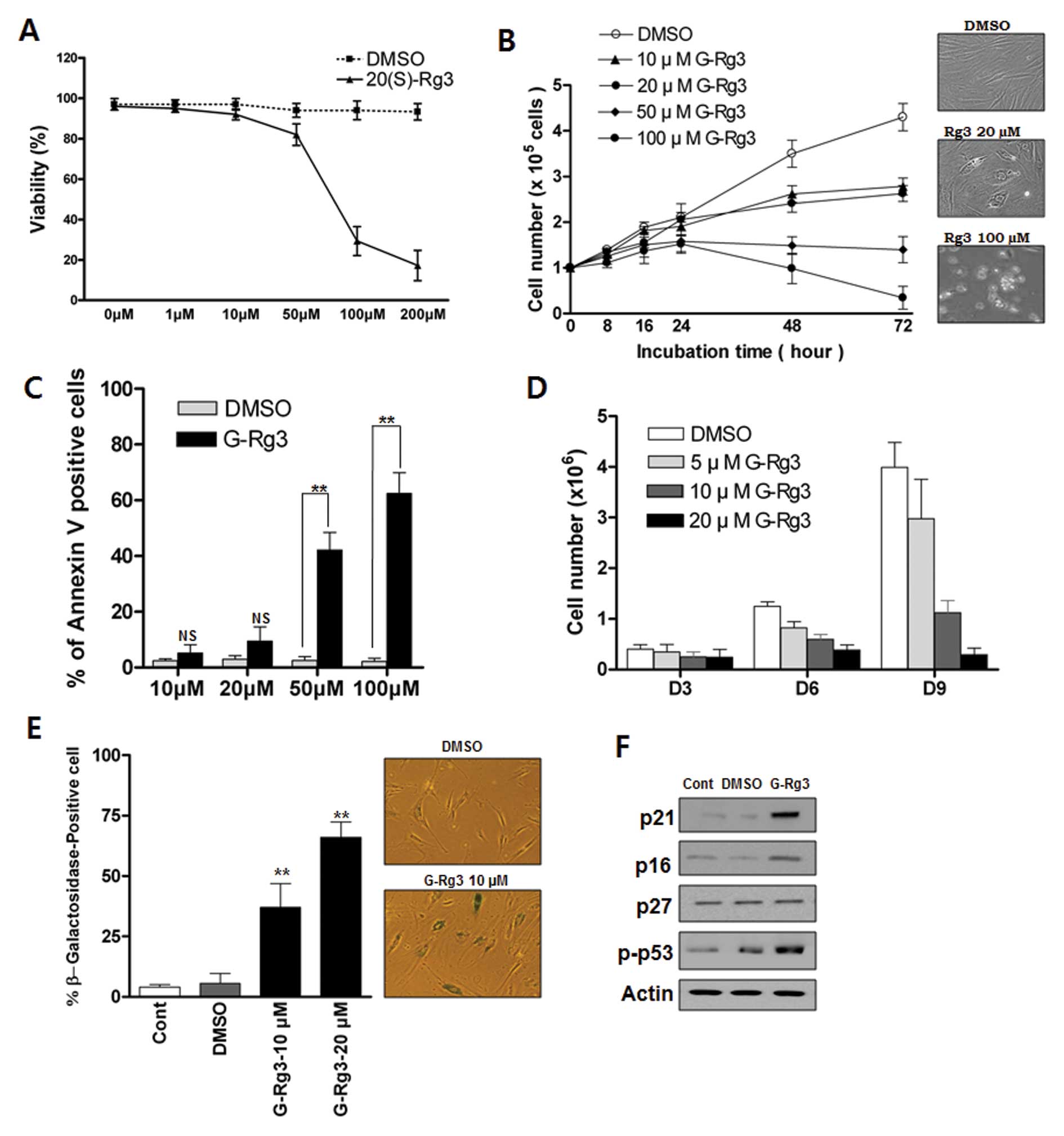
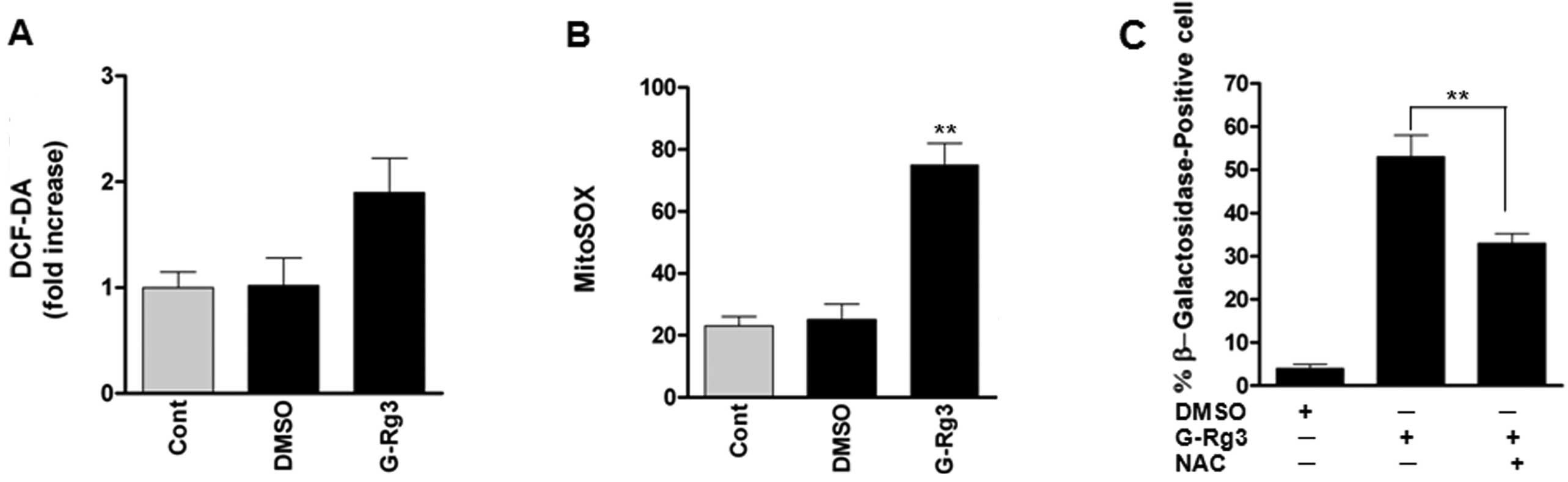
|
1.
|
Vergel M, Marin JJ, Estevez P and Carnero
A: Cellular senescence as a target in cancer control. J Aging Res.
2011:7253652010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Schmitt CA: Senescence, apoptosis and
therapy – cutting the lifelines of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:286–295. 2003.
|
|
3.
|
Shay JW and Roninson IB: Hallmarks of
senescence in carcinogenesis and cancer therapy. Oncogene.
23:2919–2933. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Hornsby PJ: Senescence as an anticancer
mechanism. J Clin Oncol. 25:1852–1857. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Ventura A, Kirsch DG, McLaughlin ME, et
al: Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo.
Nature. 445:661–665. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Ohgaki H and Kleihues P: Genetic pathways
to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 170:1445–1453.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Kitagawa I, Yoshikawa M, Yoshihara M,
Hayashi T and Taniyama T: Chemical studies of crude drugs (1).
Constituents of Ginseng radix rubra. Yakugaku Zasshi. 103:612–622.
1983.(In Japanese).
|
|
8.
|
Helms S: Cancer prevention and
therapeutics: Panax ginseng. Altern Med Rev. 9:259–274.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Yuan HD, Quan HY, Zhang Y, Kim SH and
Chung SH: 20(S)-Ginsenoside Rg3-induced apoptosis in HT-29 colon
cancer cells is associated with AMPK signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 3:825–831. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Wang BS, Zhang LS, Song DM, Zhang JH and
Liu YM: Effect of gensenoside Rg3 on apoptosis of Hep-2 and
expression of HIF-1alha in human laryngeal cancer cell line under
anoxic conditions. Zhong Yao Cai. 32:102–106. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11.
|
Kim HS, Lee EH, Ko SR, Choi KJ, Park JH
and Im DS: Effects of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 on the proliferation
of prostate cancer cells. Arch Pharm Res. 27:429–435. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Jian J, Hu ZF and Huang Y: Effect of
ginsenoside Rg3 on Pim-3 and Bad proteins in human pancreatic
cancer cell line PANC-1. Ai Zheng. 28:461–465. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
13.
|
Dimri GP, Lee X, Basile G, et al: A
biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in
aging skin in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:9363–9367. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Solomon DA, Kim JS, Jenkins S, et al:
Identification of p18 INK4c as a tumor suppressor gene in
glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res. 68:2564–2569. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Nogueira V, Park Y, Chen CC, et al: Akt
determines replicative senescence and oxidative or oncogenic
premature senescence and sensitizes cells to oxidative apoptosis.
Cancer Cell. 14:458–470. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Dolado I and Nebreda AR: AKT and oxidative
stress team up to kill cancer cells. Cancer Cell. 14:427–429. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Campisi J and d’Adda di Fagagna F:
Cellular senescence: when bad things happen to good cells. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 8:729–740. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Schmitt CA: Cellular senescence and cancer
treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1775:5–20. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Roninson IB: Tumor cell senescence in
cancer treatment. Cancer Res. 63:2705–2715. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
te Poele RH, Okorokov AL, Jardine L,
Cummings J and Joel SP: DNA damage is able to induce senescence in
tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 62:1876–1883.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Nardella C, Clohessy JG, Alimonti A and
Pandolfi PP: Pro-senescence therapy for cancer treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 11:503–511. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Lleonart ME, Artero-Castro A and Kondoh H:
Senescence induction; a possible cancer therapy. Mol Cancer.
8:32009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Chang BD, Xuan Y, Broude EV, et al: Role
of p53 and p21waf1/ cip1 in senescence-like terminal proliferation
arrest induced in human tumor cells by chemotherapeutic drugs.
Oncogene. 18:4808–4818. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Blume-Jensen P and Hunter T: Oncogenic
kinase signalling. Nature. 411:355–365. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Testa JR and Bellacosa A: AKT plays a
central role in tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10983–10985. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Miyauchi H, Minamino T, Tateno K, Kunieda
T, Toko H and Komuro I: Akt negatively regulates the in vitro
lifespan of human endothelial cells via a p53/p21-dependent
pathway. EMBO J. 23:212–220. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Lee JJ, Kim BC, Park MJ, et al: PTEN
status switches cell fate between premature senescence and
apoptosis in glioma exposed to ionizing radiation. Cell Death
Differ. 18:666–677. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Serrano M, Lin AW, McCurrach ME, Beach D
and Lowe SW: Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence
associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell. 88:593–602.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Wright WE and Shay JW: Cellular senescence
as a tumor-protection mechanism: the essential role of counting.
Curr Opin Genet Dev. 11:98–103. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Passos JF and Von Zglinicki T: Oxygen free
radicals in cell senescence: are they signal transducers? Free
Radic Res. 40:1277–1283. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Beckman KB and Ames BN: The free radical
theory of aging matures. Physiol Rev. 78:547–581. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Ben-Porath I and Weinberg RA: The signals
and pathways activating cellular senescence. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 37:961–976. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Hagen TM, Yowe DL, Bartholomew JC, et al:
Mitochondrial decay in hepatocytes from old rats: membrane
potential declines, heterogeneity and oxidants increase. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 94:3064–3069. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Lee AC, Fenster BE, Ito H, et al: Ras
proteins induce senescence by altering the intracellular levels of
reactive oxygen species. J Biol Chem. 274:7936–7940. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Chen Q and Ames BN: Senescence-like growth
arrest induced by hydrogen peroxide in human diploid fibroblast F65
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:4130–4134. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Chen QM, Bartholomew JC, Campisi J, Acosta
M, Reagan JD and Ames BN: Molecular analysis of H2O2-induced
senescent-like growth arrest in normal human fibroblasts: p53 and
Rb control G1 arrest but not cell replication. Biochem J.
332:43–50. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|