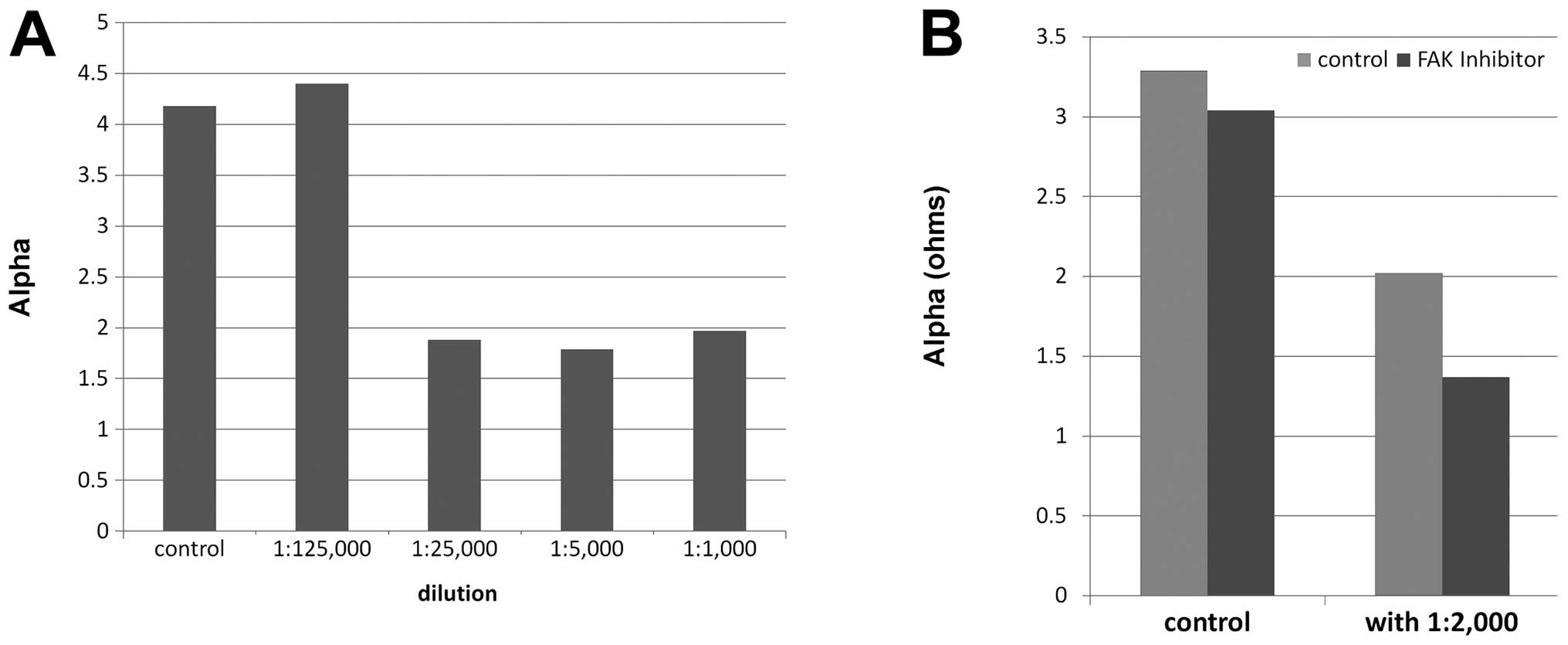
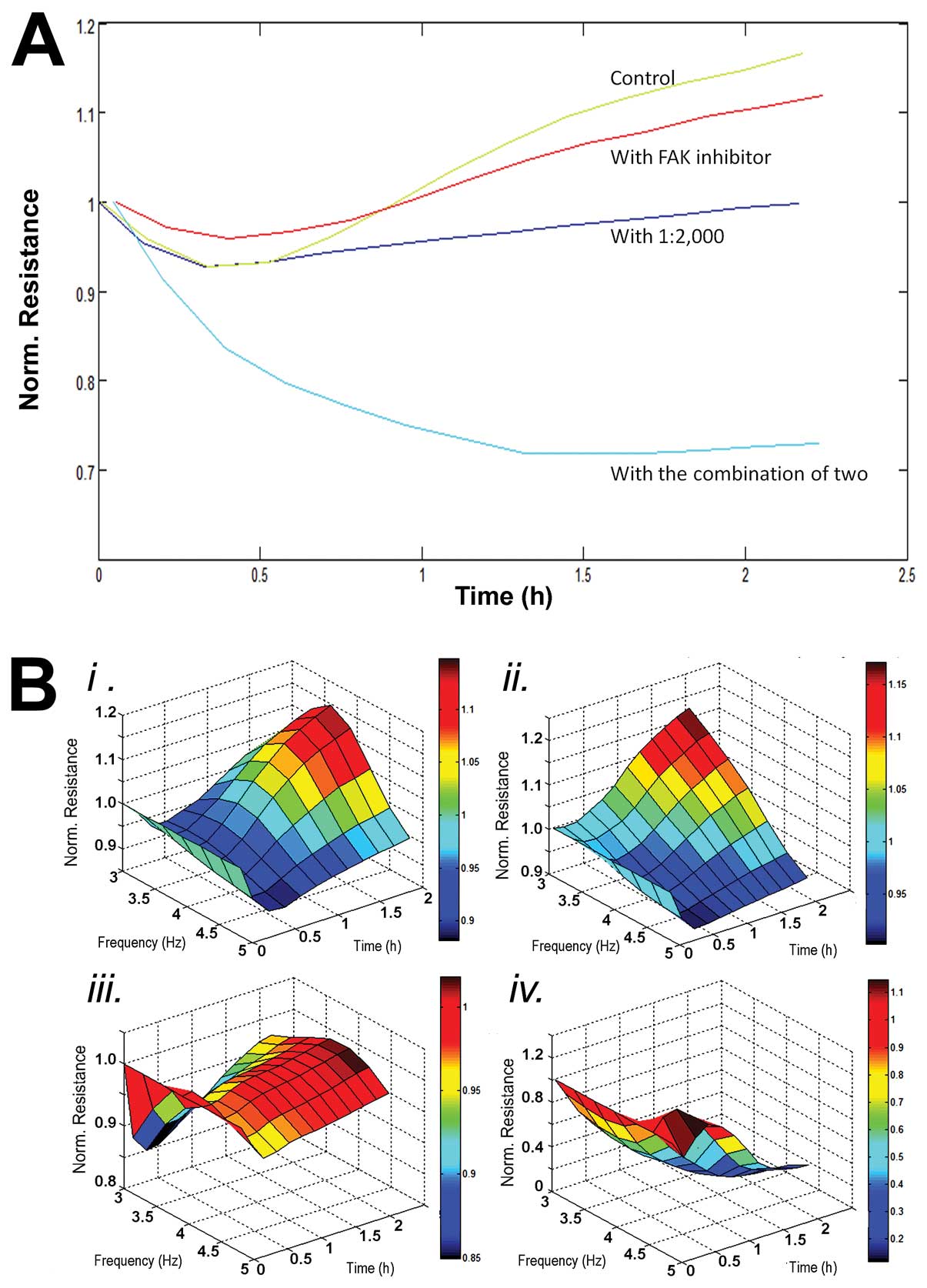
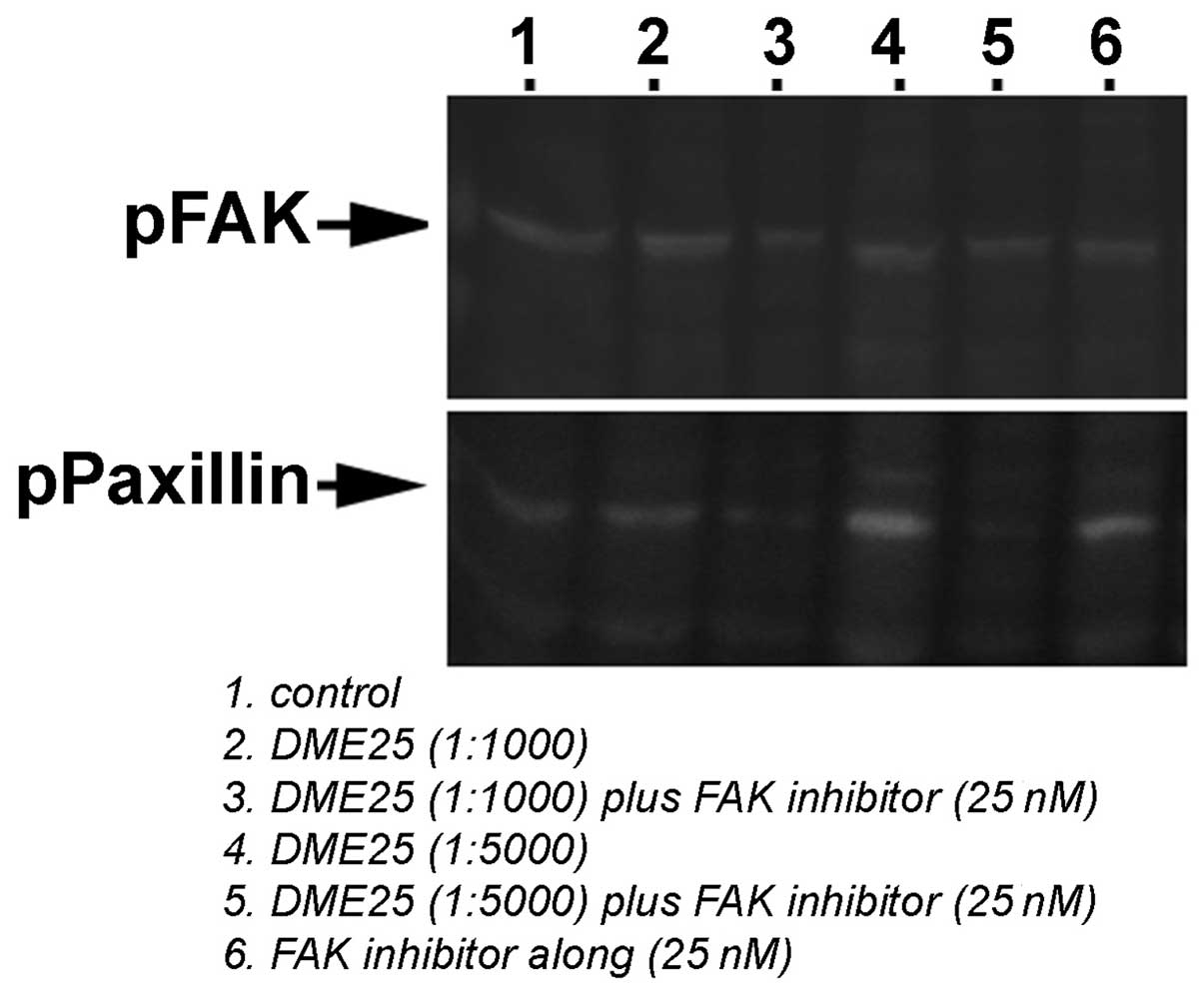
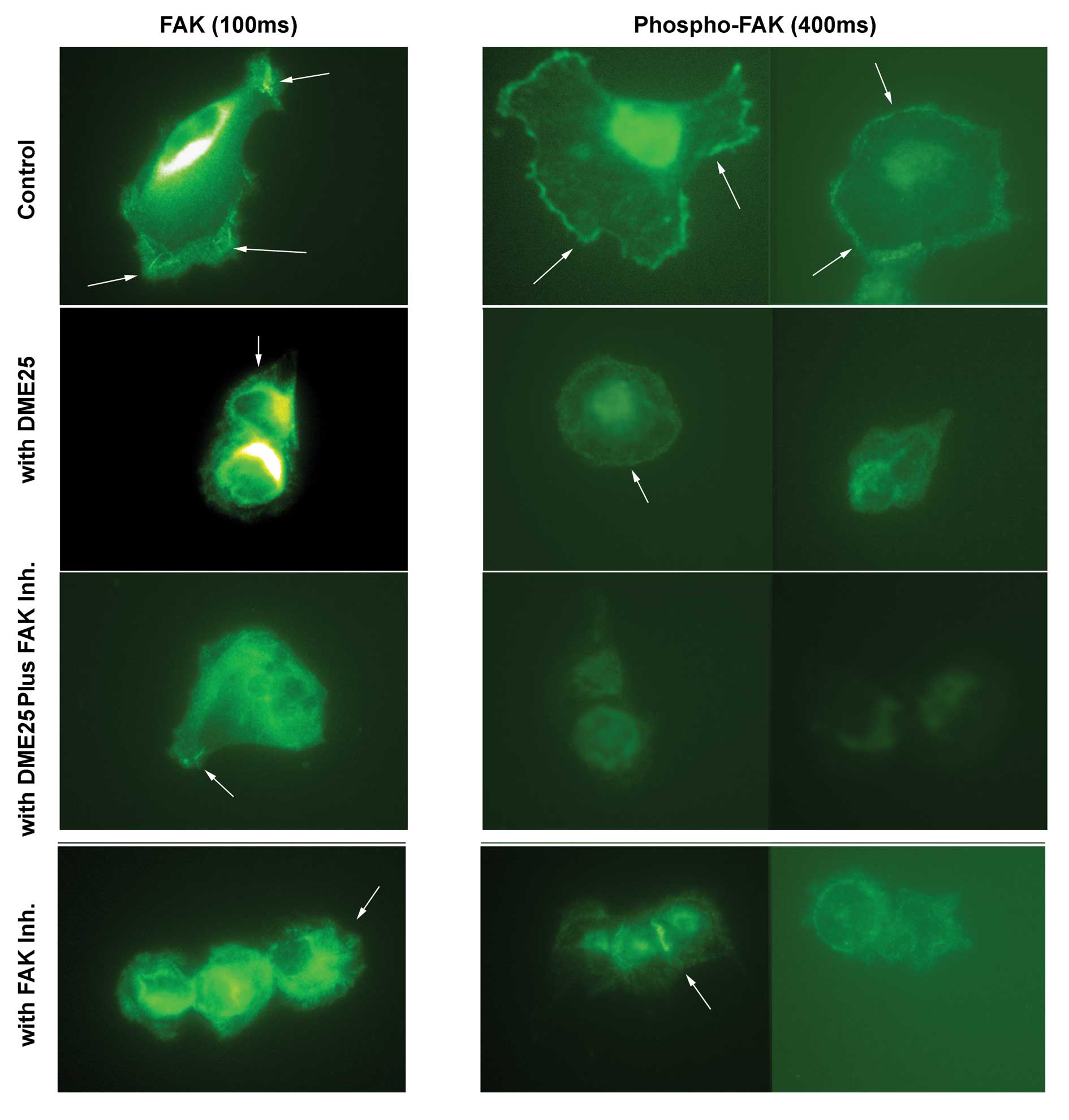
|
1.
|
Folkman J: What is the evidence that
tumors are angiogenesis dependent? J Natl Cancer Inst. 82:4–6.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Fidler IJ: Critical determinants of cancer
metastasis: rationale for therapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
(Suppl 43): S3–S10. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Folkman J and Shing Y: Angiogenesis. J
Biol Chem. 267:10931–10934. 1992.
|
|
4.
|
Folkman J: Fighting cancer by attacking
its blood supply. Sci Am. 275:150–151. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Bicknell R and Harris AL: Mechanisms and
therapeutic implications of angiogenesis. Curr Opin Oncol. 8:60–65.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
O’Reilly MS, Homgren L, Shing Y, Chen C,
Rosenthal RA, Moses M, Lane WS, Cao Y, Sage EH and Folkman J:
Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the
suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell.
79:315–328. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Harris AL: Clinical trials of
anti-vascular agent group B streptococcus toxin (CM101).
Angiogenesis. 1:36–37. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Yoshida T, Kaneko Y, Tsukamoto A, Han K,
Ichinose M and Kimura S: Suppression of hepatoma growth and
angiogenesis by a fumagillin derivative TNP470: possible
involvement of nitric oxide synthase. Cancer Res. 58:3751–3756.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Gregory RE and DeLisa AF: Paclitaxel: a
new antineoplastic agent for refractory ovarian cancer. Clin Pharm.
12:401–415. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Zhang SY, Gu CH, Gao XD and Wu YL: A
random, double-blinded and multicentre study of chemotherapy
assisted Yangzhengxiaoji capsule on treating primary hepatic
carcinoma. Chin J Diffic Compl Case. 8:461–464. 2009.
|
|
11.
|
Wang QL, Xuo CM, Wu XP, Li YX and Bi XJ:
Treatment of atypical gastric dysplasia using Yangzheng Xiaoji.
Chin J Diffic Compl Case. 7:38–39. 2009.
|
|
12.
|
Tran HT, Blumenschein GR Jr, Lu C, Meyers
CA, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Fossella FV, Zinner R, Madden T, Smythe
LG, Puduvalli VK, Munden R, Truong M and Herbst RS: Clinical and
pharmacokinetic study of TNP-470, an angiogenesis inhibitor, in
combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with solid
tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 54:308–314. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Naganuma Y, Choijamts B, Shirota K,
Nakajima K, Ogata S, Miyamoto S, Kawarabayashi T and Emoto M:
Metronomic doxifluridine chemotherapy combined with the
anti-angiogenic agent TNP-470 inhibits the growth of human uterine
carcinosarcoma xenografts. Cancer Sci. 102:1545–1552. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Van Wijngaarden J, Snoeks TJ, van Beek E,
Bloys H, Kaijzel EL, van Hinsbergh VW and Löwik CW: An in vitro
model that can distinguish between effects on angiogenesis and on
established vasculature: actions of TNP-470, marimastat and the
tubulin-binding agent Ang-510. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:1161–1165. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Woerdenbag HJ, Moskal TA, Pras N, Malingré
TM, el-Feraly FS, Kampinga HH and Konings AW: Cytotoxicity of
artemisinin-related endoperoxides to Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J
Nat Prod. 56:849–856. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Liu WM, Gravett AM and Dalgleish AG: The
antimalarial agent artesunate possesses anticancer properties that
can be enhanced by combination strategies. Int J Cancer.
128:1471–1480. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ye Li, Ji K, Ji JF and Jiang WG:
Application of electric cell-substrate impedance sensing in
evaluation of traditional medicine on the cellular functions of
gastric and colorecctal cancer cells. Cancer Metastasis Biol Treat.
17:2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18.
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox S, Hallett MB, Horrobin
DF, Scott C and Puntis MCA: Inhibition of invasion and motility of
human colon cancer cells by gamma linolenic acid. Br J Cancer.
71:744–752. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Giaever I and Keese CR: Micromotion of
mammalian cells measured electrically. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
88:7896–7900. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Keese CR, Wegener J, Walker SR and Giaever
I: Electrical wound-healing assay for cells in vitro. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:1554–1559. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Jiang WG, Ablin RJ, Kynaston HG and Mason
MD: The prostate transglutaminase (TGase-4, TGaseP) regulates the
interaction of prostate cancer and vascular endothelial cells, a
potential role for the ROCK pathway. Microvasc Res. 77:150–157.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Jiang WG, Martin TA, Lewis-Russell JM,
Douglas-Jones A, Ye L and Mansel RE: Eplin-alpha expression in
human breast cancer, the impact on cellular migration and clinical
outcome. Mol Cancer. 7:712008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Jiang WG, Hiscox SE, Parr C, Martin TA,
Matsumoto K, Nakamura T and Mansel RE: Antagonistic effect of NK4,
a novel hepatocyte growth factor variant, on in vitro angiogenesis
of human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Cancer Res. 5:3695–3703.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Sanders AJ, Ye L, Mason MD and Jiang WG:
The impact of EPLINα (epithelial protein lost in neoplasm) on
endothelial cells, angiogenesis and tumorigenesis. Angiogenesis.
13:317–326. 2010.
|
|
25.
|
Ye L, Martin TA, Parr C, Harrison GM,
Mansel RE and Jiang WG: Biphasic effects of 17-beta-estradiol on
expression of occludin and transendothelial resistance and
paracellular permeability in human vascular endothelial cells. J
Cell Physiol. 196:362–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Sanders AJ, Parr C, Martin TA, Lane J,
Mason MD and Jiang WG: Genetic upregulation of matriptase-2 reduces
the aggressiveness of prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo
and affects FAK and paxillin localisation. J Cell Physiol.
216:780–789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Matsuda S, Fujita T, Kajiya M, Takeda K,
Shiba H, Kawaguchi H and Kurihara H: Brain-derived neurotrophic
factor induces migration of endothelial cells through a
TrkB-ERK-integrin αVβ3-FAK cascade. J Cell Physiol. 227:2123–2129.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Gilmore AP and Romer LH: Inhibition of
focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling in focal adhesions decreases
cell motility and proliferation. Mol Biol Cell. 7:1209–1224. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Cai J, Parr C, Watkins G, Jiang WG and
Boulton M: Decreased pigment epithelium-derived factor expression
in human breast cancer progression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:3510–3517.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Braren R, Hu H, Kim YH, Beggs HE,
Reichardt LF and Wang R: Endothelial FAK is essential for vascular
network stability, cell survival, and lamellipodial formation. J
Cell Biol. 172:151–162. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Tavora B, Batista S, Reynolds LE, Jadeja
S, Robinson S, Kostourou V, Hart I, Fruttiger M, Parsons M and
Hodivala-Dilke KM: Endothelial FAK is required for tumour
angiogenesis. EMBO Mol Med. 2:516–528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Peng X, Ueda H, Zhou H, Stokol T, Shen TL,
Alcaraz A, Nagy T, Vassalli JD and Guan JL: Overexpression of focal
adhesion kinase in vascular endothelial cells promotes angiogenesis
in transgenic mice. Cardiovasc Res. 64:421–430. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Li S, Butler P, Wang Y, Hu Y, Han DC,
Usami S, Guan JL and Chien S: The role of the dynamics of focal
adhesion kinase in the mechanotaxis of endothelial cells. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:3546–3551. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Lechertier T and Hodivala-Dilke K: Focal
adhesion kinase and tumour angiogenesis. J Pathol. 226:404–412.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Halder J, Lin YG, Merritt WM, Spannuth WA,
Nick AM, Honda T, Kamat AA, Han LY, Kim TJ, Lu C, Tari AM, Bornmann
W, Fernandez A, Lopez-Berestein G and Sood AK: Therapeutic efficacy
of a novel focal adhesion kinase inhibitor TAE226 in ovarian
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 67:10976–10983. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Infante JR, Camidge DR, Mileshkin LR, Chen
EX, Hicks RJ, Rischin D, Fingert H, Pierce KJ, Xu H, Roberts WG,
Shreeve SM, Burris HA and Siu LL: Safety, pharmacokinetic, and
pharmacodynamic phase I dose-escalation trial of PF-00562271, an
inhibitor of focal adhesion kinase, in advanced solid tumors. J
Clin Oncol. 30:1527–1533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Stokes JB, Adair SJ, Slack-Davis JK,
Walters DM, Tilghman RW, Hershey ED, Lowrey B, Thomas KS, Bouton
AH, Hwang RF, Stelow EB, Parsons JT and Bauer TW: Inhibition of
focal adhesion kinase by PF-562,271 inhibits the growth and
metastasis of pancreatic cancer concomitant with altering the tumor
microenvironment. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:2135–2145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Cabrita MA, Jones LM, Quizi JL, Sabourin
LA, McKay BC and Addison C: Focal adhesion kinase inhibitors are
potent anti-angiogenic agents. Mol Oncol. 5:517–526. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Chen JY, Tang YA, Huang SM, Juan HF, Wu
LW, Sun YC, Wang SC, Wu KW, Balraj G, Chang TT, Li WS, Cheng HC and
Wang YC: A novel sialyltransferase inhibitor suppresses
FAK/paxillin signaling and cancer angiogenesis and metastasis
pathways. Cancer Res. 71:473–483. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Jeon J, Lee J, Kim C, An Y and Choi C:
Aqueous extract of the medicinal plant Patrinia villosa Juss.
induces angiogenesis via activation of focal adhesion kinase.
Microvasc Res. 80:303–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Chung BH, Cho YL, Kim JD, Jo HS, Won MH,
Lee H, Ha KS, Kwon YG and Kim YM: Promotion of direct angiogenesis
in vitro and in vivo by Puerariae flos extract via activation of
MEK/ERK-, PI3K/Akt/eNOS-, and Src/FAK-dependent pathways. Phytother
Res. 24:934–940. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|