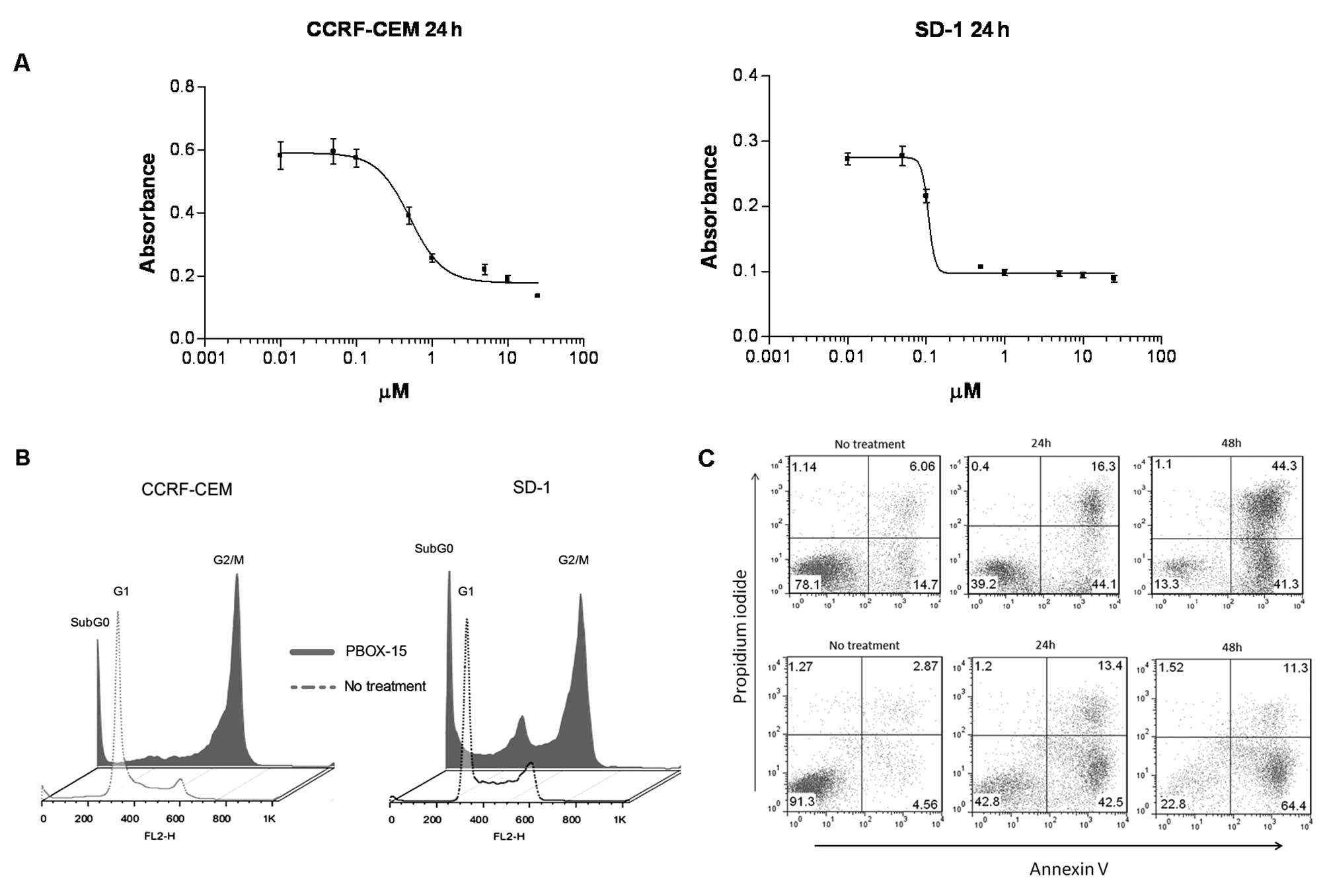
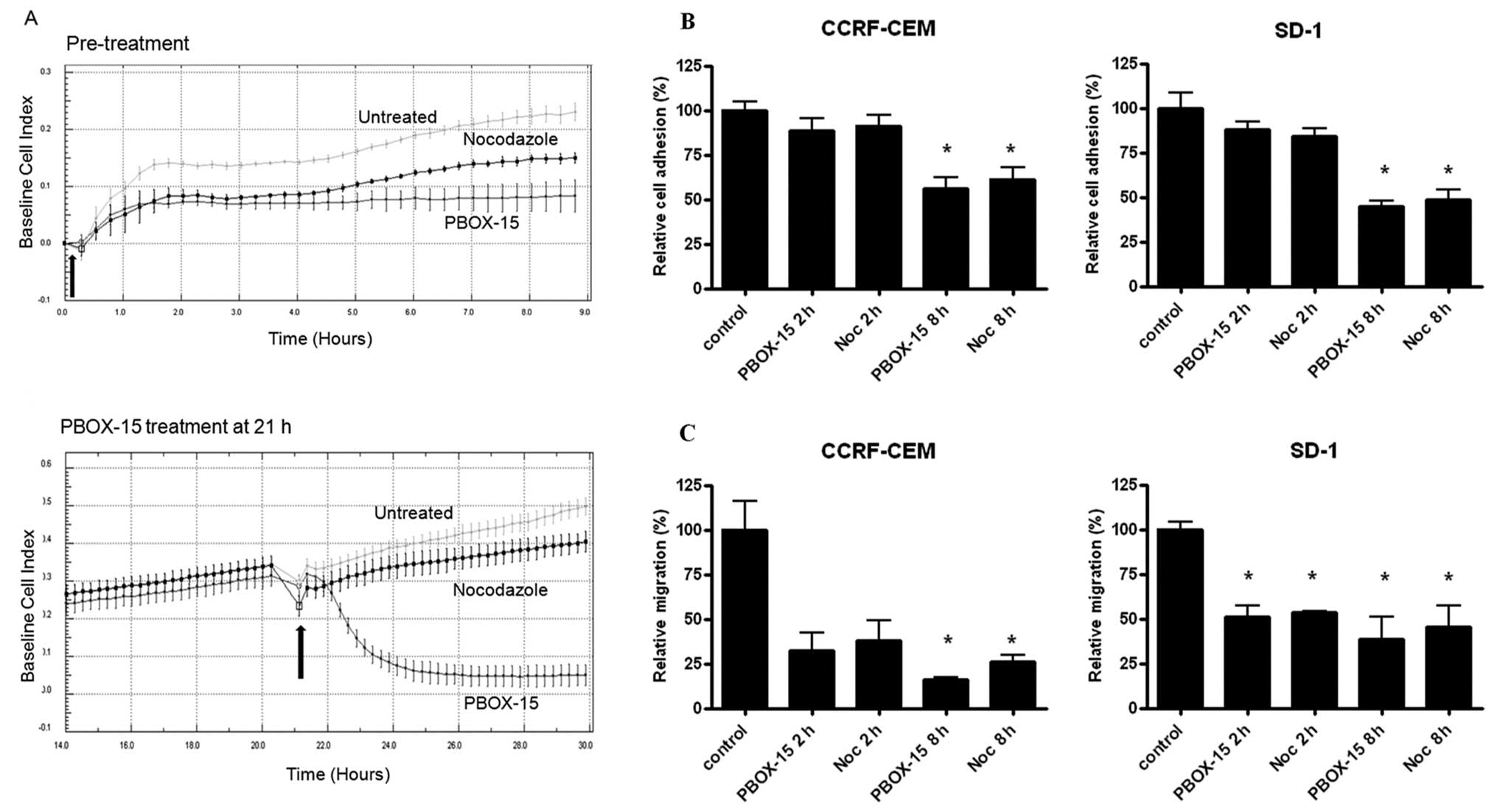
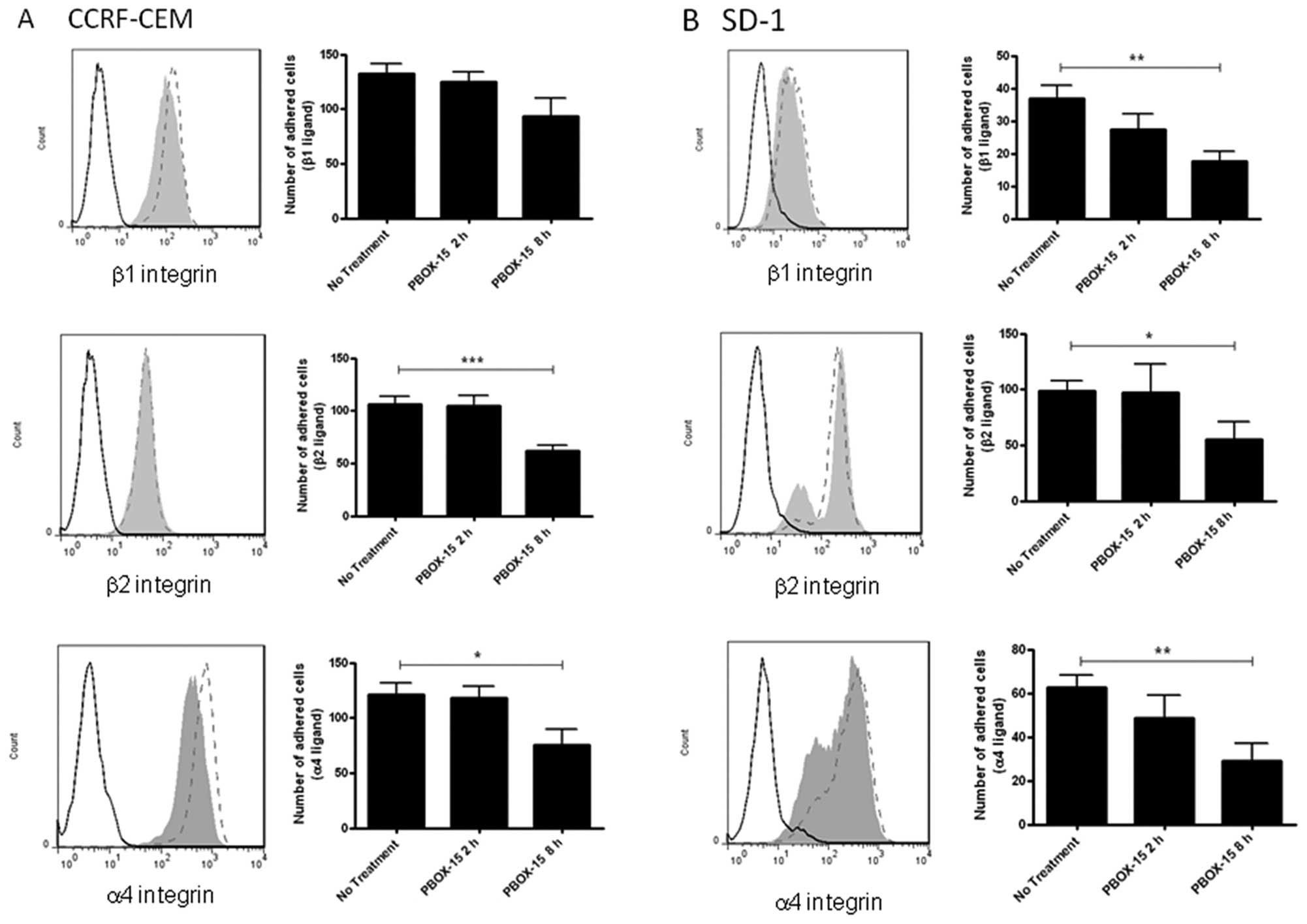
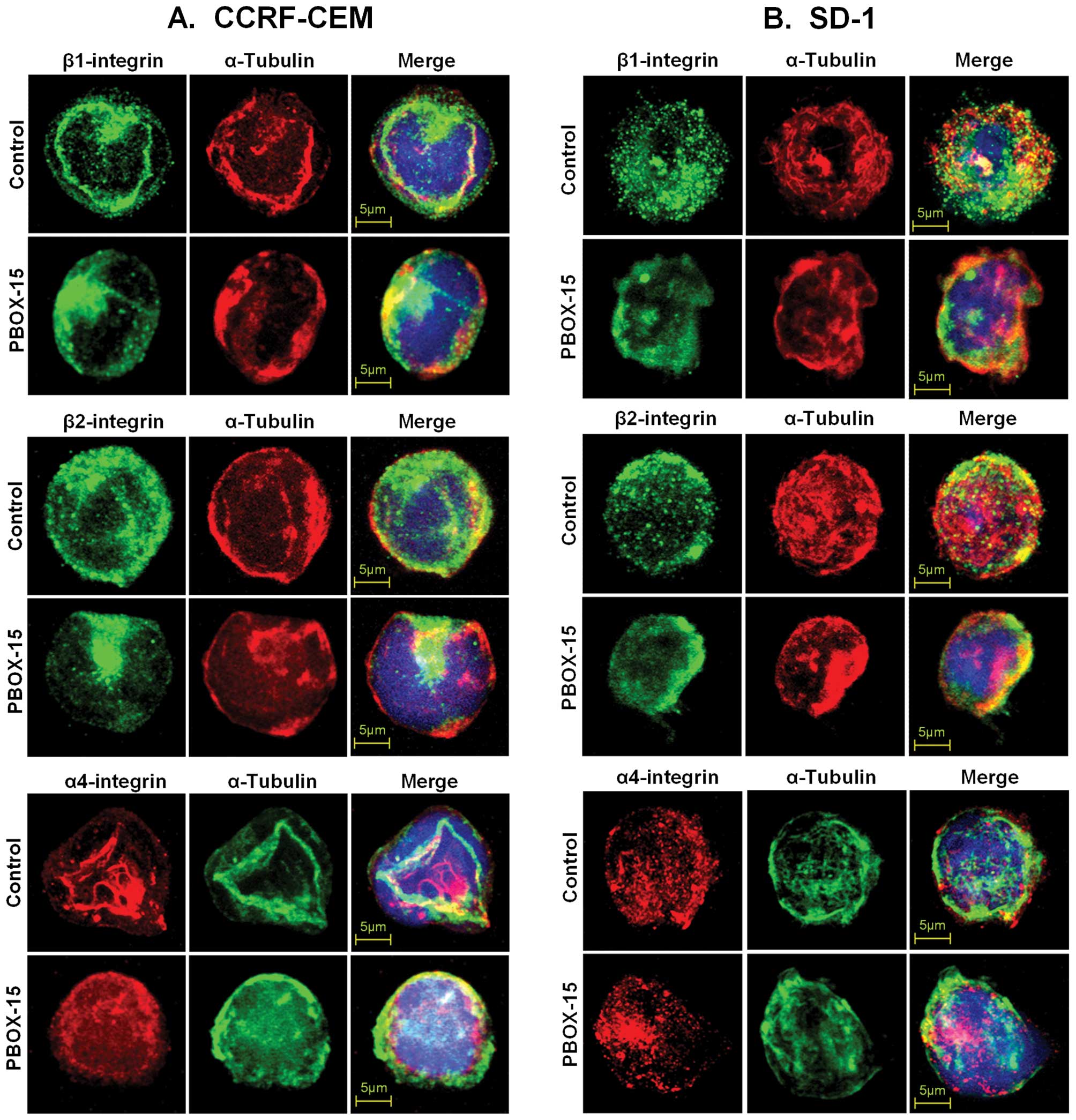
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Tiwari RC, Murray T, et al:
Cancer statistics, 2004. CA Cancer J Clin. 54:8–29. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Pui CH, Robison LL and Look AT: Acute
lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet. 371:1030–1043. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Pui CH and Evans WE: Drug therapy -
treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med.
354:166–178. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4.
|
Faderl S, O’Brien S, Pui CH, et al: Adult
acute lymphoblastic leukemia concepts and strategies. Cancer.
116:1165–1176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Mulligan JM, Greene LM, Cloonan S, et al:
Identification of tubulin as the molecular target of proapoptotic
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines. Mol Pharmacol. 70:60–70.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Greene LM, Campiani G, Lawler M, Williams
DC and Zisterer DM: BubR1 is required for a sustained mitotic
spindle checkpoint arrest in human cancer cells treated with
tubulin-targeting pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines. Mol Pharmacol.
73:419–430. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
McElligott AM, Maginn EN, Greene LM, et
al: The novel tubulin-targeting agent pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-15
induces apoptosis in poor prognostic subgroups of chronic
lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 69:8366–8375. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8.
|
Nathwani SM, Butler S, Fayne D, et al:
Novel microtubule-targeting agents, pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepines,
induce apoptosis in multi-drug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 66:585–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Forde JC, Maginn EN, McNamara G, et al:
Microtubule-targeting-compound PBOX-15 radiosensitizes cancer cells
in vitro. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:421–428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Maginn EN, Browne PV, Hayden P, et al:
PBOX-15, a novel microtubule targeting agent, induces apoptosis,
upregulates death receptors, and potentiates TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Br J Cancer. 104:281–289.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11.
|
Bright SA, McElligott AM, O’Connell JW, et
al: Novel pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine compounds display significant
activity against resistant chronic myeloid leukaemia cells in
vitro, in ex vivo patient samples and in vivo. Br J Cancer.
102:1474–1482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12.
|
Vilpo JA, Koski T and Vilpo LM: Selective
toxicity of vincristine against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells
in vitro. Eur J Haematol. 65:370–378. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Beswick RW, Ambrose HE and Wagner SD:
Nocodazole, a microtubule depolymerising agent, induces apoptosis
of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells associated with changes in
Bcl-2 phosphorylation and expression. Leuk Res. 30:427–436. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14.
|
Moon EY and Lerner A: Benzylamide sulindac
analogues induce changes in cell shape, loss of microtubules and
G(2)-M arrest in a chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cell line and
apoptosis in primary CLL cells. Cancer Res. 62:5711–5719.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Aisenberg AC and Wilkes B: Studies on
suppression of immune responses by periwinkle alkaloids vincristine
+ vinblastine. J Clin Invest. 43:2394–2403. 1964.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Park SJ, Shim WH, Ho DS, et al: A
paclitaxel-eluting stent for the prevention of coronary restenosis.
N Engl J Med. 348:1537–1545. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Manabe A, Murti KG, Coustansmith E, et al:
Adhesion-dependent survival of normal and leukemic human-B
lymphoblasts on bone-marrow stromal cells. Blood. 83:758–766.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
De la Fuente MT, Casanova B, Moyano JV, et
al: Engagement of alpha 4 beta 1 integrin by fibronectin induces in
vitro resistance of B chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to
fludarabine. J Leukoc Biol. 71:495–502. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Scimone ML, Alfantis I, Apostolou I, von
Boehmer H and von Andrian UH: A multistep adhesion cascade for
lymphoid progenitor cell homing to the thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:7006–7011. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Cox D, Brennan M and Moran N: Integrins as
therapeutic targets: lessons and opportunities. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 9:804–820. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Astier AL, Svoboda M, Hinds E, De Beaumont
R, Munoz O and Freedman AS: Integrins regulate survival of
pre-B-ALL cells through differential IAP and caspase-7
ubiquitination and degradation. Leukemia. 18:873–875. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Streuli CH and Akhtar N: Signal
co-operation between integrins and other receptor systems. Biochem
J. 418:491–506. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Zhou XM, Li JX and Kucik DF: The
microtubule cytoskeleton participates in control of beta(2)
integrin avidity. J Biol Chem. 276:44762–44769. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Verma NK, Dempsey E, Conroy J, et al: A
new microtubule-targeting compound PBOX-15 inhibits T-cell
migration via post-translational modifications of tubulin. J Mol
Med. 86:457–469. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Campiani G, Nacci V, Fiorini I, et al:
Synthesis, biological activity, and SARs of pyrrolobenzoxazepine
derivatives, a new class of specific ‘peripheral-type’
benzodiazepine receptor ligands. J Med Chem. 39:3435–3450.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
McGee MM, Gemma S, Butini S, et al:
Pyrrolo[1,5]benzoxa(thia) zepines as a new class of potent
apoptotic agents. Biological studies and identification of an
intracellular location of their drug target. J Med Chem.
48:4367–4377. 2005.
|
|
27.
|
Foley GE, Lazarus H, Farber S, Uzman BG,
Boone BA and McCarthy RE: Continuous culture of human lymphoblasts
from peripheral blood of a child with acute leukemia. Cancer.
18:522–529. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Dhut S, Gibbons B, Chaplin T and Young BD:
Establishment of a lymphoblastoid cell-line, Sd-1, expressing the
p190 bcr-abl chimeric protein. Leukemia. 5:49–55. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H and
Reutelingsperger C: A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric
detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells
using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods. 184:39–51.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30.
|
Verma NK, Dourlat J, Davies AM, et al:
STAT3-stathmin interactions control microtubule dynamics in
migrating T-cells. J Biol Chem. 284:12349–12362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Mohamed BM, Verma NK, Davies AM, et al:
Citrullination of proteins: a common post-translational
modification pathway induced by different nanoparticles in vitro
and in vivo. Nanomedicine. 7:1181–1195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Mohamed BM, Verma NK, Prina-Mello A, et
al: Activation of stress-related signalling pathway in human cells
upon SiO2 nanoparticles exposure as an early indicator of
cytotoxicity. J Nanobiotechnology. 9:292011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
McGrath LB, Onnis V, Campiani G, Williams
DC, Zisterer DM and McGee MM: Caspase-activated DNase
(CAD)-independent oligonucleosomal DNA fragmentation in chronic
myeloid leuka emia cells; a requirement for serine protease and
Mn2+-dependent acidic endonuclease activity. Apoptosis.
11:1473–1487. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Whipple RA, Matrone MA, Cho EH, et al:
Epithelial-tomesenchymal transition promotes tubulin detyrosination
and microtentacles that enhance endothelial engagement. Cancer Res.
70:8127–8137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Tiruppathi C, Malik AB, Del Vecchio PJ,
Keese CR and Giaever I: Electrical method for detection of
endothelial cell shape change in real time: assessment of
endothelial barrier function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:7919–7923.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Von Andrian UH and Mackay CR: Advances in
immunology: T-cell function and migration - two sides of the same
coin. N Engl J Med. 343:1020–1033. 2000.
|
|
37.
|
Matsunaga T, Takemoto N, Sato T, et al:
Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin is
a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute myelogenous
leukemia. Nat Med. 9:1158–1165. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Shalapour S, Hof J, Kirschner-Schwabe R,
et al: High VLA-4 expression is associated with adverse outcome and
distinct gene expression changes in childhood B-cell precursor
acute lymphoblastic leukemia at first relapse. Haematologica.
96:1627–1635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|