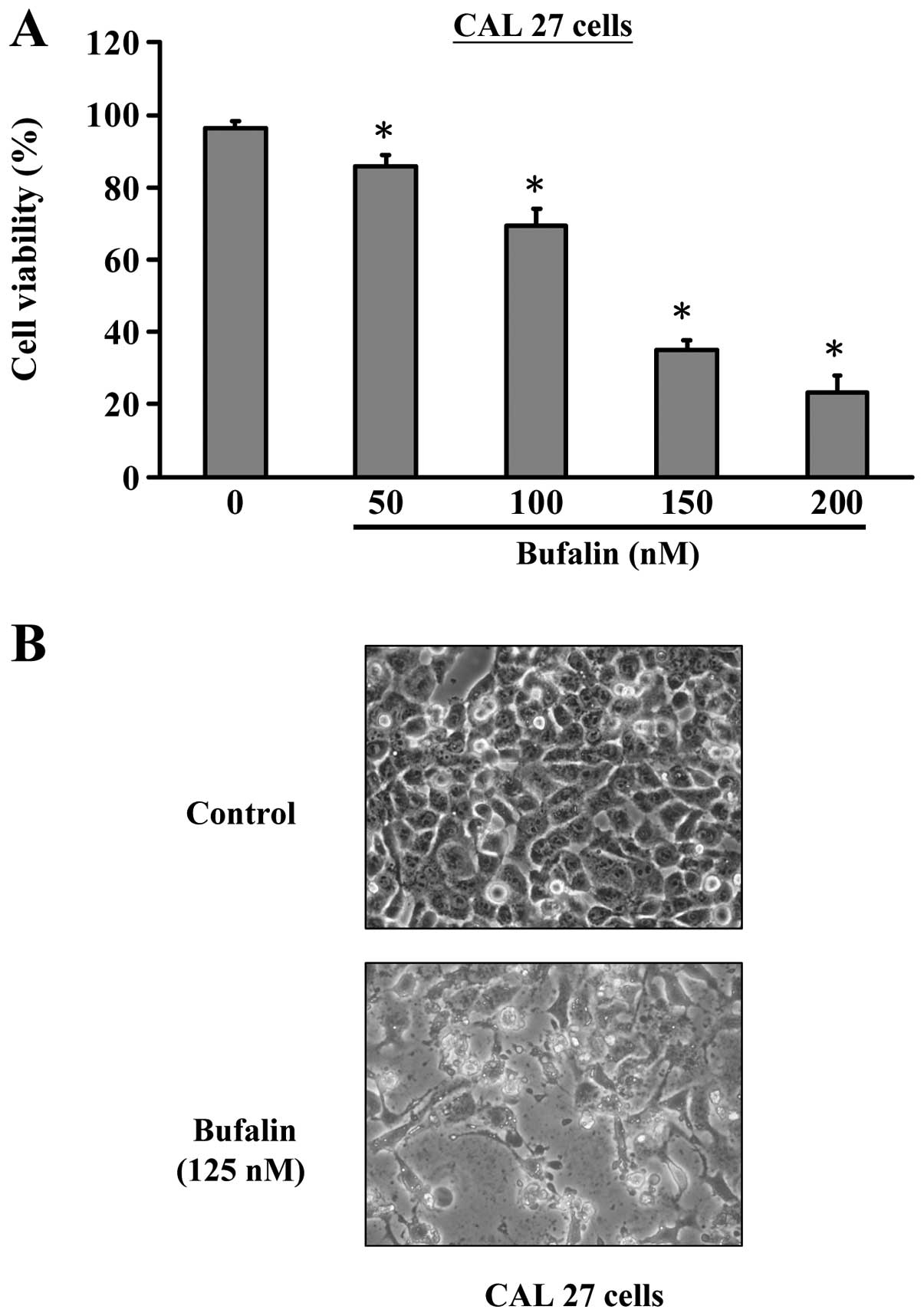
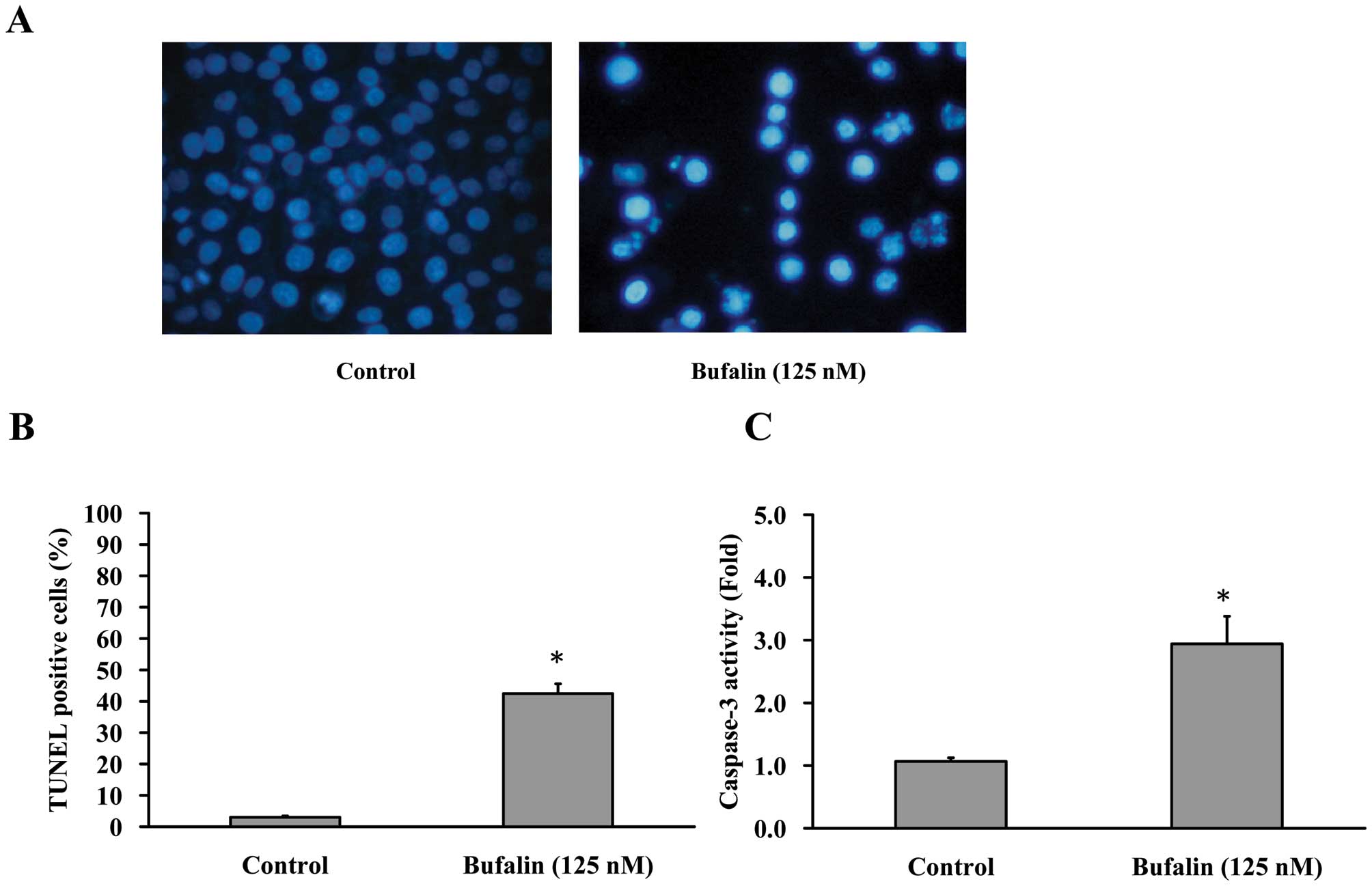
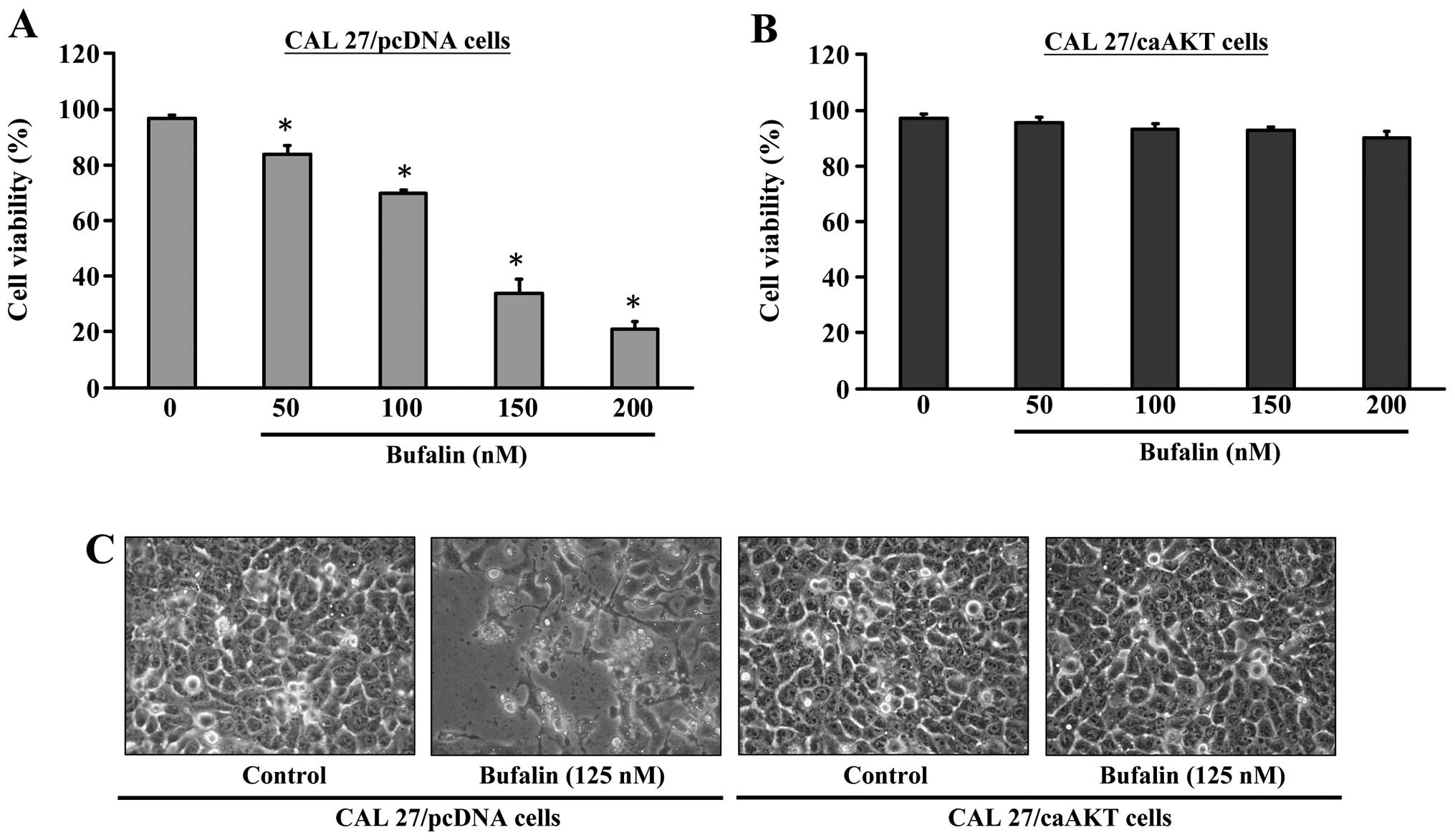
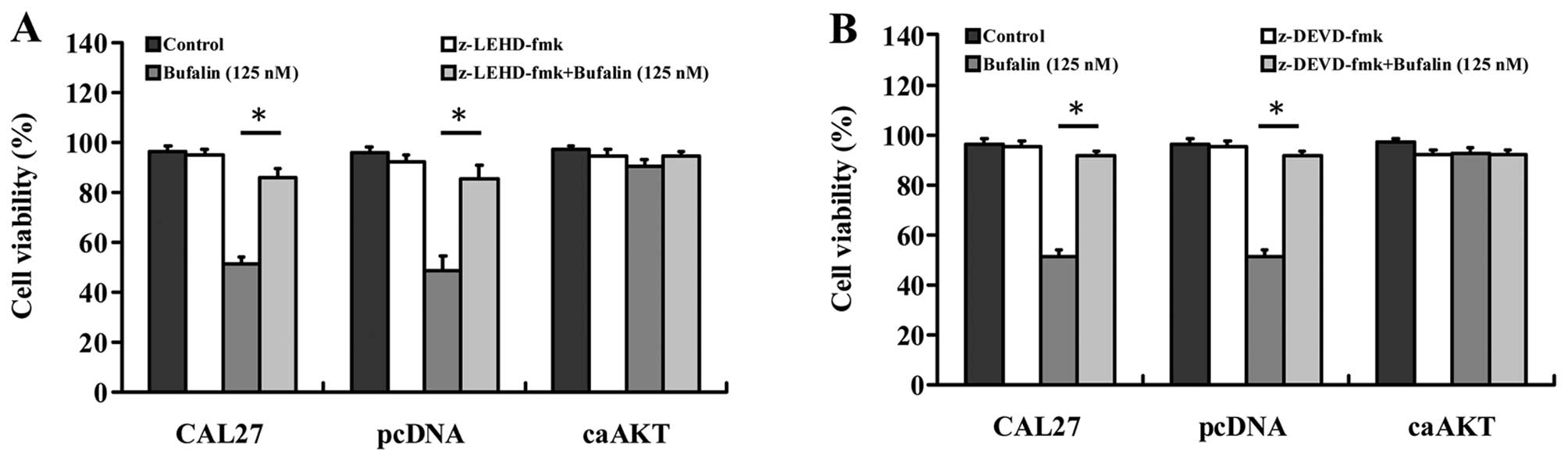
|
1.
|
Chien MH, Ying TH, Hsieh YS, et al:
Dioscorea nipponica Makino inhibits migration and invasion
of human oral cancer HSC-3 cells by transcriptional inhibition of
matrix metalloproteinase-2 through modulation of CREB and AP-1
activity. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:558–566. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Spiro RH, Alfonso AE, Farr HW and Strong
EW: Cervical node metastasis from epidermoid carcinoma of the oral
cavity and oropharynx. A critical assessment of current staging. Am
J Surg. 128:562–567. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Liu SY, Lu CL, Chiou CT, et al: Surgical
outcomes and prognostic factors of oral cancer associated with
betel quid chewing and tobacco smoking in Taiwan. Oral Oncol.
46:276–282. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Funk GF, Karnell LH, Robinson RA, Zhen WK,
Trask DK and Hoffman HT: Presentation, treatment, and outcome of
oral cavity cancer: a National Cancer Data Base report. Head Neck.
24:165–180. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Chung JG, Yang JS, Huang LJ, et al:
Proteomic approach to studying the cytotoxicity of YC-1 on U937
leukemia cells and antileukemia activity in orthotopic model of
leukemia mice. Proteomics. 7:3305–3317. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Sanjiv K, Su TL, Suman S, et al: The novel
DNA alkylating agent BO-1090 suppresses the growth of human oral
cavity cancer in xenografted and orthotopic mouse models. Int J
Cancer. 130:1440–1450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Sun Q, Sakaida T, Yue W, Gollin SM and Yu
J: Chemosensitization of head and neck cancer cells by PUMA. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:3180–3188. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L and Brenner C:
Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev.
87:99–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lai E, Teodoro T and Volchuk A:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Signaling the unfolded protein
response. Physiology (Bethesda). 22:193–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Orrenius S: Reactive oxygen species in
mitochondria-mediated cell death. Drug Metab Rev. 39:443–455. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Chiang JH, et al: Novel
quinazolinone MJ-29 triggers endoplasmic reticulum stress and
intrinsic apoptosis in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells and inhibits
leukemic mice. PLoS One. 7:e368312012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A and Krammer PH:
Caspases: Pharmacological manipulation of cell death. J Clin
Invest. 115:2665–2672. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Takai N, Kira N, Ishii T, et al: Bufalin,
a traditional oriental medicine, induces apoptosis in human cancer
cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:399–402. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Krenn L and Kopp B: Bufadienolides from
animal and plant sources. Phytochemistry. 48:1–29. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yu CH, Kan SF, Pu HF, Jea Chien E and Wang
PS: Apoptotic signaling in bufalin- and cinobufagin-treated
androgen-dependent and -independent human prostate cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 99:2467–2476. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bagrov AY, Roukoyatkina NI, Fedorova OV,
Pinaev AG and Ukhanova MV: Digitalis-like and vasoconstrictor
effects of endogenous digoxin-like factor(s) from the venom of
Bufo marinus toad. Eur J Pharmacol. 234:165–172. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Bandele OJ and Osheroff N: The efficacy of
topoisomerase II-targeted anticancer agents reflects the
persistence of drug-induced cleavage complexes in cells.
Biochemistry. 47:11900–11908. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Baldwin EL and Osheroff N: Etoposide,
topoisomerase II and cancer. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents.
5:363–372. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Huang WW, Yang JS, Pai SJ, et al: Bufalin
induces G(0)/G(1) phase arrest through inhibiting the levels of
cyclin D, cyclin E, CDK2 and CDK4, and triggers apoptosis via
mitochondrial signaling pathway in T24 human bladder cancer cells.
Mutat Res. 732:26–33. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Masuda Y, Kawazoe N, Nakajo S, Yoshida T,
Kuroiwa Y and Nakaya K: Bufalin induces apoptosis and influences
the expression of apoptosis-related genes in human leukemia cells.
Leuk Res. 19:549–556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Qi F, Inagaki Y, Gao B, et al: Bufalin and
cinobufagin induce apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via Fas- and mitochondria-mediated pathways. Cancer Sci.
102:951–958. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Han KQ, Huang G, Gu W, Su YH, Huang XQ and
Ling CQ: Anti-tumor activities and apoptosis-regulated mechanisms
of bufalin on the orthotopic transplantation tumor model of human
hepatocellular carcinoma in nude mice. World J Gastroenterol.
13:3374–3379. 2007.
|
|
23.
|
Aoki M, Batista O, Bellacosa A, Tsichlis P
and Vogt PK: The akt kinase: Molecular determinants of
oncogenicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14950–14955. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Lu CC, Yang JS, Huang AC, et al:
Chrysophanol induces necrosis through the production of ROS and
alteration of ATP levels in J5 human liver cancer cells. Mol Nutr
Food Res. 54:967–976. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Wu PP, Liu KC, Huang WW, et al: Triptolide
induces apoptosis in human adrenal cancer NCI-H295 cells through a
mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Oncol Rep. 25:551–557.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Yang JS, Hour MJ, Huang WW, Lin KL, Kuo SC
and Chung JG: MJ-29 inhibits tubulin polymerization, induces
mitotic arrest, and triggers apoptosis via cyclin-dependent kinase
1-mediated BCL-2 phosphorylation in human leukemia U937 cells. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 334:477–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Chiang JH, Yang JS, Ma CY, et al:
Danthron, an anthraquinone derivative, induces DNA damage and
caspase cascades-mediated apoptosis in SNU-1 human gastric cancer
cells through mitochondrial permeability transition pores and
Bax-triggered pathways. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:20–29. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Wu SH, Hang LW, Yang JS, et al: Curcumin
induces apoptosis in human non-small cell lung cancer NCI-H460
cells through ER stress and caspase cascade- and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Anticancer Res. 30:2125–2133.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ji BC, Hsu WH, Yang JS, et al: Gallic acid
induces apoptosis via caspase-3 and mitochondrion-dependent
pathways in vitro and suppresses lung xenograft tumor growth in
vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 57:7596–7604. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, et al:
Kaempferol induced apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and
mitochondria-dependent pathway in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells.
Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Weng LP, Brown JL and Eng C: PTEN
coordinates G(1) arrest by down-regulating cyclin d1 via its
protein phosphatase activity and up-regulating p27 via its lipid
phosphatase activity in a breast cancer model. Hum Mol Genet.
10:599–604. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Kuo CT, Hsu MJ, Chen BC, et al: Denbinobin
induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells via akt
inactivation, bad activation, and mitochondrial dysfunction.
Toxicol Lett. 177:48–58. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Qin J, Xie LP, Zheng XY, et al: A
component of green tea, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate, promotes
apoptosis in T24 human bladder cancer cells via modulation of the
PI3K/Akt pathway and Bcl-2 family proteins. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 354:852–857. 2007.
|
|
35.
|
Li D, Qu X, Hou K, et al: PI3K/Akt is
involved in bufalin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells.
Anticancer Drugs. 20:59–64. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Kawazoe N, Watabe M, Masuda Y, Nakajo S
and Nakaya K: Tiam1 is involved in the regulation of
bufalin-induced apoptosis in human leukemia cells. Oncogene.
18:2413–2421. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|