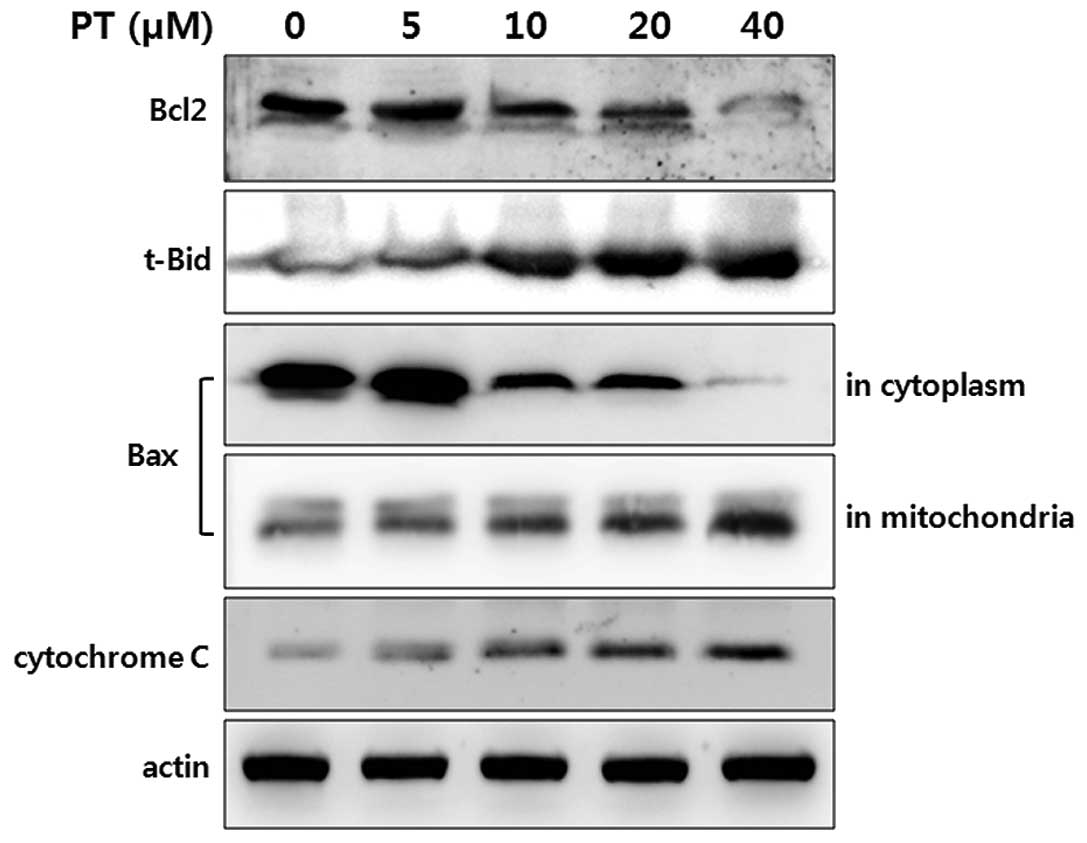
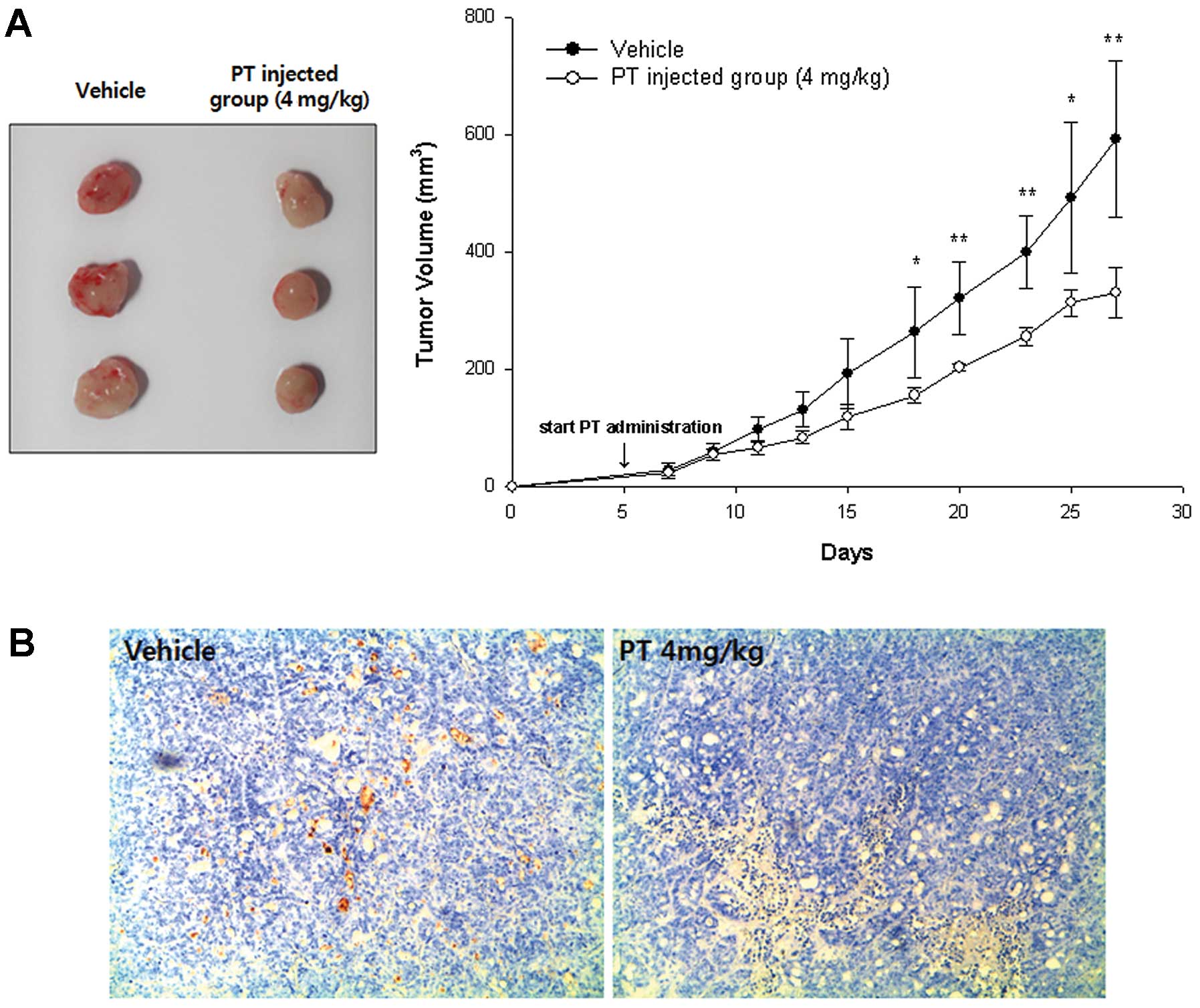
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Meyerhardt JA and Mayer RJ: Systemic
therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:476–487. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tebbutt NC, Cattell E, Midgley R,
Cunningham D and Kerr D: Systemic treatment of colorectal cancer.
Eur J Cancer. 38:1000–1015. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gusella M, Frigo AC, Bolzonella C, et al:
Predictors of survival and toxicity in patients on adjuvant therapy
with 5-fluorouracil for colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer.
100:1549–1557. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Raymond E, Faivre S, Chaney S, Woynarowski
J and Cvitkovic E: Cellular and molecular pharmacology of
oxaliplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 1:227–235. 2002.
|
|
6
|
Knight DW: Feverfew: chemistry and
biological activity. Nat Prod Rep. 12:271–276. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Murphy JJ, Heptinstall S and Mitchell JR:
Randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial of feverfew in
migraine prevention. Lancet. 2:189–192. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hehner SP, Heinrich M, Bork PM, et al:
Sesquiterpene lactones specifically inhibit activation of NF-kappa
B by preventing the degradation of I kappa B-alpha and I kappa
B-beta. J Biol Chem. 273:1288–1297. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lyss G, Knorre A, Schmidt TJ, Pahl HL and
Merfort I: The anti-inflammatory sesquiterpene lactone helenalin
inhibits the transcription factor NF-kappaB by directly targeting
p65. J Biol Chem. 273:33508–33516. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang S, Ong CN and Shen HM: Critical
roles of intracellular thiols and calcium in parthenolide-induced
apoptosis in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
208:143–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wen J, You KR, Lee SY, Song CH and Kim DG:
Oxidative stress-mediated apoptosis. The anticancer effect of the
sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide J Biol Chem. 277:38954–38964.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pajak B, Gajkowska B and Orzechowski A:
Molecular basis of parthenolide-dependent proapoptotic activity in
cancer cells. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 46:129–135. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mathema VB, Koh YS, Thakuri BC and
Sillanpaa M: Parthenolide, a sesquiterpene lactone, expresses
multiple anti-cancer and anti-inflammatory activities.
Inflammation. 35:560–565. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao LJ, Xu YH and Li Y: Effect of
parthenolide on proliferation and apoptosis in gastric cancer cell
line SGC7901. J Dig Dis. 10:172–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang S, Ong CN and Shen HM: Involvement
of proapoptotic Bcl-2 family members in parthenolide-induced
mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 211:175–188.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen YC, Shen SC, Lee WR, et al: Emodin
induces apoptosis in human promyeloleukemic HL-60 cells accompanied
by activation of caspase 3 cascade but independent of reactive
oxygen species production. Biochem Pharmacol. 64:1713–1724. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Grutter MG: Caspases: key players in
programmed cell death. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 10:649–655. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang JC and Cortopassi GA: Induction of
the mitochondrial permeability transition causes release of the
apoptogenic factor cytochrome c. Free Radic Biol Med. 24:624–631.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tacchini L, De Ponti C, Matteucci E,
Follis R and Desiderio MA: Hepatocyte growth factor-activated
NF-kappaB regulates HIF-1 activity and ODC expression, implicated
in survival, differently in different carcinoma cell lines.
Carcinogenesis. 25:2089–2100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dai Y, Guzman ML, Chen S, et al: The NF
(nuclear factor)-kappaB inhibitor parthenolide interacts with
histone deacetylase inhibitors to induce MKK7/JNK1-dependent
apoptosis in human acute myeloid leukaemia cells. Br J Haematol.
151:70–83. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Nakshatri H, Rice SE and Bhat-Nakshatri P:
Antitumor agent parthenolide reverses resistance of breast cancer
cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
through sustained activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase. Oncogene.
23:7330–7344. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Carlisi D, D’Anneo A, Angileri L, et al:
Parthenolide sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to TRAIL by
inducing the expression of death receptors through inhibition of
STAT3 activation. J Cell Physiol. 226:1632–1641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen KF, Tai WT, Liu TH, et al: Sorafenib
overcomes TRAIL resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through the inhibition of STAT3. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5189–5199.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu C, Chen F, Rushing JW, et al:
Antiproliferative activities of parthenolide and golden feverfew
extract against three human cancer cell lines. J Med Food. 9:55–61.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fernandes-Alnemri T, Litwack G and Alnemri
ES: CPP32, a novel human apoptotic protein with homology to
Caenorhabditis elegans cell death protein Ced-3 and
mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. J Biol Chem.
269:30761–30764. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mehmet H: Caspases find a new place to
hide. Nature. 403:29–30. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang E and Korsmeyer SJ: Molecular
thanatopsis: a discourse on the BCL2 family and cell death. Blood.
88:386–401. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Green DR and Reed JC: Mitochondria and
apoptosis. Science. 281:1309–1312. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Reed JC: Double identity for proteins of
the Bcl-2 family. Nature. 387:773–776. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Terrones O, Antonsson B, Yamaguchi H, et
al: Lipidic pore formation by the concerted action of proapoptotic
BAX and tBID. J Biol Chem. 279:30081–30091. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Van Mau N, Kajava AV, Bonfils C, Martinou
JC and Harricane MC: Interactions of Bax and tBid with lipid
monolayers. J Membr Biol. 207:1–9. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Coutts AS and La Thangue N: The p53
response during DNA damage: impact of transcriptional cofactors.
Biochem Soc Symp. 181–189. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Borner C: The Bcl-2 protein family:
sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol.
39:615–647. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ferrara N, Hillan KJ, Gerber HP and
Novotny W: Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF
antibody for treating cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 3:391–400. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang S, Pettaway CA, Uehara H, Bucana CD
and Fidler IJ: Blockade of NF-kappaB activity in human prostate
cancer cells is associated with suppression of angiogenesis,
invasion, and metastasis. Oncogene. 20:4188–4197. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oka D, Nishimura K, Shiba M, et al:
Sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide suppresses tumor growth in a
xenograft model of renal cell carcinoma by inhibiting the
activation of NF-kappaB. Int J Cancer. 120:2576–2581. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weng SX, Sui MH, Chen S, et al:
Parthenolide inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells
through induction of G0/G1 phase cell cycle arrest. J Zhejiang Univ
Sci B. 10:528–535. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|