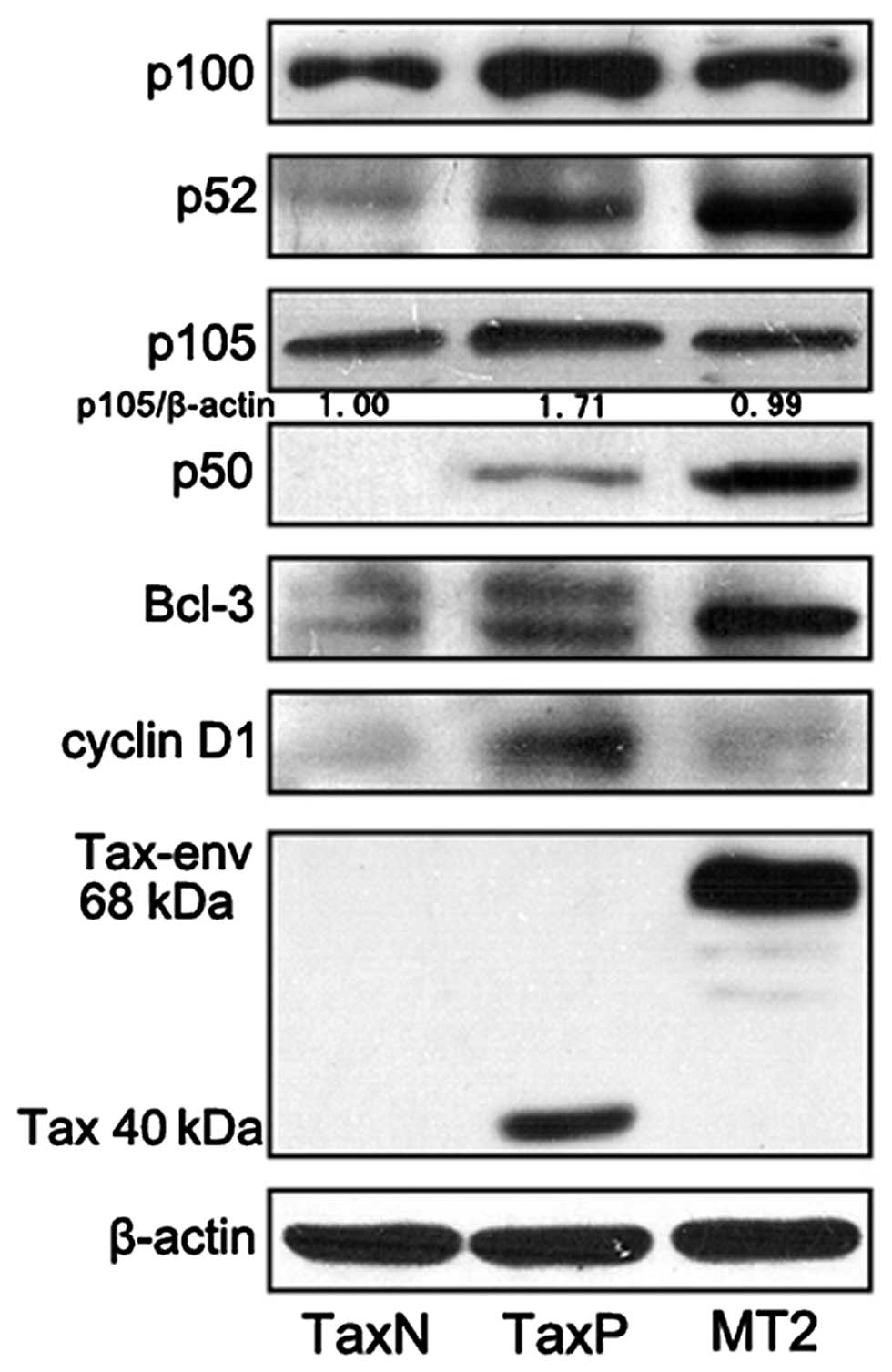
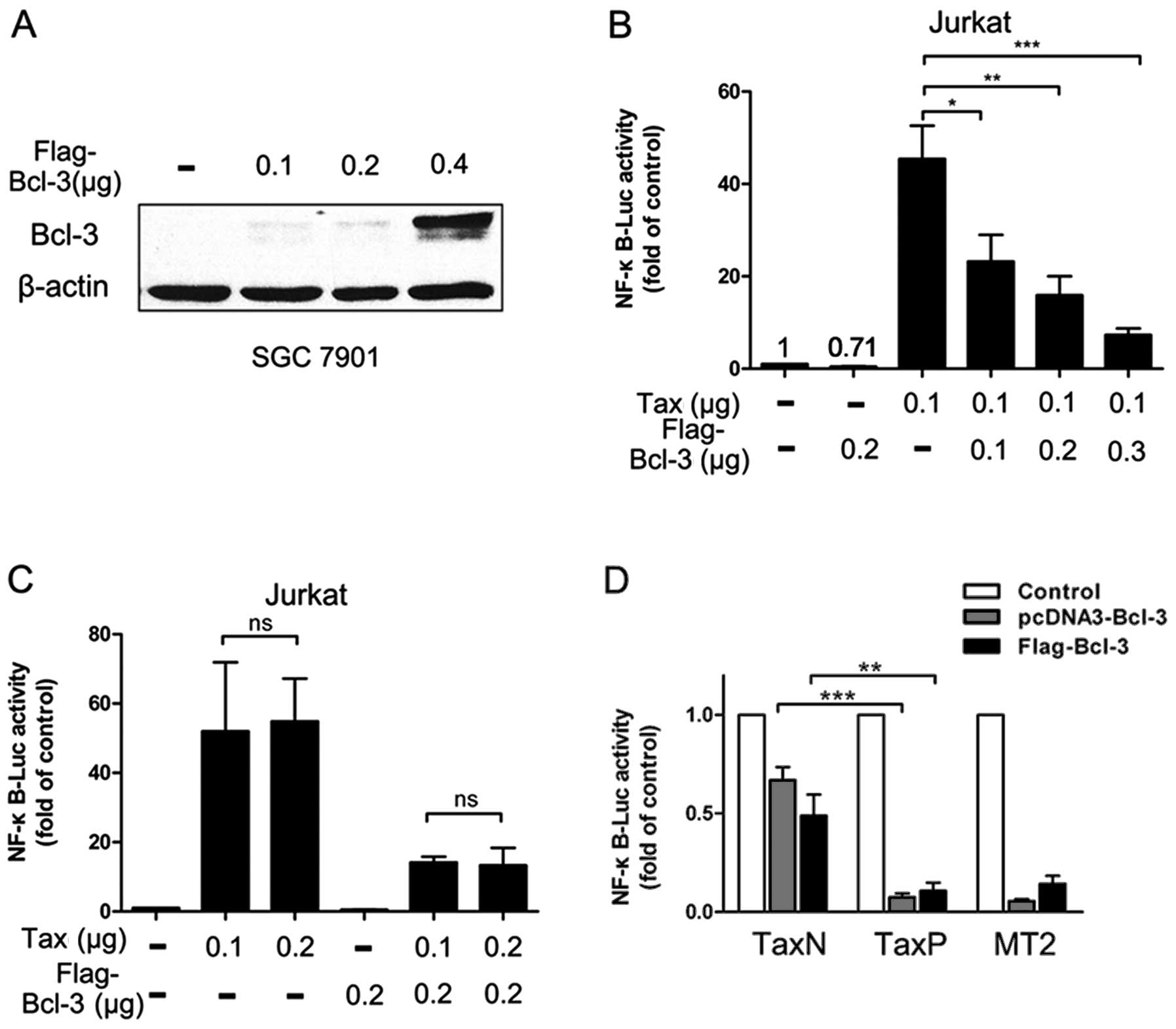
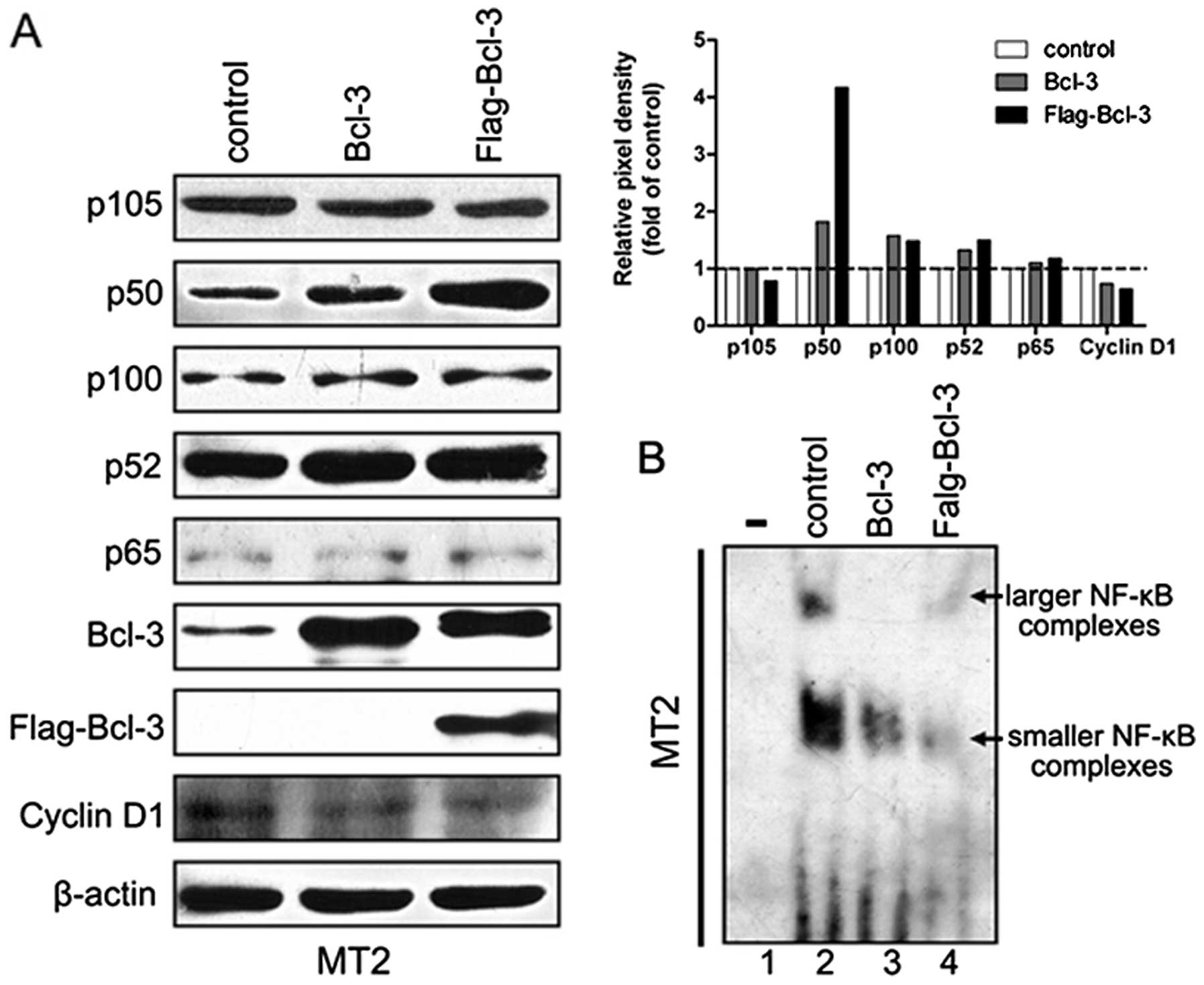
|
1.
|
Gessain A, Barin F, Vernant JC, et al:
Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with
tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 2:407–410. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Yoshida M, Miyoshi I and Hinuma Y:
Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of
human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:2031–2035. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Osame M, Usuku K, Izumo S, et al: HTLV-I
associated myelopathy, a new clinical entity. Lancet. 1:1031–1032.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Harhaj E and Harhaj N: Mechanisms of
Persistent NF-κB Activation by HTLV-I Tax. Int Union Biochem Mol
Biol: Life. 57:83–91. 2005.
|
|
5.
|
Shvarzbeyn J and Huleihel M: Effect of
propolis and caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on NFκB activation
by HTLV-1 Tax. Antiviral Res. 90:108–115. 2011.
|
|
6.
|
Yasunaga J, Lin FC, Lu X and Jeang KT:
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 20 targets TRAF6 and human T cell
leukemia virus type 1 tax to negatively regulate NF-κB signaling. J
Virol. 85:6212–6219. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Azran I, Jeang K-T and Aboud M: High
levels of cytoplasmic HTLV-1 Tax mutant proteins retain a
Tax-NF-κB-CBP ternary complex in the cytoplasm. Oncogene.
24:4521–4530. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Hayden MS, West AP and Ghosh S: SnapShot:
NF-κB signaling Pathways. Cell. 127:1286–1287. 2006.
|
|
9.
|
Hironaka N, Mochida K, Mori N, Maeda M,
Yamamoto N and Yamaoka S: Tax-independent constitutive IκB kinase
activation in adult T-cell leukemia cells. Neoplasia. 6:266–278.
2004.
|
|
10.
|
Michel F, Soler-Lopez M, Petosa C, Cramer
P, Siebenlist U and Muller CW: Crystal structure of the ankyrin
repeat domain of Bcl-3: a unique member of the IkappaB protein
family. EMBO J. 20:6180–6190. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Courtois G and Gilmore TD: Mutations in
the NF-kappaB signaling pathway: implications for human disease.
Oncogene. 25:6831–6843. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Palmer S and Chen YH: Bcl-3, a
multifaceted modulator of NF-κB-mediated gene transcription.
Immunol Res. 42:210–218. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
McKeithan TW, Takimoto GS, Ohno H, et al:
BCL3 rearrangements and t(14;19) in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
and other B-cell malignancies: a molecular and cytogenetic study.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 20:64–72. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Bundy DL and McKeithan TW: Diverse effects
of BCL3 phosphorylation on its modulation of NF-kappaB p52
homodimer binding to DNA. J Biol Chem. 272:33132–33139. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Fujita T, Nolan GP, Liou HC, Scott ML and
Baltimore D: The candidate proto-oncogene bcl-3 encodes a
transcriptional coactivator that activates through NF-kappa B p50
homodimers. Genes Dev. 7:1354–1363. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Franzoso G, Bours V, Azarenko V, et al:
The oncoprotein Bcl-3 can facilitate NF-kappa B-mediated
transactivation by removing inhibiting p50 homodimers from select
kappa B sites. EMBO J. 12:3893–3901. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Bours V, Franzoso G, Azarenko V, et al:
The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappa B
motifs via association with DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell.
72:729–739. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Franzoso G, Bours V, Park S,
Tomita-Yamaguchi M, Kelly K and Siebenlist U: The candidate
oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-kappa B-mediated
inhibition. Nature. 359:339–342. 1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Inoue J, Takahara T, Akizawa T and Hino O:
Bcl-3, a member of the I kappa B proteins, has distinct specificity
towards the Rel family of proteins. Oncogene. 8:2067–2073.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Nolan GP, Fujita T, Bhatia K, et al: The
bcl-3 proto-oncogene encodes a nuclear I kappa B-like molecule that
preferentially interacts with NF-kappa B p50 and p52 in a
phosphorylation-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 13:3557–3566.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Caamano JH, Perez P, Lira SA and Bravo R:
Constitutive expression of Bc1-3 in thymocytes increases the DNA
binding of NF-kappaB1 (p50) homodimers in vivo. Mol Cell Biol.
16:1342–1348. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kabuta T, Hakuno F, Cho Y, et al: Insulin
receptor substrate-3, interacting with Bcl-3, enhances p50 NF-κB
activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:697–702. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Brocke-Heidrich K, Ge B, Cvijic H, et al:
BCL3 is induced by IL-6 via Stat3 binding to intronic enhancer HS4
and represses its own transcription. Oncogene. 25:7297–7304. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Kim YM, Sharma N and Nyborg JK: The
proto-oncogene Bcl3, induced by Tax, represses Tax-mediated
transcription via p300 displacement from the human T-cell leukemia
virus type 1 promoter. J Virol. 82:11939–11947. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Saito K, Saito M, Taniura N, Okuwa T and
Ohara Y: Activation of the PI3K-Akt pathway by human T cell
leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) oncoprotein Tax increases Bcl3
expression, which is associated with enhanced growth of
HTLV-1-infected T cells. Virology. 403:173–180. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Xia YSY, Gao Y, Guo JQ, Song XF and Wang
H: Establishment of the tax gene expression cell lines and their
biological activity. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
16:1425–1429. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Kress AK, Schneider G, Pichler K, Kalmer
M, Fleckenstein B and Grassmann R: Elevated cyclic AMP levels in T
lymphocytes transformed by human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1.
J Virol. 84:8732–8742. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Ishikawa C, Nakachi S, Senba M, Sugai M
and Mori N: Activation of AID by human T-cell leukemia virus Tax
oncoprotein and the possible role of its constitutive expression in
ATL genesis. Carcinogenesis. 32:110–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Boxus M, Twizere J-C, Legros S, Dewulf
J-F, Kettmann R and Willems L: The HTLV-1 Tax interactome.
Retrovirology. 5:762008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Sun SC and Ballard DW: Persistent
activation of NF-kappaB by the tax transforming protein of HTLV-1:
hijacking cellular IkappaB kinases. Oncogene. 18:6948–6958. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Li XH and Gaynor RB: Mechanisms of
NF-kappaB activation by the HTLV type 1 tax protein. AIDS Res Hum
Retroviruses. 16:1583–1590. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Kfoury Y, Nasr R, Hermine O, de The H and
Bazarbachi A: Proapoptotic regimes for HTLV-I-transformed cells:
targeting Tax and the NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Death Differ.
12(Suppl 1): 871–877. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Mori N, Yamada Y, Ikeda S, et al: Bay
11-7082 inhibits transcription factor NF-kappaB and induces
apoptosis of HTLV-I-infected T-cell lines and primary adult T-cell
leukemia cells. Blood. 100:1828–1834. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
O’Mahony AM: Human T-cell lymphotropic
virus type 1 Tax induction of biologically active NF-κB requires
IκB kinase-1-mediated phosphorylation of RelA/p65. J Biol Chem.
279:18137–18145. 2004.
|
|
35.
|
Sun SC, Elwood J, Beraud C and Greene WC:
Human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax activation of NF-kappa B/Rel
involves phosphorylation and degradation of I kappa B alpha and
RelA (p65)-mediated induction of the c-rel gene. Mol Cell Biol.
14:7377–7384. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|