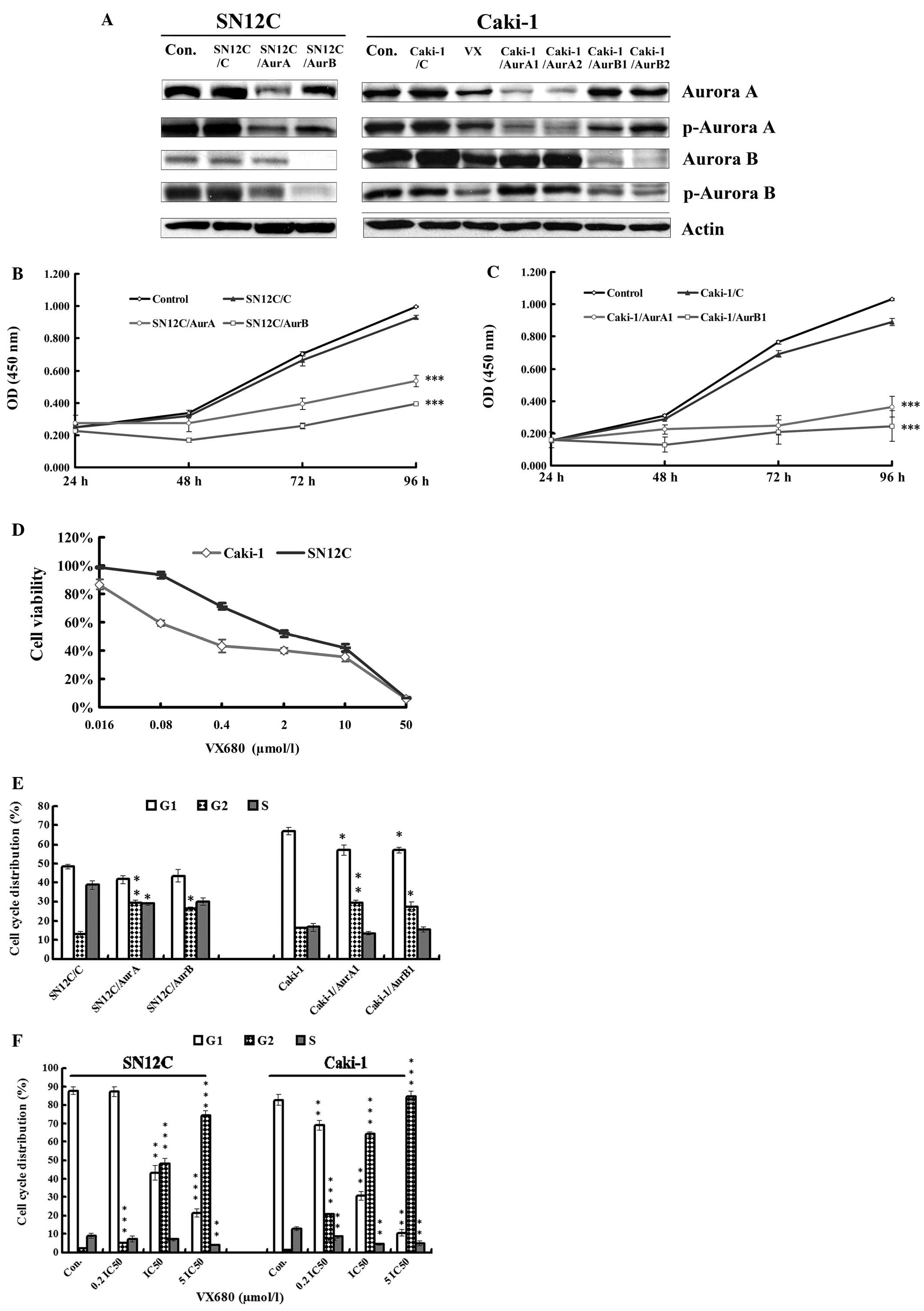
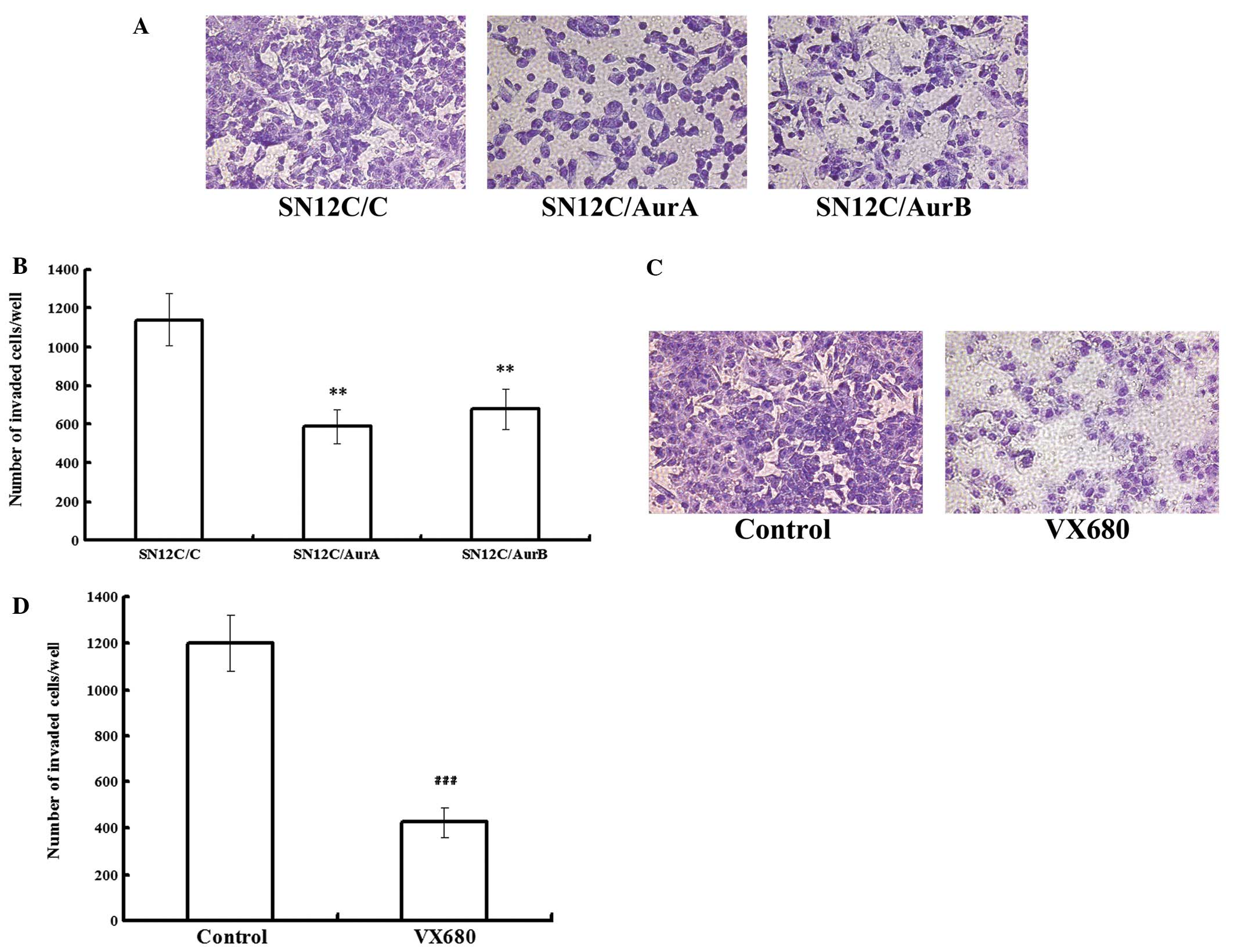
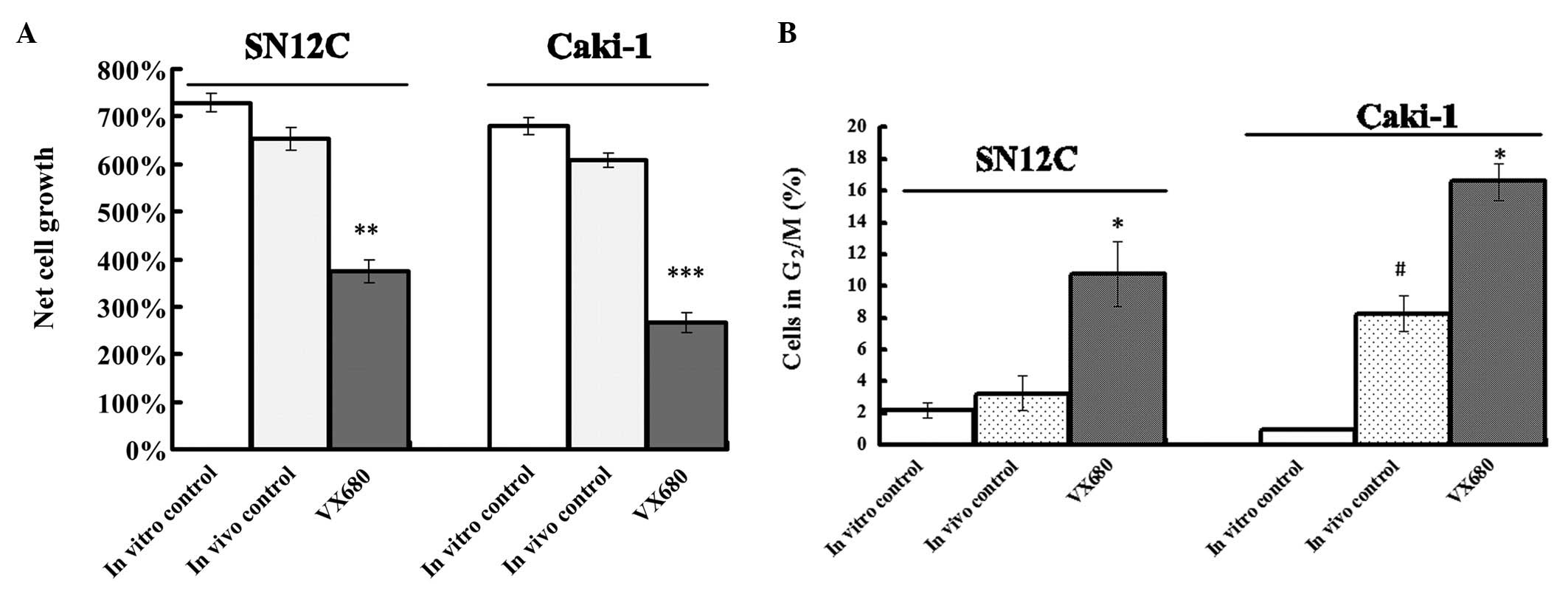
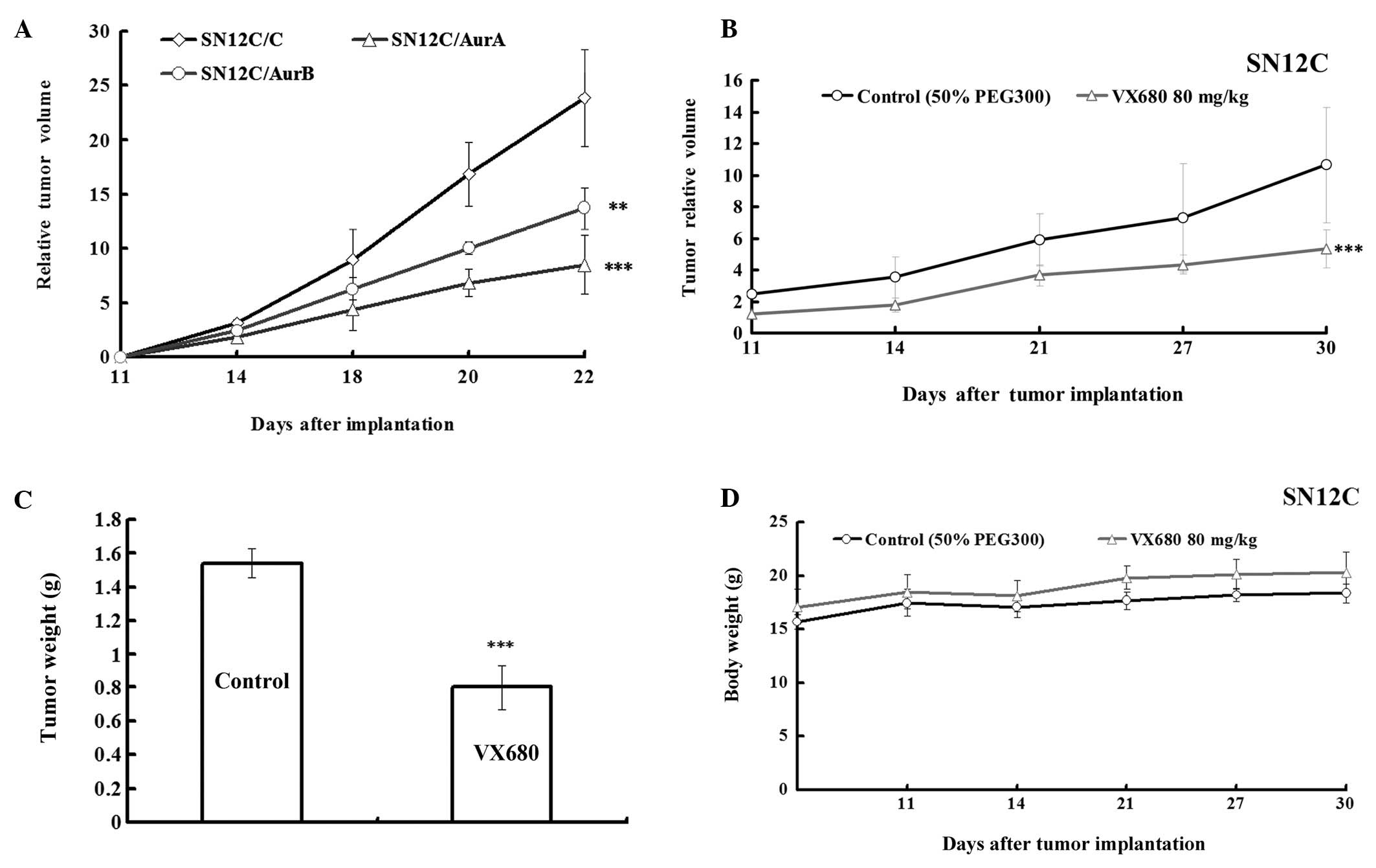
|
1.
|
Bensalah K and Patard JJ: Kidney cancer in
2010: drugs, surgery and survival in RCC. Nat Rev Urol. 8:66–68.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Chowdhury S and Choueiri TK: Recent
advances in the systemic treatment of metastatic papillary renal
cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 9:373–379. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Chowdhury S, Matrana MR, Tsang C, et al:
Systemic therapy for metastatic non-clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma: recent progress and future directions. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 25:853–869. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Keen N and Taylor S: Aurora-kinase
inhibitors as anticancer agents. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:927–936. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Tyler RK, Shpiro N, Marquez R and Eyers
PA: VX-680 inhibits Aurora A and Aurora B kinase activity in human
cells. Cell Cycle. 6:2846–2854. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Yang H, He L, Kruk P, et al: Aurora-A
induces cell survival and chemoresistance by activation of Akt
through a p53-dependent manner in ovarian cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 119:2304–2312. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Dutertre S, Cazales M, Quaranta M, et al:
Phosphorylation of CDC25B by Aurora-A at the centrosome contributes
to the G2-M transition. J Cell Sci. 117:2523–2531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Gizatullin F, Yao Y, Kung V, et al: The
Aurora kinase inhibitor VX-680 induces endoreduplication and
apoptosis preferentially in cells with compromised p53-dependent
postmitotic checkpoint function. Cancer Res. 66:7668–7677. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9.
|
Merk BC, Owens JL, Lopes MB, et al: STAT6
expression in glioblastoma promotes invasive growth. BMC Cancer.
11:1842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Cloos J, Temmink O, Ceelen M, et al:
Involvement of cell cycle control in bleomycin-induced mutagen
sensitivity. Environ Mol Mutagen. 40:79–84. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Temmink OH, Prins HJ, van Gelderop E and
Peters GJ: The Hollow Fibre Assay as a model for in vivo
pharmacodynamics of fluoropyrimidines in colon cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 96:61–66. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Li Y, Zhang ZF, Chen J, et al:
VX680/MK-0457, a potent and selective Aurora kinase inhibitor,
targets both tumor and endothelial cells in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Am J Transl Res. 2:296–308. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Huang D, Ding Y, Luo WM, et al: Inhibition
of MAPK kinase signaling pathways suppressed renal cell carcinoma
growth and angiogenesis in vivo. Cancer Res. 68:81–88. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Harrington EA, Bebbington D, Moore J, et
al: VX-680, a potent and selective small-molecule inhibitor of the
Aurora kinases, suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nat Med.
10:262–267. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Teicher BA: Newer cytotoxic agents:
attacking cancer broadly. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1610–1617. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Suzuki T, Urano T, Miki Y, et al: Nuclear
cyclin B1 in human breast carcinoma as a potent prognostic factor.
Cancer Sci. 98:644–651. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Perdiguero E and Nebreda AR: Regulation of
Cdc25C activity during the meiotic G2/M transition. Cell Cycle.
3:733–737. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Singh SV, Herman-Antosiewicz A, Singh AV,
et al: Sulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25C. J Biol Chem. 279:25813–25822. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, et
al: Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and
physiological functions. Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Lee SJ, Park K, Ha SD, et al: Gleditsia
sinensis thorn extract inhibits human colon cancer cells: the role
of ERK1/2, G2/M-phase cell cycle arrest and p53 expression.
Phytother Res. 24:1870–1876. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Meraldi P, Honda R and Nigg EA: Aurora
kinases link chromosome segregation and cell division to cancer
susceptibility. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 14:29–36. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Gautschi O, Heighway J, Mack PC, et al:
Aurora kinases as anticancer drug targets. Clin Cancer Res.
14:1639–1648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Lee EC, Frolov A, Li R, et al: Targeting
Aurora kinases for the treatment of prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
66:4996–5002. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lee YM, Ting CM, Cheng YK, et al:
Mechanisms of 2-methoxyestradiol-induced apoptosis and G2/M
cell-cycle arrest of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett.
268:295–307. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Margolis SS, Perry JA, Weitzel DH, et al:
A role for PP1 in the Cdc2/Cyclin B-mediated positive feedback
activation of Cdc25. Mol Biol Cell. 17:1779–1789. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Ray G, Dhar G, Van Veldhuizen PJ, et al:
Modulation of cell-cycle regulatory signaling network by
2-methoxyestradiol in prostate cancer cells is mediated through
multiple signal transduction pathways. Biochemistry. 45:3703–3713.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27.
|
Cheng Y, Qiu F, Ye YC, et al: Oridonin
induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis via activating ERK-p53 apoptotic
pathway and inhibiting PTK-Ras-Raf-JNK survival pathway in murine
fibrosarcoma L929 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 490:70–75. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Hsu YL, Kuo PL, Lin LT and Lin CC: Asiatic
acid, a triterpene, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest through
activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in human breast cancer
cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 313:333–344. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Guruvayoorappan C and Kuttan G:
Amentoflavone inhibits experimental tumor metastasis through a
regulatory mechanism involving MMP-2, MMP-9, prolyl hydroxylase,
lysyl oxidase, VEGF, ERK-1, ERK-2, STAT-1, NM23 and cytokines in
lung tissues of C57BL/6 mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
30:711–727. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|