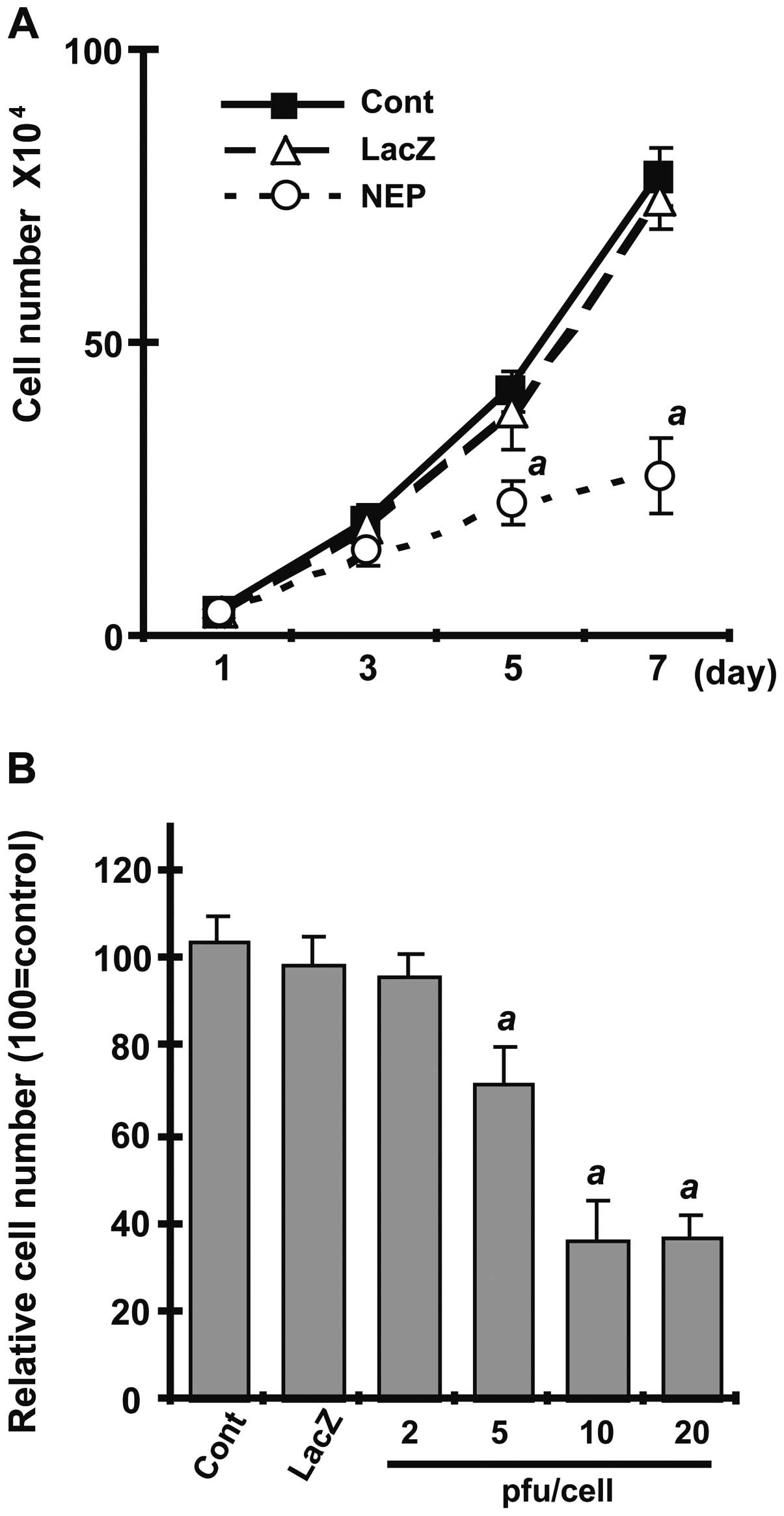
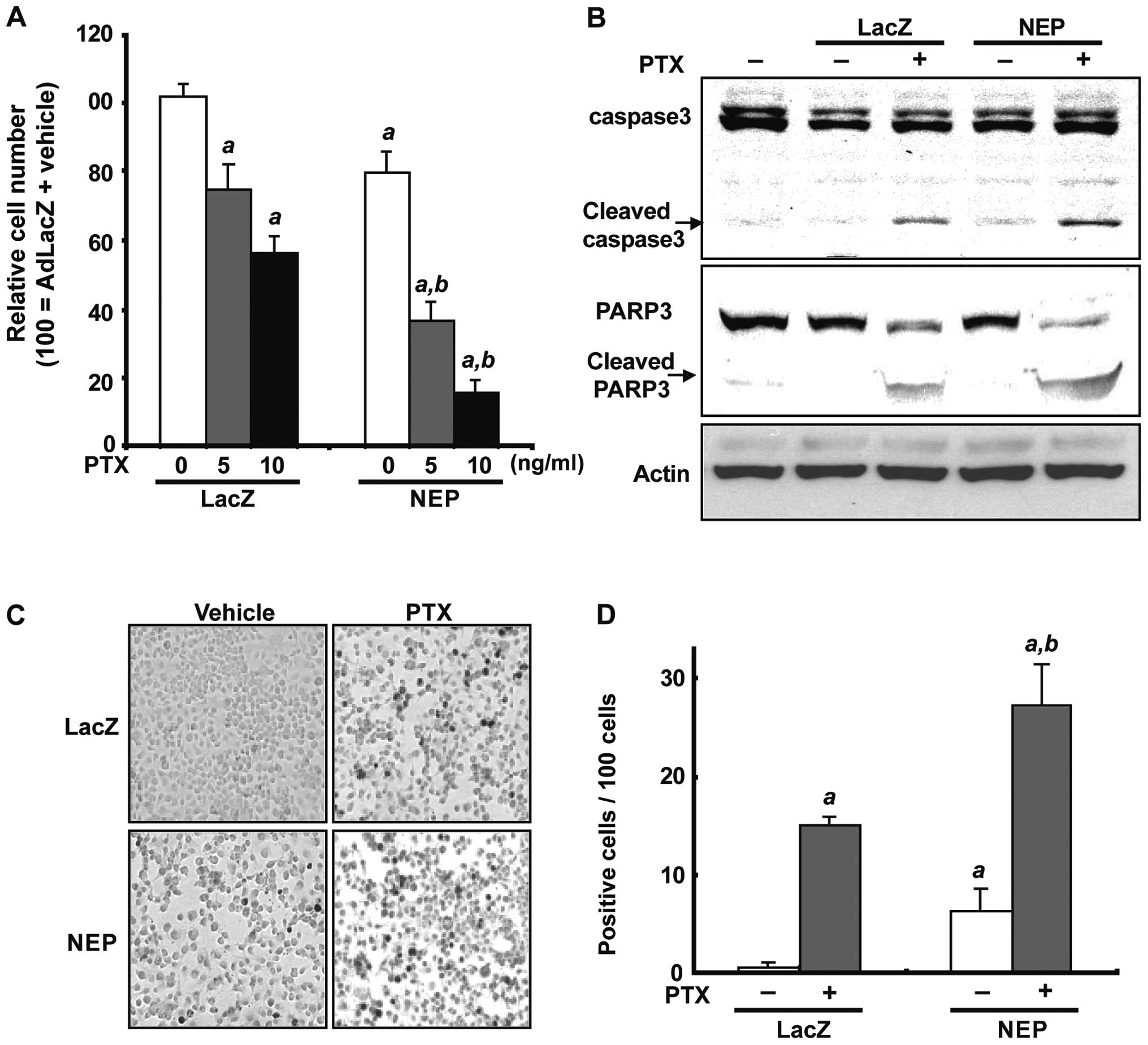
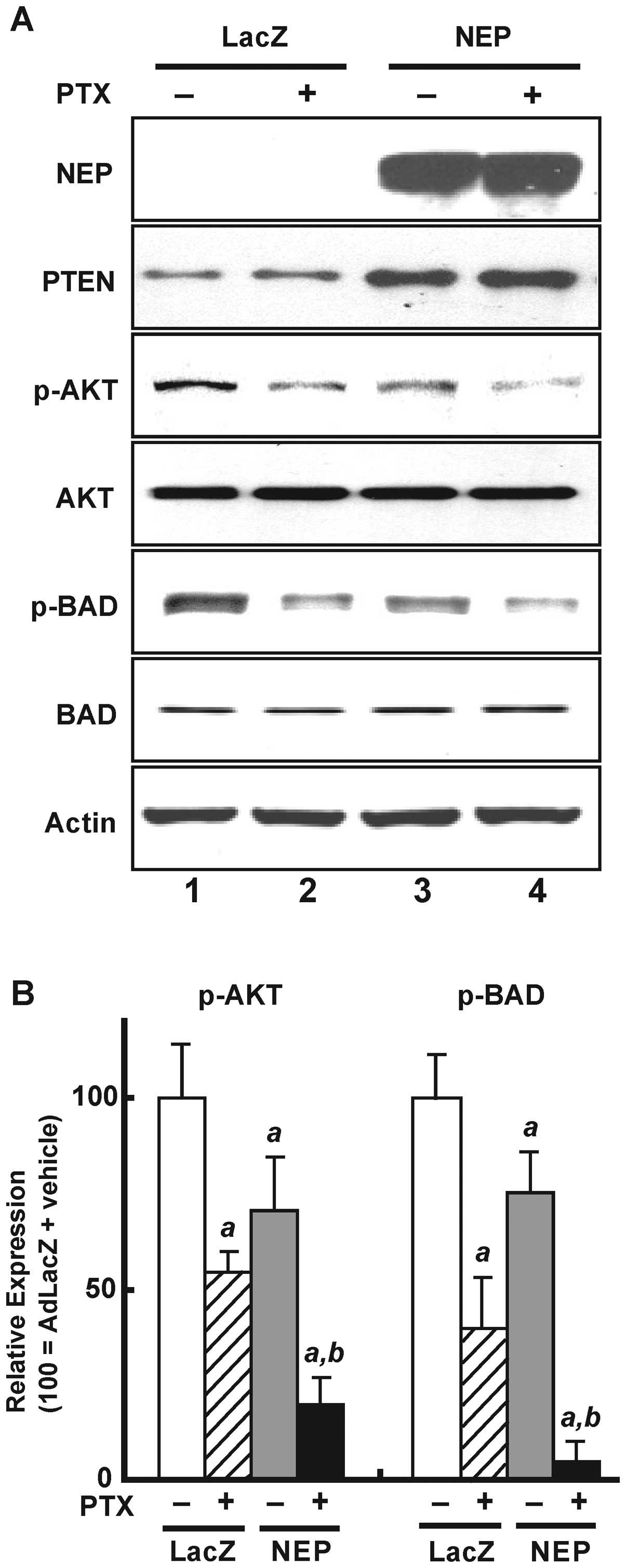
|
1
|
Turner AJ: Exploring the structure and
function of zinc metallopeptidases: old enzymes and new
discoveries. Biochem Soc Trans. 31:723–727. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Maguer-Satta V, Besancon R and
Bachelard-Cascales E: Concise review: neutral endopeptidase (CD10):
a multifaceted environment actor in stem cells, physiological
mechanisms, and cancer. Stem Cells. 29:389–396. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Papandreou CN, Usmani B, Geng YP,
Bogenrieder T, Freeman RH, Wilk S, Finstad CL, Reuter VE, Powell
CT, Scheinberg D, Magill C, Scher HI, Albino AP and Nanus DM:
Neutral endopeptidase 24.11 loss in metastatic human prostate
cancer contributes to androgen-independent progression. Nat Med.
4:50–57. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Freedland SJ, Seligson DB, Liu AY, Pantuck
AJ, Paik SH, Horvath S, Wieder JA, Zisman A, Nguyen D, Tso CL,
Palotie AV and Belldegrun AS: Loss of CD10 (neutral endopeptidase)
is a frequent and early event in human prostate cancer. Prostate.
55:71–80. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Osman I, Yee H, Taneja SS, Levinson B,
Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Chang C, Nobert C and Nanus DM: Neutral
endopeptidase protein expression and prognosis in localized
prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4096–4100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Usmani BA, Shen R, Janeczko M, Papandreou
CN, Lee WH, Nelson WG, Nelson JB and Nanus DM: Methylation of the
neutral endopeptidase gene promoter in human prostate cancers. Clin
Cancer Res. 6:1664–1670. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sumitomo M, Shen R, Walburg M, Dai J, Geng
Y, Navarro D, Boileau G, Papandreou CN, Giancotti FG, Knudsen B and
Nanus DM: Neutral endopeptidase inhibits prostate cancer cell
migration by blocking focal adhesion kinase signaling. J Clin
Invest. 106:1399–1407. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dai J, Shen R, Sumitomo M, Goldberg JS,
Geng Y, Navarro D, Xu S, Koutcher JA, Garzotto M, Powell CT and
Nanus DM: Tumor suppressive effects of neutral endopeptidase in
androgen-independent prostate cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res.
7:1370–1377. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sumitomo M, Iwase A, Zheng R, Navarro D,
Kaminetzky D, Shen R, Georgescu MM and Nanus DM: Synergy in tumor
suppression by direct interaction of neutral endopeptidase with
PTEN. Cancer Cell. 5:67–78. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwase A, Shen R, Navarro D and Nanus DM:
Direct binding of neutral endopeptidase 24.11 to
ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) proteins competes with the interaction
of CD44 with ERM proteins. J Biol Chem. 279:11898–11905. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Osman I, Dai J, Mikhail M, Navarro D,
Taneja SS, Lee P, Christos P, Shen R and Nanus DM: Loss of neutral
endopeptidase and activation of protein kinase B (Akt) is
associated with prostate cancer progression. Cancer. 107:2628–2636.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sumitomo M, Asano T, Asakuma J, Asano T,
Nanus DM and Hayakawa M: Chemosensitization of androgen-independent
prostate cancer with neutral endopeptidase. Clin Cancer Res.
10:260–266. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mancuso A, Oudard S and Sternberg CN:
Effective chemotherapy for hormone-refractory prostate cancer
(HRPC): present status and perspectives with taxane-based
treatments. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 61:176–185. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Orr GA, Verdier-Pinard P, McDaid H and
Horwitz SB: Mechanisms of Taxol resistance related to microtubules.
Oncogene. 22:7280–7295. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim SH, Juhnn YS and Song YS: Akt
involvement in paclitaxel chemoresistance of human ovarian cancer
cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1095:82–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weng D, Song X, Xing H, Ma X, Xia X, Weng
Y, Zhou J, Xu G, Meng L, Zhu T, Wang S and Ma D: Implication of the
Akt2/survivin pathway as a critical target in paclitaxel treatment
in human ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 273:257–265. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang H, Yu D, Agrawal S and Zhang R:
Experimental therapy of human prostate cancer by inhibiting MDM2
expression with novel mixed-backbone antisense oligonucleotides: in
vitro and in vivo activities and mechanisms. Prostate. 54:194–205.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Horiguchi A, Zheng R, Goodman OB Jr, Shen
R, Guan H, Hersh LB and Nanus DM: Lentiviral vector neutral
endopeptidase gene transfer suppresses prostate cancer tumor
growth. Cancer Gene Ther. 14:583–589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades N and Koutsilieris
M: The Akt pathway: molecular targets for anti-cancer drug
development. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:235–256. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Horiguchi A, Chen DY, Goodman OB Jr, Zheng
R, Shen R, Guan H, Hersh LB and Nanus DM: Neutral endopeptidase
inhibits prostate cancer tumorigenesis by reducing FGF-2-mediated
angiogenesis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 11:79–87. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Souza PL, Russell PJ and Kearsley J:
Role of the Akt pathway in prostate cancer. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 9:163–175. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Siepmann M, Kumar S, Mayer G and Walter J:
Casein kinase 2 dependent phosphorylation of neprilysin regulates
receptor tyrosine kinase signaling to Akt. PLoS One. 5:e131342010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sumitomo M, Asano T, Asakuma J, Asano T,
Horiguchi A and Hayakawa M: ZD1839 modulates paclitaxel response in
renal cancer by blocking paclitaxel-induced activation of the
epidermal growth factor receptor-extracellular signal-regulated
kinase pathway. Clin Cancer Res. 10:794–801. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Priulla M, Calastretti A, Bruno P,
Azzariti A, Paradiso A, Canti G and Nicolin A: Preferential
chemosensitization of PTEN-mutated prostate cells by silencing the
Akt kinase. Prostate. 67:782–789. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
McGrogan BT, Gilmartin B, Carney DN and
McCann A: Taxanes, microtubules and chemoresistant breast cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1785:96–132. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Naghavi MH, Valente S, Hatziioannou T, de
Los SK, Wen Y, Mott C, Gundersen GG and Goff SP: Moesin regulates
stable microtubule formation and limits retroviral infection in
cultured cells. EMBO J. 26:41–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haedicke J, de Los SK, Goff SP and Naghavi
MH: The Ezrinradixin-moesin family member ezrin regulates stable
microtubule formation and retroviral infection. J Virol.
82:4665–4670. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Niv MY, Iida K, Zheng R, Horiguchi A, Shen
R and Nanus DM: Rational redesign of neutral endopeptidase binding
to merlin and moesin proteins. Protein Sci. 18:1042–1050. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Terawaki S, Kitano K and Hakoshima T:
Structural basis for type II membrane protein binding by ERM
proteins revealed by the radixin-neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (NEP)
complex. J Biol Chem. 282:19854–19862. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reyland ME, Anderson SM, Matassa AA,
Barzen KA and Quissell DO: Protein kinase C delta is essential for
etoposide-induced apoptosis in salivary gland acinar cells. J Biol
Chem. 274:19115–19123. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matassa AA, Carpenter L, Biden TJ,
Humphries MJ and Reyland ME: PKCdelta is required for
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in salivary epithelial cells. J
Biol Chem. 276:29719–29728. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sumitomo M, Ohba M, Asakuma J, Asano T,
Kuroki T, Asano T and Hayakawa M: Protein kinase Cdelta amplifies
ceramide formation via mitochondrial signaling in prostate cancer
cells. J Clin Invest. 109:827–836. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Majumder PK, Pandey P, Sun X, Cheng K,
Datta R, Saxena S, Kharbanda S and Kufe D: Mitochondrial
translocation of protein kinase C delta in phorbol ester-induced
cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 275:21793–21796.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sumitomo M, Shen R, Goldberg JS, Dai J,
Navarro D and Nanus DM: Neutral endopeptidase promotes phorbol
ester-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells by inhibiting
neuropeptide-induced protein kinase C delta degradation. Cancer
Res. 60:6590–6596. 2000.
|
|
35
|
Freytag SO, Stricker H, Peabody J, Pegg J,
Paielli D, Movsas B, Barton KN, Brown SL, Lu M and Kim JH:
Five-year follow-up of trial of replication-competent
adenovirus-mediated suicide gene therapy for treatment of prostate
cancer. Mol Ther. 15:636–642. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Patel P, Young JG, Mautner V, Ashdown D,
Bonney S, Pineda RG, Collins SI, Searle PF, Hull D, Peers E,
Chester J, Wallace DM, Doherty A, Leung H, Young LS and James ND: A
phase I/II clinical trial in localized prostate cancer of an
adenovirus expressing nitroreductase with CB1984. Mol Ther.
17:1292–1299. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hong Y, Beckett C, Belyaev ND and Turner
AJ: The impact of amyloid precursor protein signalling and histone
deacetylase inhibition on neprilysin expression in human prostate
cells. Int J Cancer. 130:775–786. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|