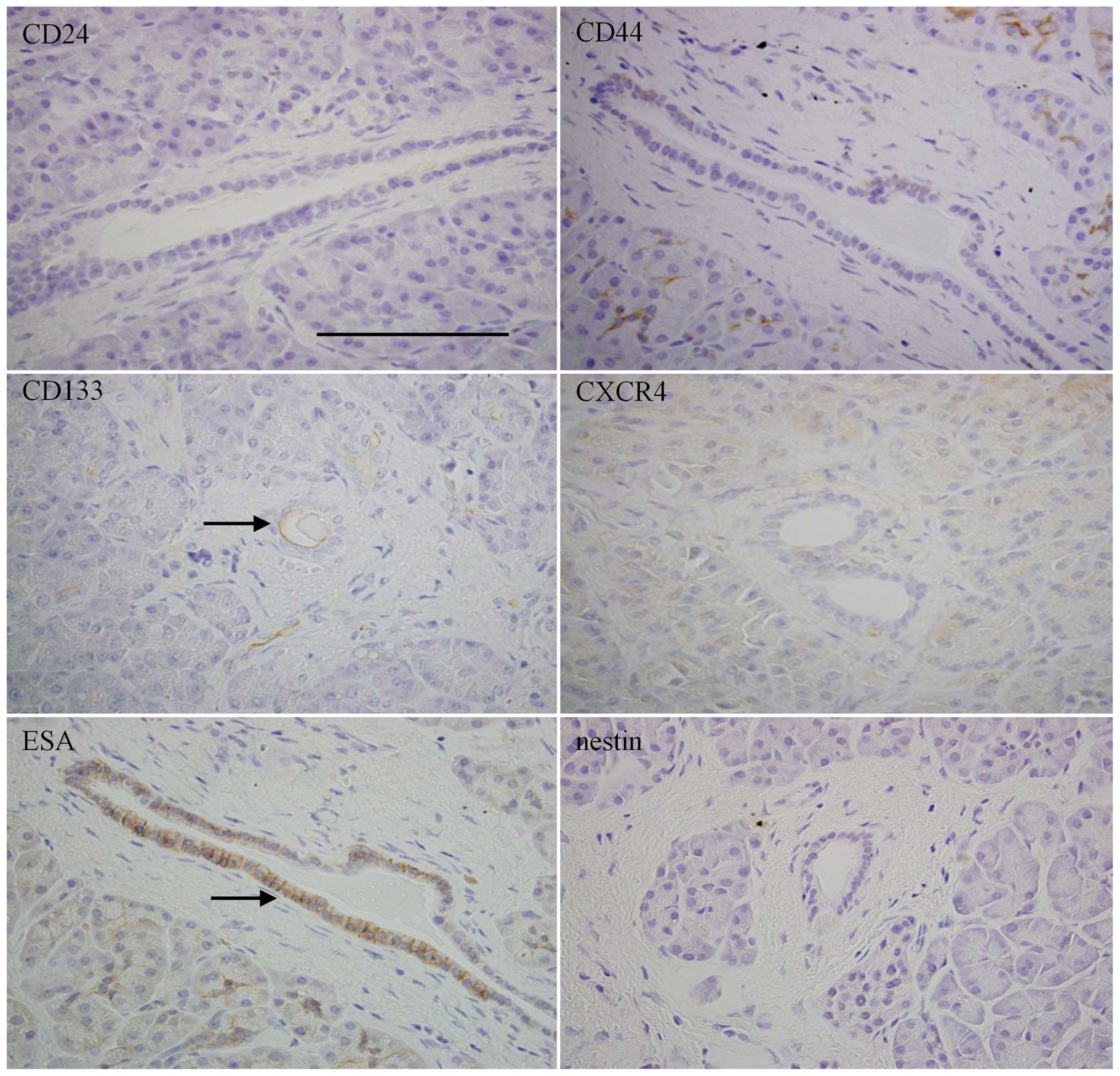
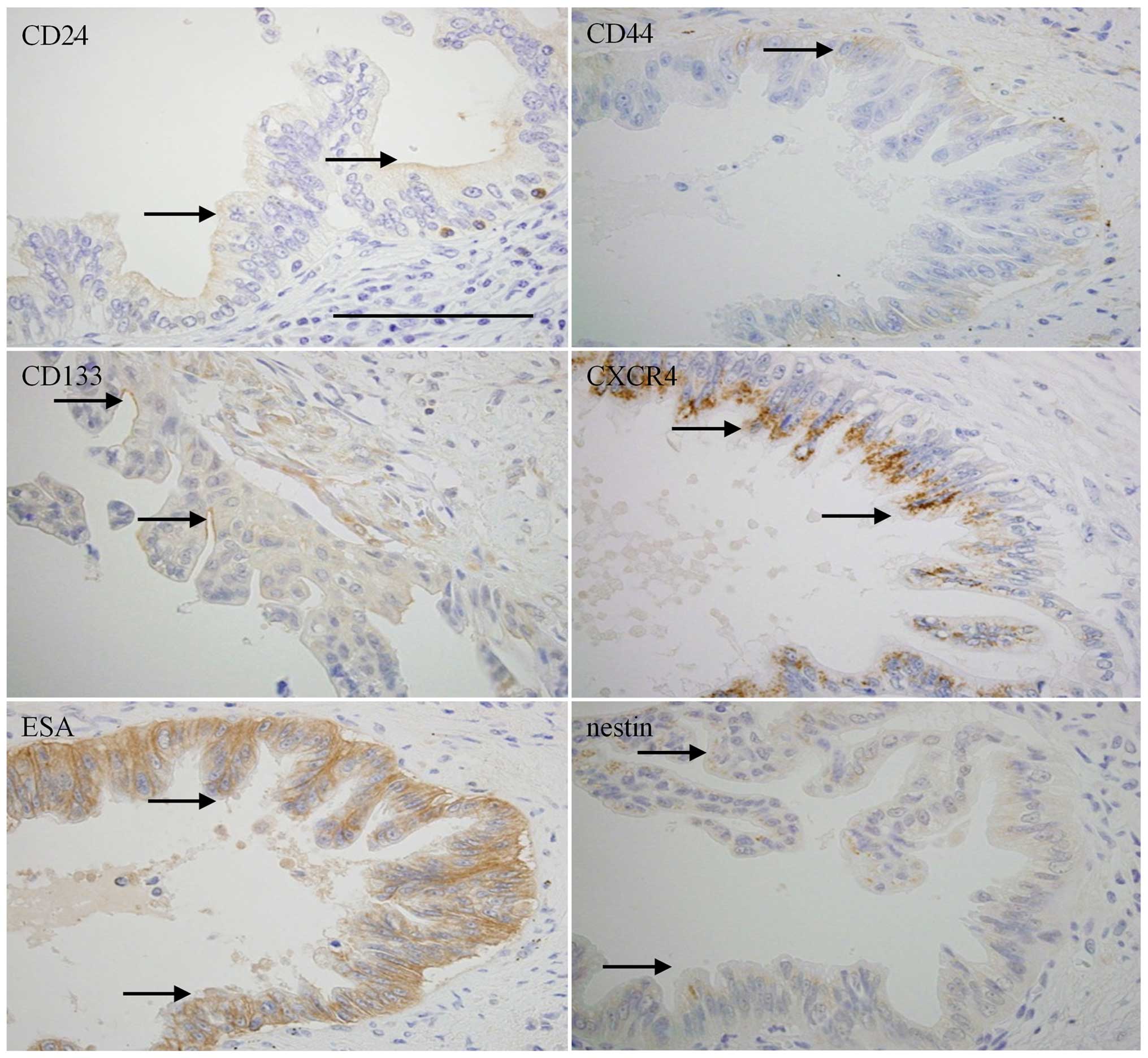
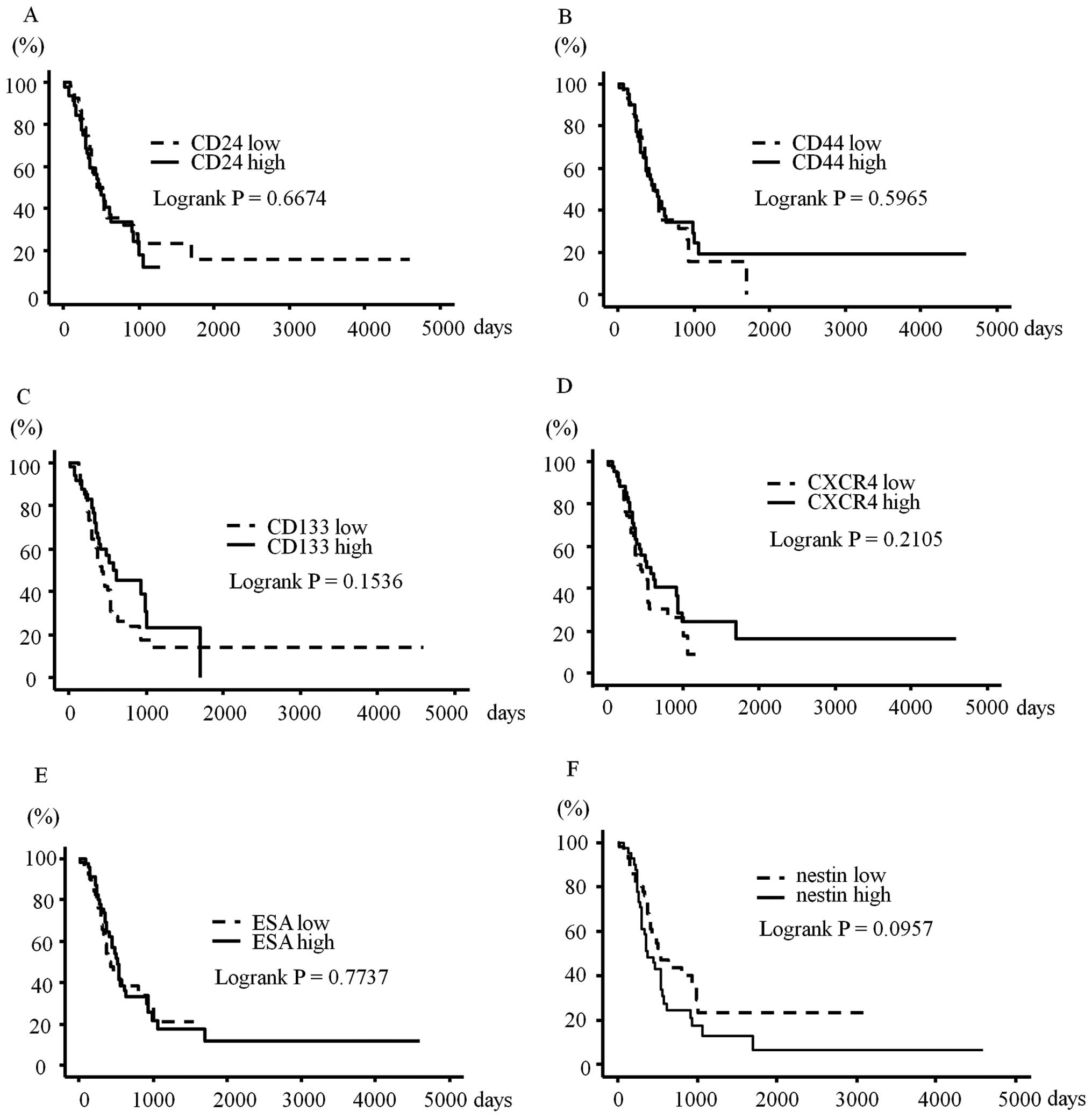
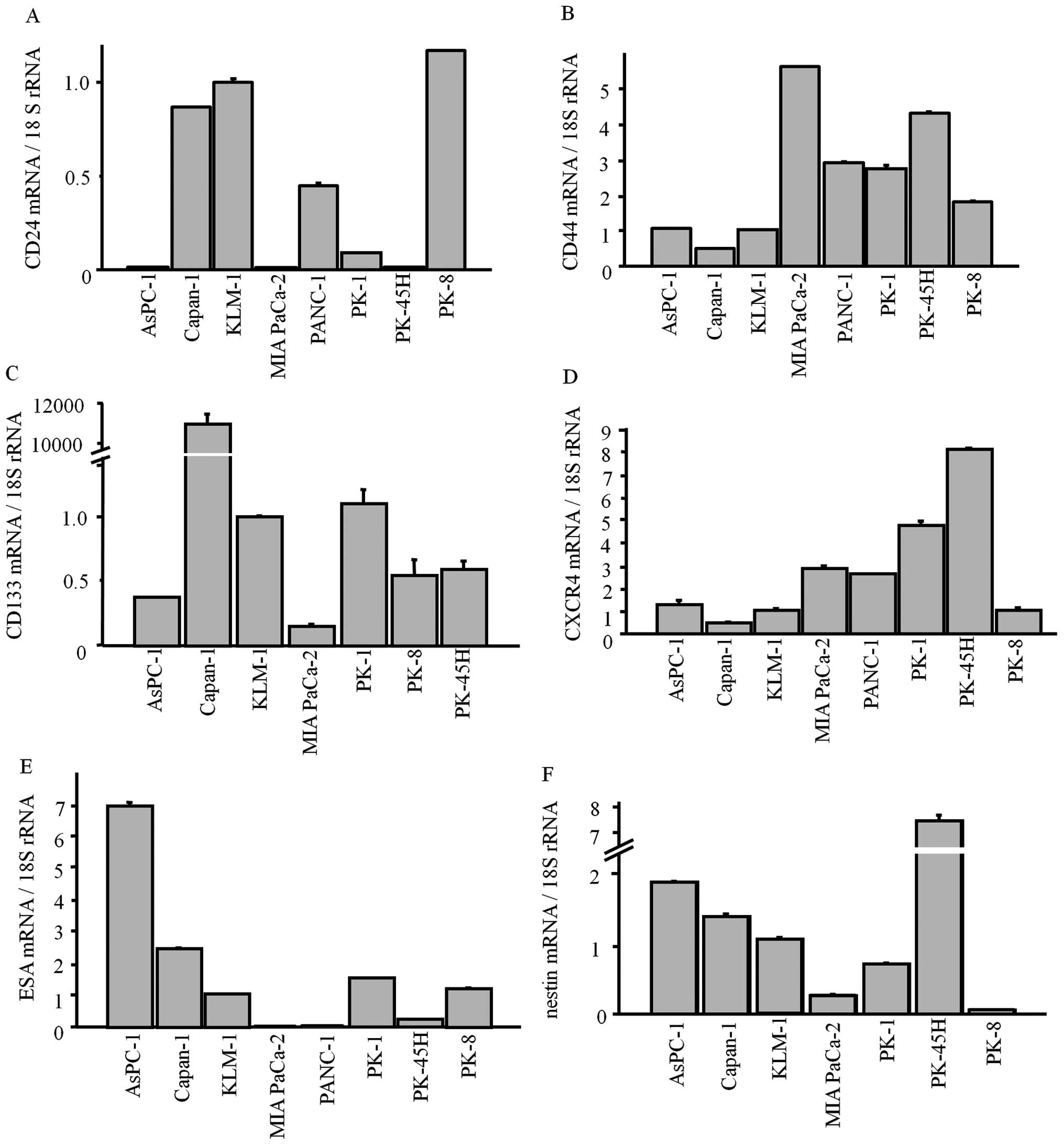
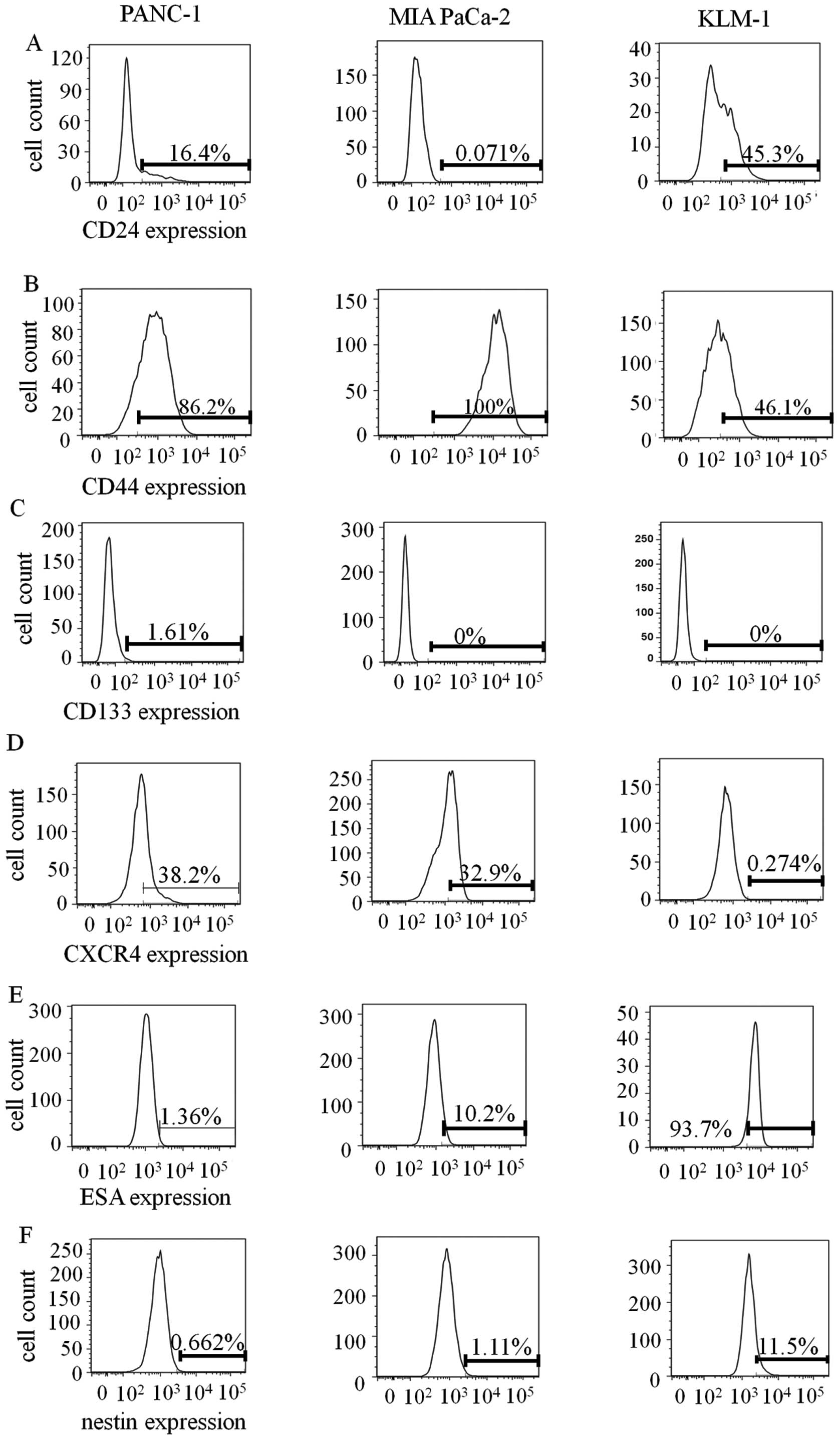
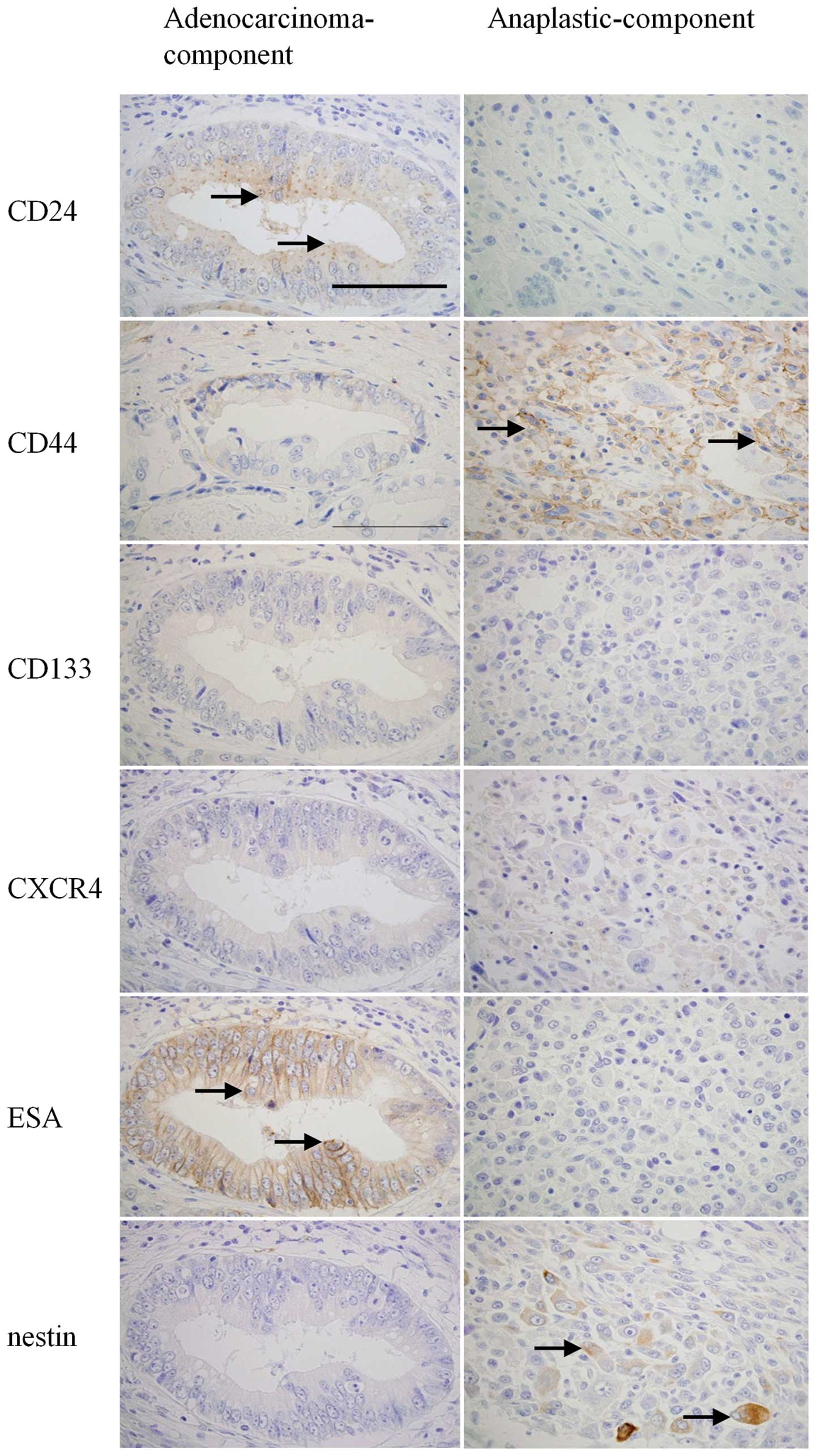
|
1
|
Bissell MJ and Labarge MA: Context, tissue
plasticity, and cancer: are tumor stem cells also regulated by the
microenvironment? Cancer Cell. 7:17–23. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Hruban RH, Maitra A and Goggins M: Update
on pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
1:306–316. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li C, Heidt DG, Dalerba P, et al:
Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res.
67:1030–1037. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang P, Wang CY, Gou SM, Wu HS, Liu T and
Xiong JX: Isolation and biological analysis of tumor stem cells
from pancreatic adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
14:3903–3907. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ikenaga N, Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, et al:
Characterization of CD24 expression in intraductal papillary
mucinous neoplasms and ductal carcinoma of the pancreas. Hum
Pathol. 41:1466–1474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hong SP, Wen J, Bang S, Park S and Song
SY: CD44-positive cells are responsible for gemcitabine resistance
in pancreatic cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 125:2323–2331. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li C, Wu JJ, Hynes M, et al: c-Met is a
marker of pancreatic cancer stem cells and therapeutic target.
Gastroenterology. 141:2218–2227.e5. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, et al:
Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth
and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell.
1:313–323. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olempska M, Eisenach PA, Ammerpohl O,
Ungefroren H, Fandrich F and Kalthoff H: Detection of tumor stem
cell markers in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 6:92–97. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim MP, Fleming JB, Wang H, et al: ALDH
activity selectively defines an enhanced tumor-initiating cell
population relative to CD133 expression in human pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 6:e206362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Maeda S, Shinchi H, Kurahara H, et al:
CD133 expression is correlated with lymph node metastasis and
vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression in pancreatic
cancer. Br J Cancer. 98:1389–1397. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marechal R, Demetter P, Nagy N, et al:
High expression of CXCR4 may predict poor survival in resected
pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 100:1444–1451. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kawamoto M, Ishiwata T, Cho K, et al:
Nestin expression correlates with nerve and retroperitoneal tissue
invasion in pancreatic cancer. Hum Pathol. 40:189–198. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clevers H: The cancer stem cell: premises,
promises and challenges. Nat Med. 17:313–319. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J,
et al: Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a new nomenclature and
classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am J Surg
Pathol. 25:579–586. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Carriere C, Seeley ES, Goetze T,
Longnecker DS and Korc M: The Nestin progenitor lineage is the
compartment of origin for pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:4437–4442. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aigner S, Sthoeger ZM, Fogel M, et al:
CD24, a mucin-type glycoprotein, is a ligand for P-selectin on
human tumor cells. Blood. 89:3385–3395. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ponta H, Sherman L and Herrlich PA: CD44:
from adhesion molecules to signalling regulators. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 4:33–45. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Immervoll H, Hoem D, Sakariassen PO,
Steffensen OJ and Molven A: Expression of the ‘stem cell marker’
CD133 in pancreas and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas. BMC
Cancer. 8:482008.
|
|
22
|
Raffel A, Eisenberger CF, Cupisti K, et
al: Increased EpCAM expression in malignant insulinoma: potential
clinical implications. Eur J Endocrinol. 162:391–398. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ishiwata T, Matsuda Y and Naito Z: Nestin
in gastrointestinal and other cancers: effects on cells and tumor
angiogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 17:409–418. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsuda Y, Naito Z, Kawahara K, Nakazawa
N, Korc M and Ishiwata T: Nestin is a novel target for suppressing
pancreatic cancer cell migration, invasion and metastasis. Cancer
Biol Ther. 11:512–523. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee HJ, You DD, Choi DW, et al:
Significance of CD133 as a cancer stem cell markers focusing on the
tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cell lines. J Korean Surg Soc.
81:263–270. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|