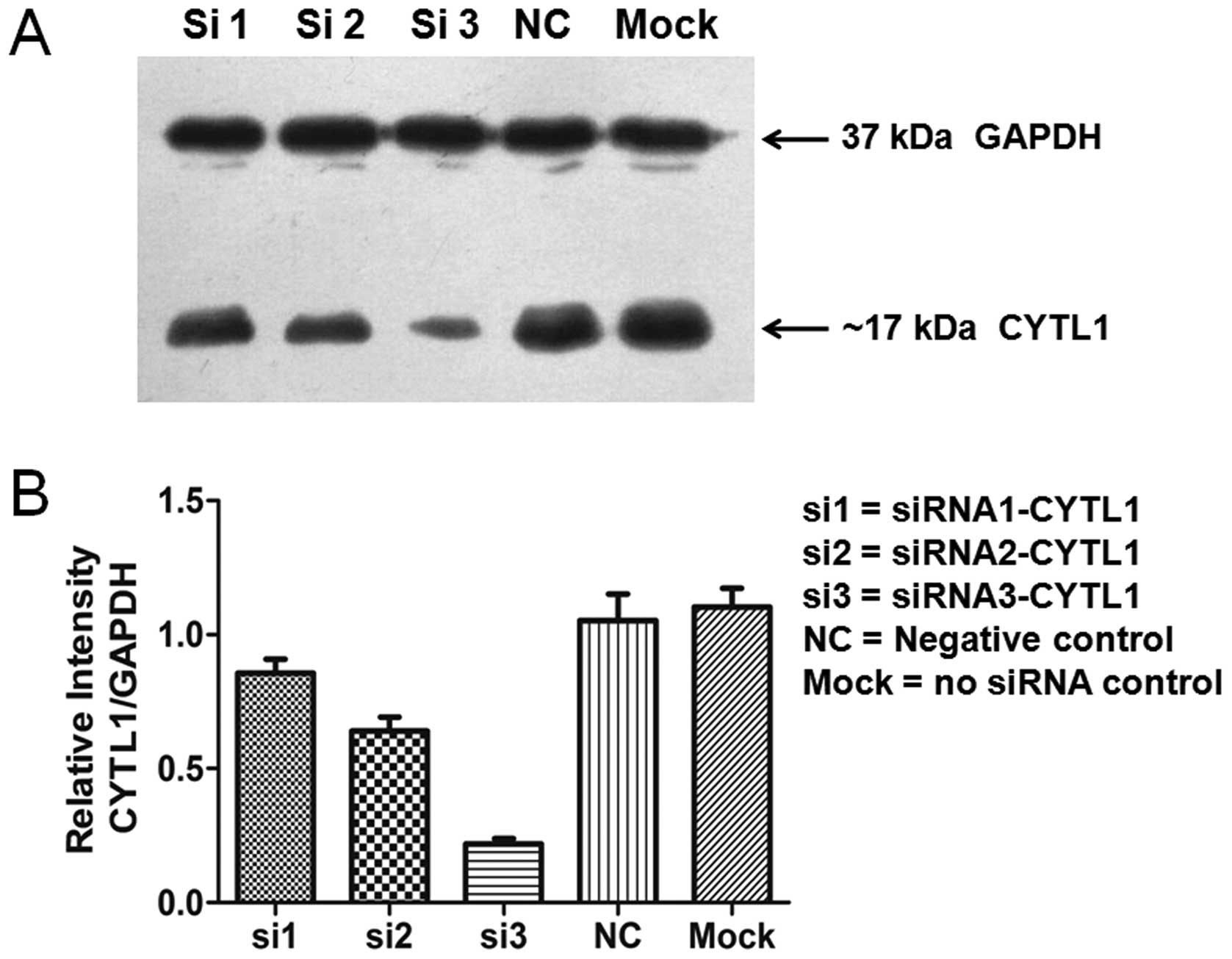
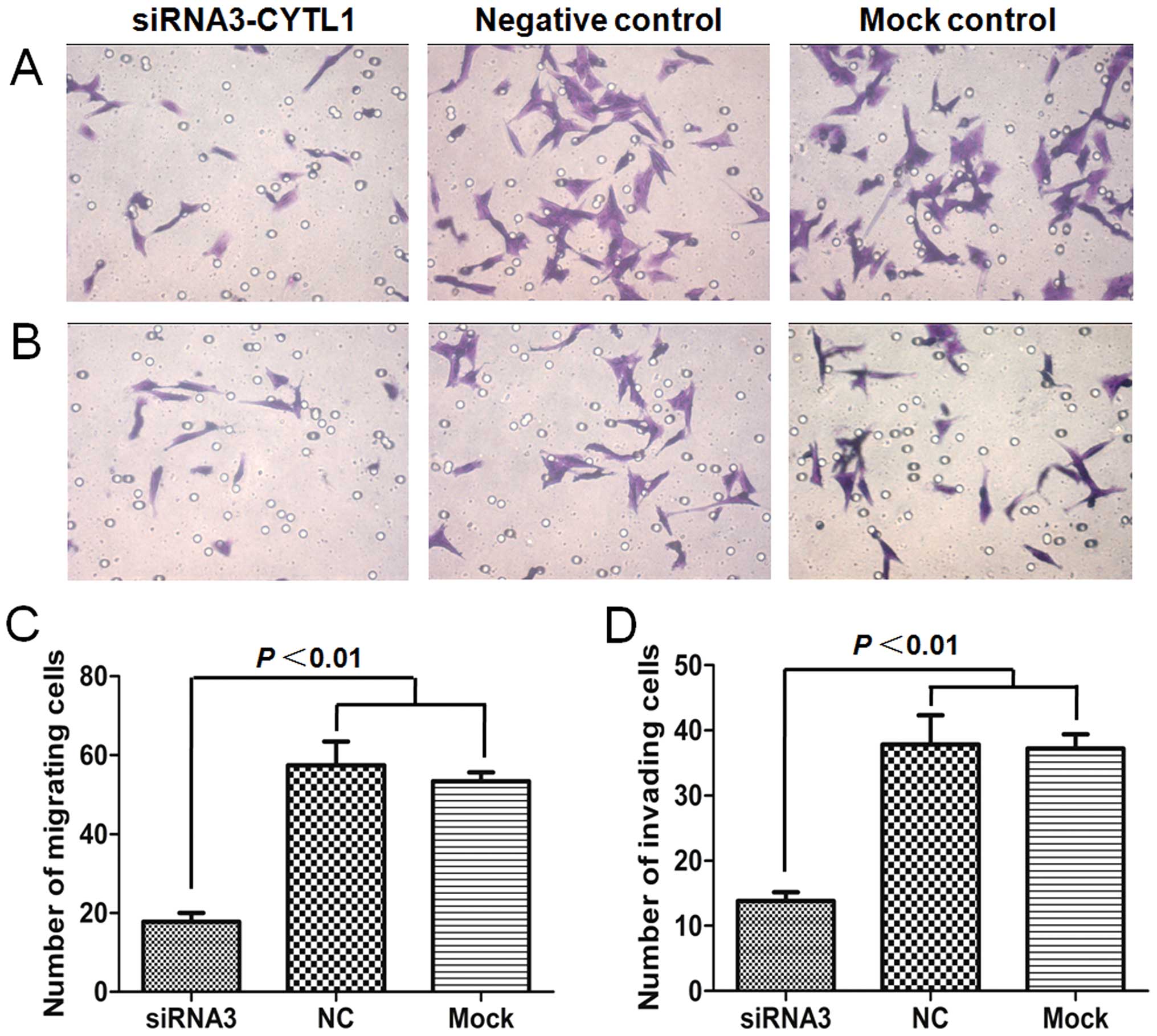
|
1
|
McHugh K: Renal and adrenal tumours in
children. Cancer Imaging. 7:41–51. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu H, Zheng J, Xiao X, et al:
Environmental endocrine disruptors promote invasion and metastasis
of SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cells. Oncol Rep. 23:129–139.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rha SE, Byun JY, Jung SE, Chun HJ, Lee HG
and Lee JM: Neurogenic tumors in the abdomen: tumor types and
imaging characteristics. Radiographics. 23:29–43. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pistoia V, Bianchi G, Borgonovo G and
Raffaghello L: Cytokines in neuroblastoma: from pathogenesis to
treatment. Immunotherapy. 3:895–907. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Metelitsa LS, Wu HW, Wang H, et al:
Natural killer T cells infiltrate neuroblastomas expressing the
chemokine CCL2. J Exp Med. 199:1213–1221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang L, Yeger H, Das B, Irwin MS and
Baruchel S: Tissue microenvironment modulates CXCR4 expression and
tumor metastasis in neuroblastoma. Neoplasia. 9:36–46. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng Y, Huebener N, Fest S, et al:
Fractalkine (CX3CL1)- and interleukin-2-enriched neuroblastoma
microenvironment induces eradication of metastases mediated by T
cells and natural killer cells. Cancer Res. 67:2331–2338. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Raffaghello L, Cocco C, Corrias MV,
Airoldi I and Pistoia V: Chemokines in neuroectodermal tumour
progression and metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:97–102. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu X, Rapp N, Deans R and Cheng L:
Molecular cloning and chromosomal mapping of a candidate cytokine
gene selectively expressed in human CD34+ cells.
Genomics. 65:283–292. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hermansson M, Sawaji Y, Bolton M, et al:
Proteomic analysis of articular cartilage shows increased type II
collagen synthesis in osteoarthritis and expression of inhibin
betaA (activin A), a regulatory molecule for chondrocytes. J Biol
Chem. 279:43514–43521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim JS, Ryoo ZY and Chun JS: Cytokine-like
1 (Cytl1) regulates the chondrogenesis of mesenchymal cells. J Biol
Chem. 282:29359–29367. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jeon J, Oh H, Lee G, et al: Cytokine-like
1 knock-out mice (Cytl1-/-) show normal cartilage and bone
development but exhibit augmented osteoarthritic cartilage
destruction. J Biol Chem. 286:27206–27213. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chao C, Joyce-Shaikh B, Grein J, et al:
C17 prevents inflammatory arthritis and associated joint
destruction in mice. PLoS One. 6:e222562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Begley LA, Kasina S, MacDonald J and
Macoska JA: The inflammatory microenvironment of the aging prostate
facilitates cellular proliferation and hypertrophy. Cytokine.
43:194–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kwon YJ, Lee SJ, Koh JS, et al:
Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and the gene expression
change in lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 7:20–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tomczak A and Pisabarro MT: Identification
of CCR2-binding features in Cytl1 by a CCL2-like chemokine model.
Proteins. 79:1277–1292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:131–142. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chambers AF, Groom AC and MacDonald IC:
Dissemination and growth of cancer cells in metastatic sites. Nat
Rev Cancer. 2:563–572. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pienta KJ and Loberg R: The ‘emigration,
migration, and immigration’ of prostate cancer. Clin Prostate
Cancer. 4:24–30. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Vicari AP and Caux C: Chemokines in
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 13:143–154. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Gross N and Meier R: Chemokines in
neuroectodermal cancers: the crucial growth signal from the soil.
Semin Cancer Biol. 19:103–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Geminder H, Sagi-Assif O, Goldberg L, et
al: A possible role for CXCR4 and its ligand, the CXC chemokine
stromal cell-derived factor-1, in the development of bone marrow
metastases in neuroblastoma. J Immunol. 167:4747–4757. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ara T and DeClerck YA: Mechanisms of
invasion and metastasis in human neuroblastoma. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 25:645–657. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elbashir SM, Harborth J, Weber K and
Tuschl T: Analysis of gene function in somatic mammalian cells
using small interfering RNAs. Methods. 26:199–213. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zamore PD: RNA interference: listening to
the sound of silence. Nat Struct Biol. 8:746–750. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Burnett JC, Rossi JJ and Tiemann K:
Current progress of siRNA/shRNA therapeutics in clinical trials.
Biotechnol J. 6:1130–1146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Patel R, T’Wallant NC, Herbert MH, White
D, Murison JG and Reid G: The potency of siRNA-mediated growth
inhibition following silencing of essential genes is dependent on
siRNA design and varies with target sequence. Oligonucleotides.
19:317–328. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Suggate EL, Ahmed Z, Read ML, et al:
Optimisation of siRNA-mediated RhoA silencing in neuronal cultures.
Mol Cell Neurosci. 40:451–462. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao M, Yang H, Jiang X, et al:
Lipofectamine RNAiMAX: an efficient siRNA transfection reagent in
human embryonic stem cells. Mol Biotechnol. 40:19–26. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nabzdyk CS, Chun M, Pradhan L and Logerfo
FW: High throughput RNAi assay optimization using adherent cell
cytometry. J Transl Med. 9:482011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|