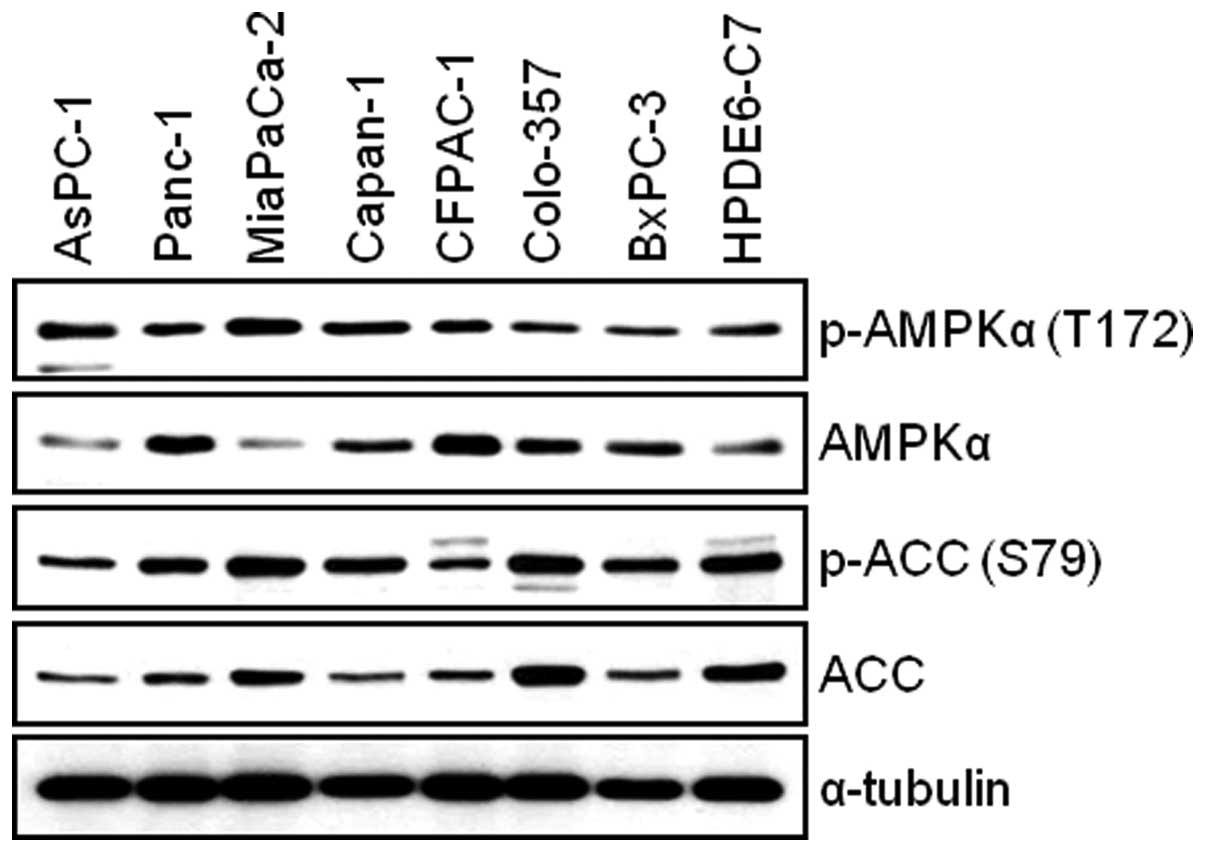
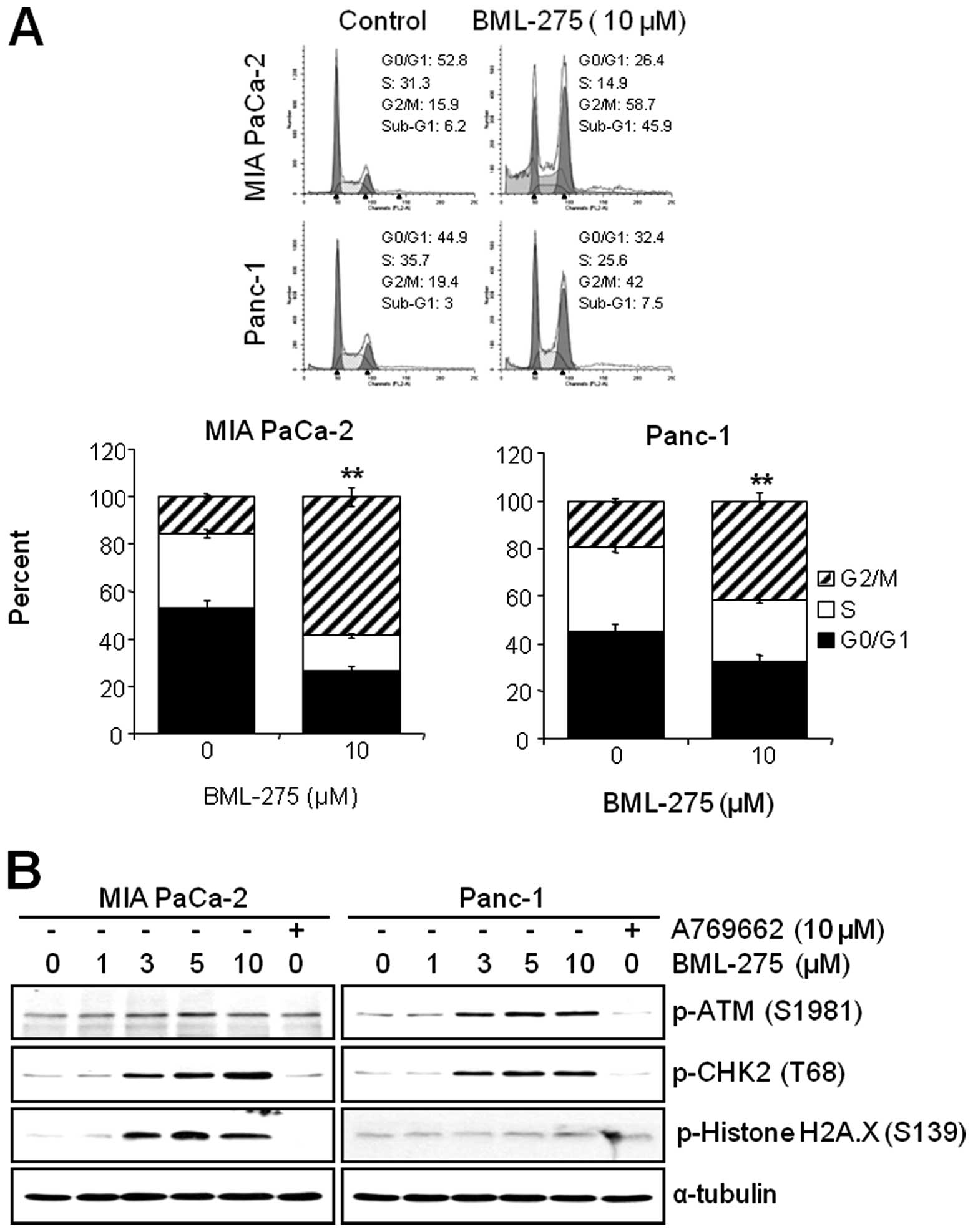
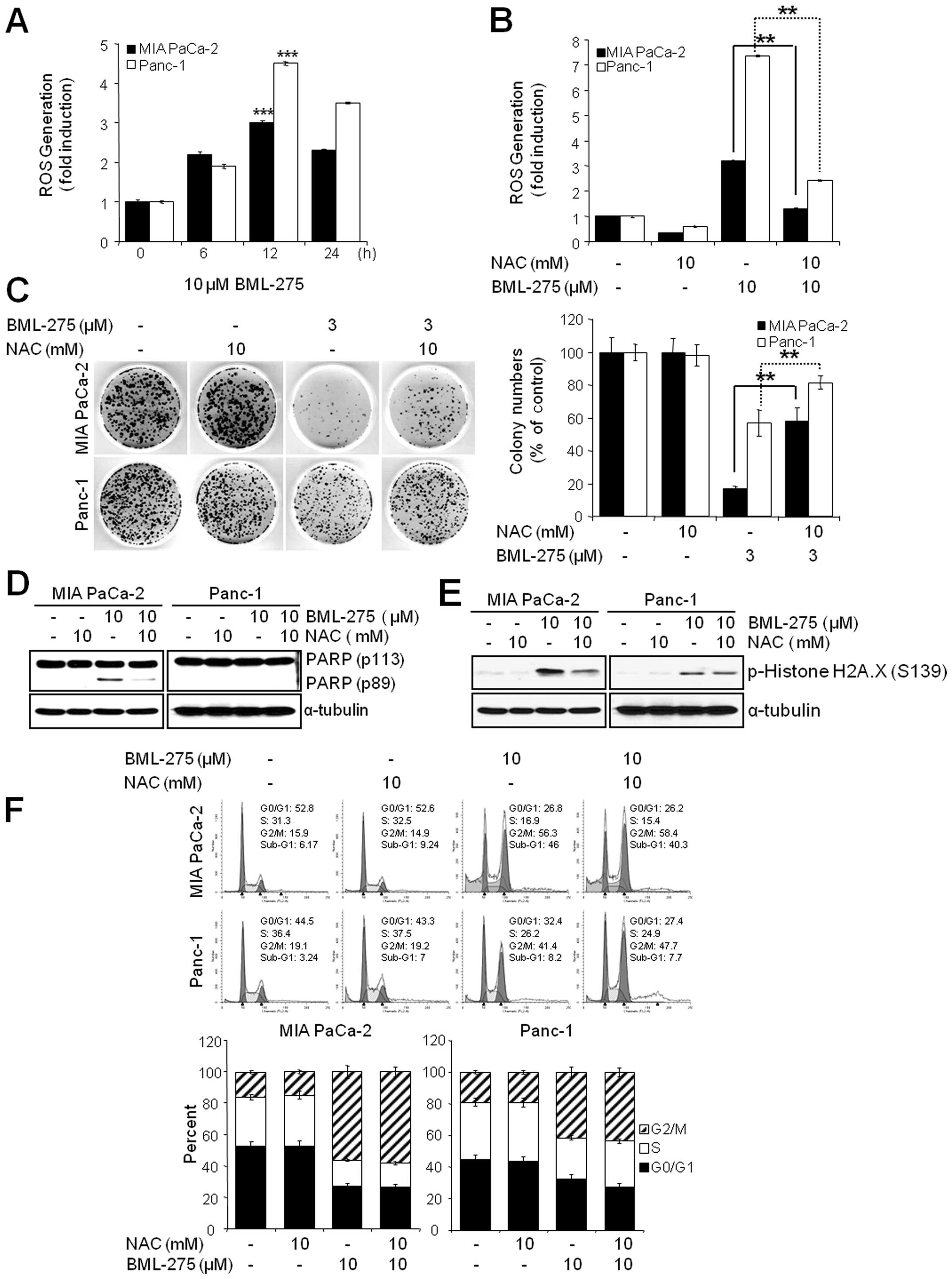
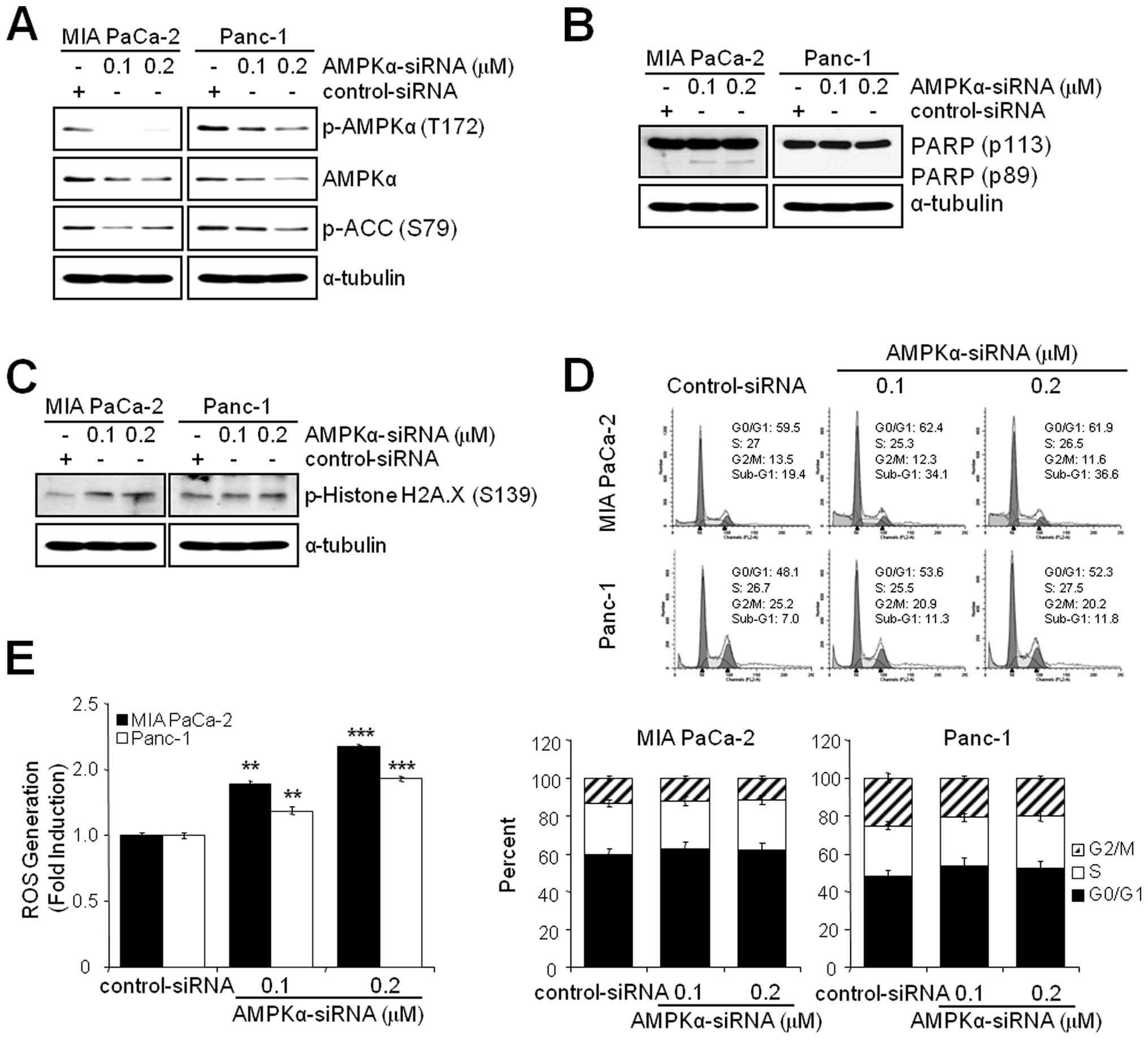
|
1.
|
A JemalR SiegelJ XuE WardCancer
statistics, 2010CA Cancer J Clin60277300201010.3322/caac.20073
|
|
2.
|
MR KeighleyGastrointestinal cancers in
EuropeAliment Pharmacol
Ther18730200310.1046/j.0953-0673.2003.01722.x
|
|
3.
|
DG HardieAMP-activated/SNF1 protein
kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energyNat Rev Mol Cell
Biol8774785200710.1038/nrm224917712357
|
|
4.
|
DG HardieD CarlingThe AMP-activated
protein kinase - fuel gauge of the mammalian cells?Eur J
Biochem246259273199710.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00259.x9208914
|
|
5.
|
DG HardieJW ScottDA PanER HudsonManagement
of cellular energy by the AMP-activated protein kinase systemFEBS
Lett546113120200310.1016/S0014-5793(03)00560-X12829246
|
|
6.
|
D CarlingThe AMP-activated protein kinase
cascade - a unifying system for energy controlTrends Biochem
Sci291824200410.1016/j.tibs.2003.11.00514729328
|
|
7.
|
DG HardieThe AMP-activated protein kinase
pathway - new players upstream and downstreamJ Cell
Sci11754795487200410.1242/jcs.0154015509864
|
|
8.
|
BB KahnT AlquierD CarlingDG
HardieAMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides
clues to modern understanding of metabolismCell
Metab11525200510.1016/j.cmet.2004.12.00316054041
|
|
9.
|
SA HawleyDA PanKJ MustardL RossJ BainAM
EdelmanBG FrenguelliDG HardieCalmodulin-dependent protein kinase
kinase-beta is an alternative upstream kinase for AMP-activated
protein kinaseCell
Metab2919200510.1016/j.cmet.2005.05.00916054095
|
|
10.
|
RL HurleyKA AndersonJM FranzoneBE KempAR
MeansLA WittersThe Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein
kinase kinases are AMP-activated protein kinase kinasesJ Biol
Chem2802906029066200515980064
|
|
11.
|
A WoodsK DickersonR HeathSP HongM
MomcilovicSR JohnstoneM CarlsonD
CarlingCa2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
kinase-beta acts upstream of AMP-activated protein kinase in
mammalian cellsCell Metab221332005
|
|
12.
|
C CampàsJM LopezAF SantidriánM BarragánB
BellosilloD ColomerJ GilAcadesine activates AMPK and induces
apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells but not in T
lymphocytesBlood10136743680200312522004
|
|
13.
|
BA KefasY CaiK KerchhofsZ LingG MartensH
HeimbergD PipeleersM Van de CasteeleMetformin-induced stimulation
of AMP-activated protein kinase in beta-cells impairs their glucose
responsiveness and can lead to apoptosisBiochem
Pharmacol68409416200410.1016/j.bcp.2004.04.003
|
|
14.
|
M SaitohK NagaiK NakagawaT YamamuraS
YamamotoT NishizakiAdenosine induces apoptosis in the human gastric
cancer cells via an intrinsic pathway relawant to activation of
AMP-activated protein kinaseBiochem
Pharmacol6720052011200410.1016/j.bcp.2004.01.020
|
|
15.
|
R RattanS GiriAK SinghI
Singh5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside
inhibits cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via
AMP-activated protein kinaseJ Biol
Chem2803958239593200510.1074/jbc.M50744320016176927
|
|
16.
|
W ZhouWF HanLE LandreeJN ThupariML PinnT
BililignEK KimA VadlamudiSM MedghlchiR El MeskiniGV RonnettCA
TownsendFP KuhajdaFatty acid synthase inhibition activates
AMP-activated protein kinase in SKOV3 human ovarian cancer
cellsCancer
Res6729646971200710.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-343917409402
|
|
17.
|
A IsakovicL HarhajiD StevanovicZ MarkovicM
Sumarac-DumanovicV StarcevicD MicicV TrajkovicDual antiglioma
action of metformin: cell cycle arrest and mitochondria-dependent
apoptosisCell Mol Life
Sci6412901302200710.1007/s00018-007-7080-417447005
|
|
18.
|
R OkoshiT OzakiH YamamotoK AndoN KoidaS
OnoT KodaT KamijoA NakagamaraH KizakiActivation of AMP-activated
protein kinase induces p53-dependent apoptotic cell death in
response to energetic stressJ Biol
Chem28339793987200810.1074/jbc.M70523220018056705
|
|
19.
|
TK SenquptaGM LeclercTT Hsieh-KinserGJ
leclercI SinghJC BarredoCytotoxic effect of
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside (AICAR) on
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells: implication for
targeted therapyMol Cancer646200710.1186/1476-4598-6-4617623090
|
|
20.
|
P BaumannS Mandl-WeberB EmmerichC StrakaR
SchmidmaierInhibition of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein
kinase induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma cellsAnticancer
Drugs18405410200710.1097/CAD.0b013e32801416b617351392
|
|
21.
|
HU ParkS SuyM DannerV DaileyY ZhangH LiDR
HydukeBT CollinsG GagnonB KallakuryD KumarML BrownA FornaceA
DritschiloSP CollinsAMP-activated protein kinase promotes human
prostate cancer cell growth and survivalMol Cancer
Ther8733741200910.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-063119372545
|
|
22.
|
L VuvicevicM MisirkicK JanjetovicL
Harhaji-TrajkovicM PricaD StevanovicE IsenovicE SudarM
Sumarac-DumanovicD MicicV TrajkovicAMP-activated protein
kinase-dependent and-independent mechanisms underlying in vitro
antiglioma action of compound CBiochem
Pharmacol7716841693200910.1016/j.bcp.2009.03.00519428322
|
|
23.
|
J JinTD MullenQ HouJ BielawskiA BielawskaX
ZhangLM ObeidYA HannunYT HsuAMPK inhibitor compound C stiumulates
ceramine production and promotes BAx redistribution and apoptosis
in MCF-7 breast carcinoma cellsJ Lipid
Res5023892397200910.1194/jlr.M900119-JLR20019528633
|
|
24.
|
JH JangTJ LeeES YangS Min doYH KimSH KimYH
ChoiJW ParkKS ChoiTK KwonCompound C sensitizes caki renal cancer
cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen
species-mediated down-regulation of c-FLIPL and Mcl-1Exp Cell
Res31621942203201010.1016/j.yexcr.2010.04.02820451517
|
|
25.
|
Q ZhuB ShenB ZhangW ZhangSH ChinJ JinDF
LiaoInhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase pathway sensitizes
human leukemia K562 cells to nontoxic concentration of
doxorubicinMol Cell
Biochem340275281201010.1007/s11010-010-0428-320339906
|
|
26.
|
HS KimJT HwangH YunSG ChiSJ LeeI KangKS
YoonWJ ChoeSS KimJ HaInhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase
sensitizes cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis via
hyper-induction of p53J Biol
Chem28337313742200810.1074/jbc.M70443220018079115
|
|
27.
|
K CollinsT JacksNP PavletichThe cell cycle
and cancerProc Natl Acad Sci
USA9427762778199710.1073/pnas.94.7.27769096291
|
|
28.
|
JK BuolamwiniCell cycle molecular targets
in novel anti-cancer drug discoveryCurr Pharm
Des6379392200010.2174/138161200340094810788588
|
|
29.
|
M HajduchL HavlieekJ VeselyR NovotnyV
MihalM StrnadSynthetic cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors. New
generation of potent anti-cancer drugsAdv Exp Med
Biol457341353199910.1007/978-1-4615-4811-9_3710500810
|
|
30.
|
J PinesFour-dimensional control of the
cell cycleNat Cell Biol1E73E79199910.1038/1104110559915
|
|
31.
|
WR TaylorGR StarkRegulation of the G2/M
transition by
p53Oncogene2018031815200110.1038/sj.onc.120425211313928
|
|
32.
|
S UedaH NakamuraH MasutaniT SasadaA
TakabayashiY YamaokaJ YodoiBaicalin induces apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway as prooxidantMol
Immunol38781791200210.1016/S0161-5890(01)00115-811841838
|
|
33.
|
KB BeckmanBN AmesOxidative decay of DNAJ
Biol Chem2721963319636199710.1074/jbc.272.32.196339289489
|
|
34.
|
J CadetT DelatourT DoukiD GasparuttoJP
PougetJL RavanatS SauvaigoHydroxyl radicals and DNA base
damageMutal Res424921199910.1016/S0027-5107(99)00004-4
|
|
35.
|
MM VilenchikAG KnudsonEndogenous DNA
double-strand breaks:production, fidelity of repair and induction
of cancerProc Natl Acad Sci
USA1001287112876200310.1073/pnas.213549810014566050
|
|
36.
|
T FurukawaWP DuquidL RosenbergJ VialletDA
GallowayMS TsaoLong-term culture and immortalization of epithelial
cells from normal adult human pancreatic ducts transfected by the
E6E7 gene of human papilloma virus 16Am J
Pathol1481763177019968669463
|
|
37.
|
HQ DuongHJ KimHJ KangYS SeongI BaeZSTK474,
a PI3K inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and sensitizes human
pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells to gemcitabineOncol
Rep27182188201221993922
|
|
38.
|
DG HardieD CarlingM CarlsonThe
AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinase subfamily: metabolic sensors of
the eukaryotic cells?Annu Rev
Biochem67821855199810.1146/annurev.biochem.67.1.8219759505
|
|
39.
|
M LeeJT HwangHJ LeeSN JungI KangSG ChiSS
KimJ HaAMP-activated protein kinase activity is critical for
hypoxia-inducible factor-1 transcriptional activity and its target
gene expression under hypoxic conditions in DU145 cellsJ Biol
Chem2783965339661200310.1074/jbc.M306104200
|
|
40.
|
H YunM LeeSS KimJ HaGlucose deprivation
increases mRNA stability of vascular endothelial growth factor
through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in DU145
prostate carcinomaJ Biol
Chem28099639972200510.1074/jbc.M412994200
|
|
41.
|
K KatoT OguraA KishimotoY MinegishiN
NakajimaM MiyazakiH EsumiCritical roles of AMP-activated protein
kinase in constitutive tolerance of cancer cells to nutrient
deprivation and tumor
formationOncogene2160826090200210.1038/sj.onc.120573712203120
|
|
42.
|
H EsumiK IzuishiK KatoK HashimotoY
KurashimaA KishimotoT OguraT OzawaHypoxia and nitric oxide
treatment confer tolerance to glucose starvation in a
5′-AMP-activated protein kinase dependent mannerJ Biol
Chem2773279132798200212091379
|
|
43.
|
MM ShawWK GurrRJ McCrimmonDF SchordererRS
Sherwin5′AMP-activated protein kinase alpha deficiency enhances
stress-induced apoptosis in BHK and PC12 cellsJ Cell Mol
Med112862982007
|
|
44.
|
D TrachoothamJ AlexandreP HuangTargeting
cancer cells by ROS-mediated mechanisms: a radical therapeutic
approach?Nat Rev Drug Discov8579591200910.1038/nrd280319478820
|
|
45.
|
J LuoNL SoliminiSJ ElledqePrinciples of
cancer therapy: oncogene and non-oncogene
addictionCell136823837200910.1016/j.cell.2009.02.02419269363
|
|
46.
|
M LobrichPA JeggoThe impact of a negligent
G2/M checkpoint on genomic instability and cancer inductionNat Rev
Cancer7861869200710.1038/nrc224817943134
|
|
47.
|
VA SmitsRH MedemaChecking out the G(2)/M
transitionBiochim Biophys
Acta1519112200110.1016/S0167-4781(01)00204-411406266
|
|
48.
|
T GotohK OhsumiT MatsuiH TakisawaT
KishimotoInactivation of the checkpoint kinase Cds1 is dependent on
cyclin B-Cdc2 kinase activation at the meiotic G2/M-phase
transition in xenopus oocytesJ Cell Sci11433973406200111591827
|
|
49.
|
SV SinghA Herman-AntosiewiczAV SinghKL
LewSK SrivastavaR KamathKD BrownL ZhangR
BaskaranSulforaphane-induced G2/M phase cell cycle arrest involves
checkpoint kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of cell division cycle
25CJ Biol Chem2792581325822200410.1074/jbc.M31353820015073169
|
|
50.
|
W HuanwenL ZhiyongS XiaohuaR XinyuW KaiL
TonghuaIntrinsic chemoresistance to gemcitabine is associated with
constitutive and laminin-induced phosphorylation of FAK in
pancreatic cancer cell linesMol
Cancer8125200910.1186/1476-4598-8-12520021699
|
|
51.
|
JN KreutzerM RuzzeneB GuerraEnhancing
chemosensitivity to gemcitabine via RNA interfence targeting the
catalytic subunits of protein kinase CK2 in human pancreatic cancer
cellsBMC Cancer1040201010.1186/1471-2407-10-44020718998
|
|
52.
|
AV DanilovD NeupaneAS NagarajaEV
FeofanovaLA HumphriesJ DiRenzoM KorcDeltaNp63alpha-mediated
induction of epidermal growth factor receptor promotes pancreatic
cancer cell growth and chemoresistancePloS
One6e26815201110.1371/journal.pone.002681522053213
|
|
53.
|
W HagmannR JesnowskiJM LöhrInterdependence
of gemcitabine treatment, transporter expression, and resistance in
human pancreatic carcinoma cellsNeoplasia12740747201020824050
|
|
54.
|
Z YaoY OkabayashiY YutsudoT KitamuraW
OgawaM KasugaRole of Akt in growth and survival of Panc-1
pancreatic cancer
cellsPancreas244246200210.1097/00006676-200201000-0000611741181
|