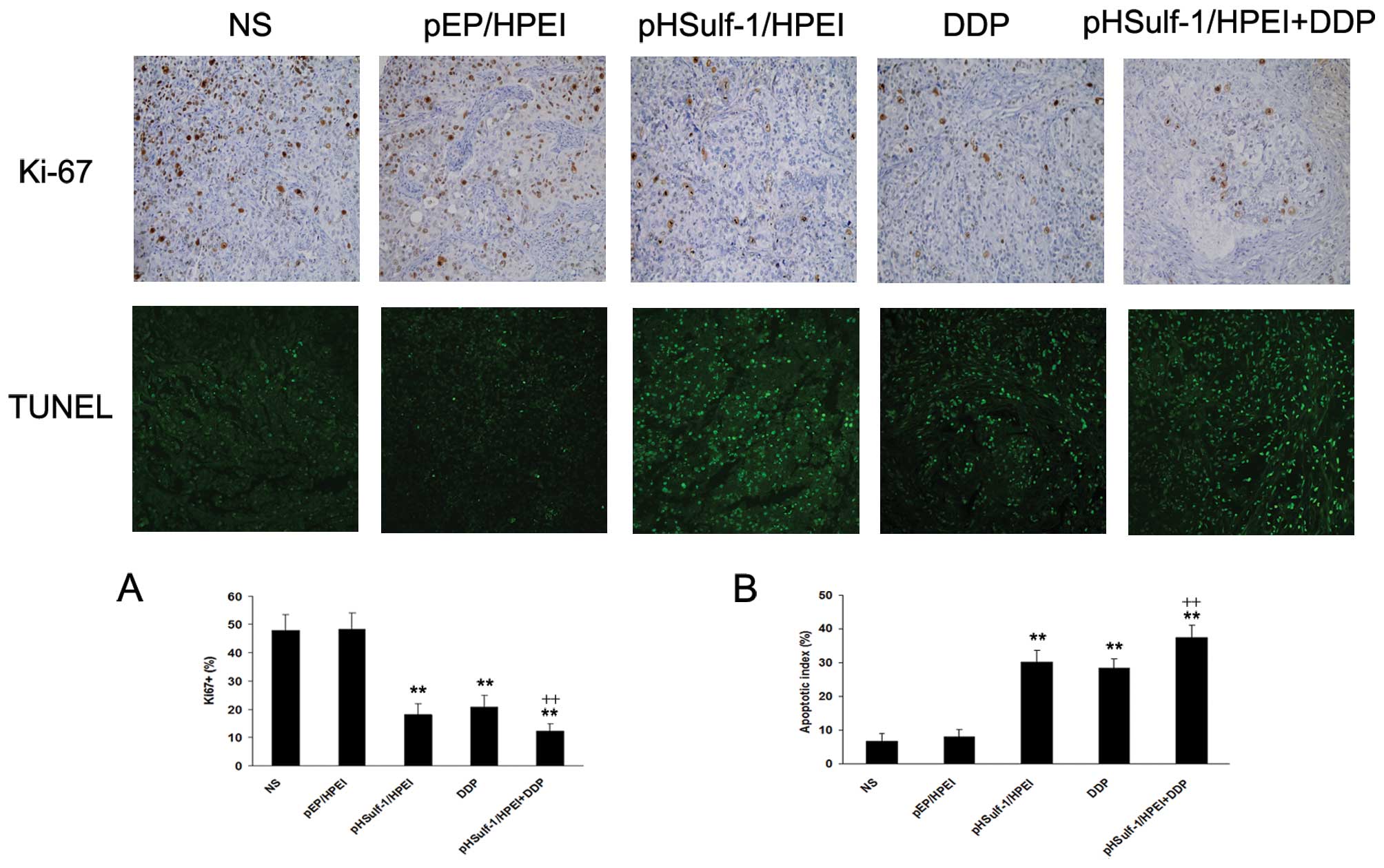
|
1
|
Shridhar V, Sen A, Chien J, Staub J, Avula
R, Kovats S, Lee J, Lillie J and Smith DI: Identification of
underexpressed genes in early- and late-stage primary ovarian
tumors by suppression subtraction hybridization. Cancer Res.
62:262–270. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morimoto-Tomita M, Uchimura K, Werb Z,
Hemmerich S and Rosen SD: Cloning and characterization of two
extracellular heparin-degrading endosulfatases in mice and humans.
J Biol Chem. 277:49175–49185. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ai X, Do AT, Kusche-Gullberg M, Lindahl U,
Lu K and Emerson CP Jr: Substrate specificity and domain functions
of extracellular heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatases, QSulf1 and
QSulf2. J Biol Chem. 281:4969–4976. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dhoot GK, Gustafsson MK, Ai X, Sun W,
Standiford DM and Emerson CP Jr: Regulation of Wnt signaling and
embryo patterning by an extracellular sulfatase. Science.
293:1663–1666. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Selva EM and Perrimon N: Role of heparan
sulfate proteoglycans in cell signaling and cancer. Adv Cancer Res.
83:67–80. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin X: Functions of heparan sulfate
proteoglycans in cell signaling during development. Development.
131:6009–6021. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lai JP, Chien J, Staub J, Avula R, Greene
EL, Matthews TA, Smith DI, Kaufmann SH, Roberts LR and Shridhar V:
Loss of HSulf-1 up-regulates heparin-binding growth factor
signaling in cancer. J Biol Chem. 278:23107–23117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lai JP, Chien J, Strome SE, Staub J,
Montoya DP, Greene EL, Smith DI, Roberts LR and Shridhar V: HSulf-1
modulates HGF-mediated tumor cell invasion and signaling in head
and neck squamous carcinoma. Oncogene. 23:1439–1447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lai JP, Chien JR, Moser DR, Staub JK,
Aderca I, Montoya DP, Matthews TA, Nagorney DM, Cunningham JM,
Smith DI, Greene EL, Shridhar V and Roberts LR: hSulf1sulfatase
promotes apoptosis of hepatocellular cancer cells by decreasing
heparin-binding growth factor signaling. Gastroenterology.
126:231–248. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai Y, Yang Y, MacLeod V, Yue X, Rapraeger
AC, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, Sasisekharan R and Sanderson RD:
HSulf-1 and HSulf-2 are potent inhibitors of myeloma tumor growth
in vivo. J Biol Chem. 280:40066–40073. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Narita K, Staub J, Chien J, Meyer K, Bauer
M, Friedl A, Ramakrishnan S and Shridhar V: HSulf-1 inhibits
angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 66:6025–6032.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu P, Khurana A, Rattan R, Kalloger S,
Dowdy S, Gilks B and Shridhar V: Regulation of HSulf-1 expression
by variant hepatic nuclear factor 1 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
69:4843–4850. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Staub J, Chien J, Pan Y, Qian X, Narita K,
Aletti G, Roberts LR, Molina J and Shridhar V: Epigenetic silencing
of HSulf-1 in ovarian cancer: implications in chemoresistance.
Oncogene. 26:4969–4978. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lai JP, Sandhu DS, Shire AM and Roberts
LR: The tumor suppressor function of human sulfatase 1 (SULF1) in
carcinogenesis. J Gastrointest Cancer. 39:149–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ozols RF: Progress in ovarian cancer: an
overview and perspective. EJC (Suppl). 1:43–55. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gonzalez VM, Fuertes MA, Alonso C and
Perez JM: Is cisplatin-induced cell death always produced by
apoptosis? Mol Pharmacol. 59:657–663. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fuertes MA, Alonso C and Perez JM:
Biochemical modulation of cisplatin mechanisms of action:
enhancement of antitumor activity and circumvention of drug
resistance. Chem Rev. 103:645–662. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reed E: Platinum-DNA adduct, nucleotide
excision repair and platinum based anti-cancer chemotherapy. Cancer
Treat Rev. 24:331–344. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cohen SM and Lippard SJ: Cisplatin: from
DNA damage to cancer chemotherapy. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol.
67:93–130. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Edelstein ML, Abedi MR, Wixon J and
Edelstein RM: Gene therapy clinical trials worldwide 1989–2004-an
overview. J Gene Med. 6:597–602. 2004.
|
|
22
|
Anderson DG, Peng W, Akinc A, Hossain N,
Kohn A, Padera R, Langer R and Sawicki JA: A polymer library
approach to suicide gene therapy for cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:16028–16033. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ferber D: Gene therapy. Safer and
virus-free? Science. 294:1638–1642. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lv H, Zhang S, Wang B, Cui S and Yan J:
Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery.
J Control Release. 114:100–109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Neu M, Fischer D and Kissel T: Recent
advances in rational gene transfer vector design based on
poly(ethyleneimine) and its derivatives. J Gene Med. 7:992–1009.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kunath K, von Harpe A, Fischer D, Petersen
H, Bickel U, Voigt K and Kissel T: Low-molecular-weight
polyethyleneimine as a non-viral vector for DNA delivery:
comparison of physicochemical properties, transfection efficiency
and in vivo distribution with high-molecular-weight
polyethyleneimine. J Control Release. 89:113–125. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wen Y, Pan S, Luo X, Zhang X, Zhang W and
Feng M: A biodegradable low molecular weight polyethyleneimine
derivative as low toxicity and efficient gene vector. Bioconjug
Chem. 20:322–332. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gosselin MA, Guo W and Lee RJ: Efficient
gene transfer using reversibly cross-linked low molecular weight
polyethyleneimine. Bioconjug Chem. 12:989–994. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Forrest ML, Koerber JT and Pack DW: A
degradable polyethyleneimine derivative with low toxicity for
highly efficient gene delivery. Bioconjug Chem. 14:934–940. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jeon O, Yang HS, Lee TJ and Kim BS:
Heparin-conjugated polyethyleneimine for gene delivery. J Control
Release. 132:236–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gou ML, Men K, Zhang J, Li YH, Song J, Luo
S, Shi HS, Wen YJ, Guo G, Huang MJ, Zhao X, Qian ZY and Wei YQ:
Efficient inhibition of C-26 colon carcinoma by VSVMP gene
delivered by biodegradable cationic nanogel derived from
polyethyleneimine. ACS Nano. 4:5573–5584. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu P, Gou ML, Yi T, Xie C, Qi XR, Zhou
ST, Deng HX, Wei YQ and Zhao X: Efficient inhibition of an
intraperitoneal xenograft model of human ovarian cancer by HSulf-1
gene delivered by biodegradable cationic heparin-polyethyleneimine
nanogels. Oncol Rep. 27:363–370. 2012.
|
|
33
|
Lin XJ, Chen XC, Wang L, Wei YQ, Kan B,
Wen YJ, He X and Zhao X: Dynamic progression of an intraperitoneal
xenograft model of human ovarian cancer and its potential for
preclinical trials. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 26:467–474.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hoffmann J, Schirner M, Menrad A and
Schneider MR: A highly sensitive model for quantification of in
vivo tumor angiogenesis induced by alginate-encapsulated tumor
cells. Cancer Res. 57:3847–3851. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
He QM, Wei YQ, Tian L, Zhao X, Su JM, Yang
L, Lu Y, Kan B, Lou YY, Huang MJ, Xiao F, Liu JY, Hu B, Luo F,
Jiang Y, Wen YJ, Deng HX, Li J, Niu T and Yang JL: Inhibition of
tumor growth with a vaccine based on xenogeneic homologous
fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 in mice. J Biol Chem.
278:21831–21836. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu L, Hofmann J, Zaloudek C, Ferrara N,
Hamilton T and Jaffe RB: Vascular endothelial growth factor
immunoneutralization plus paclitaxel markedly reduces tumor burden
and ascites in athymic mouse model of ovarian cancer. Am J Pathol.
161:1917–1924. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Klement G, Baruchel S, Rak J, Man S, Clark
K, Hicklin DJ, Bohlen P and Kerbel RS: Continuous low-dose therapy
with vinblastine and VEGF receptor-2 antibody induces sustained
tumor regression without overt toxicity. J Clin Invest.
105:R15–R24. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Neri D and Bicknell R: Tumour vascular
targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:436–446. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|