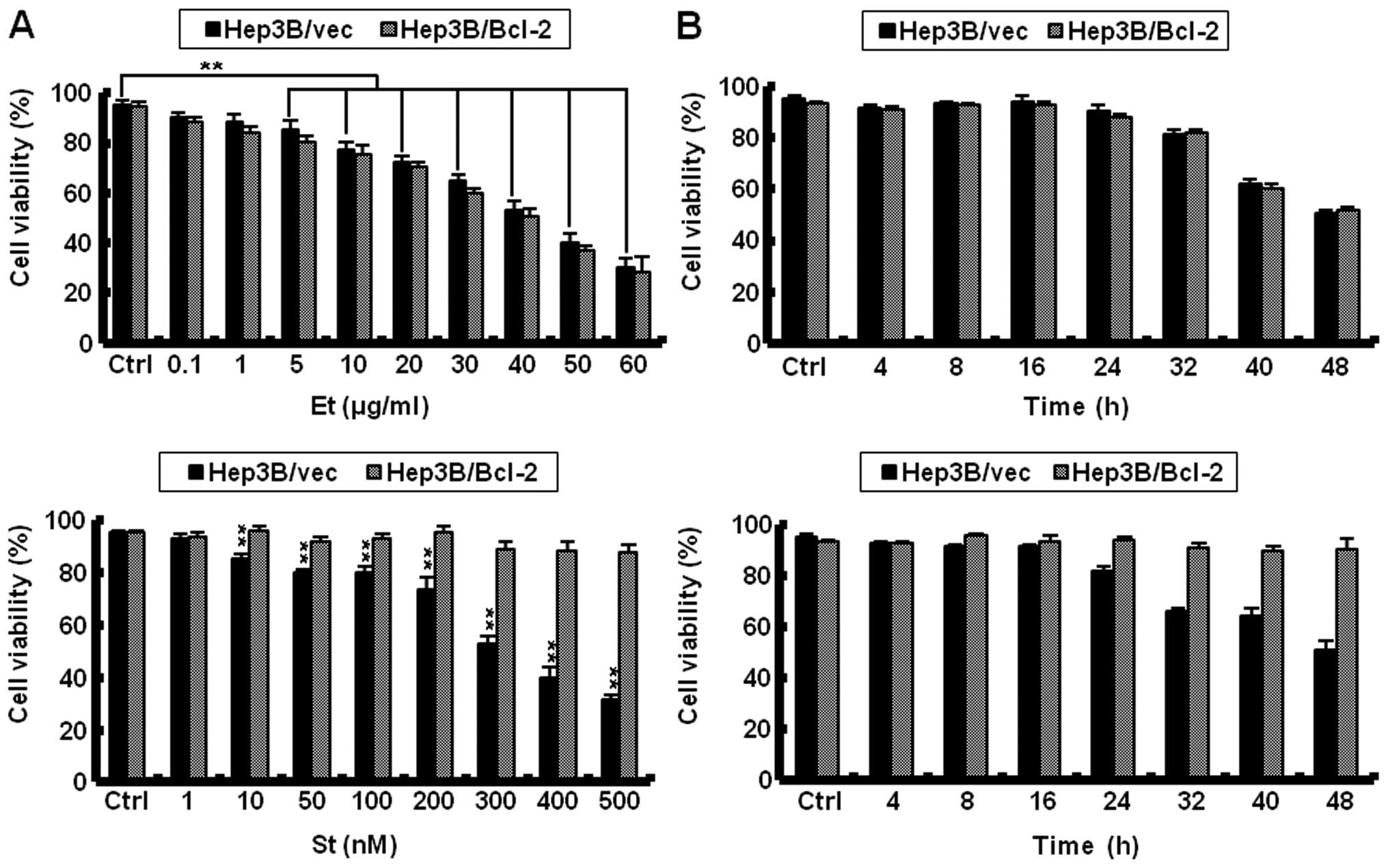
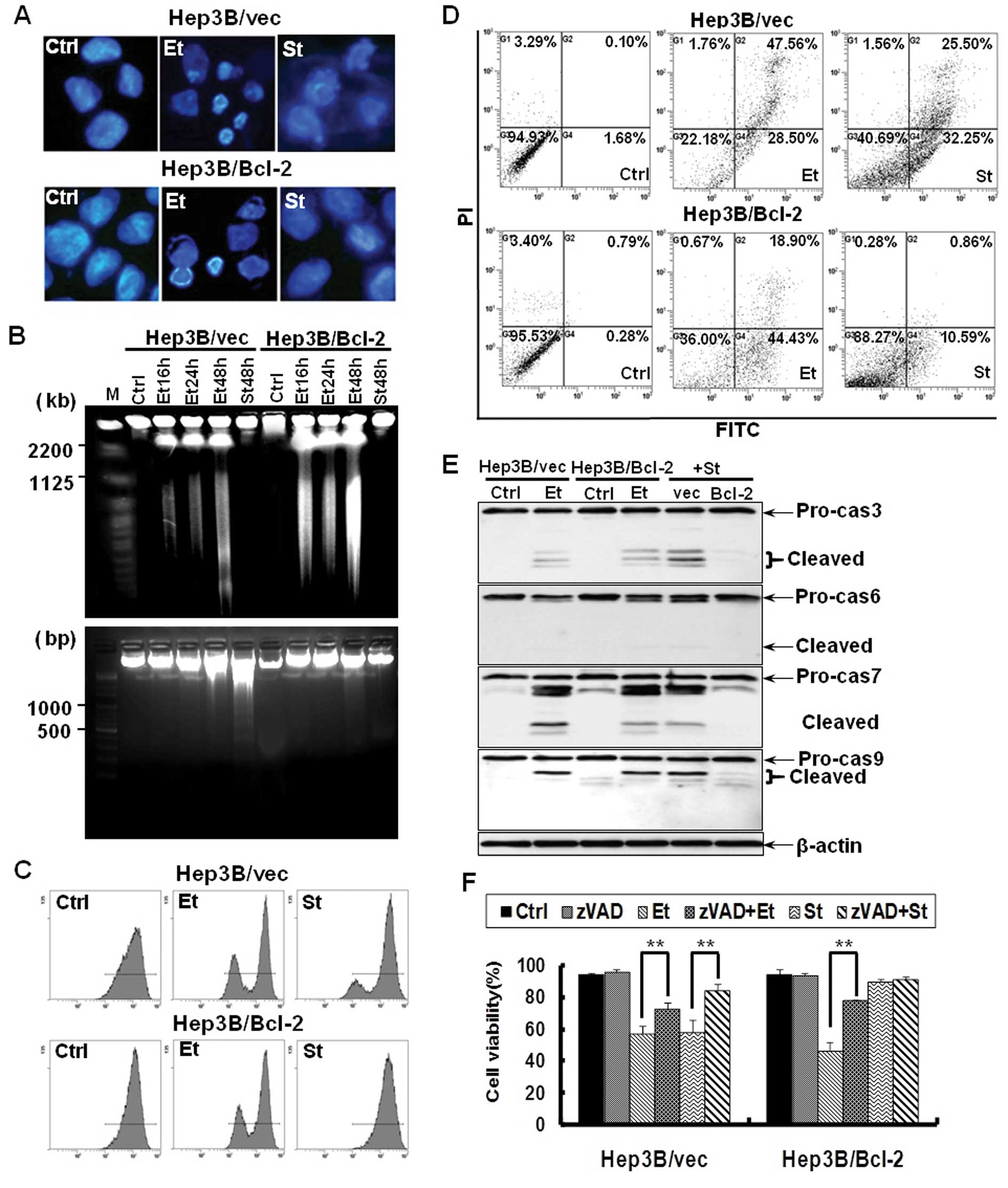
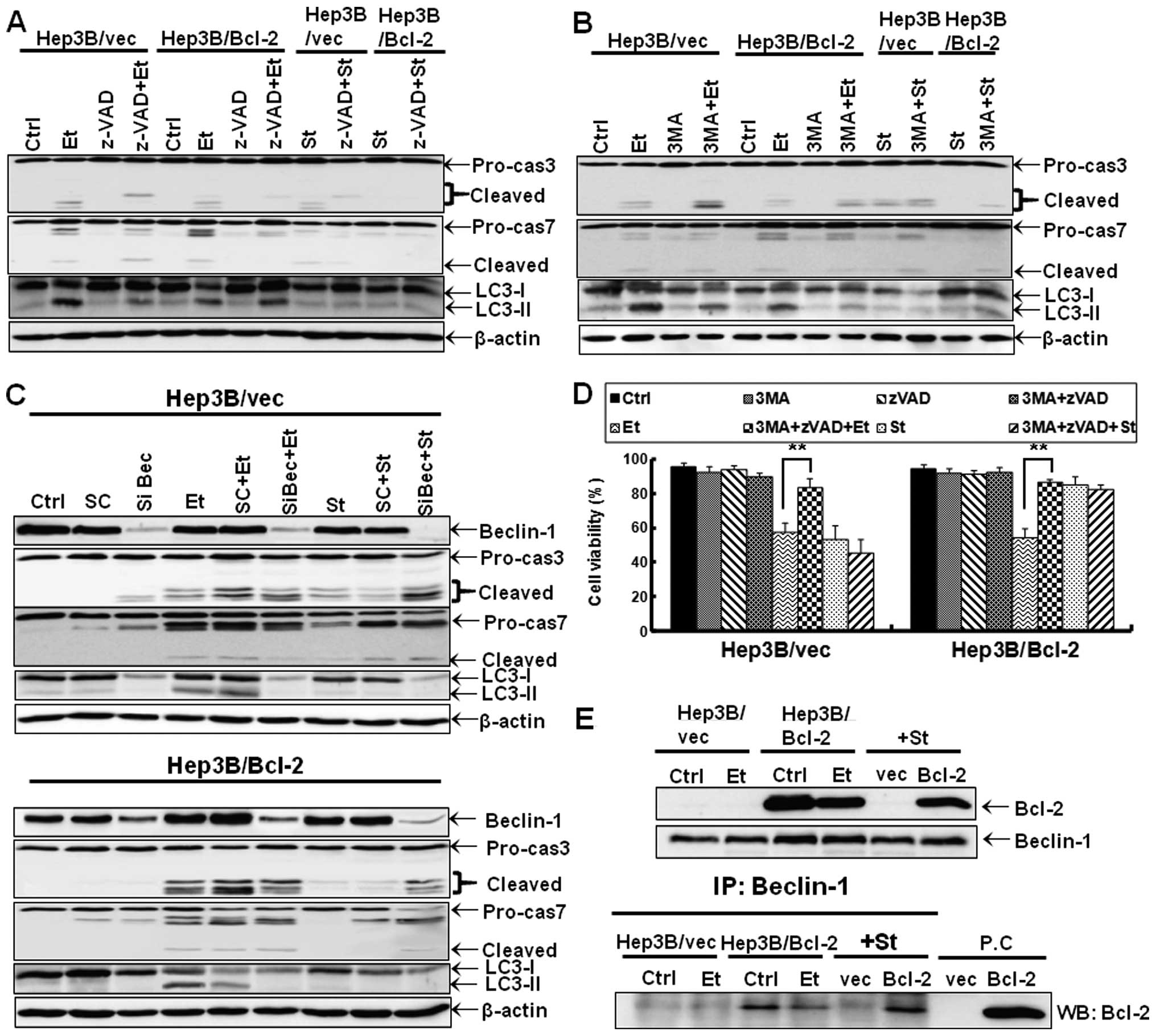
|
1
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Vandenabeele P,
Abrams J, Alnemri ES, Baehrecke EH, Blagosklonny MV, El-Deiry WS,
Golstein P, Green DR, Hengartner M, Knight RA, Kumar S, Lipton SA,
Malorni W, Nunez G, Peter ME, Tschopp J, Yuan J, Piacentini M,
Zhivotovsky B and Melino G: Classification of cell death:
recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death. Cell
Death Differ. 16:3–11. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murphy KM, Streips UN and Lock RB: Bcl-2
inhibits a Fas-induced conformational change in the Bax N terminus
and Bax mitochondrial translocation. J Biol Chem. 27:17225–17228.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Foyouzi-Youssefi R, Arnaudeau S, Borner C,
Kelley WL, Tschopp J, Lew DP, Demaurex N and Krause KH: Bcl-2
decreases the free Ca2+ concentration within the
endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:5723–5728. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saeki K, You A, Okuma E, Yazaki Y, Susin
SA, Demaurex N and Krause KH: Bcl-2 down-regulation causes
autophagy in a caspase-independent manner in human leukemic HL60
cells. Cell Death Differ. 7:1263–1269. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin-1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang XH, Kleeman LK, Jiang HH, Gordon G,
Goldman JE, Berry G, Herman B and Levine B: Protection against
fatal Sindbis virus encephalitis by Beclin, a novel
Bcl-2-interacting protein. J Virol. 72:8586–8596. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Reed JC, Miyashita T, Takayama S, Wang HG,
Sato T, Krajewski S, Aime-Sempe C, Bodrug S, Kitada S and Hanada M:
BCL-2 family proteins: regulators of cell death involved in the
pathogenesis of cancer and resistance to therapy. J Cell Biochem.
60:23–32. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Letai AG: Diagnosing and exploiting
cancer’s addiction to blocks in apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer.
8:121–132. 2008.
|
|
11
|
Real PJ, Cao Y, Wang R, Nikolovska-Coleska
Z, Sanz-Ortiz J, Wang S and Fernandez-Luna JL: Breast cancer cells
can evade apoptosis-mediated selective killing by a novel small
molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2. Cancer Res. 64:7947–7953. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Ay and Liu LF: DNA topoisomerases:
Essential enzymes and lethal targets. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.
3:191–218. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dubrez L, Goldwasser F, Genne P, Pommier Y
and Solary E: The role of cell cycle regulation and apoptosis
triggering in determining the sensitivity of leukemic cells to
topoisomerase I and II inhibitors. Leukemia. 9:1013–1024.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cohn AL, Myers JW, Mamus S, Deur C, Nicol
S, Hood K, Khan MM, Ilegbodu D and Asmar L: A phase II study of
pemetrexed in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Invest New Drugs. 26:381–386. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lee JO, Lee KW, Oh DY, Kim JH, Im SA, Kim
TY and Bang YJ: Combination chemotherapy with capecitabine and
cisplatin for patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma.
Ann Oncol. 20:1402–1407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan JN, Chao Y, Lee WP, Li CP, Lee RC,
Chang FY, Yen SH, Lee SD and Whang-Peng J: Chemotherapy with
etoposide, doxorubicin, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and leucovorin
for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol.
25:201–206. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA and Lowe SW:
Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell.
108:153–164. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gewirtz DA: A critical evaluation of the
mechanisms of action proposed for the antitumor effects of the
anthracycline antibiotics Adriamycin and daunorubicin. Biochem
Pharmacol. 57:727–741. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jordan MA and Wilson L: Microtubules as a
target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:253–265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ravikumar B, Berger Z, Vacher C, O’Kane CJ
and Rubinsztein DC: Rapamycin pre-treatment protects against
apoptosis. Hum Mol Genet. 15:1209–1216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Colell A, Ricci JE, Tait S, Milasta S,
Maurer U, Bouchier-Hayes L, Fitzgerald P, Guio-Carrion A,
Waterhouse NJ, Li CW, Mari B, Barbry P, Newmeyer DD, Beere HM and
Green DR: GAPDH and autophagy preserve survival after apoptotic
cytochrome c release in the absence of caspase activation. Cell.
129:983–997. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tsujimoto Y and Shimizu S: Another way to
die: autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ. 12(Suppl
2): 1528–1534. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gozuacik D and Kimchi A: Autophagy as a
cell death and tumor suppressor mechanism. Oncogene. 23:2891–2906.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shimizu S, Kanaseki T, Mizushima N, Mizuta
T, Arakawa-Kobayashi S, Thompson CB and Tsujimoto Y: Role of Bcl-2
family proteins in a non-apoptotic programmed cell death dependent
on autophagy genes. Nat Cell Biol. 6:1221–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee SW, Song YS, Lee SY, Yoon YG, Lee SH,
Park BS, Yun I, Choi H, Kim K, Chung WT and Yoo YH: Downregulation
of protein kinase CK2 activity facilitates tumor necrosis
factor-α-mediated chondrocyte death through apoptosis and
autophagy. PLoS One. 6:e191632011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hande KR: Etoposide: Four decades of
development of a topoisomeraseII inhibitor. Eur J Cancer.
34:1514–1521. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pommier Y, Pourquier P, Fan Y and
Strumberg D: Mechanism of action of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I
and drugs targeted to the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1400:83–105. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Debatin KM, Poncet D and Kroemer G:
Chemotherapy: targeting the mitochondrial cell death pathway.
Oncogene. 21:8786–8803. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park JW, Choi YJ, Suh SI, Baek WK, Suh MH,
Jin IN, Min DS, Woo JH, Chang JS, Passaniti A, Lee YH and Kwon TK:
Bcl-2 overexpression attenuates resveratrol-induced apoptosis in
U937 cells by inhibition of caspase-3 activity. Carcinogenesis.
22:1633–1639. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee JS, Jeong SH, Soung YH, Kim TH, Choi
HJ, Park BS, Kwon TK and Yoo YH: SAHA treatment overcomes the
anti-apoptotic effects of Bcl-2 and is associated with the
formation of mature PML nuclear bodies in human leukemic U937
cells. Chem Biol Interact. 18:61–70. 2009.
|
|
33
|
Han W, Li S, Qiu S, Lu Q, Pan Q, Gu Y, Luo
J and Hu X: Shikonin circumvents cancer drug resistance by
induction of a necroptotic death. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:641–649.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stendel R, Biefer HR, Dékány GM, Kubota H,
Münz C, Wang S, Mohler H, Yonekawa Y and Frei K: The antibacterial
substance taurolidine exhibits anti-neoplastic action based on a
mixed type of programmed cell death. Autophagy. 5:194–210. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tomic T, Botton T, Cerezo M, Robert G,
Luciano F, Puissant A, Gounon P, Allegra M, Bertolotto C, Bereder
JM, Tartare-Deckert S, Bahadoran P, Auberger P, Ballotti R and
Rocchi S: Metformin inhibits melanoma development through autophagy
and apoptosis mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2:e1992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Koff A, Giordano A, Desai D, Yamashita K,
Harper JW, Elledge S, Nishimoto T, Morgan DO, Franza BR and Roberts
JM: Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the
G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 257:1689–1694. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Elledge SJ and Harper JW: Cdk inhibitors:
on the threshold of checkpoints and development. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 6:847–852. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sidle A, Palaty C, Dirks P, Wiggan O,
Kiess M, Gill RM, Wong AK and Hamel PA: Activity of the
retinoblastoma family proteins, pRB, p107, and p130, during
cellular proliferation and differentiation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol
Biol. 31:237–271. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sandal T: Molecular aspects of the
mammalian cell cycle and cancer. Oncologist. 7:73–81. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Knudsen KE, Booth D, Naderi S,
Sever-Chroneos Z, Fribourg AF, Hunton IC, Feramisco JR, Wang JY and
Knudsen ES: RB-dependent S-phase response to DNA damage. Mol Cell
Biol. 20:7751–776. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li M, Jiang X, Liu D, Na Y, Gao GF and Xi
Z: Autophagy protects LNCaP cells under androgen deprivation
conditions. Autophagy. 4:54–60. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou F, Yang Y and Xing D: Bcl-2 and
Bcl-xL play important roles in the crosstalk between autophagy and
apoptosis. FEBS J. 278:403–413. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ciechomska IA, Goemans GC, Skepper JN and
Tolkovsky AM: Bcl-2 complexed with beclin-1 maintains full
anti-apoptotic function. Oncogene. 28:2128–214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|