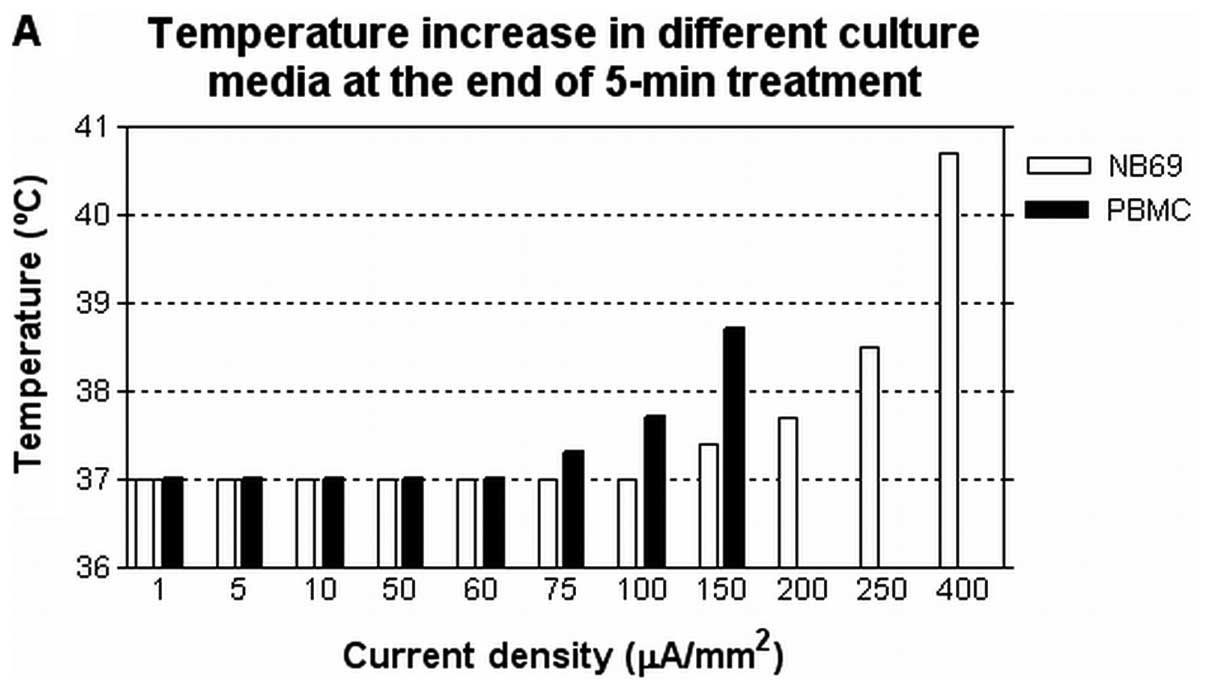
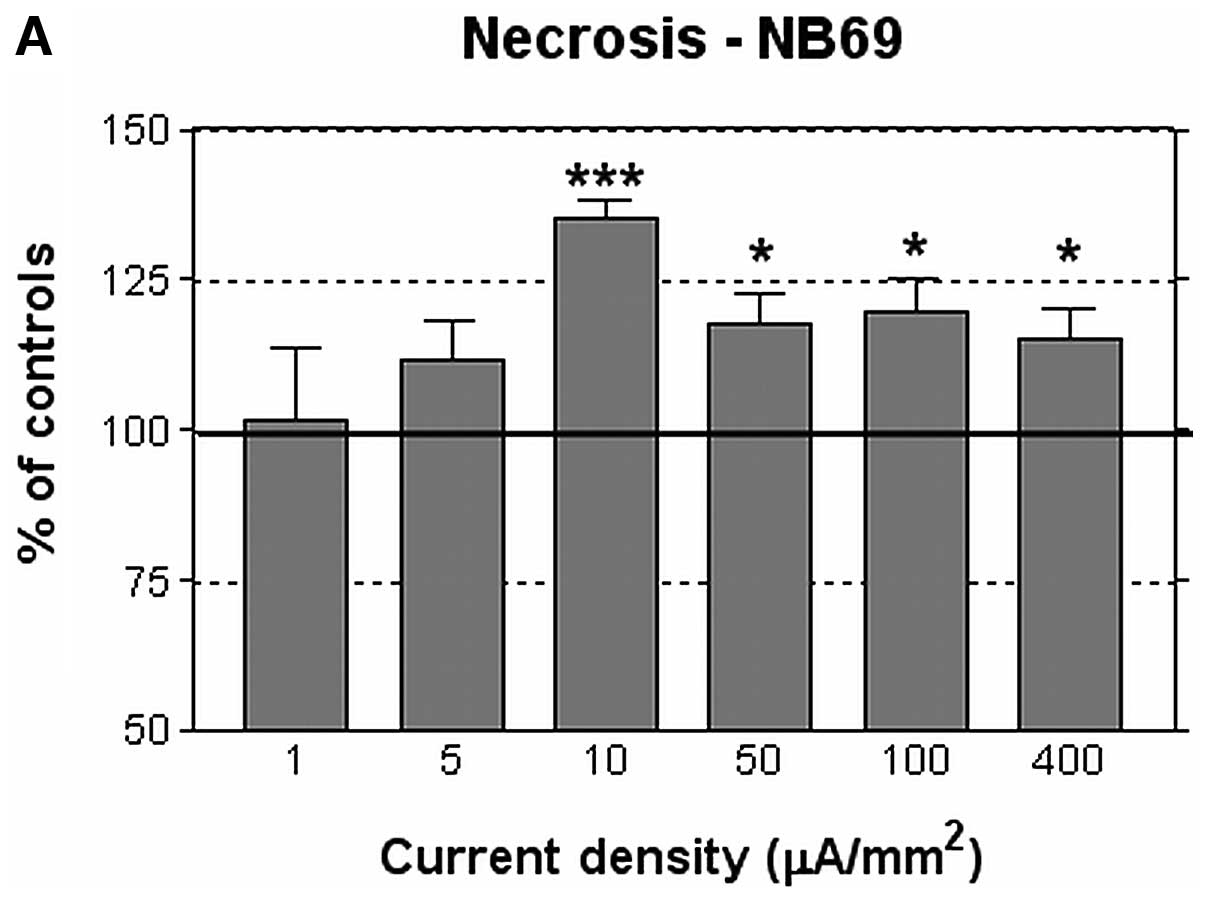
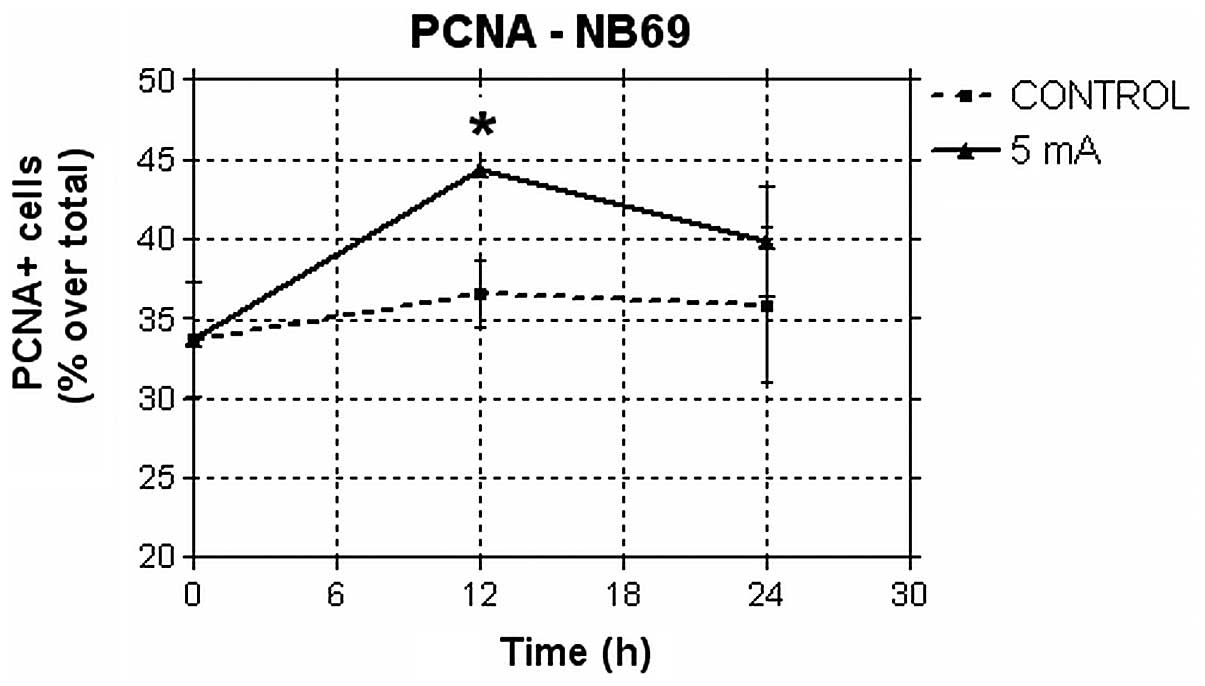
|
1
|
Ottawa Panel: Ottawa panel evidence based
clinical practice guidelines for electrotherapy and thermotherapy
interventions in the management of rheumatoid arthritis in adults.
Phys Ther. 84:1016–1043. 2004.
|
|
2
|
Ricci NA, Dias CN and Driusso P: The use
of electrothermal and phototherapeutic methods for the treatment of
fibromyalgia syndrome: a systematic review. Rev Bras Fisioter.
14:1–9. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sersa G, Jarm T, Kotnit T, Koer A,
Podkrajsek M, Sentjurc M, Miklavcic D, Kadivec M, Kranic S, Secerov
A and Cemazar M: Vascular disrupting action of electroporation and
electrochemotherapy with bleomycin in murine sarcoma. Br J Cancer.
98:388–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kirson ED, Dbaly V, Tovarys F, Vymazal J,
Soustiel JF, Itzhaki A, Mordechovich D, Steinberg-Shapira S,
Gurvich Z, Shneiderman R, et al: Alternating electric fields arrest
cell proliferation in animal tumor models and human brain tumors.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:10152–10157. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Garon EB, Sawcer D, Vernier PT, Tang T,
Sun Y, Marcu L, Gundersen MA and Koeffler HP: In vitro and in vivo
evaluation and a case report of intense nanosecond pulsed electric
field as a local therapy for human malignancies. Int J Cancer.
121:675–682. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fiorentini G, Giovanis P, Rossi S, Dentico
P, Paola R, Turrisi G and Bernardeschi P: A phase II clinical study
on relapsed malignant gliomas treated with electro-hyperthermia. In
Vivo. 20:721–724. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamisawa T, Tu Y, Egawa N, Karasawa K,
Matsuda T, Tsuruta K and Okamoto A: Thermo-chemo-radiotherapy for
advanced bile duct carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 11:4206–4209.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Grimnes S and Martinsen ØG: Joule effect
and temperature rise. Bioimpedance and Bioelectricity Basics.
Academic Press: Harcourt and Technology Co.; London: pp. 71–73.
2000
|
|
9
|
Ley A, Cladellas M, Colet P, de las Heras
P, Florensa J, Prim J, Roussos J, Ariza A and Calbet J:
Transferencia eléctrica capacitiva (TEC): Técnica no invasiva de
hipertermia profunda en el tratamiento de los gliomas cerebrales.
Resultados preliminares. Neurocirugía. 3:118–123. 1992.(In
Spanish).
|
|
10
|
Ley A, Ariza A and Rosell R: Tratamiento
quirúrgico de los gliomas malignos. Hipertermia. Tumores del
Sistema Nervioso Central. Epidemiologia, Nosología y Terapéutica,
Doyma: Barcelona: pp. 55–64. 1993, (In Spanish).
|
|
11
|
Ley A: Hipertermia intracraneal no
invasiva mediante la técnica de Transferencia Eléctrica Capacitiva
(TEC). Resultados de la termometría cerebral e intratumoral.
Neurocirugía. 14:41–45. 2003.(In Spanish).
|
|
12
|
Sakamoto T, Katoh H, Shimizu T, Yamashita
I, Takemori S, Tazawa K and Fujimaki M: Clinical results of
treatment of advanced carcinoma with hyperthermia in combination
with chemoradiotherapy. Chest. 112:1487–1493. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Matsui Y, Nakagana A, Kamiyama Y, Yamamoto
K, Kubo N and Nakase Y: Selective thermocoagulation of unresectable
pancreatic cancers by using radiofrequency capacitive heating.
Pancreas. 20:14–20. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohguri T, Imada H, Yahara K, Kakeda S,
Tomimatsu A, Kato F, Nomoto S, Terashima H and Korogi Y: Effect of
8-MHz radiofrequency-capacitive regional hyperthermia with strong
superficial cooling for unresectable or recurrent colorectal
cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 20:465–475. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hernández-Bule ML, Trillo MA, Bazán E,
Martínez-Pascual MA, Leal J and Úbeda A: Niveles atérmicos de
corrientes eléctricas usadas en terapia por transferencia eléctrica
capacitiva inducen efectos citotóxicos parciales en cultivos de
neuroblastoma humano. Neurocirugía. 15:366–371. 2004.(In
Spanish).
|
|
16
|
Hernández-Bule ML, Trillo MA, Cid MA, Leal
J and Ubeda A: In vitro exposure to 0.57 MHz electric
currents exerts cytostatic effects in HepG2 human hepatocarcinoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 30:583–592. 2007.
|
|
17
|
Hernández-Bule ML, Cid MA, Trillo MA, Leal
J and Ubeda A: Cytostatic response of HepG2 to 0.57 MHz electric
currents mediated by changes in cell cycle control proteins. Int J
Oncol. 37:1399–1405. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang E, Yin Y, Zhao M, Forrester JV and
McCaig CD: Physiological electric fields control the G1/S phase
cell cycle checkpoint to inhibit endothelial cell proliferation.
FASEB J. 17:458–460. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kirson ED, Gurvich Z, Shneiderman R, Dekel
E, Itzhaki A, Wasserman Y, Schatzberger R and Palti Y: Disruption
of cancer cell replication by alternating electric fields. Cancer
Res. 64:3288–3295. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Boyum A: Isolation of leucocytes from
human blood. A two-phase system for removal of red cells with
methylcellulose as erythrocyte-aggregating agent. Scand J Clin Lab
Invest (Suppl). 97:9–29. 1968.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rodríguez-Martín E, Canals S, Casarejos
MJ, de Bernardo S, Handler A and Mena MA: L-DOPA and
glia-conditioned medium have additive effects on tyrosine
hydroxylase expression in human catecholamine-rich neuroblastoma
NB69 cells. J Neurochem. 78:535–545. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kato S, Asada R, Kageyama K, Saitoh Y and
Miwa N: Anticancer effects of 6-O-palmitoyl-ascorbate combined with
a capacitive-resistive electric transfer hyperthermic apparatus as
compared with ascorbate in relation to ascorbyl radical generation.
Cytotechnology. 63:425–435. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Aslan JE and Thomas G: Death by committee:
organellar trafficking and communication in apoptosis. Traffic.
10:1390–1404. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Woods AL, Hall PA, Shepherd NA, Hanby AM,
Waseem NH, Lane DP and Levison DA: The assessment of proliferating
cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining in primary
gastrointestinal lymphomas and its relationship to histological
grade, S+G2+M phase fraction (flow cytometric analysis) and
prognosis. Histophatology. 19:21–27. 1991.
|
|
25
|
Connolly KM and Bogdanffy MS: Evaluation
of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) as an endogenous
marker of cell proliferation in rat liver: a dual-stain comparison
with 5-bromo-2′-deoxyuridine. J Histochem Cytochem. 41:1–6.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nakano A, Norihito W, Yasuhiro N,
Takashimizu S and Matsuzaki S: Immunohistochemical studies on the
expression of P-glycoprotein and p53 in relation to histological
differentiation and cell proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatol Res. 25:158–165. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Feder MK and Gilbert F: Clonal evolution
in a human neuroblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 70:1051–1056.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Acosta S, Lavarino C, Paris R, García I,
de Torres C, Rodríguez E, Beleta H and Mora J: Comprehensive
characterization of neuroblastoma cell line subtypes reveals
bilineage potential similar to neural crest stem cells. BMC Dev
Biol. 12:9–12. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|