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kawakami K, Enokida H, Chiyomaru T, et al:
The functional significance of miR-1 and miR-133a in renal cell
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 2011.[Epub ahead of print].
|
|
31
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, et al:
Identification of novel molecular targets regulated by tumor
suppressive miR-1/miR-133a in maxillary sinus squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 39:1099–1107. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|