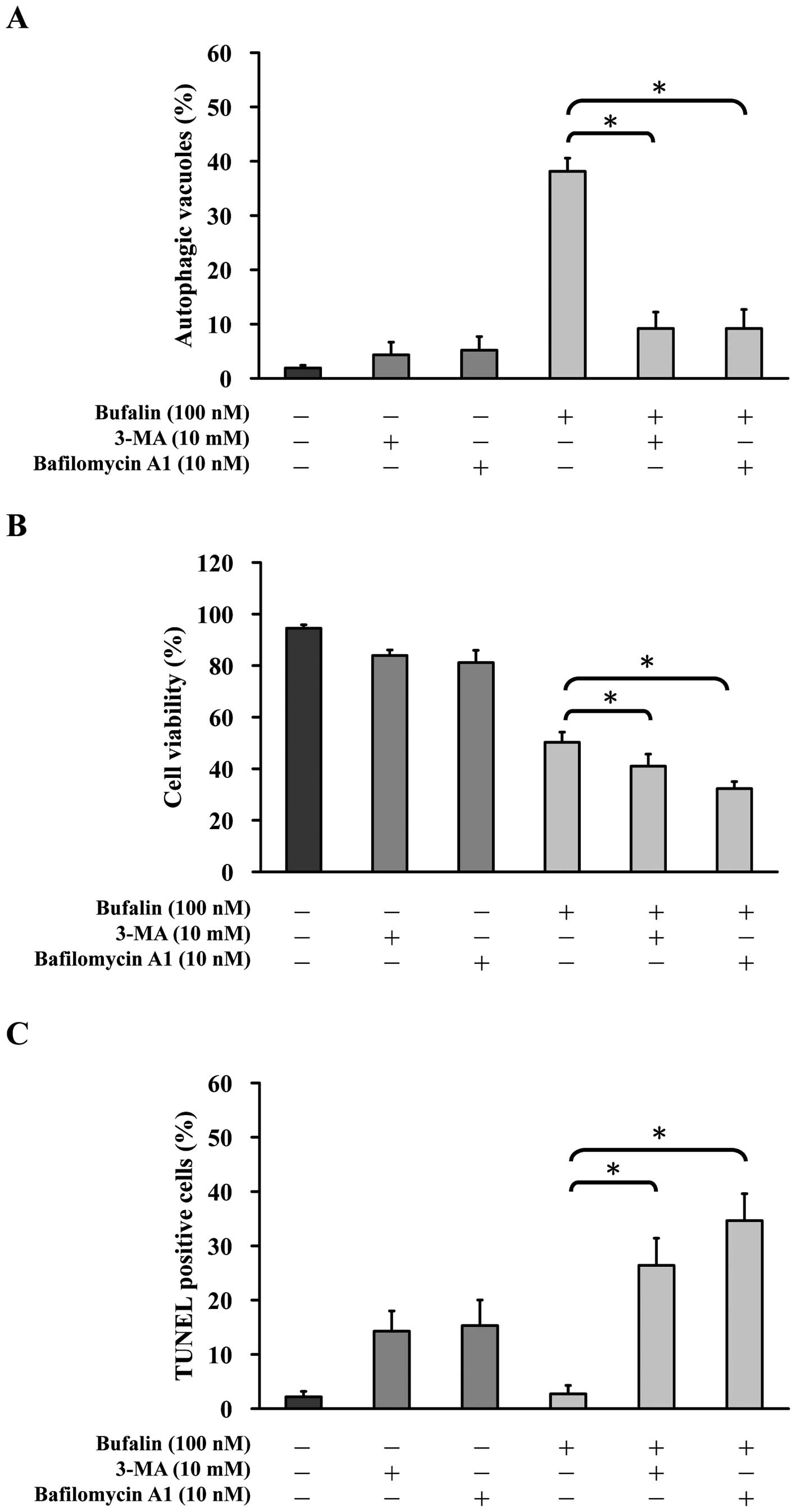
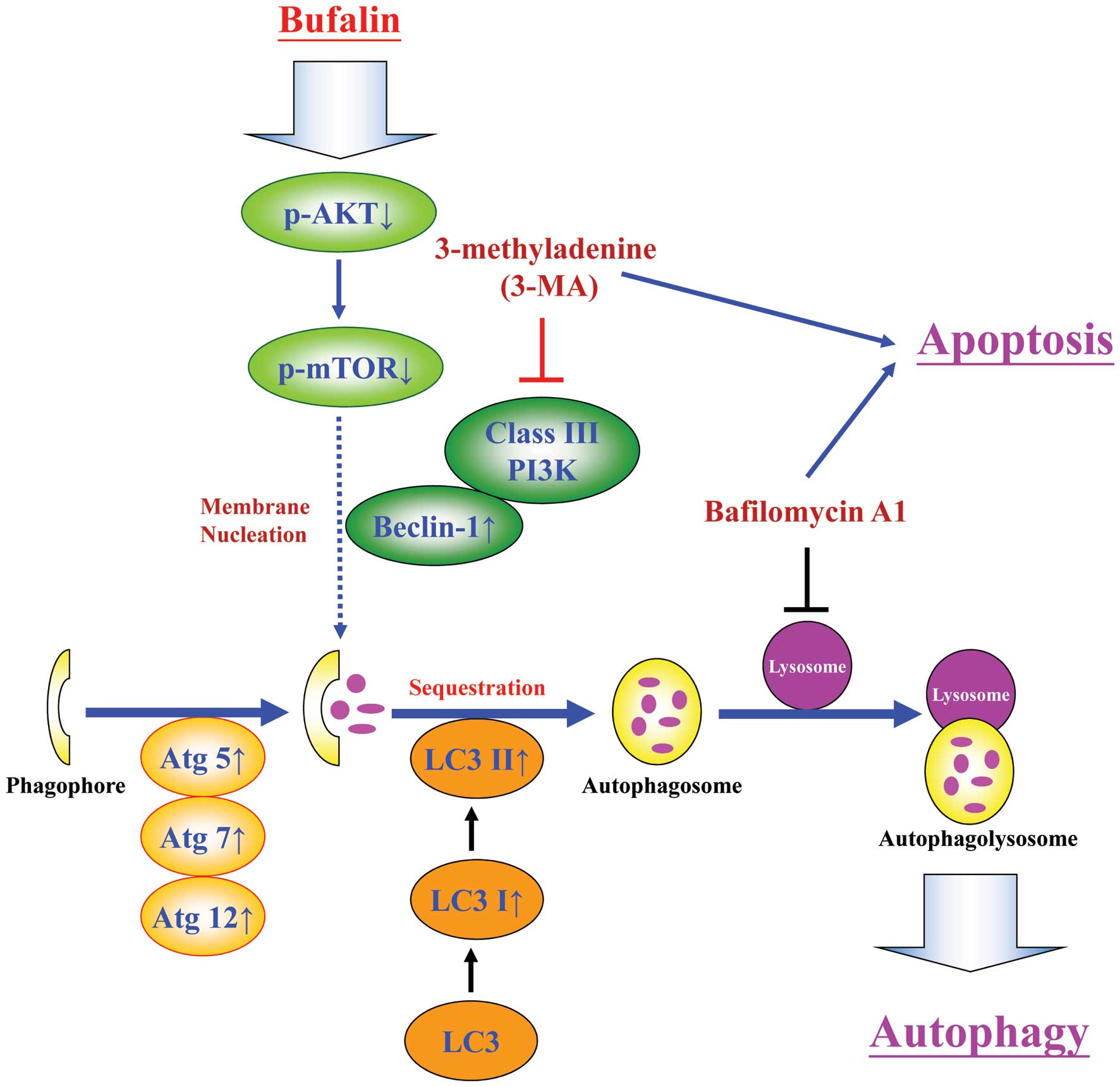
|
1
|
Tazi el M, Essadi I, M’Rabti H, Touyar A
and Errihani PH: Systemic treatment and targeted therapy in
patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Am J Med Sci.
3:167–175. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shariff MI, Cox IJ, Gomaa AI, Khan SA,
Gedroyc W and Taylor-Robinson SD: Hepatocellular carcinoma: current
trends in worldwide epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis and
therapeutics. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:353–367. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Simonetti RG, Camma C, Fiorello F, Politi
F, D’Amico G and Pagliaro L: Hepatocellular carcinoma. A worldwide
problem and the major risk factors. Dig Dis Sci. 36:962–972.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Takahashi H and Wands JR: Prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma: known to be poor: yet difficult to
predict. J Nucl Med. 32:235–236. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim JW, Lee JO, Han SW, et al: Clinical
outcomes of sorafenib treatment in patients with metastatic
hepatocellular carcinoma who had been previously treated with
fluoropyrimidine plus platinum-based chemotherapy. Am J Clin Oncol.
34:125–129. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Luo HY, Yang JY, Liu ZM, Lin QY and Yan
LN: Reversal of multidrug resistance gene MDR1 and MRP of
drug-resistant human hepatocellular carcinoma cells SMMC-7721/ADM
with antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 12:85–87. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Chang CS, Huang WT, Yang SS, Yeh HZ, Kao
CH and Chen GH: Effect of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance
associated protein gene expression on Tc-99m MIBI imaging in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nucl Med Biol. 30:111–117. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shen DW, Lu YG, Chin KV, Pastan I and
Gottesman MM: Human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines exhibit
multidrug resistance unrelated to MRD1 gene expression. J Cell Sci.
98:317–322. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dai R, Chen R and Li H: Cross-talk between
PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK pathways mediates endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced cell cycle progression and cell death in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Oncol. 34:1749–1757.
2009.
|
|
10
|
Chen GG, Chan UP, Bai LC, et al: ZBP-89
reduces the cell death threshold in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
by increasing caspase-6 and S phase cell cycle arrest. Cancer Lett.
283:52–58. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu SC and Zhang Y: Cyclin-dependent kinase
1 (CDK1)-mediated phosphorylation of enhancer of zeste 2 (Ezh2)
regulates its stability. J Biol Chem. 286:28511–28519. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hong KU, Kim HJ, Kim HS, et al:
Cdk1-cyclin B1-mediated phosphorylation of tumor-associated
microtubule-associated protein/cytoskeleton-associated protein 2 in
mitosis. J Biol Chem. 284:16501–16512. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang JS, Hour MJ, Huang WW, Lin KL, Kuo SC
and Chung JG: MJ-29 inhibits tubulin polymerization, induces
mitotic arrest, and triggers apoptosis via cyclin-dependent kinase
1-mediated Bcl-2 phosphorylation in human leukemia U937 cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:477–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rieder CL: Mitosis in vertebrates: the
G2/M and M/A transitions and their associated checkpoints.
Chromosome Res. 19:291–306. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dustin P: Mitosis and differentiation; new
thoughts on the biochemical regulation of growth in the
vertebrates. Arch Anat Histol Embryol. 34:195–201. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Choi KS: Autophagy and cancer. Exp Mol
Med. 44:109–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Naumann P, Fortunato F, Zentgraf H,
Buchler MW, Herr I and Werner J: Autophagy and cell death signaling
following dietary sulforaphane act independently of each other and
require oxidative stress in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol.
39:101–109. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Lee J, Giordano S and Zhang J: Autophagy,
mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signalling.
Biochem J. 441:523–540. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCormick J, Knight RA, Barry SP, et al:
Autophagy in the stress-induced myocardium. Front Biosci (Elite
Ed). 4:2131–2141. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Zhang Q, Tian R, et al: Lysosomal
transmembrane protein LAPTM4B promotes autophagy and tolerance to
metabolic stress in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 71:7481–7489. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kung HJ: Targeting tyrosine kinases and
autophagy in prostate cancer. Horm Cancer. 2:38–46. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bursch W, Karwan A, Mayer M, et al: Cell
death and autophagy: cytokines, drugs, and nutritional factors.
Toxicology. 254:147–157. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martinez-Borra J and Lopez-Larrea C:
Autophagy and self-defense. Adv Exp Med Biol. 738:169–184. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anders HJ and Schlondorff DO: Innate
immune receptors and autophagy: implications for autoimmune kidney
injury. Kidney Int. 78:29–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Munafo DB and Colombo MI: A novel assay to
study autophagy: regulation of autophagosome vacuole size by amino
acid deprivation. J Cell Sci. 114:3619–3629. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang ZJ, Chee CE, Huang S and Sinicrope
FA: The role of autophagy in cancer: therapeutic implications. Mol
Cancer Ther. 10:1533–1541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meschini S, Condello M, Lista P and
Arancia G: Autophagy: molecular mechanisms and their implications
for anticancer therapies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 11:357–379.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karantza-Wadsworth V and White E: Role of
autophagy in breast cancer. Autophagy. 3:610–613. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kelekar A: Autophagy. Ann NY Acad Sci.
1066:259–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tanida I, Ueno T and Kominami E: LC3
conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
36:2503–2518. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ropolo A, Bagnes CI, Molejon MI, et al:
Chemotherapy and autophagy-mediated cell death in pancreatic cancer
cells. Pancreatology. 12:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guo XL, Li D, Hu F, et al: Targeting
autophagy potentiates chemotherapy-induced apoptosis and
proliferation inhibition in hepatocarcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
320:171–179. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yousefi S and Simon HU: Autophagy in
cancer and chemotherapy. Results Probl Cell Differ. 49:183–190.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xie CM, Chan WY, Yu S, Zhao J and Cheng
CH: Bufalin induces autophagy-mediated cell death in human colon
cancer cells through reactive oxygen species generation and JNK
activation. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1365–1375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lan YH, Chiang JH, Huang WW, et al:
Activations of both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways in HCT 116
human colorectal cancer cells contribute to apoptosis through
p53-mediated ATM/Fas signaling by Emilia sonchifolia
extract, a folklore medicinal plant. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2012:1781782012.
|
|
36
|
Lu HF, Lai KC, Hsu SC, et al: Curcumin
induces apoptosis through FAS and FADD, in caspase-3-dependent and
-independent pathways in the N18 mouse-rat hybrid retina ganglion
cells. Oncol Rep. 22:97–104. 2009.
|
|
37
|
Lin HL, Yang JS, Yang JH, et al: The role
of Ca2+ on the DADS-induced apoptosis in mouse-rat
hybrid retina ganglion cells (N18). Neurochem Res. 31:383–393.
2006.
|
|
38
|
Chen HY, Lu HF, Yang JS, et al: The novel
quinolone CHM-1 induces DNA damage and inhibits DNA repair gene
expressions in a human osterogenic sarcoma cell line. Anticancer
Res. 30:4187–4192. 2010.
|
|
39
|
Chiu YJ, Hour MJ, Lu CC, et al: Novel
quinazoline HMJ-30 induces U-2 OS human osteogenic sarcoma cell
apoptosis through induction of oxidative stress and up-regulation
of ATM/p53 signaling pathway. J Orthop Res. 29:1448–1456. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Huang SM, Yang JS, Tsai SC, et al: The
novel synthesized
2-(3-(methylamino)phenyl)-6-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)quinolin-4-one (Smh-3)
compound induces G2/M phase arrest and
mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic cell death through inhibition of
CDK1 and AKT activity in HL-60 human leukemia cells. Int J Oncol.
38:1357–1364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chung JG, Yang JS, Huang LJ, et al:
Proteomic approach to studying the cytotoxicity of YC-1 on U937
leukemia cells and antileukemia activity in orthotopic model of
leukemia mice. Proteomics. 7:3305–3317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li YC, Lin HJ, Yang JH, et al:
Baicalein-induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress
through elevations of reactive oxygen species and mitochondria
dependent pathway in mouse-rat hybrid retina ganglion cells (N18).
Neurochem Res. 34:418–429. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yang JS, Chen GW, Hsia TC, et al: Diallyl
disulfide induces apoptosis in human colon cancer cell line (COLO
205) through the induction of reactive oxygen species, endoplasmic
reticulum stress, caspases casade and mitochondrial-dependent
pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 47:171–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Tseng MT, Lu X, Duan X, et al: Alteration
of hepatic structure and oxidative stress induced by intravenous
nanoceria. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 260:173–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Xiao D, Bommareddy A, Kim SH, Sehrawat A,
Hahm ER and Singh SV: Benzyl isothiocyanate causes FoxO1-mediated
autophagic death in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e325972012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Huang WW, Yang JS, Pai SJ, et al: Bufalin
induces G(0)/G(1) phase arrest through inhibiting the levels of
cyclin D, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4, and triggers apoptosis via
mitochondrial signaling pathway in T24 human bladder cancer cells.
Mutat Res. 732:26–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ip SW, Chu YL, Yu CS, et al: Bee venom
induces apoptosis through intracellular Ca2+-modulated
intrinsic death pathway in human bladder cancer cells. Int J Urol.
19:61–70. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chiou SK, Hoa N and Hodges A: Sulindac
sulfide induces autophagic death in gastric epithelial cells via
survivin down-regulation: a mechanism of NSAIDs-induced gastric
injury. Biochem Pharmacol. 81:1317–1323. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Enomoto A, Murakami H, Asai N, et al:
Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility via
Girdin/APE. Dev Cell. 9:389–402. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, et al: LC3,
a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Seglen PO and Gordon PB: 3-Methyladenine:
specific inhibitor of autophagic/lysosomal protein degradation in
isolated rat hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:1889–1892.
1982. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T,
Moriyama Y, Masaki R and Tashiro Y: Bafilomycin A1 prevents
maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between
autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E
cells. Cell Struct Funct. 23:33–42. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lee MJ, Chen HM, Tzang BS, et al: Ocimum
gratissimum aqueous extract protects H9c2 myocardiac cells from
H(2) O(2)-induced cell apoptosis through akt signalling. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2011:5780602011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Robbins D, Gu X, Shi R, et al: The
chemopreventive effects of Protandim: modulation of p53
mitochondrial translocation and apoptosis during skin
carcinogenesis. PLoS One. 5:e119022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Meng Z, Yang P, Shen Y, et al: Pilot study
of huachansu in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma,
nonsmall-cell lung cancer, or pancreatic cancer. Cancer.
115:5309–5318. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Han KQ, Huang G, Gu W, Su YH, Huang XQ and
Ling CQ: Anti-tumor activities and apoptosis-regulated mechanisms
of bufalin on the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of human
hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3374–3379. 2007.
|
|
57
|
Ondrouskova E, Soucek K, Horvath V and
Smarda J: Alternative pathways of programmed cell death are
activated in cells with defective caspase-dependent apoptosis. Leuk
Res. 32:599–609. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Takai N, Ueda T, Nishida M, Nasu K and
Narahara H: Bufalin induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Mol Med. 21:637–643. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hong SH and Choi YH: Bufalin induces
apoptosis through activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic
pathways in human bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:114–120.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jing Y, Watabe M, Hashimoto S, Nakajo S
and Nakaya K: Cell cycle arrest and protein kinase modulating
effect of bufalin on human leukemia ML1 cells. Anticancer Res.
14:1193–1198. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Yin JQ, Shen JN, Su WW, et al: Bufalin
induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma U-2OS and U-2OS
methotrexate300-resistant cell lines. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
28:712–720. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Codogno P: Autophagy in cell survival and
death. J Soc Biol. 199:233–241. 2005.(In French).
|
|
63
|
Hoyer-Hansen M and Jaattela M: Autophagy:
an emerging target for cancer therapy. Autophagy. 4:574–580. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Eum KH and Lee M: Crosstalk between
autophagy and apoptosis in the regulation of paclitaxel-induced
cell death in v-Ha-ras-transformed fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem.
348:61–68. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kanzawa T, Kondo Y, Ito H, Kondo S and
Germano I: Induction of autophagic cell death in malignant glioma
cells by arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 63:2103–2108.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM,
Kondo Y and Kondo S: Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death
in malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell
death protein BNIP3. Oncogene. 24:980–991. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bareford MD, Park MA, Yacoub A, et al:
Sorafenib enhances pemetrexed cytotoxicity through an
autophagy-dependent mechanism in cancer cells. Cancer Res.
71:4955–4967. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ullen A, Farnebo M, Thyrell L, et al:
Sorafenib induces apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer cells
in vitro. Int J Oncol. 37:15–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Huang SW, Liu KT, Chang CC, et al:
Imiquimod simultaneously induces autophagy and apoptosis in human
basal cell carcinoma cells. Br J Dermatol. 163:310–320. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen A, Yu J, Zhang L, et al: Microarray
and biochemical analysis of bufalin-induced apoptosis of HL-60
Cells. Biotechnol Lett. 31:487–494. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, Jea Chien E and Wang
PS: Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated
androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 99:2467–2476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, et al: PI3K/Akt is
involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 20:59–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hoyer-Hansen M and Jaattela M:
AMP-activated protein kinase: a universal regulator of autophagy?
Autophagy. 3:381–383. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Shi WY, Xiao D, Wang L, et al: Therapeutic
metformin/AMPK activation blocked lymphoma cell growth via
inhibition of mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy. Cell Death
Dis. 3:e2752012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Corcelle E, Djerbi N, Mari M, et al:
Control of the autophagy maturation step by the MAPK ERK and p38:
lessons from environmental carcinogens. Autophagy. 3:57–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Levine B, Sinha S and Kroemer G: Bcl-2
family members: dual regulators of apoptosis and autophagy.
Autophagy. 4:600–606. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Inbal B, Bialik S, Sabanay I, Shani G and
Kimchi A: DAP kinase and DRP-1 mediate membrane blebbing and the
formation of autophagic vesicles during programmed cell death. J
Cell Biol. 157:455–468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liu L-X, Liu Z-H, Jiang H-C, et al:
Overexpression of Akt-1 gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Chinese J Cancer Res. 14:161–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|