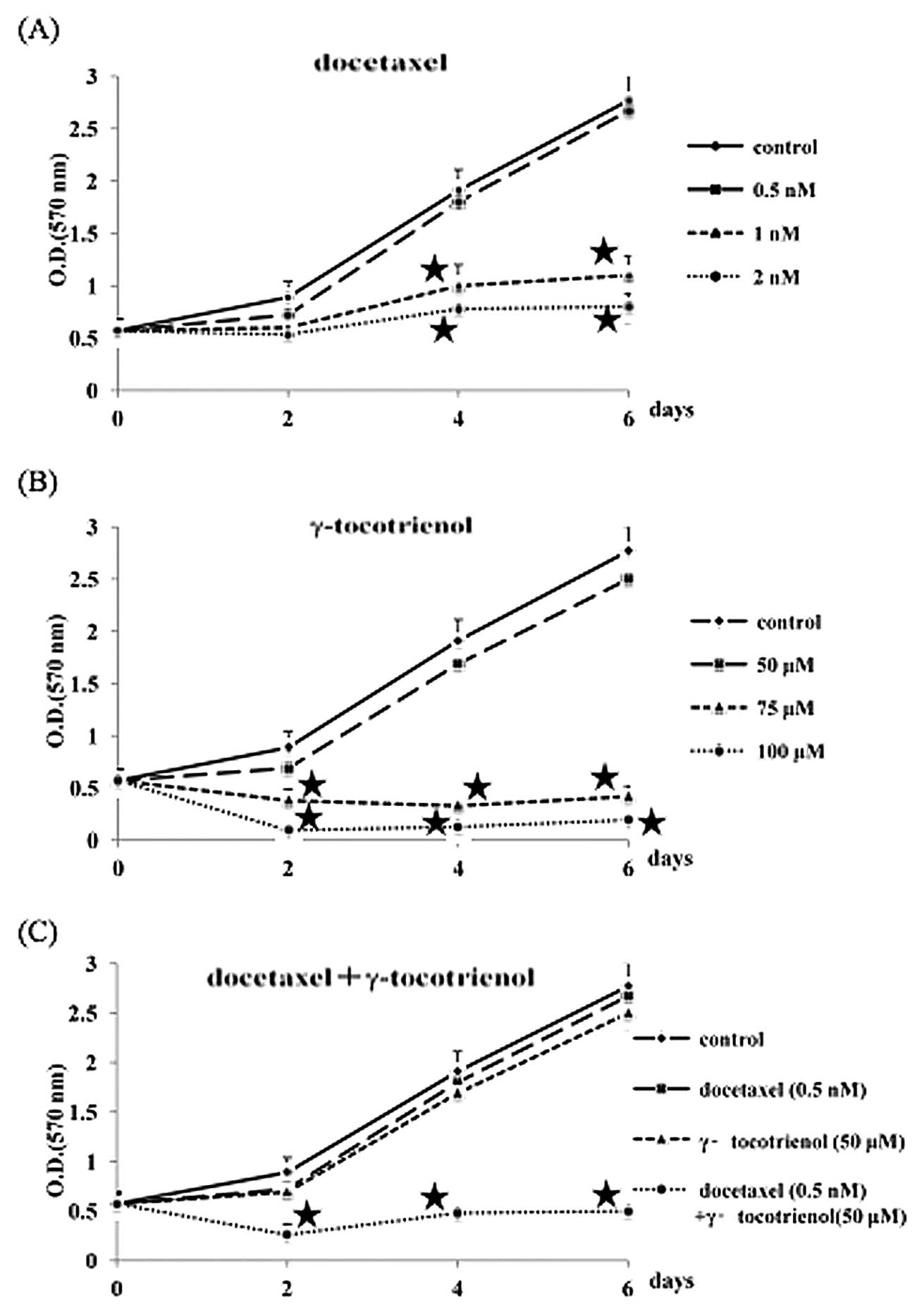
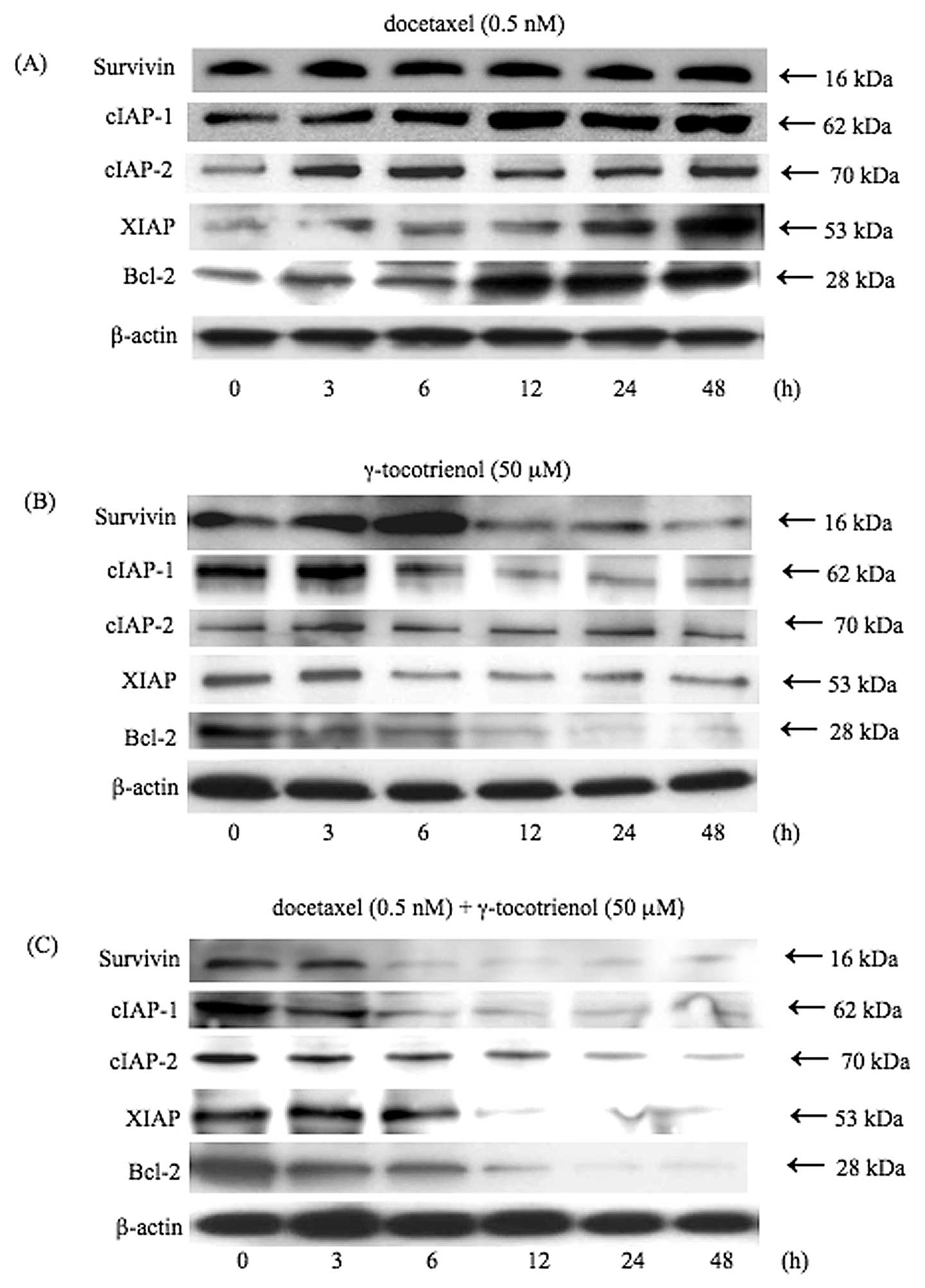
|
1.
|
Forastiere AA and Urba SG: Experimental
therapeutic approaches for recurrent head and neck cancer. Cancer
Treat Res. 74:263–281. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Colevas AD and Posner MR: Docetaxel in
head and neck cancer: a review. Am J Clin Oncol. 21:482–486. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Eisenhauer EA and Vermorken JB: The
taxoids. Comparative clinical pharmacology and therapeutic
potential. Drugs. 55:5–30. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Schoffski P, Catimel G, Planting AS, et
al: Docetaxel and cisplatin: an active regimen in patients with
locally advanced, recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
of the head and neck. Results of a Phase II study of the EORTC
Early Clinical Studies Group. Ann Oncol. 10:119–122. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5.
|
Couteau C, Chouaki N, Leyvraz S, et al: A
Phase II study of docetaxel in patients with metastatic squamous
cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Br J Cancer. 81:457–462. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Vaux DL and Korsmeyer SJ: Cell death in
development. Cell. 96:245–254. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Fulda S, Susin S, Kroemer G and Debatin
KM: Molecular ordering of apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs in
neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 58:4453–4460. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Ferreira CG, Span SW, Peters GJ, Kruyt FAE
and Giaccone G: Chemotherapy triggers apoptosis in a
caspase-8-dependent and mitochondria-controlled manner in the
non-small cell lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. Cancer Res.
60:7133–7141. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Scaffidi C, Fulda S, Srinivasan A, et al:
Two CD95 (APO-1/Fas) signaling pathways. EMBO J. 17:1675–1687.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, et al:
Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9
complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Fernades-Alnemri
T and Alnemri ES: Autoactivation of procaspase-9 by Apaf-1-mediated
oligomerization. Mol Cell. 1:949–957. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Baldwin AS Jr: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-κB. J Clin
Invest. 107:241–246. 2001.
|
|
13.
|
Chu Z-L, McKinsey TA, Liu L, Gentry JJ,
Malim MH and Ballard DW: Suppression of tumor necrosis
factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under
NF-κB control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:10057–10062.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Zhu L, Fukuda S, Cordis G, Das DK and
Maulik N: Anti-apoptotic protein survival plays a significant role
in tubular morphogenesis of human coronary arteriolar endothelial
cells by hypoxic preconditioning. FEBS Lett. 508:369–374. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15.
|
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Scheurich P and
Wajant H: NF-κB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a
cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol
Cell Biol. 21:3964–3973. 2001.
|
|
16.
|
Azuma M, Tamatani T, Ashida Y, Takashima
R, Harada K and Sato M: Cisplatin induces apoptosis in oral
squamous carcinoma cells by the mitochondria-mediated but not the
NF-κB-suppressed pathway. Oral Oncol. 39:282–289. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Tamatani T, Azuma M, Ashida Y, et al:
Enhanced radio-sensitization and chemosensitization in
NF-κB-suppressed human oral cancer cells via the inhibition of
γ-irradiation- and 5-FU-induced production of IL-6 and IL-8. Int J
Cancer. 108:912–921. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Wada S: Cancer preventive effects of
vitamin E. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 13:156–164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19.
|
McIntyre BS, Briski KP, Gapor A and
Sylvester PW: Antiproliferative and apoptotic effects of
tocopherols and tocotrienols on preneoplastic and neoplastic mouse
mammary epithelial cells. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 224:292–301. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
McIntyre BS, Briski KP, Tirmenstein MA,
Fariss MW, Gapor A and Sylvester PW: Antiproliferative and
apoptotic effects of tocopherols and tocotrienols on normal mouse
mammary epithelial cells. Lipids. 35:171–180. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Shah SJ and Sylvester PW: γ-Tocotrienol
inhibits neoplastic mammary epithelial cell proliferation by
decreasing Akt and nuclear factor κB activity. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 230:235–241. 2005.
|
|
22.
|
Ahn KS, Sethi G, Krishnan K and Aggarwal
BB: γ-Tocotrienol inhibits nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway
through inhibition of receptor-interacting protein and TAK1 leading
to suppression of antiapoptotic gene products and potentiation of
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:809–820. 2007.
|
|
23.
|
Tamatani T, Azuma M, Aota K, Yamashita T,
Bando T and Sato M: Enhanced IκB kinase activity is responsible for
the augmented activity of NF-κB in human head and neck carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 171:165–172. 2001.
|
|
24.
|
Imbert V, Rupec RA, Livolsi A, et al:
Tyrosine phosphorylation of IκB-α activates NF-κB without
proteolytic degradation. Cell. 85:787–798. 1996.
|
|
25.
|
Kluck RM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Green DR and
Newmeyer DD: The release of cytochrome c from mitochondria: a
primary site for Bcl-2 regulation of apoptosis. Science.
275:1132–1136. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
You M, Ku P-T, Hrdlickova R and Bose HR
Jr: ch-IAP1, a member of the inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein family,
is a mediator of the antiapoptotic activity of the v-rel
oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 17:7328–7341. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Catz SD and Johnson JL: Transcriptional
regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor κB and its significance in
prostate cancer. Oncogene. 20:7342–7351. 2001.
|
|
28.
|
Grumont RJ, Rourke IJ and Gerondakis S:
Rel-dependent induction of A1 transcription is required to protect
B cells from antigen receptor ligation-induced apoptosis. Genes
Dev. 13:400–411. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Kuwana T, Smith JJ, Muzio M, Dixit V,
Newmeyer DD and Kornbluth S: Apoptosis induction by caspase-8 is
amplified through the mitochondrial release of cytochrome c. J Biol
Chem. 273:16589–16594. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Ding Z, Yang X, Pater A and Tang SC:
Resistance to apoptosis is correlated with the reduced caspase-3
activation and enhanced expression of antiapoptotic proteins in
human cervical multidrug-resistant cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 270:415–420. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Clark JR and Frei E III: Chemotherapy for
head and neck cancer: progress and controversy in the management of
patients with MO disease. Semin Oncol. 16:44–57. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Azuma M, Motegi K, Aota K, Yamashita T,
Yoshida H and Sato M: TGF-β1 inhibits NF-κB activity through
induction of IκB-α expression in human salivary gland cells: a
possible mechanism of growth suppression by TGF-β1. Exp Cell Res.
250:213–211. 1999.
|
|
33.
|
Kunnumakkara AB, Sung B, Ravindran J, et
al: γ-Tocotrienol inhibits pancreatic tumors and sensitizes them to
gemcitabine treatment by modulating the inflammatory
microenvironment. Cancer Res. 70:8695–8705. 2010.
|
|
34.
|
Manu KA, Shanmugam MK, Ramachandran L, et
al: First evidence that γ-tocotrienol inhibits the growth of human
gastric cancer and chemosensitizes it to capecitabine in a
xenograft mouse model through the modulation of NF-κB pathway. Clin
Cancer Res. 18:2220–2229. 2012.
|
|
35.
|
Wada S, Satomi Y, Murakoshi M, Noguchi N,
Yoshikawa T and Nishino H: Tumor suppressive effects of tocotrienol
in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Lett. 229:181–191. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36.
|
Agarwal MK, Agarwal ML, Athar M and Gupta
S: Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil activates p53, modulates
Bax/Bcl2 ratio and induces apoptosis independent of cell cycle
association. Cell Cycle. 3:205–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Naito Y, Shimozawa M, Kuroda M, et al:
Tocotrienols reduce 25-hydroxylcholesterol-induced
monocyte-endothelial cell interaction by inhibiting the surface
expression of adhesion molecules. Atherosclerosis. 180:19–25. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Eitsuka T, Nakagawa K and Miyazawa T:
Down-regulation of telomerase activity in DLD-1 human colorectal
adenocarcinoma cells by tocotrienol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
348:170–175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Miyazawa T, Inokuchi H, Hirokane H,
Tsuzuki T, Nakagawa K and Igarashi M: Anti-angiogenic potential of
tocotrienol in vitro. Biochemistry (Mosc). 69:67–69. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappa B: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.
|
|
41.
|
Liu X, Zou H, Slaughter C and Wang X: DFF,
a heterodimeric protein that functions downstream of caspase-3 to
trigger DNA fragmentation during apoptosis. Cell. 89:175–184. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42.
|
Shearwin-Whyatt L, Baliga B, Doumanis J
and Kumar S: Chimeric caspase molecules with potent cell killing
activity in apoptosis-resistant cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
282:1114–1119. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|