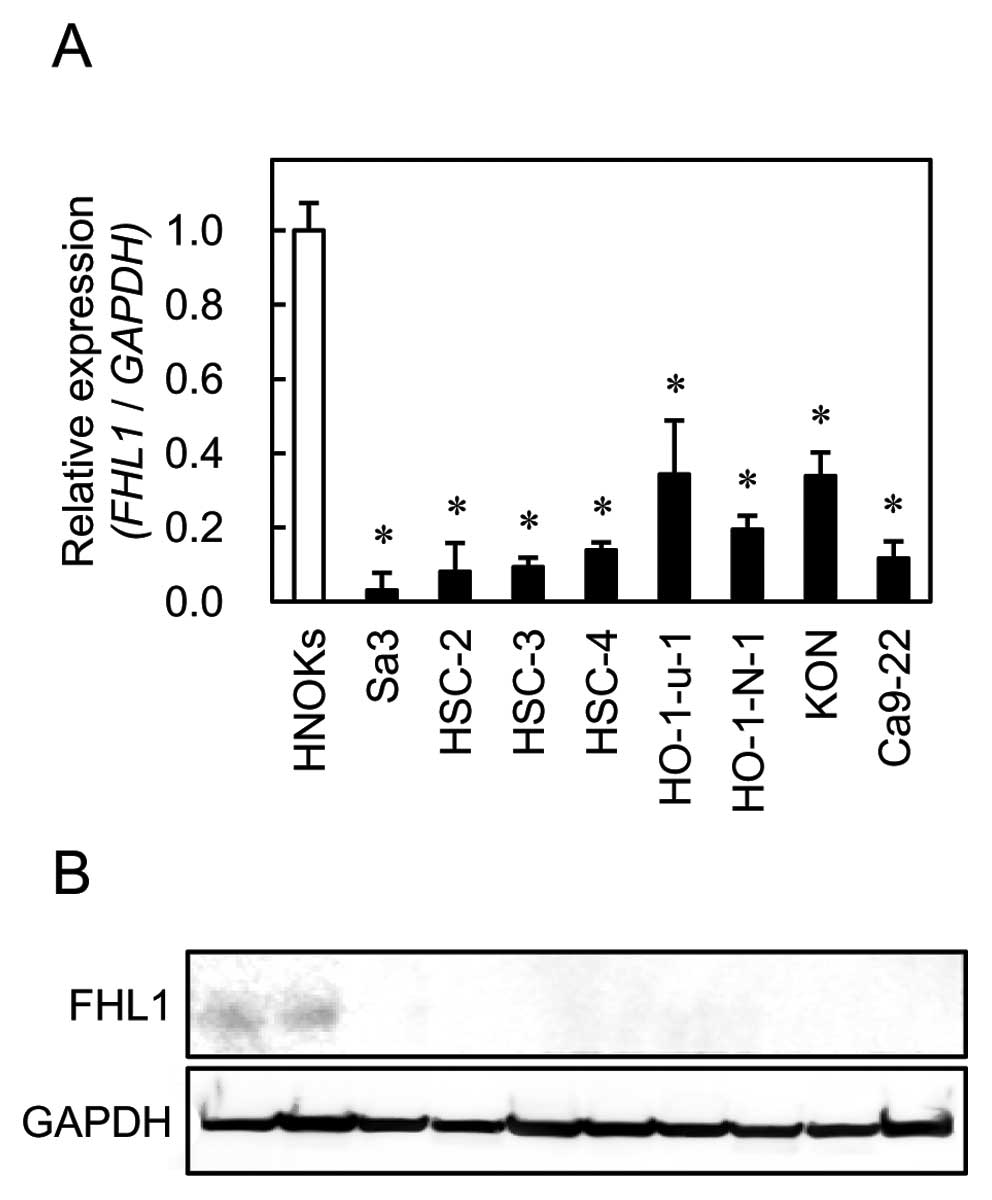
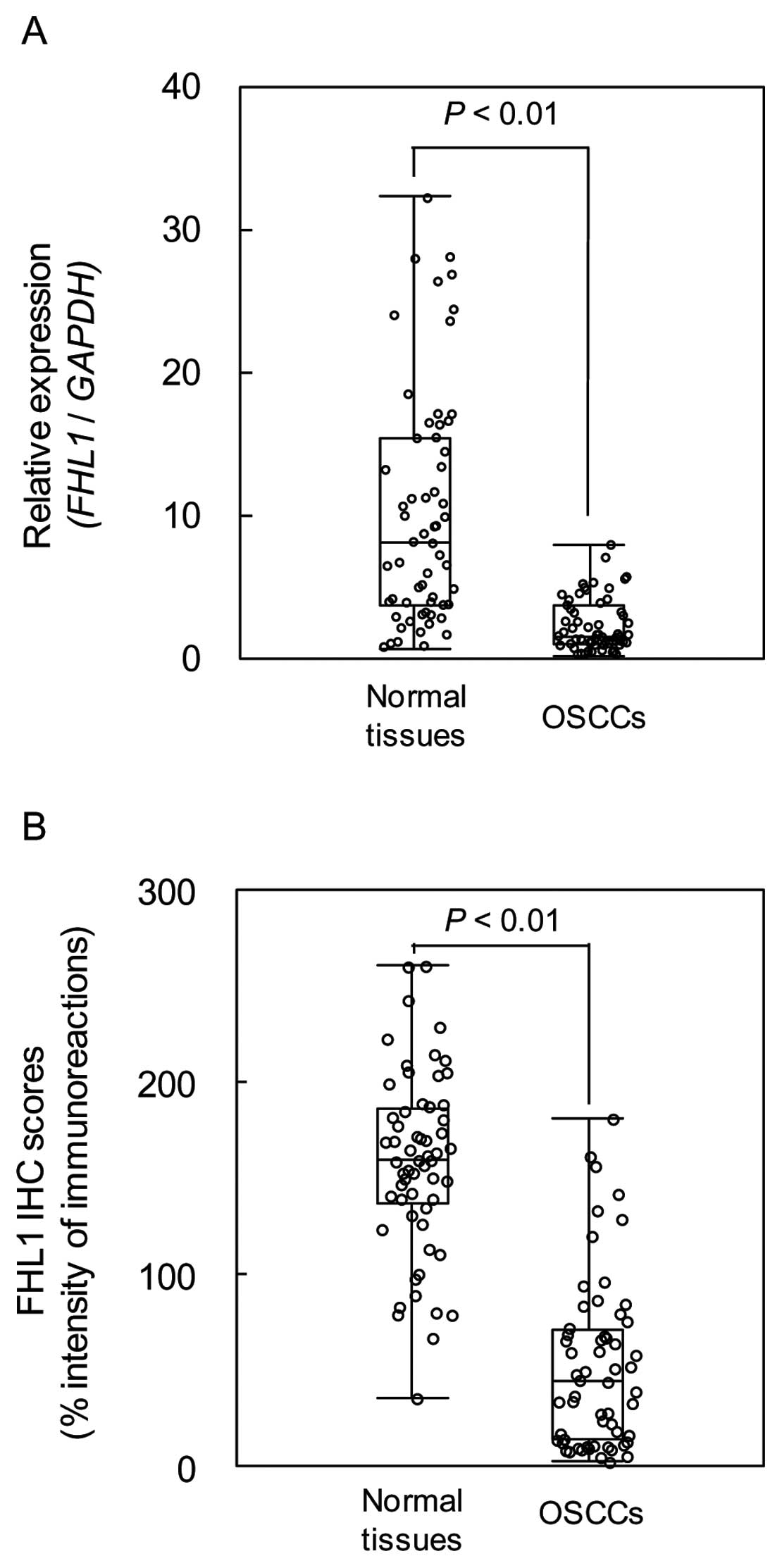
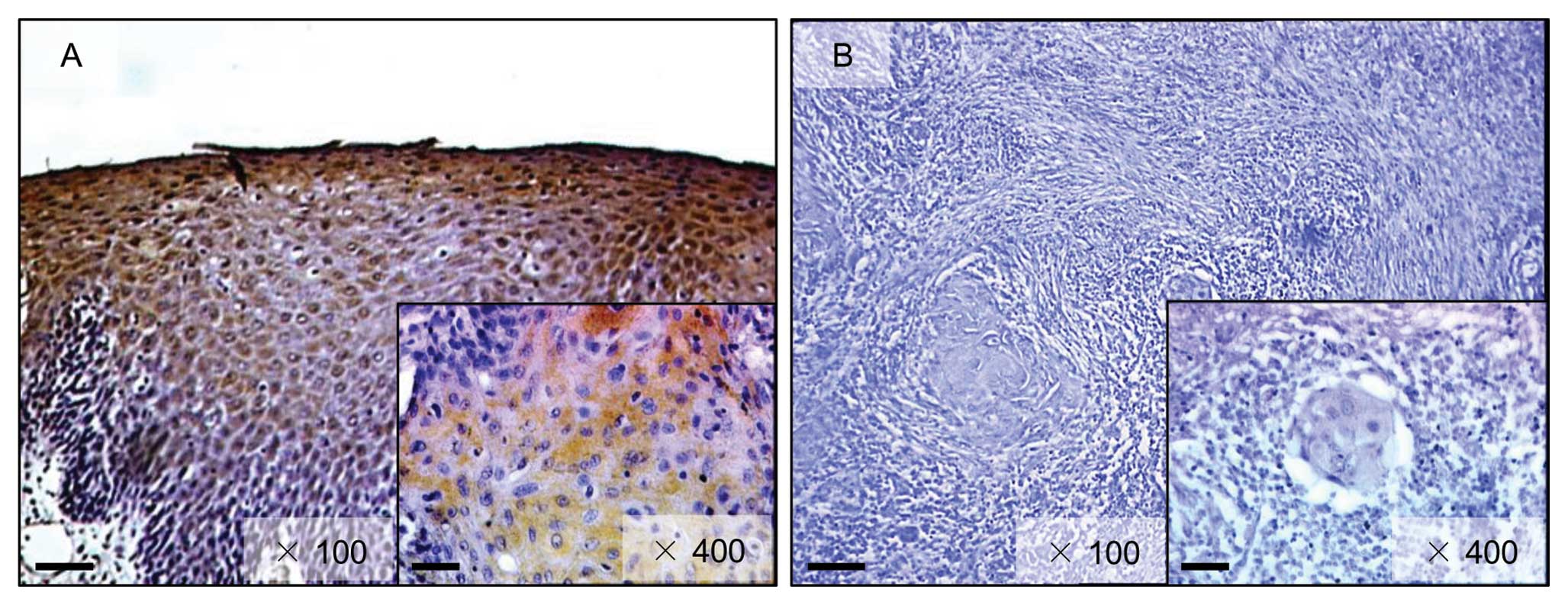
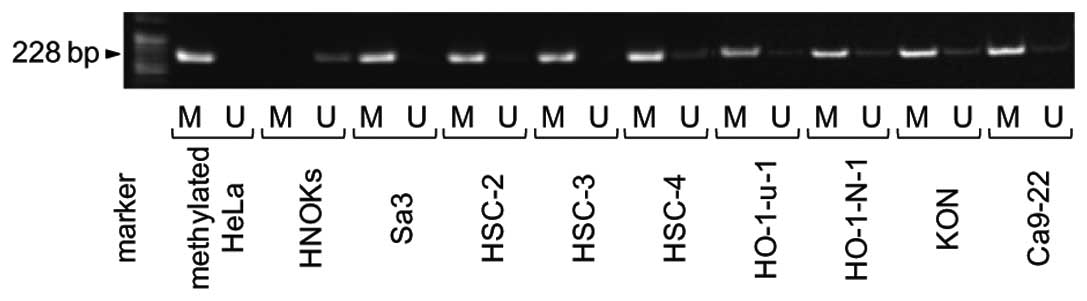
|
1.
|
Lippman SM, Sudbø J and Hong WK: Oral
cancer prevention and the evolution of molecular-targeted drug
development. J Clin Oncol. 23:346–356. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3.
|
Bettendorf O, Piffkò J and Bànkfalvi A:
Prognostic and predictive factors in oral squamous cell cancer:
important tools for planning individual therapy? Oral Oncol.
40:110–119. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Kademani D: Oral cancer. Mayo Clin Proc.
82:878–887. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Tatsumoto T, Xie X, Blumenthal R, Okamoto
I and Miki T: Human ECT2 is an exchange factor for Rho GTPases,
phosphorylated in G2/M phases, and involved in cytokinesis. J Cell
Biol. 147:921–928. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Shinozuka K, Uzawa K, Fushimi K, et al:
Downregulation of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion
molecule 1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with tumor
progression and poor prognosis. Oncology. 76:387–397. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Brown S, McGrath MJ, Ooms LM, Gurung R,
Maimone MM and Mitchell CA: Characterization of two isoforms of the
skeletal muscle LIM protein 1, SLIM1. Localization of SLIM1 at
focal adhesions and the isoform slimmer in the nucleus of myoblasts
and cytoplasm of myotubes suggests distinct roles in the
cytoskeleton and in nuclear-cytoplasmic communication. J Biol Chem.
274:27083–27091. 1999.
|
|
8.
|
McGrath MJ, Mitchell CA, Coghill ID,
Robinson PA and Brown S: Skeletal muscle LIM protein 1 (SLIM1/FHL1)
induces alpha 5 beta 1-integrin-dependent myocyte elongation. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 285:C1513–C1526. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Loughna PT, Mason P, Bayol S and Brownson
C: The LIM-domain protein FHL1 (SLIM 1) exhibits functional
regulation in skeletal muscle. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 3:136–140.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Chen DH, Raskind WH, Parson WW, et al: A
novel mutation in FHL1 in a family with X-linked scapuloperoneal
myopathy: phenotypic spectrum and structural study of FHL1
mutations. J Neurol Sci. 296:22–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Oku N, Sasabe E, Ueta E, Yamamoto T and
Osaki T: Tight junction protein claudin-1 enhances the invasive
activity of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by promoting
cleavage of laminin-5 gamma2 chain via matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and membrane-type MMP-1. Cancer Res. 66:5251–5257. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Sakashita K, Mimori K, Tanaka F, et al:
Clinical significance of loss of Fhl1 expression in human gastric
cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 15:2293–2300. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Fackler MJ, McVeigh M, Mehrotra J, et al:
Quantitative multiplex methylation-specific PCR assay for the
detection of promoter hypermethylation in multiple genes in breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 64:4442–4452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Fuks F: DNA methylation and histone
modifications: teaming up to silence genes. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
15:490–495. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Hassig CA and Schreiber SL: Nuclear
histone acetylases and deacetylases and transcriptional regulation:
HATs off to HDACs. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 1:300–308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Huang L: Targeting histone deacetylases
for the treatment of cancer and inflammatory diseases. J Cell
Physiol. 209:611–616. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Endo Y, Uzawa K, Mochida Y, et al:
Sarcoendoplasmic reticulum Ca(2+) ATPase type 2 downregulated in
human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 110:225–231.
2004.
|
|
18.
|
Shimada K, Uzawa K, Kato M, et al:
Aberrant expression of RAB1A in human tongue cancer. Br J Cancer.
92:1915–1921. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Saito K, Uzawa K, Endo Y, et al: Plasma
membrane Ca2+ ATPase isoform 1 down-regulated in human
oral cancer. Oncol Rep. 15:49–55. 2006.
|
|
20.
|
Kasamatsu A, Uzawa K, Nakashima D, et al:
Galectin-9 as a regulator of cellular adhesion in human oral
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Int J Mol Med. 16:269–273.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Sakuma K, Kasamatsu A, Yamatoji M, et al:
Expression status of Zic family member 2 as a prognostic marker for
oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:553–559.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Tanaka C, Uzawa K, Shibahara T, Yokoe H,
Noma H and Tanzawa H: Expression of an inhibitor of apoptosis,
survivin, in oral carcinogenesis. J Dent Res. 82:607–611. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Kouzu Y, Uzawa K, Kato M, et al: WISP-2
expression in human salivary gland tumors. Int J Mol Med.
17:567–573. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Onda T, Uzawa K, Endo Y, et al: Ubiquitous
mitochondrial creatine kinase downregulated in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 94:698–709. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Sakuma T, Uzawa K, Onda T, et al: Aberrant
expression of histone deacetylase 6 in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 29:117–124. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Kato Y, Uzawa K, Yamamoto N, et al:
Overexpression of Septin1: possible contribution to the development
of oral cancer. Int J Oncol. 31:1021–1028. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Nomura H, Uzawa K, Yamano Y, et al:
Overexpression and altered subcellular localization of
autophagy-related 16-like 1 in human oral squamous-cell carcinoma:
correlation with lymphovascular invasion and lymph-node metastasis.
Hum Pathol. 40:83–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28.
|
Iyoda M, Kasamatsu A, Ishigami T, et al:
Epithelial cell transforming sequence 2 in human oral cancer. PloS
One. 5:e140822010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yamatoji M, Kasamatsu A, Kouzu Y, et al:
Dermatopontin: a potential predictor for metastasis of human oral
cancer. Int J Cancer. 130:2903–2911. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Lombardi DP, Geradts J, Foley JF, Chiao C,
Lamb PW and Barrett JC: Loss of KAI1 expression in the progression
of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 59:5724–5731. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Verburg FA, Wäschle K, Reiners C,
Giovanella L and Lentjes EG: Heterophile antibodies rarely
influence the measurement of thyroglobulin and thyroglobulin
antibodies in differentiated thyroid cancer patients. Horm Metab
Res. 42:736–739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Li LC and Dahiya R: MethPrimer: designing
primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics. 18:1427–1431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Van der Auwera I, Van Laere SJ, Van den
Bosch SM, et al: Aberrant methylation of the adenomatous polyposis
coli (APC) gene promoter is associated with the inflammatory breast
cancer phenotype. Br J Cancer. 99:1735–1742. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Kimura H, Hayashi-Takanaka Y, Goto Y,
Takizawa N and Nozaki N: The organization of histone H3
modifications as revealed by a of specific monoclonal antibodies.
Cell Struct Funct. 33:61–73. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Wang LL, Qiu GR, Fu WN, Yuan ZW and Sun
KL: Transcriptional regulation of Fhl1 by estradiol in rat
myoblastocytes. Steroids. 75:368–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Shen Y, Jia Z, Nagele RG, Ichikawa H and
Goldberg GS: SRC uses Cas to suppress Fhl1 in order to promote
nonanchored growth and migration of tumor cells. Cancer Res.
66:1543–1552. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Fryknas M, Wickenberg-Bolin U, Goransson
H, et al: Molecular markers for discrimination of benign and
malignant follicular thyroid tumors. Tumour Biol. 27:211–220. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Li X, Jia Z, Shen Y, et al: Coordinate
suppression of Sdpr and Fhl1 expression in tumors of the breast,
kidney, and prostate. Cancer Sci. 99:1326–1333. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Yuan J, Luo RZ, Fujii S, et al: Aberrant
methylation and silencing of ARHI, an imprinted tumor suppressor
gene in which the function is lost in breast cancers. Cancer Res.
63:4174–4180. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Chen K, Sawhney R, Khan M, et al:
Methylation of multiple genes as diagnostic and therapeutic markers
in primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol
Head Neck Surg. 133:1131–1138. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Henken FE, Wilting SM, Overmeer RM, et al:
Sequential gene promoter methylation during HPV-induced cervical
carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 97:1457–1464. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Magdinier F and Wolffe AP: Selective
association of the methyl-CpG binding protein MBD2 with the silent
p14/p16 locus in human neoplasia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:4990–4995. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43.
|
Cheung P and Lau P: Epigenetic regulation
by histone methylation and histone variants. Mol Endocrinol.
19:563–573. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44.
|
Hong S, Derfoul A, Pereira-Mouries L and
Hall DJ: A novel domain in histone deacetylase 1 and 2 mediates
repression of cartilage-specific genes in human chondrocytes. FASEB
J. 23:3539–3552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|